Wide QRS tachycardia

Raja Selvaraj. Professor of Cardiology, JIPMER
06-06-2020
Introduction
Definition
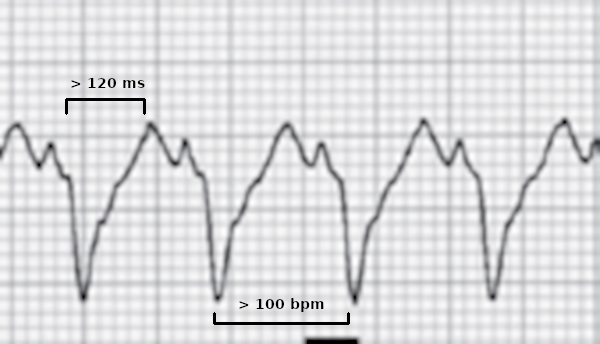
What are the causes
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Supraventricular tachycardia
- Rate related aberrancy
- Preexisting bundle branch block
- Preexcited / antidromic tachycardia
Why important to identify
- Acute management
- Long term management
VT vs SVT - Concept
- Involvement of atria
- Usually part of tachycardia mechanism (SVT) - exceptions
- Not part of tachycardia mechanism (VT)
- Use of specialized conducting system
- Ventricular activation uses HPS, but HPS conduction abnormalities (SVT with aberrancy)
- Ventricular activation originates outside of HPS (VT) - exceptions
VT vs Preexcited tachycardia - Concept
- Both originate in ventricular muscle - Morphology cannot differentiate
- Differences
- APs are restricted to specific locations
