Diagnostic maneuvers for narrow QRS tachycardia
Raja Selvaraj
JIPMER
Introduction
Narrow QRS tachycardia
- Regular, rate > 100, QRSd < 120
- AT, AVNRT, orthodromic AVRT
- Clues
- Preexcitation in sinus rhythm / with atrial pacing
- Dual AV nodal physiology
- Manner of induction
General approach
- What is the situation / pattern ?
- What are the differential diagnoses ?
- What are the electrophysiologic differences ?
- What pacing maneuvers can differentiate ?
Patterns
- A = V
- Central atrial activation, VA < 70
- Eccentric atrial activation
- Central atrial activation, VA > 70
- A > V
- V > A
NQRST, central A, VA < 70
Central atrial activation, very short VA
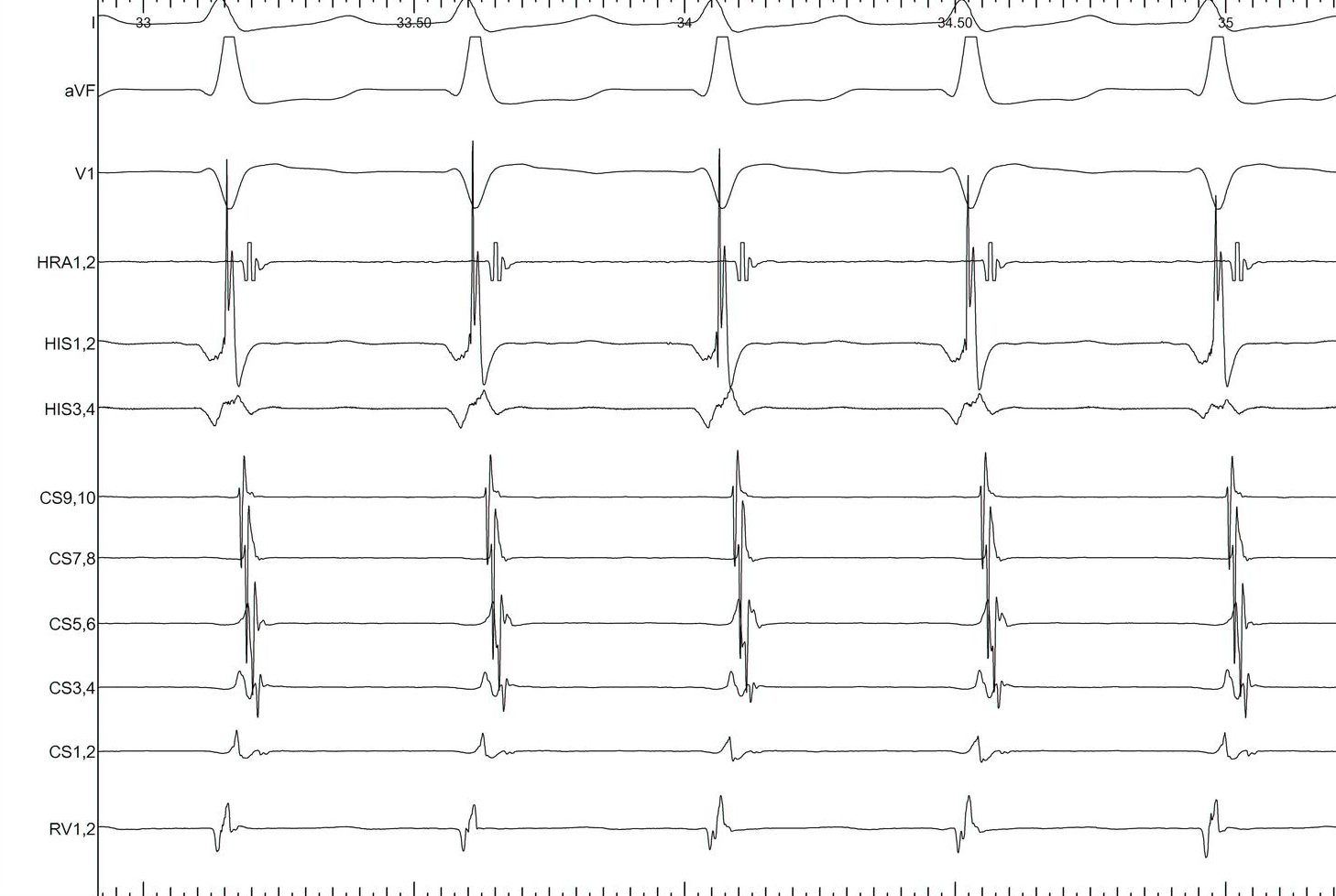
Differential diagnosis
- Typical (Slow-fast) AVNRT
- Atrial tachycardia
- Junctional tachycardia
Which pacing maneuver ?
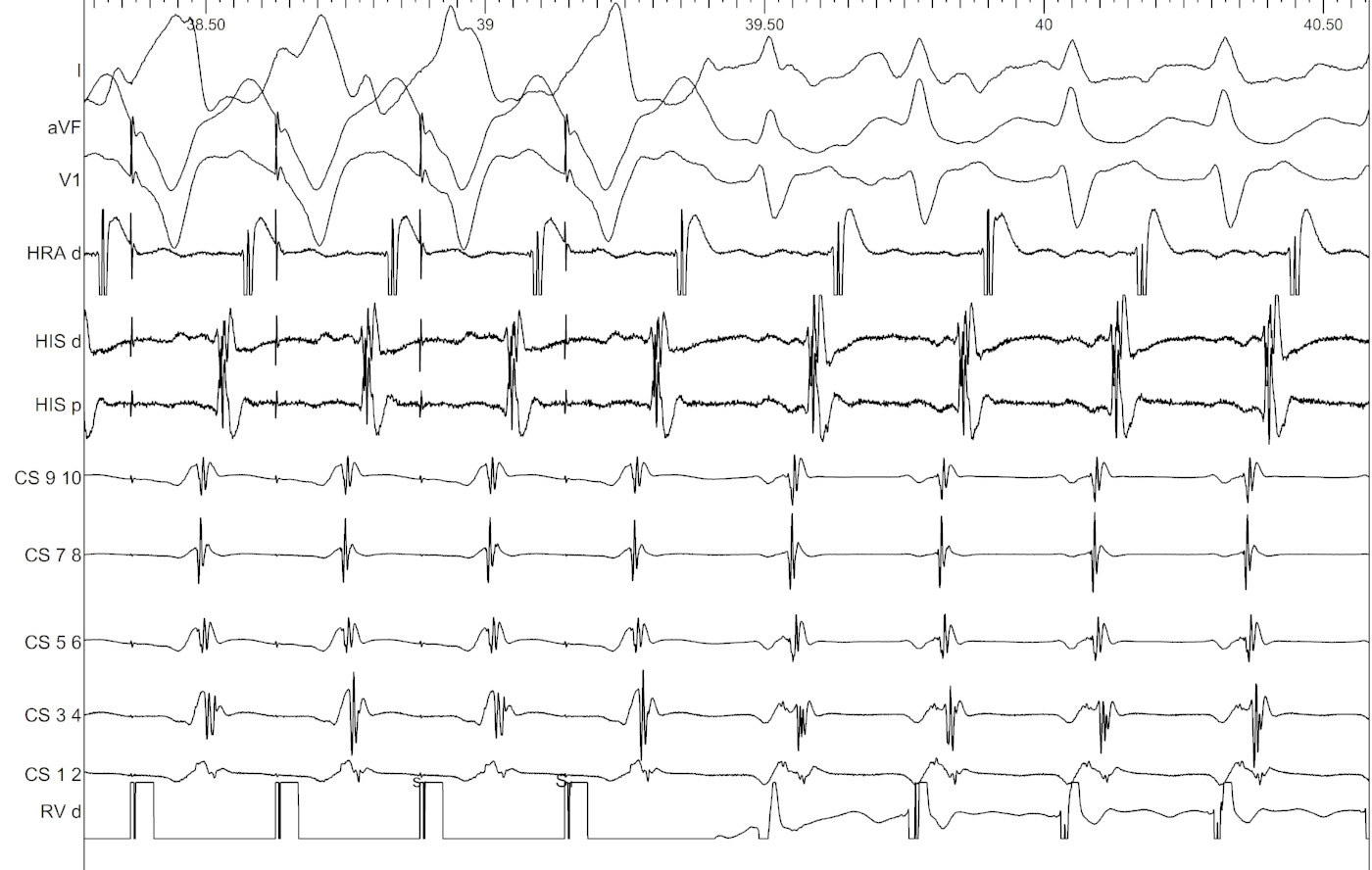
- Ventricular overdrive pacing
- Simple to perform
- Relatively simple to interpret
- Provides lot of information
Setting up
- Burst pacing from right ventricle (apex / base)
- Sync on and functional
- Tachycardia CL - 20 / 30 ms
- Pace until atrium entrained
- Stop pacing
What to look for ?