- Atrium involved in preexcited tachycardias
General approach
Sequential approach
- Regularity
- Atrial activation
- Morphology
- Sinus ECG
- Response to AV blocking drugs / maneuvers
Regularity
- Sustained monomorphic VT and SVT usually very regular
- Significant irregularity points to AF
Atrial activation
- Number of P - less, equal or more
- VA relationship - 1:1, other VA conduction, dissociation
- Morphology of P - sinus / retrograde
Morphology
- QRS width
- LBBB like / RBBB like
- Frontal axis
- Morphology in V1 and V6
- Early activation vs late activation
Morphology - Terminology
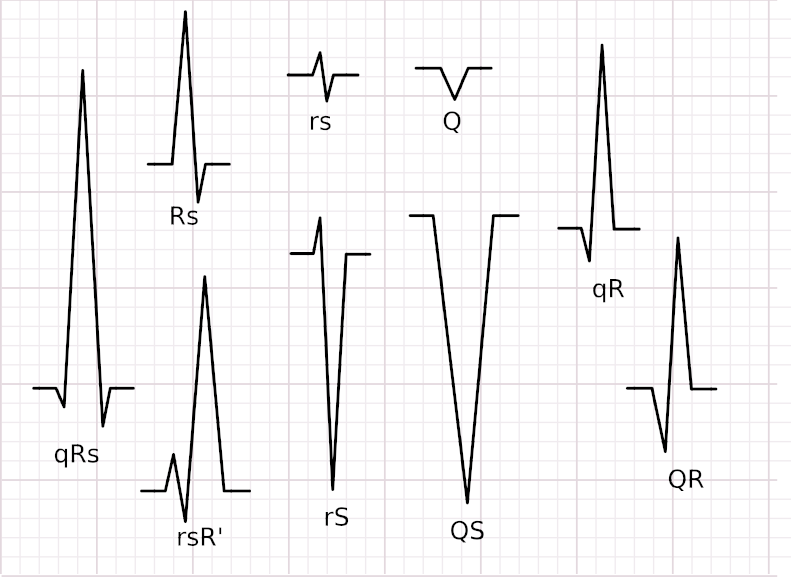
Morphology - Identify typical patterns
- RBBB/LBBB, inferior axis, qS aVL and aVR - Outflow tract VT
- RBBB / LAD, relatively narrow QRS - ILVT
- LBBB / LAD - ARVC / Atriofascicular (Mahaim) pathway
Sinus ECG
- Evidence of MI - Correlate with VT origin
- ARVC
- Bundle branch block - SVT with aberrancy / BBRT
- Preexcitation - AVRT with aberrancy / preexcited tachycardia
Adenosine
- Termination
- Transient slowing with AV block
- No change
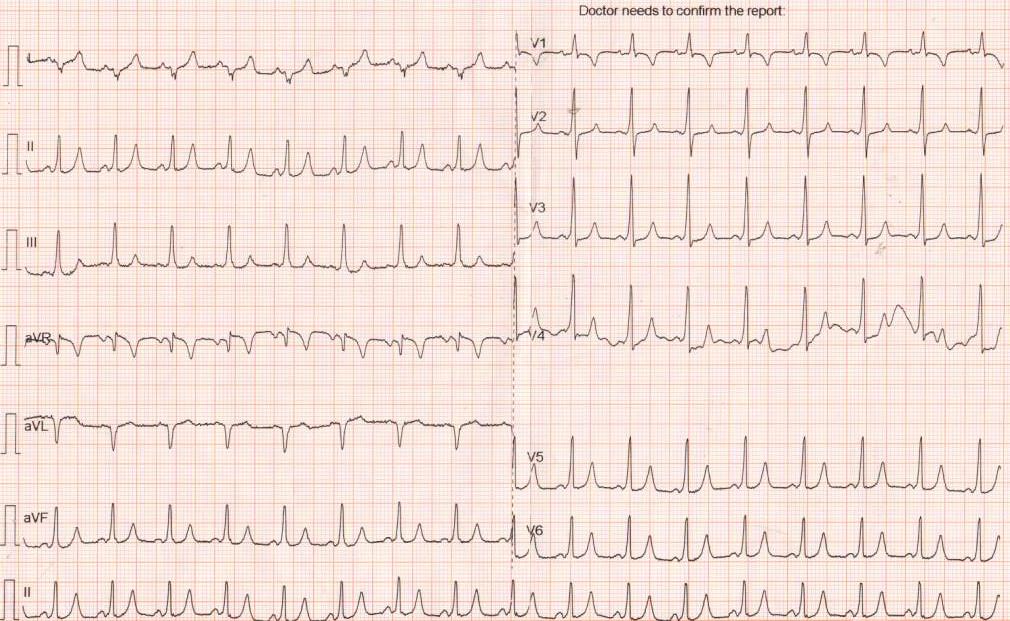
Examples
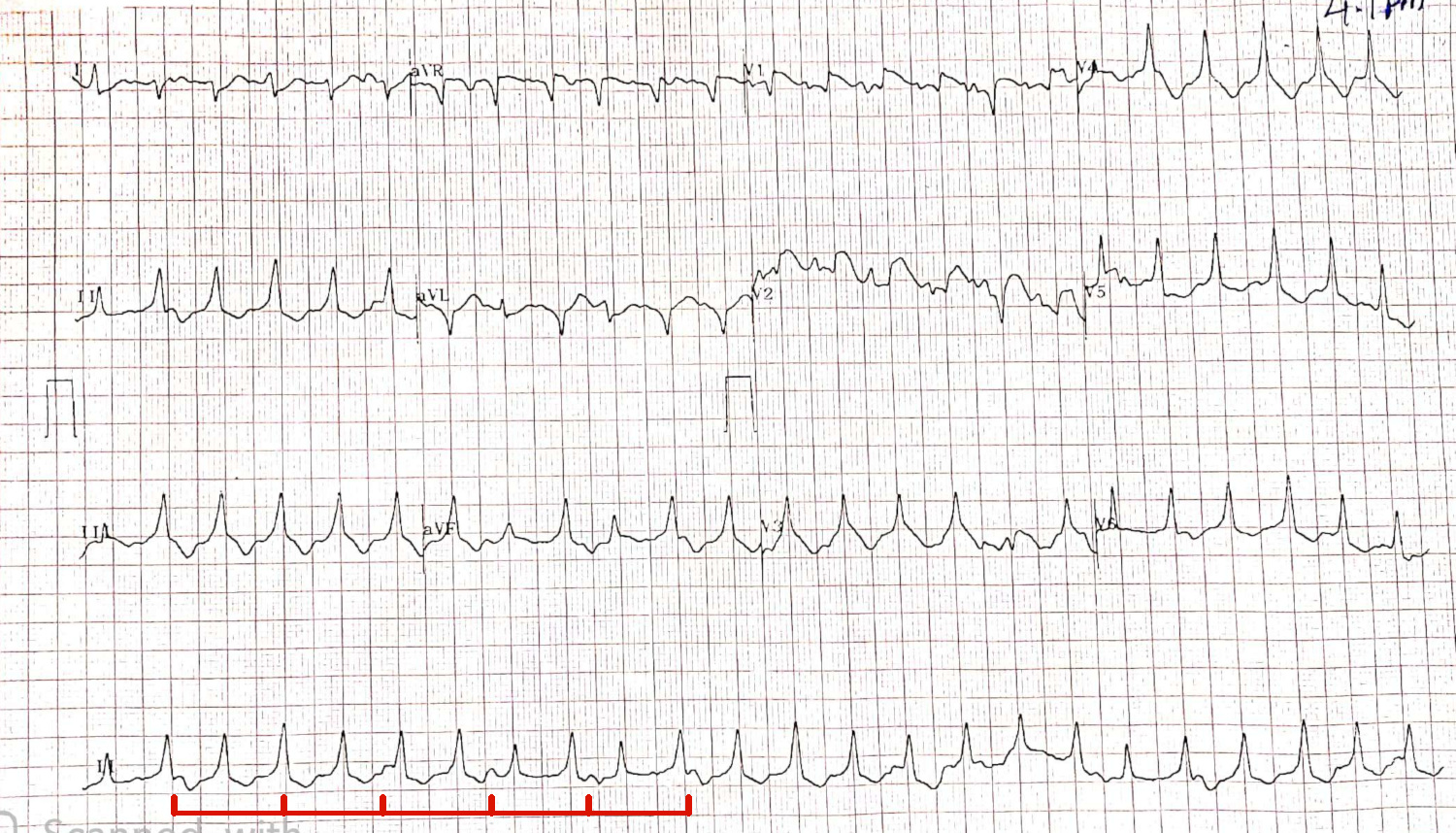
52 M with palpitations
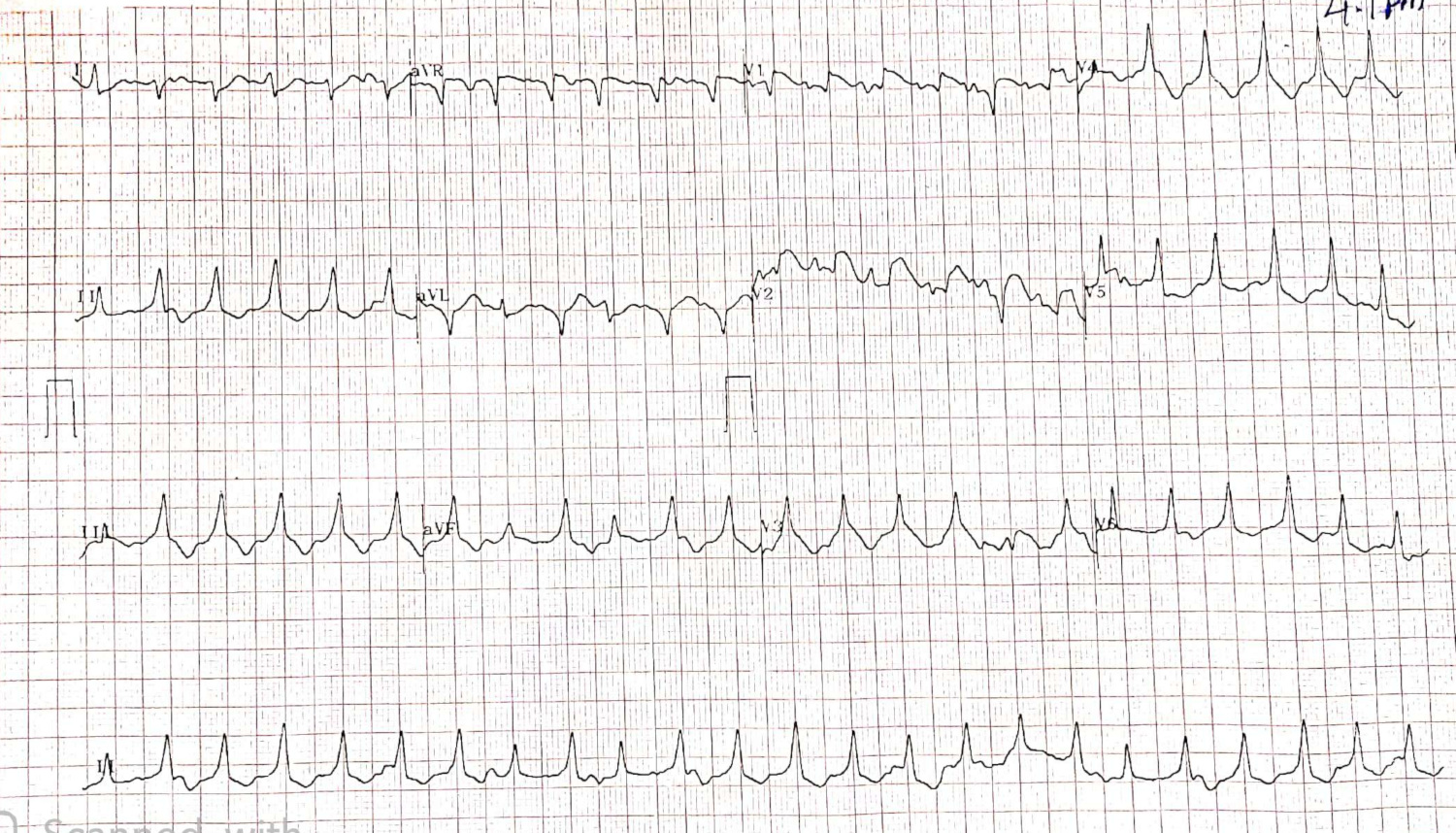
Dissociated, slower sinus rhythm