- Don't 'eyeball'
- Was the atrium entrained ?
- Does tachycardia continue ?
- Which is the last entrained A ?
- Sequence - VAV or VAAV
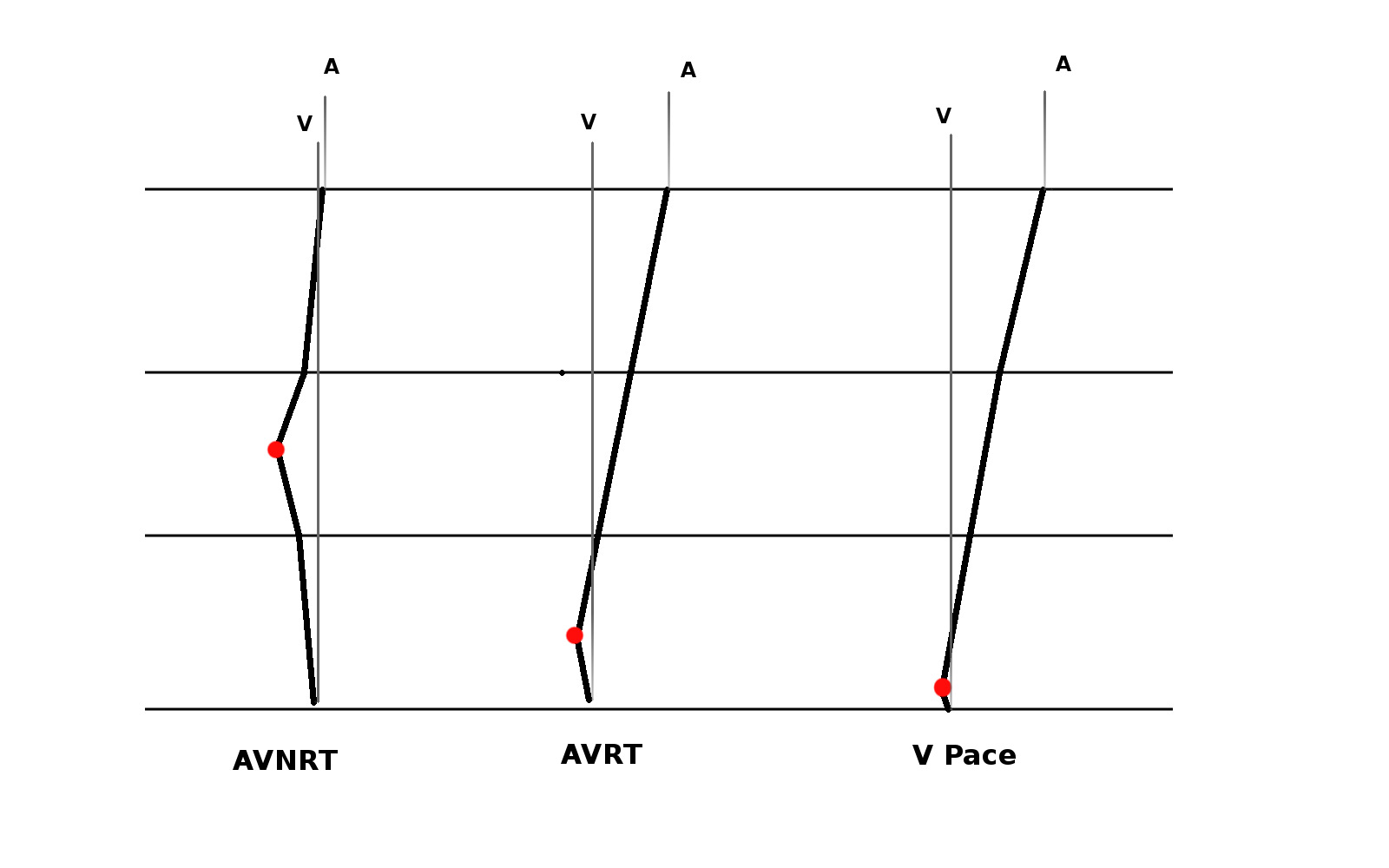
Response
- Atrium not entrained - AT / AVNRT
- VAAV - AT
- VAV - AVNRT
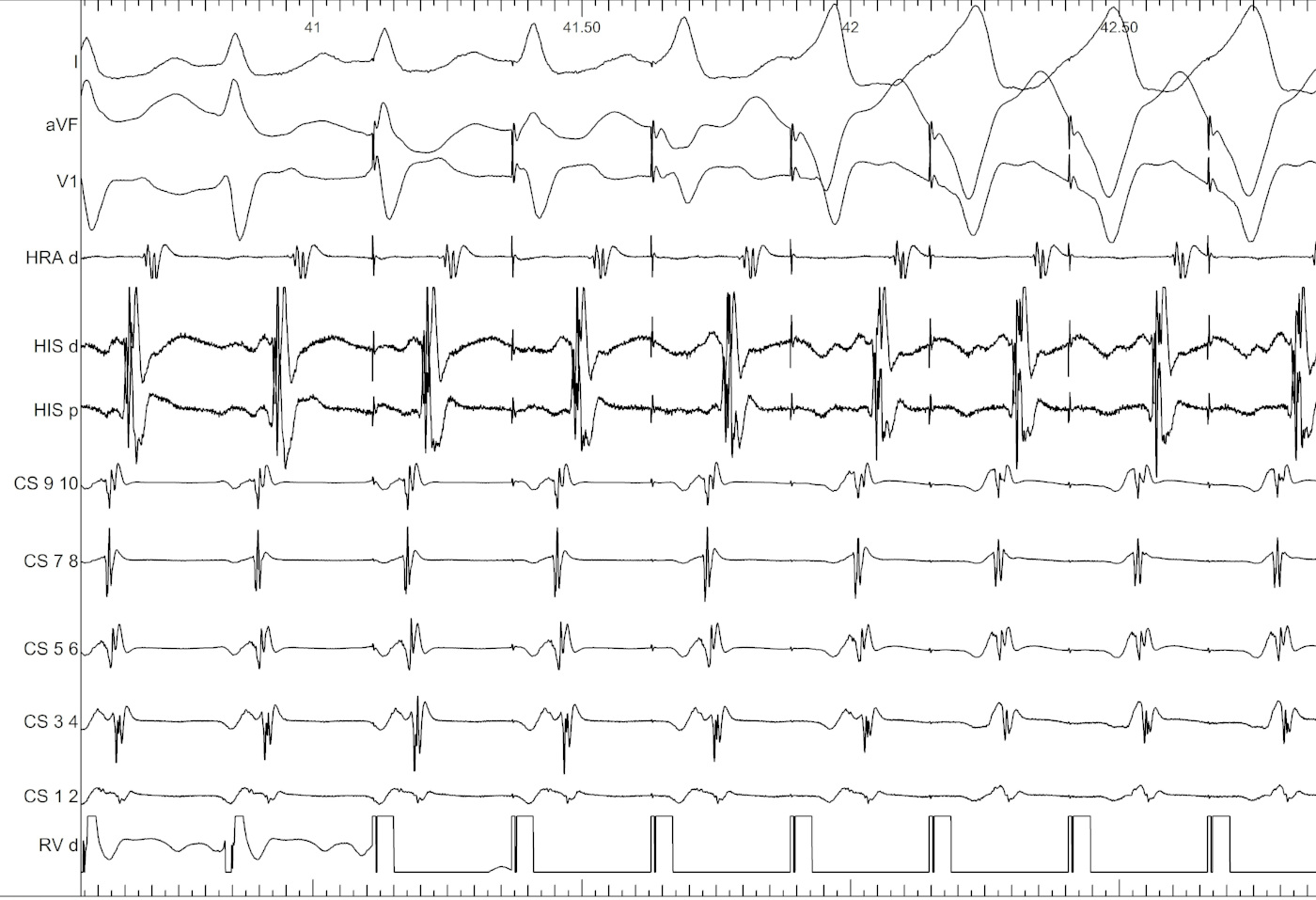
Ventricular overdrive pacing
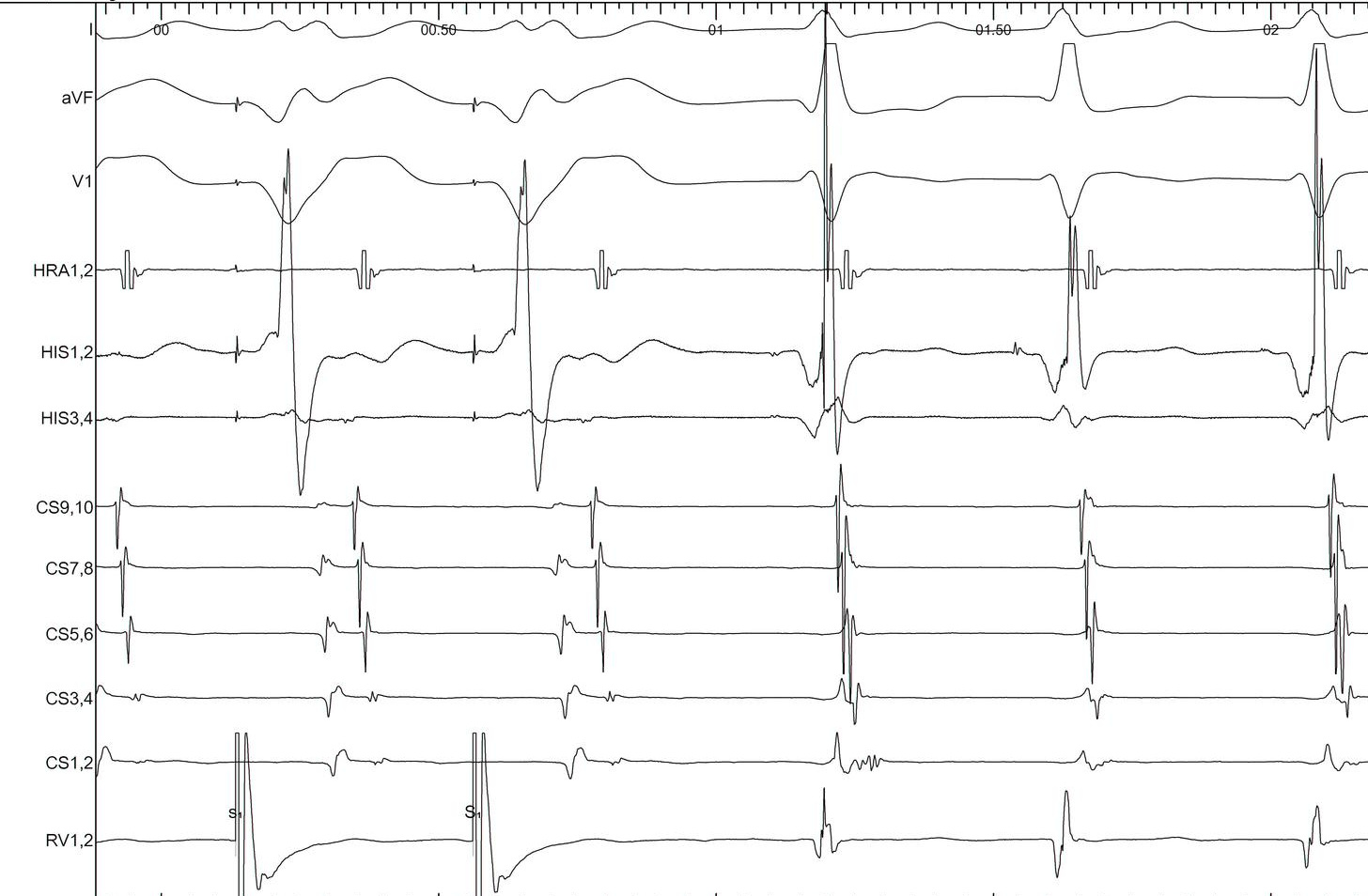
Eccentric atrial activation
Eccentric atrial activation
Differential diagnoses
- AVRT
- AT
Response to VOP
- Unable to entrain - AT
- Identical atrial activation, VAV - AVRT
- Different atrial activation, VAAV / failure of atrial capture - AT
Ventricular overdrive pacing
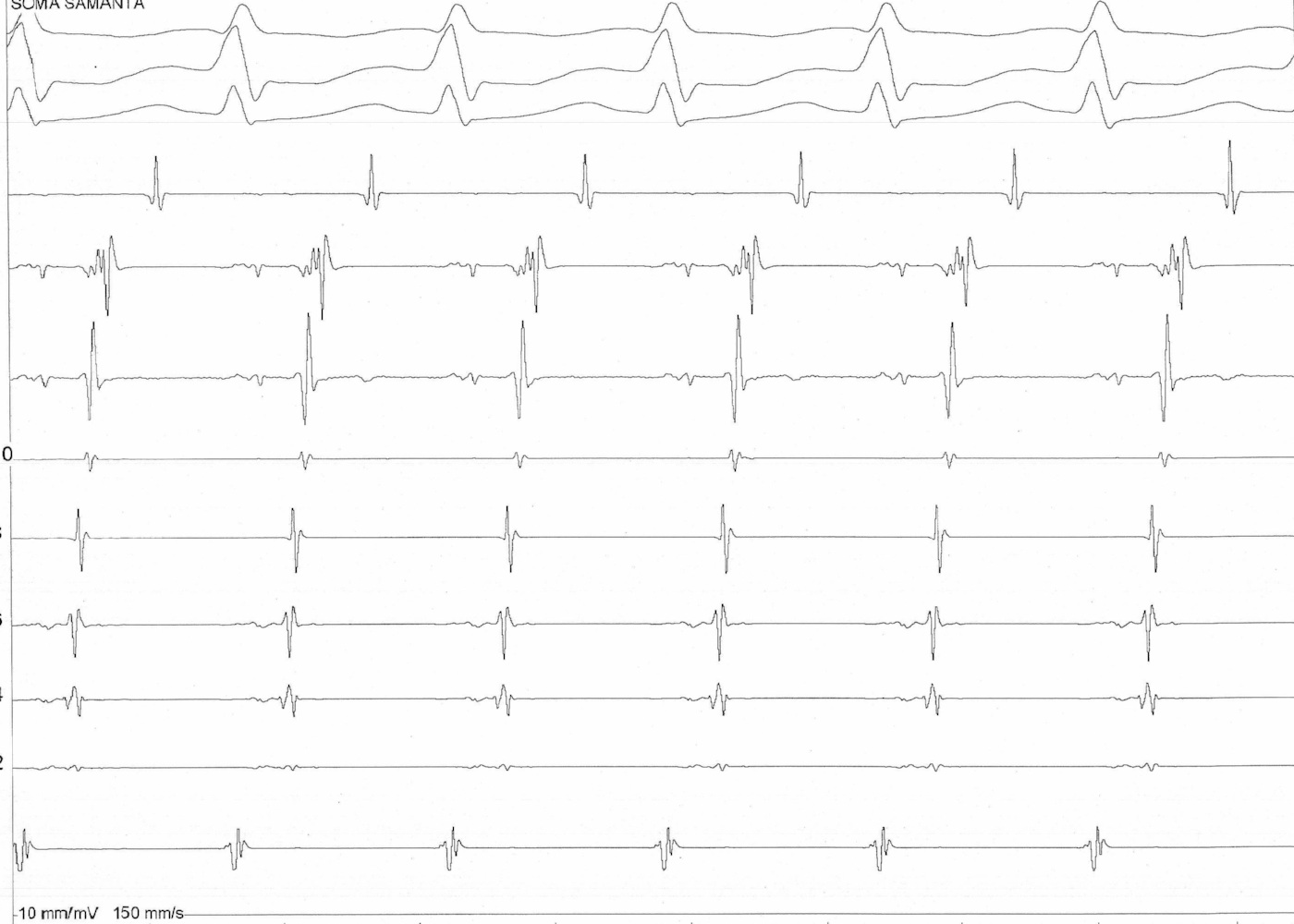
Narrow QRS tachycardia, VA > 70
NQRST with VA > 70 ms and central VA
Differential diagnoses
- AVNRT - Slow fast / slow slow / fast slow
- AVRT
- AT
- VOP again most useful
Rule out (or in) AT
AVNRT vs AVRT
SA / VA intervals
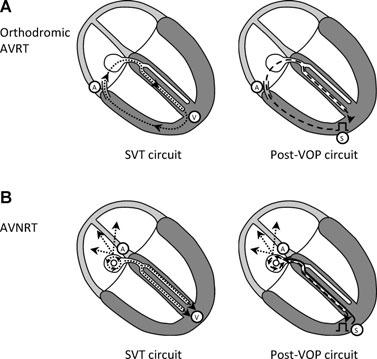
Sequential vs parallel activation
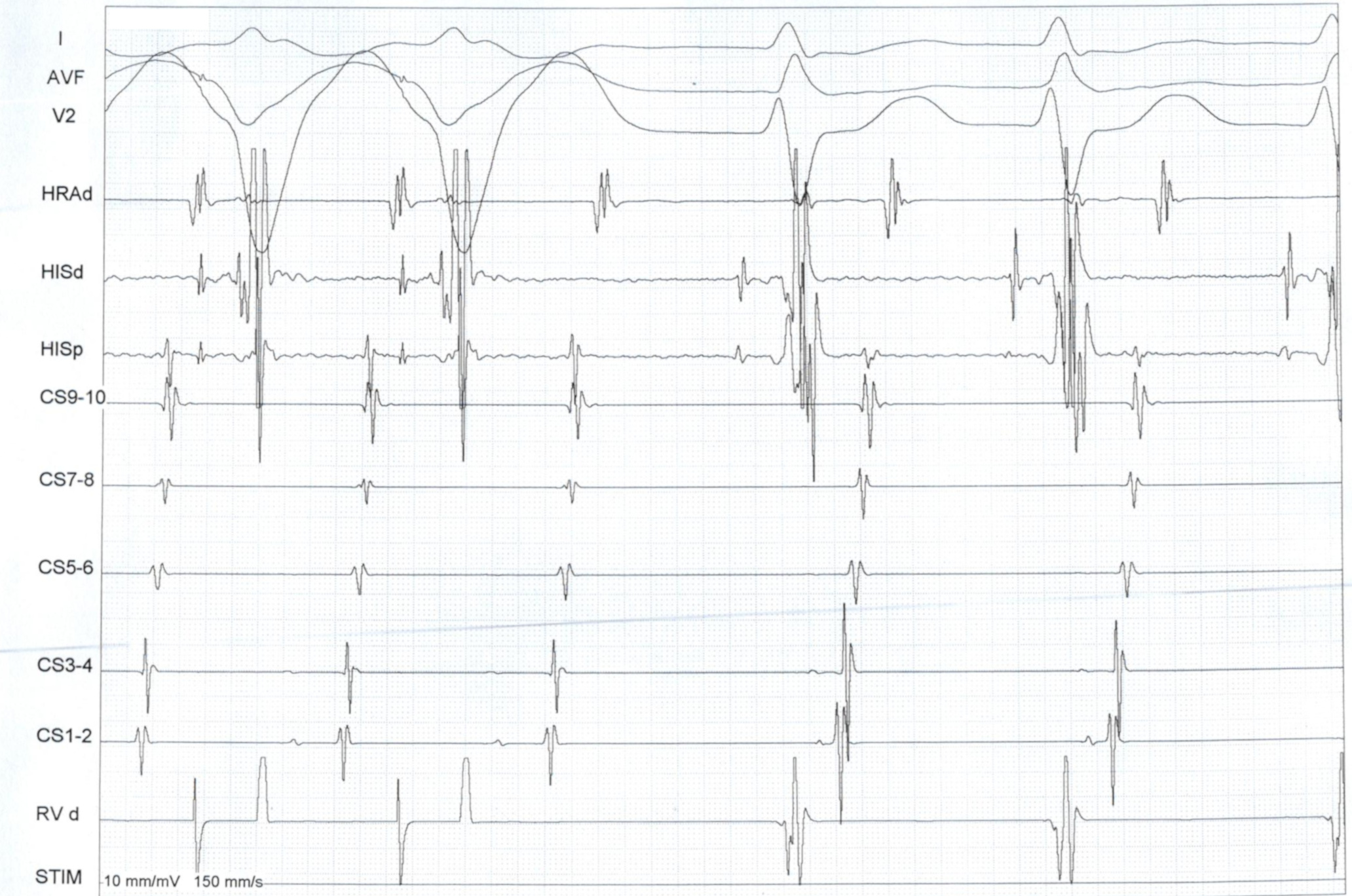
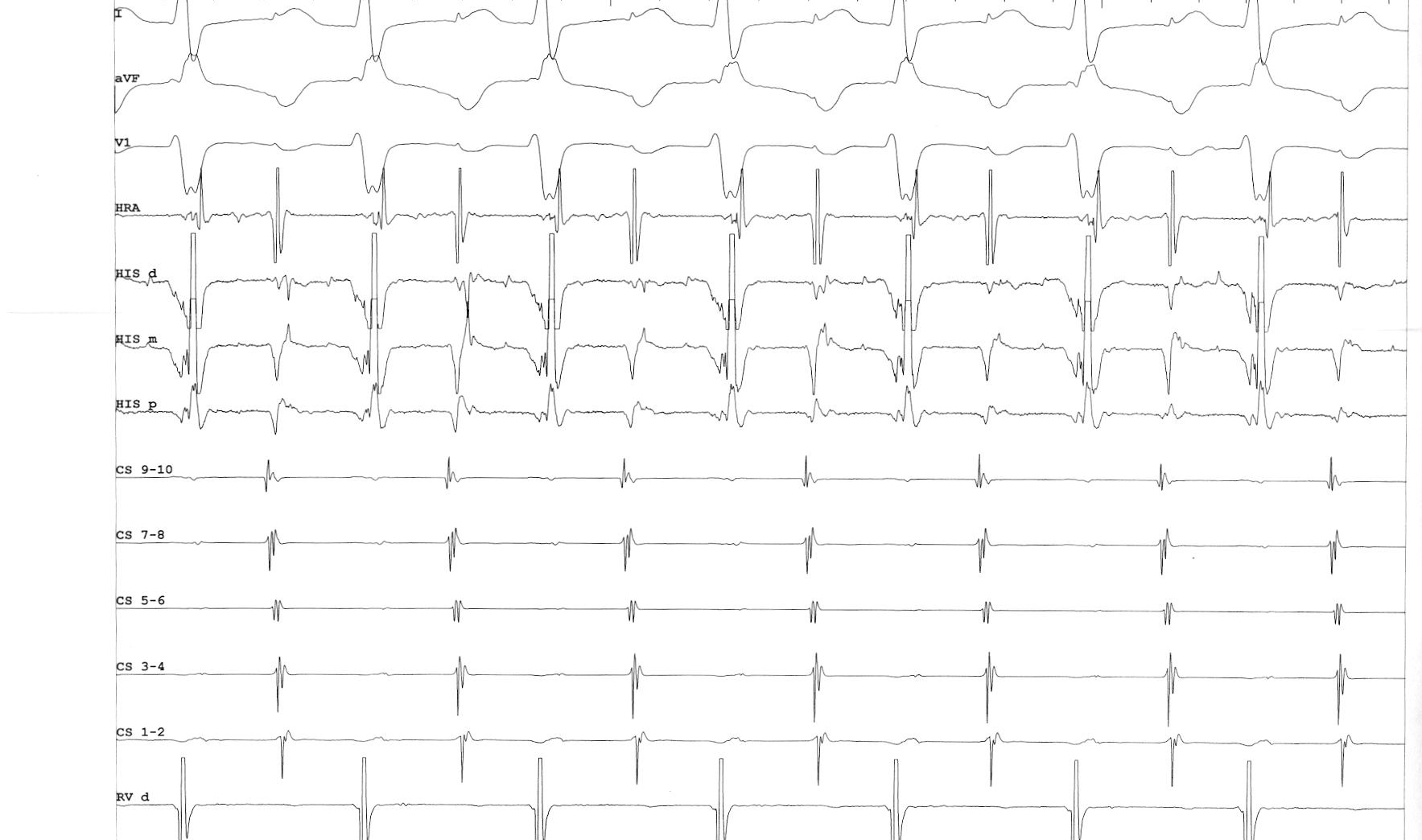
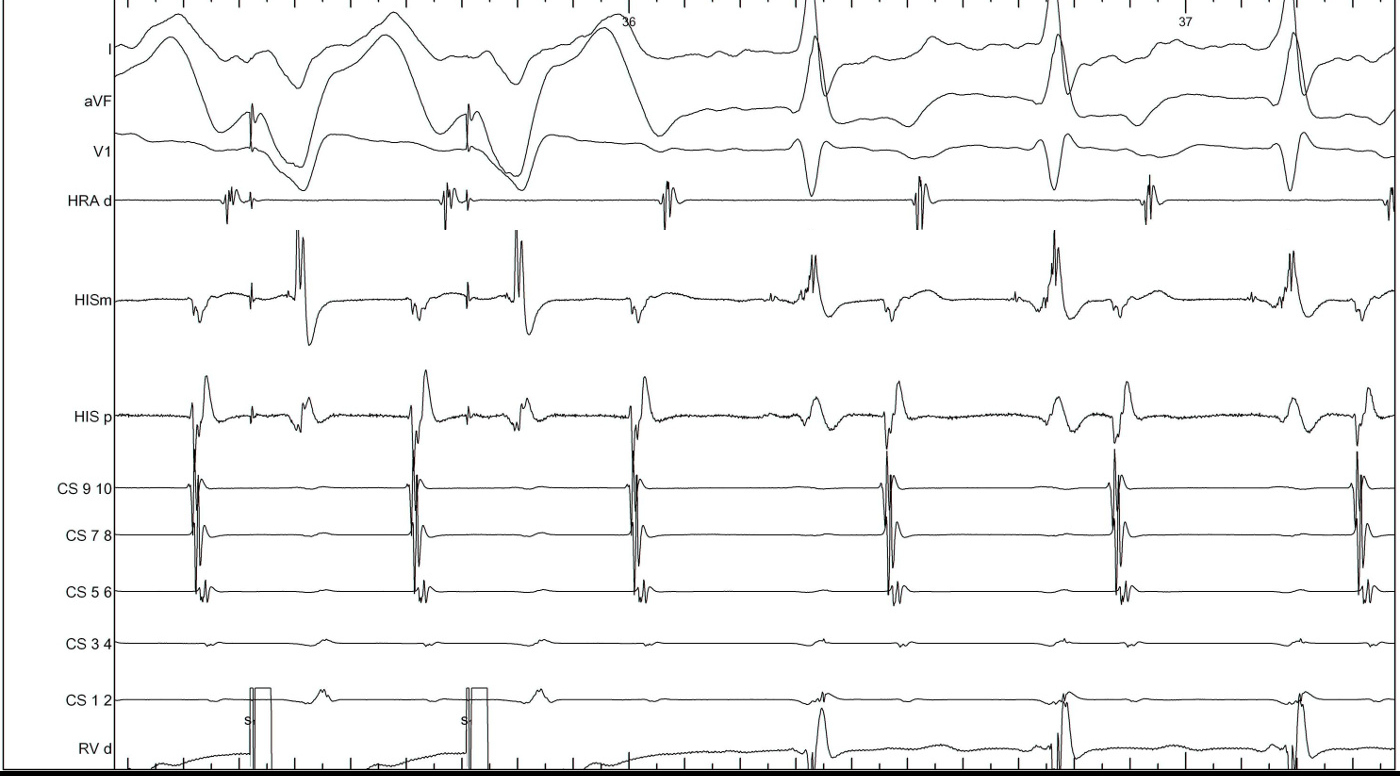
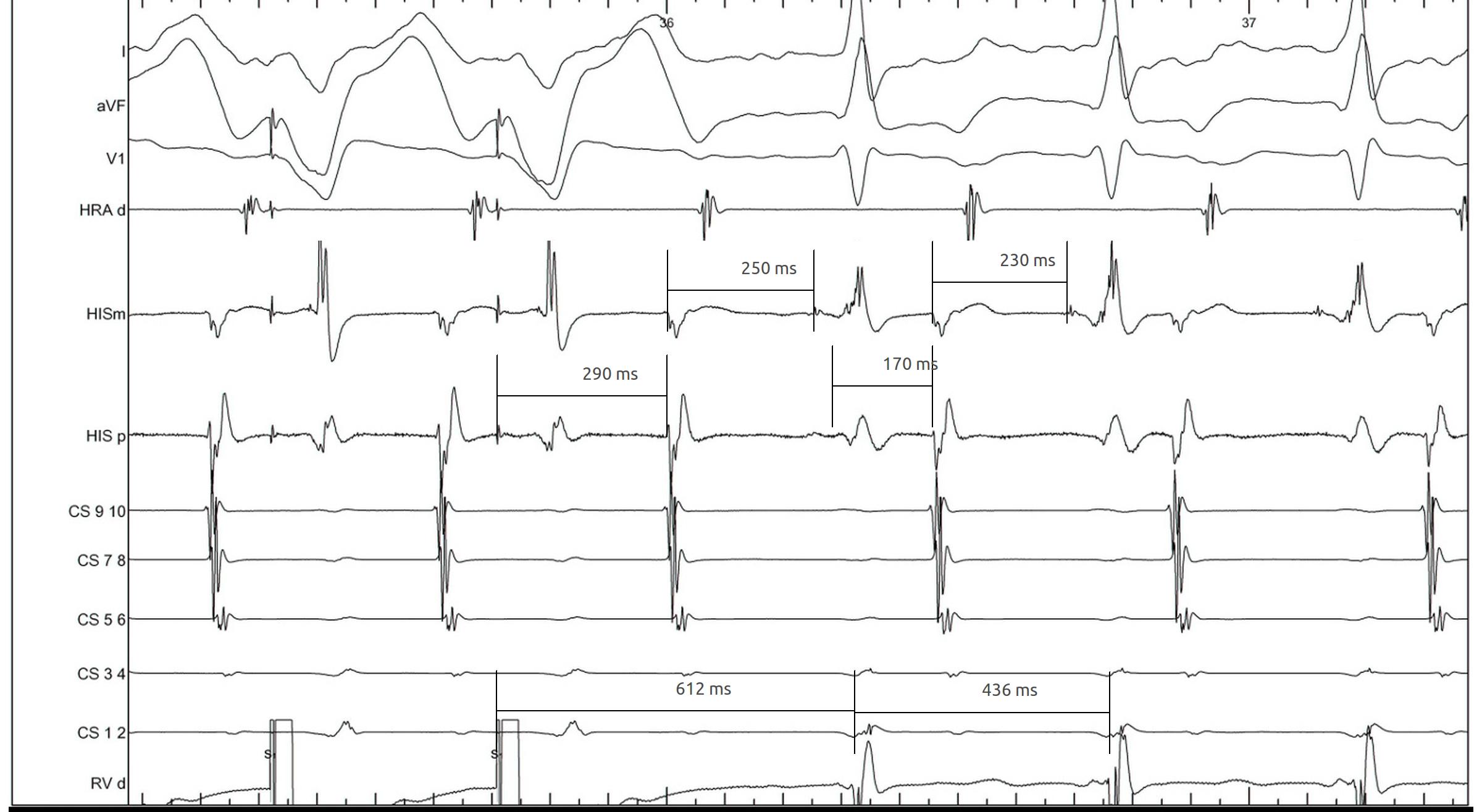
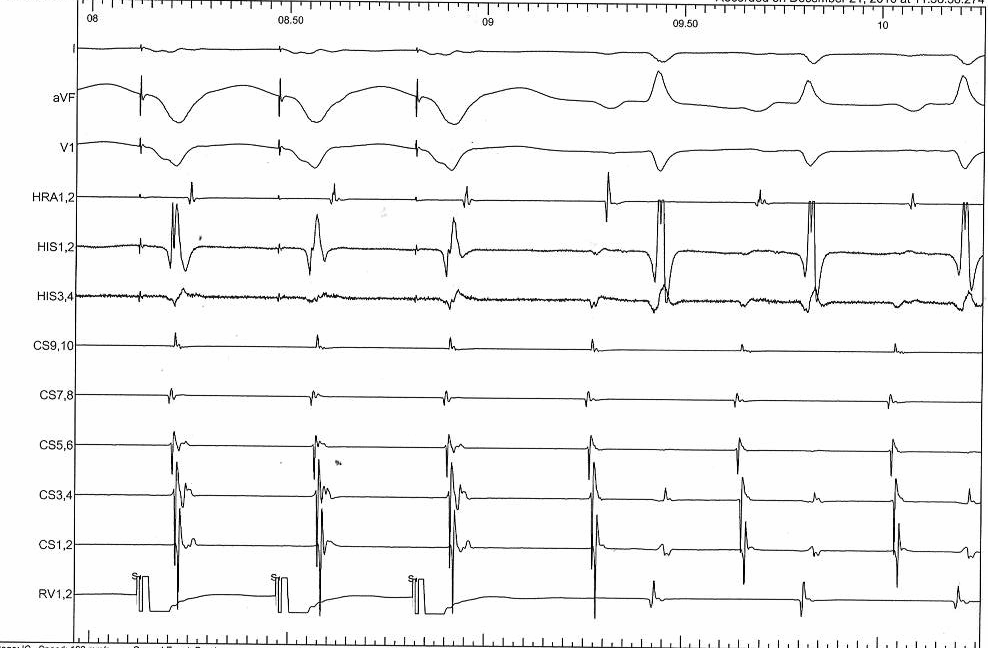
RV pacing in narrow QRS tachycardia.
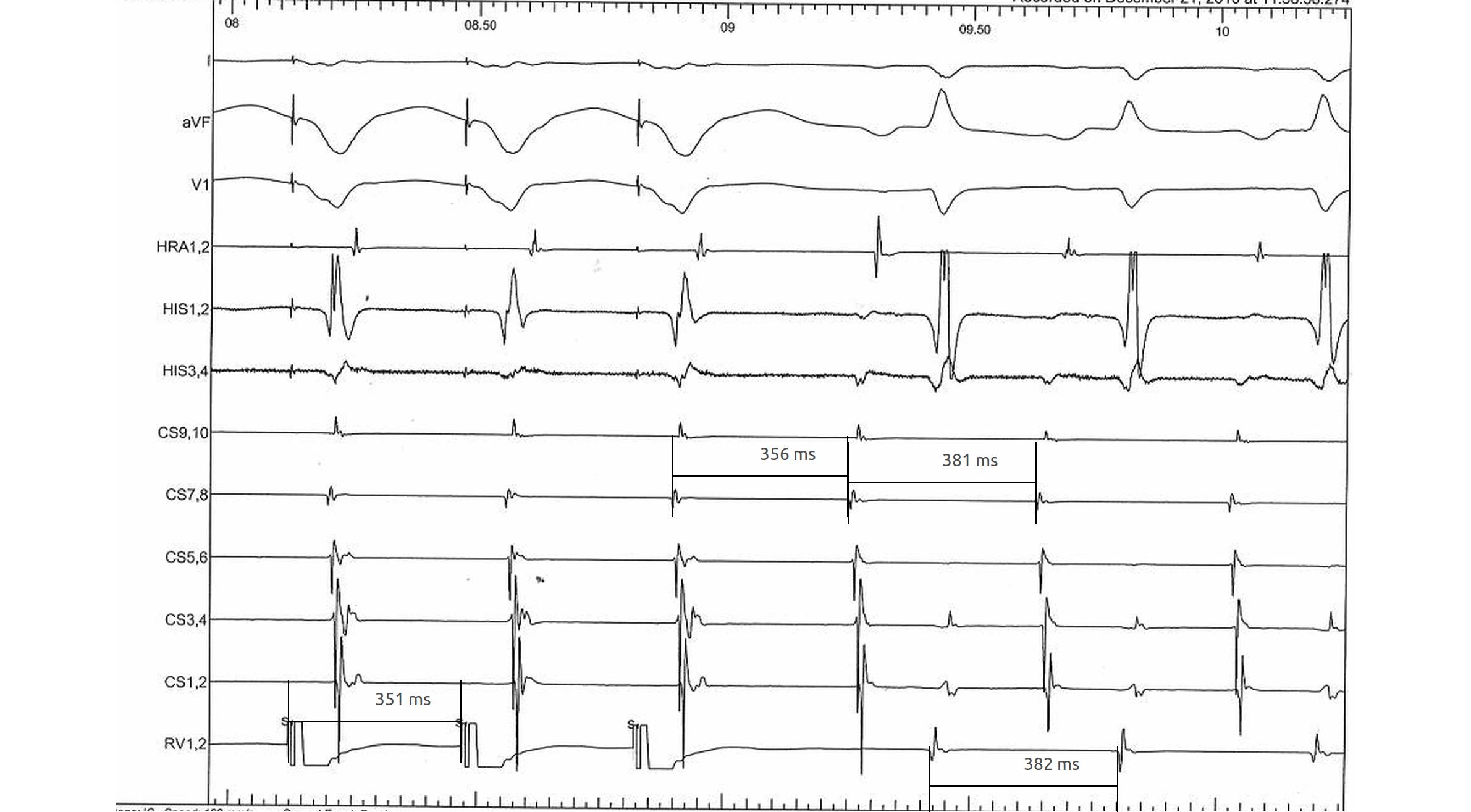
Measurements
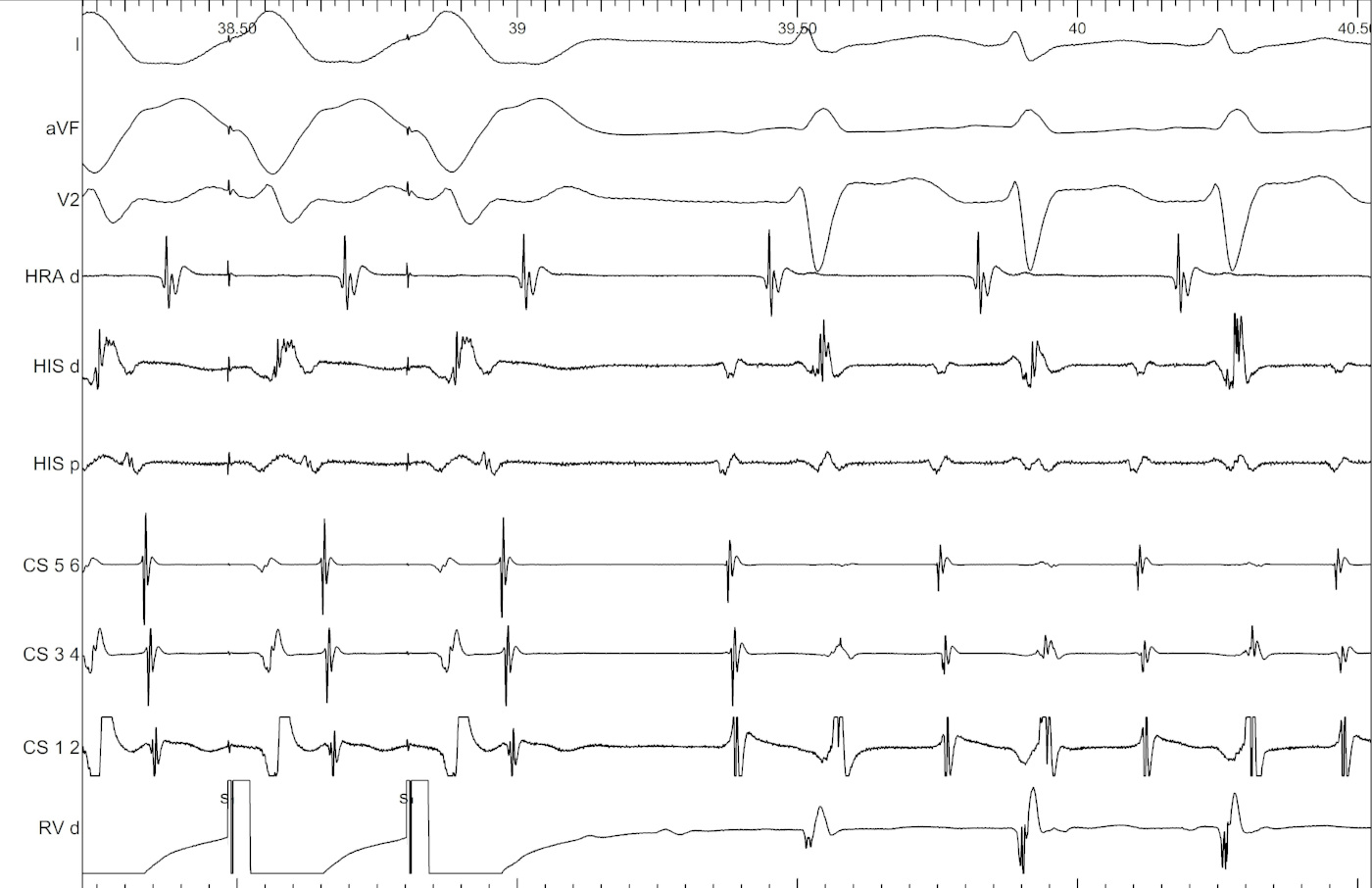
RV pacing in AT - VAAV
VOP always terminates tachycardia - What would you do?
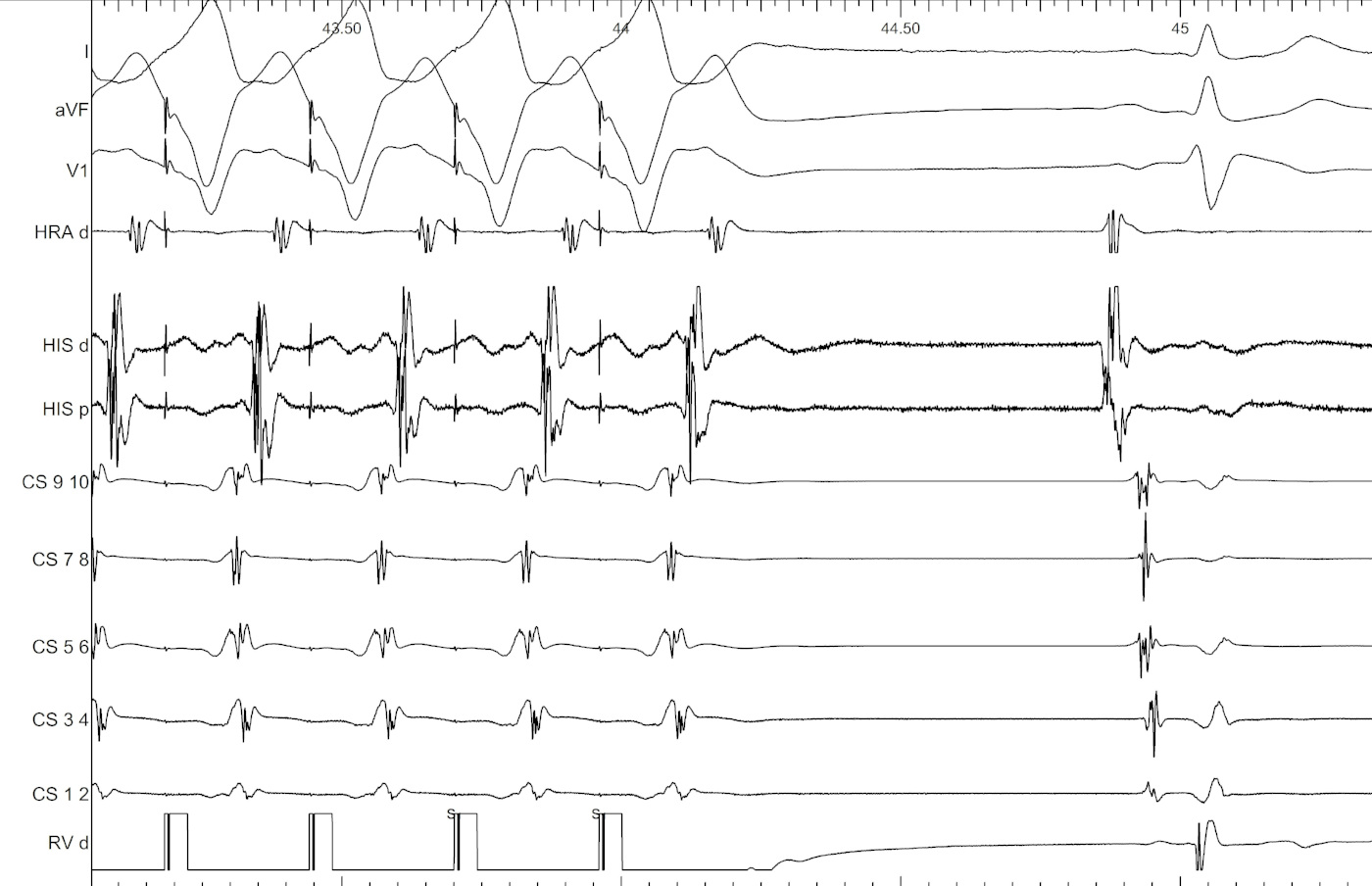
Beginning of entrainment can give a clue
- Dandamudi … Vijayaraman. A novel approach to differentiating orthodromic reciprocating tachycardia from atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia. Heart Rhythm. 2010 Sep;7(9):1326-9.
- AlMahameed … Michaud GF. New criteria during right ventricular pacing to determine the mechanism of supraventricular tachycardia. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2010 Dec;3(6):578-84.
Entrainment with Isoprenaline
Other clues
Spontaneous termination
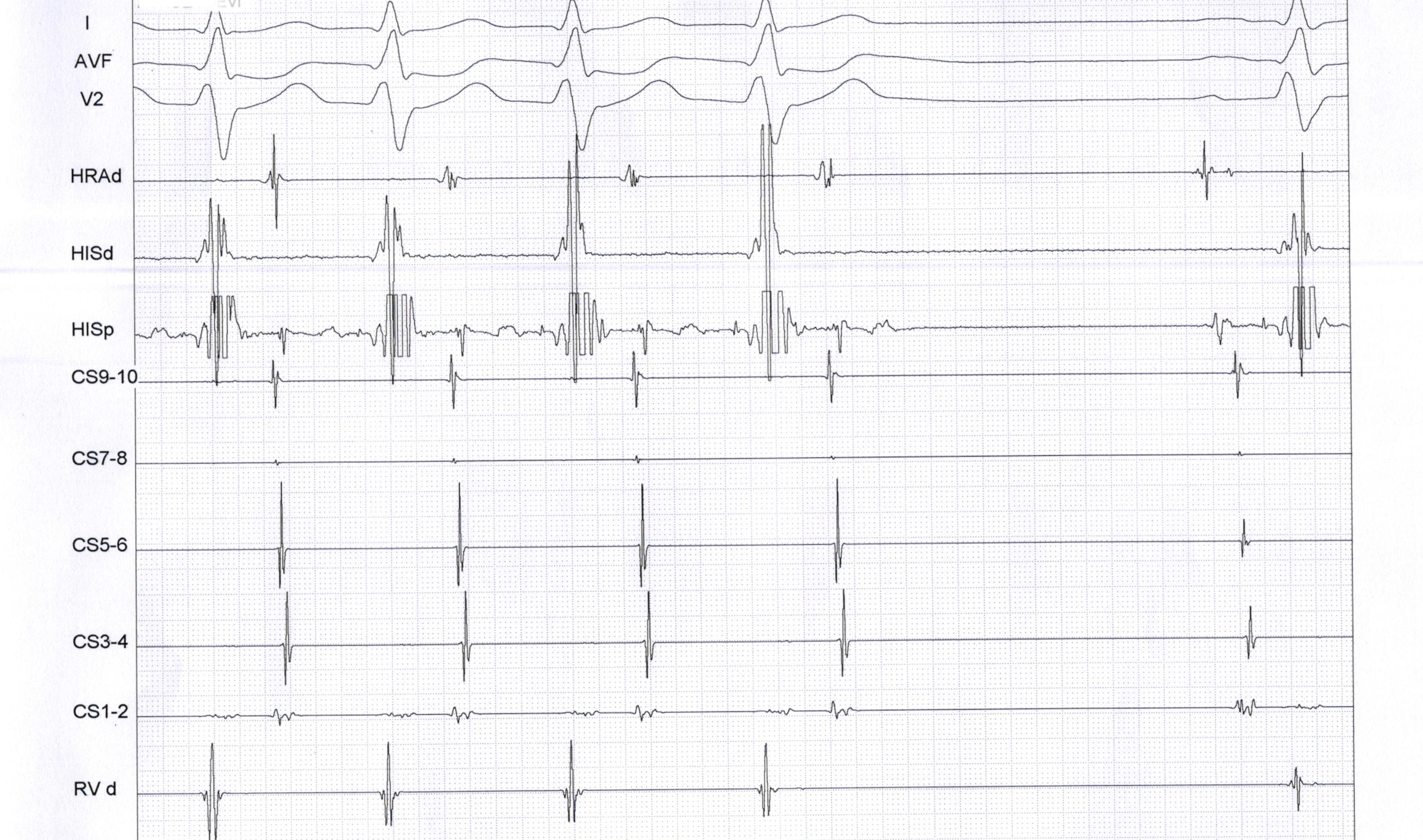
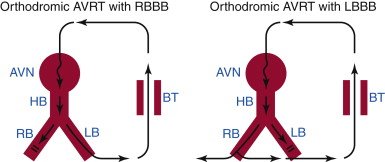
Bundle branch block
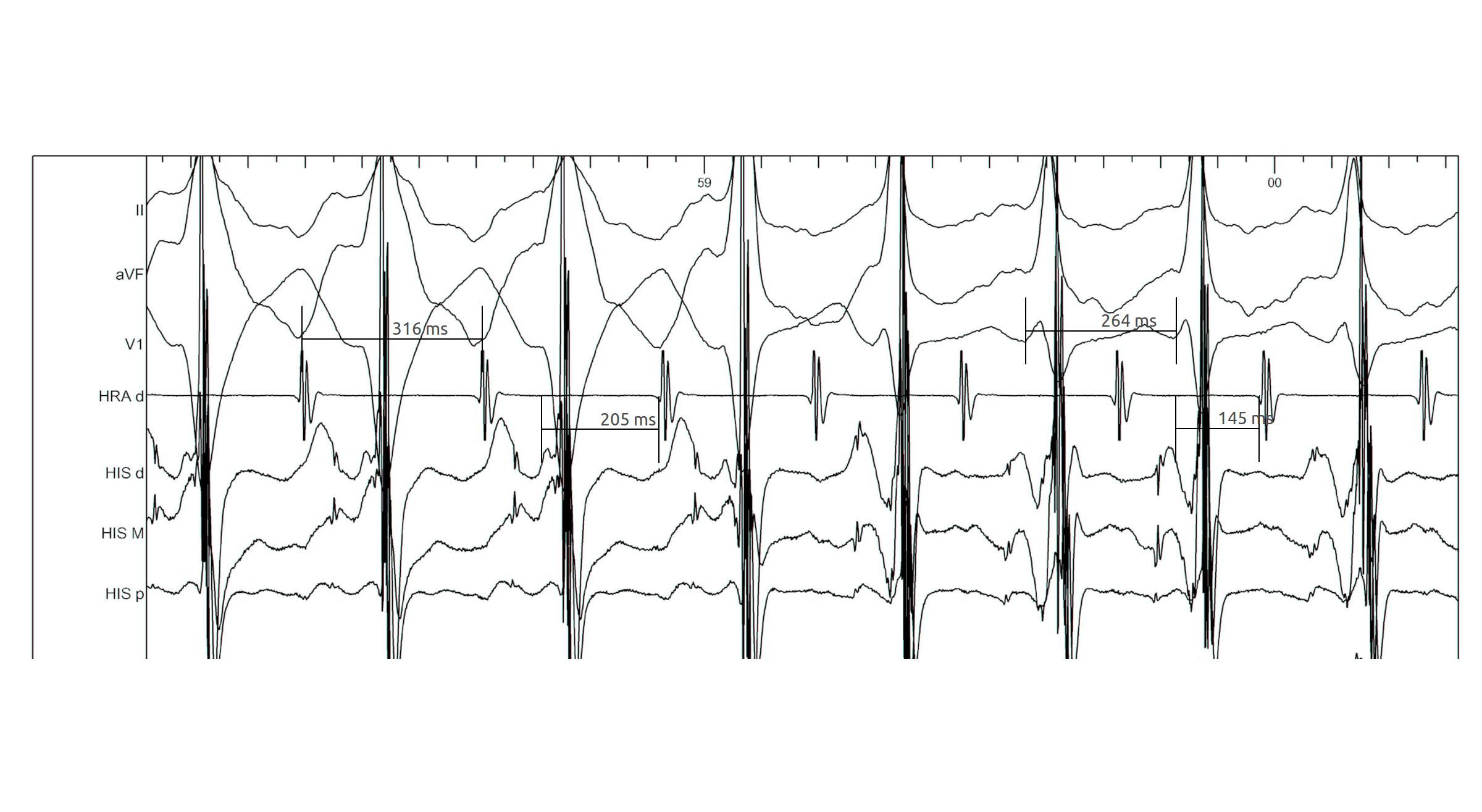
Bundle branch block
Summary
Approach to evaluation of tachycardia
- eccentric atrial activation - vop
- overdrive with same eccentric activation / VAV - AVRT
- overdrive with different activation / VAAV - AT
- VA diss - AT
- central atrial activation
- Very short VA
- VOP - VAAV vs VAV
- Longer VA
- VOP - VAAV vs VAV
- SAVA / PPI
- Very short VA
Summary
- VAAV identifies AT, VAV rules out
- SA - VA and PPI - TCL are longer for AVNRT
- Can use basal pacing if responses are equivocal
- A entrained earlier for AVRT, entrained before His