35 F, repaired TOF
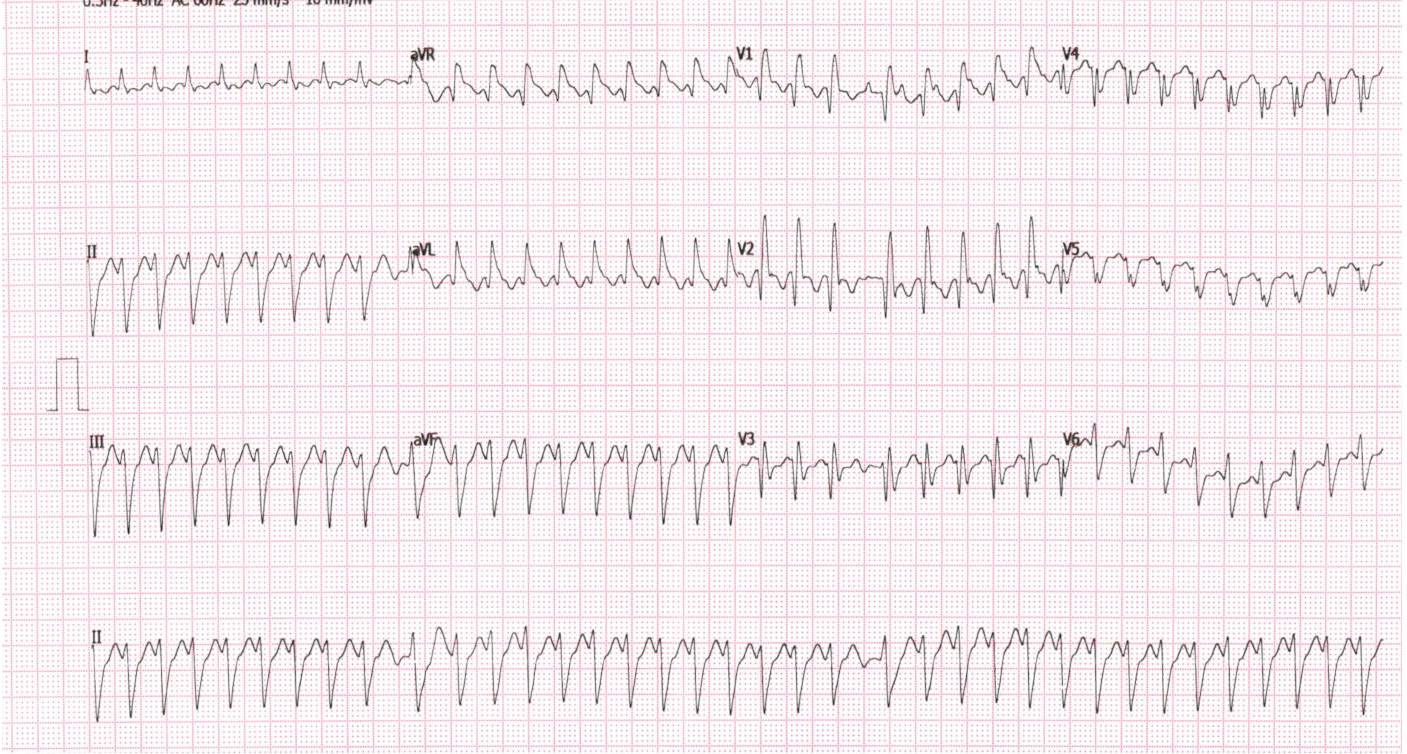
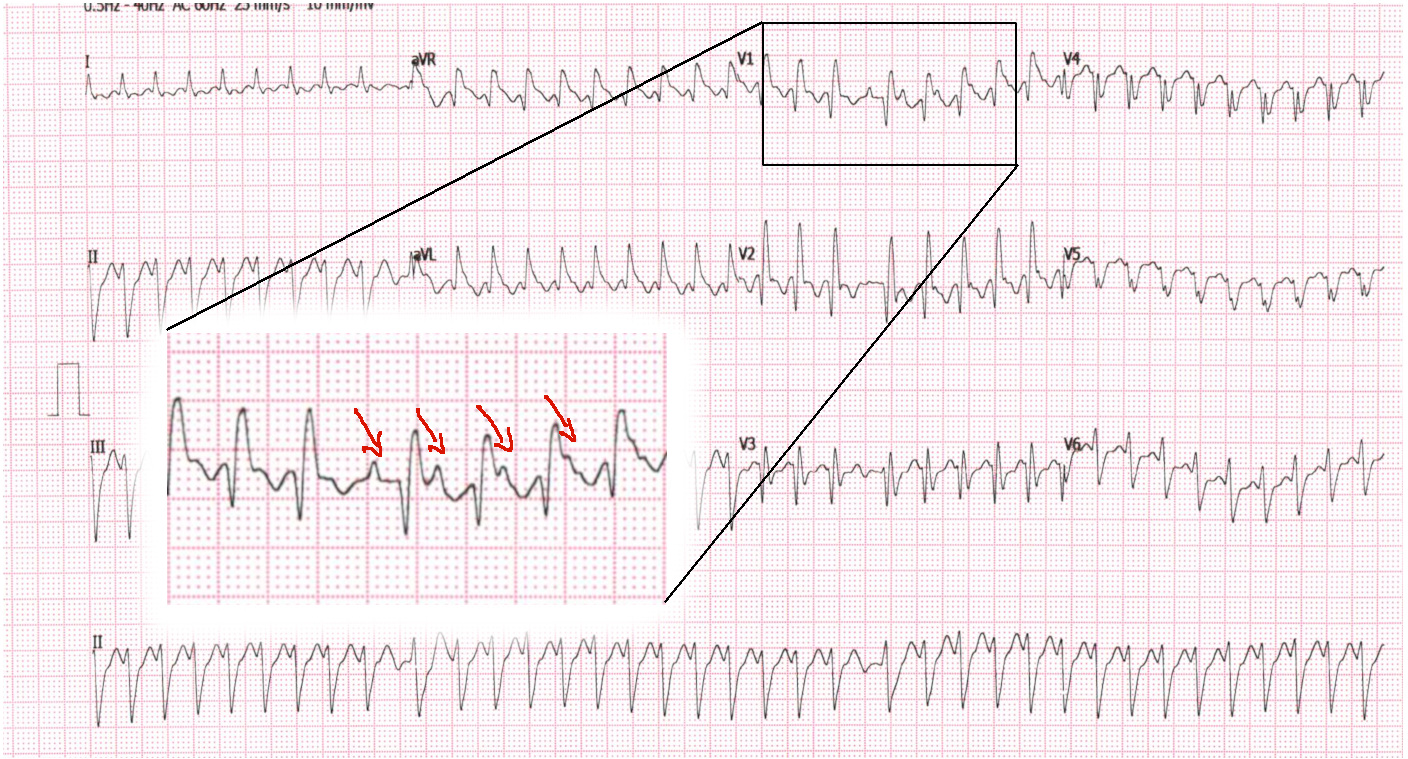
After treatment with Dilzem
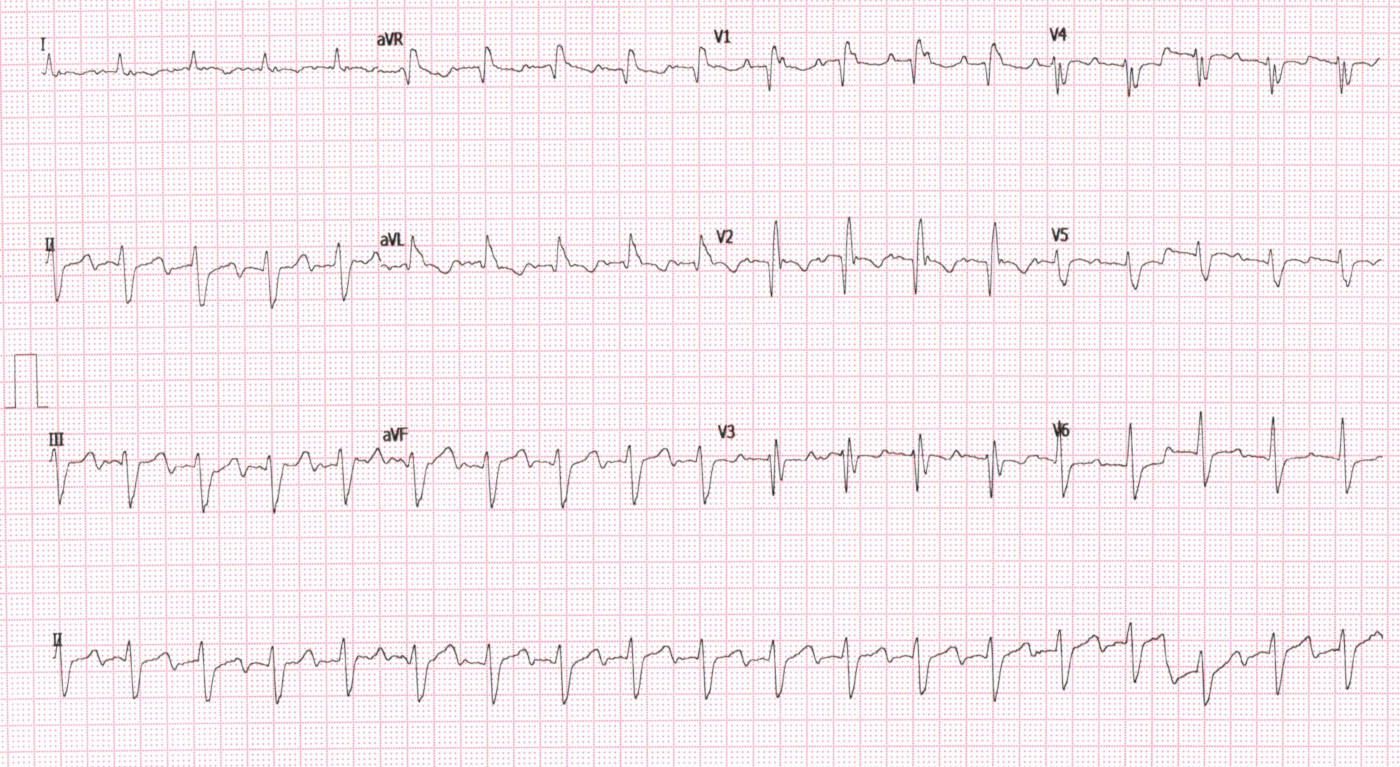
35 M, Normal heart
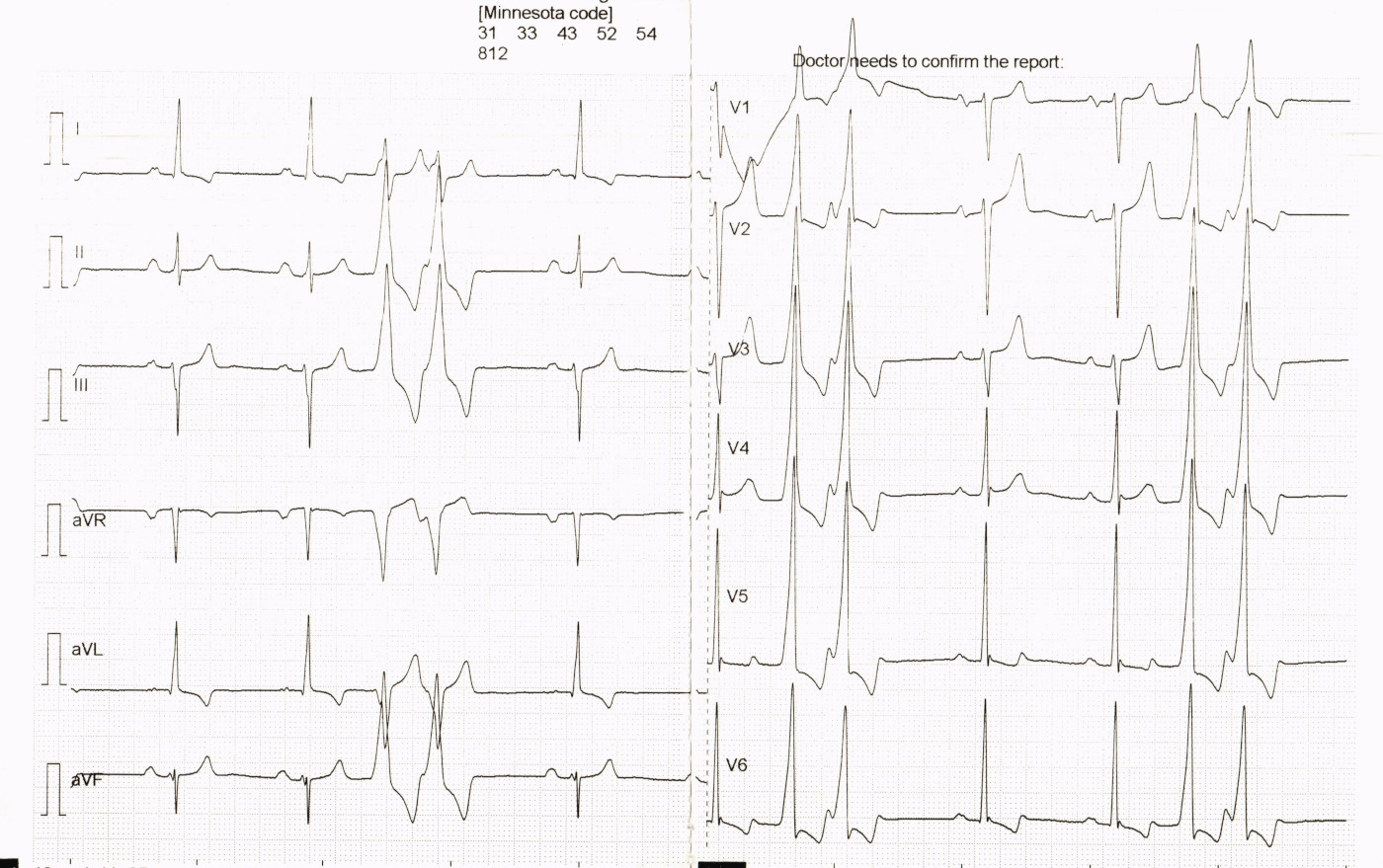
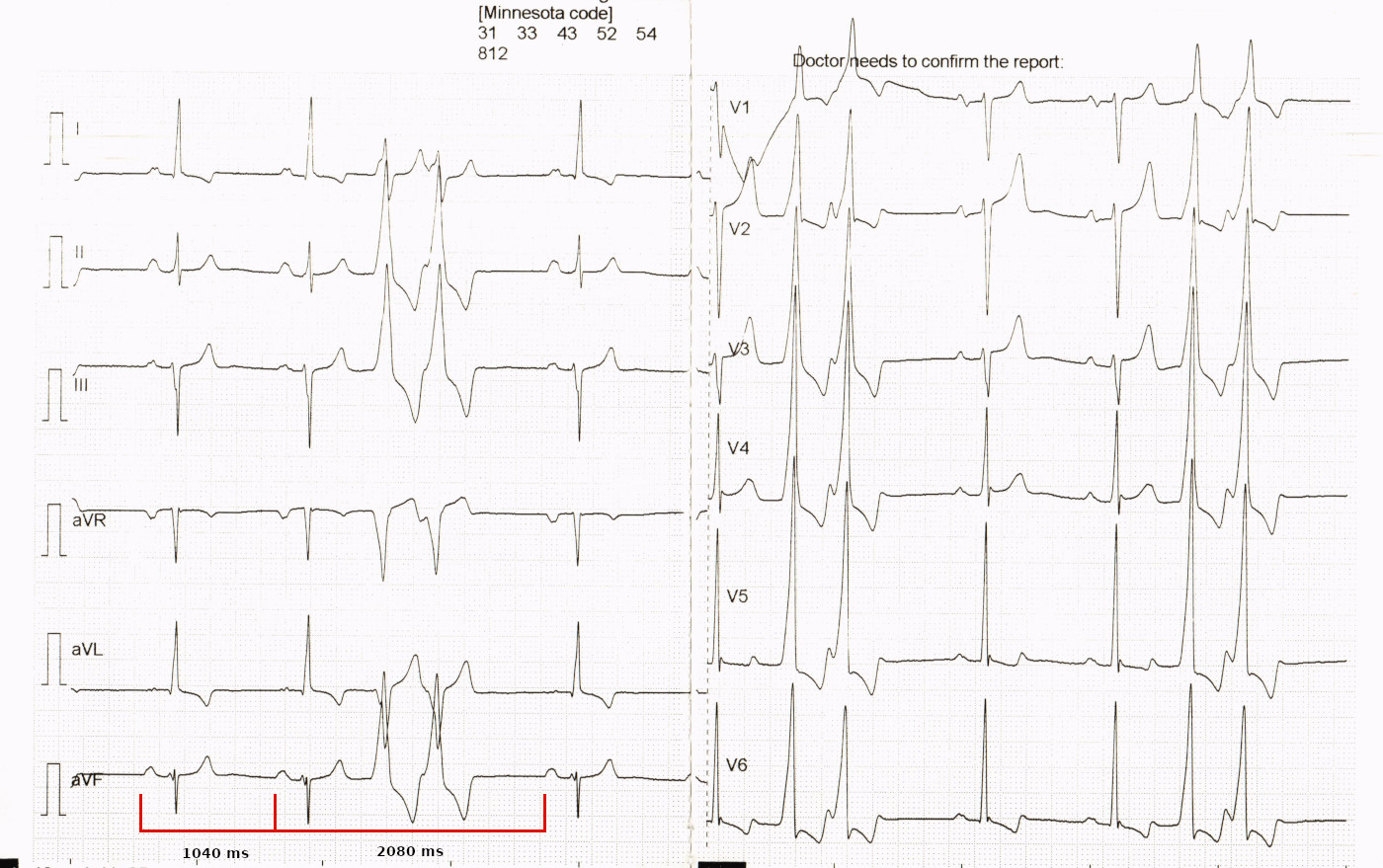
33 M with palpitations
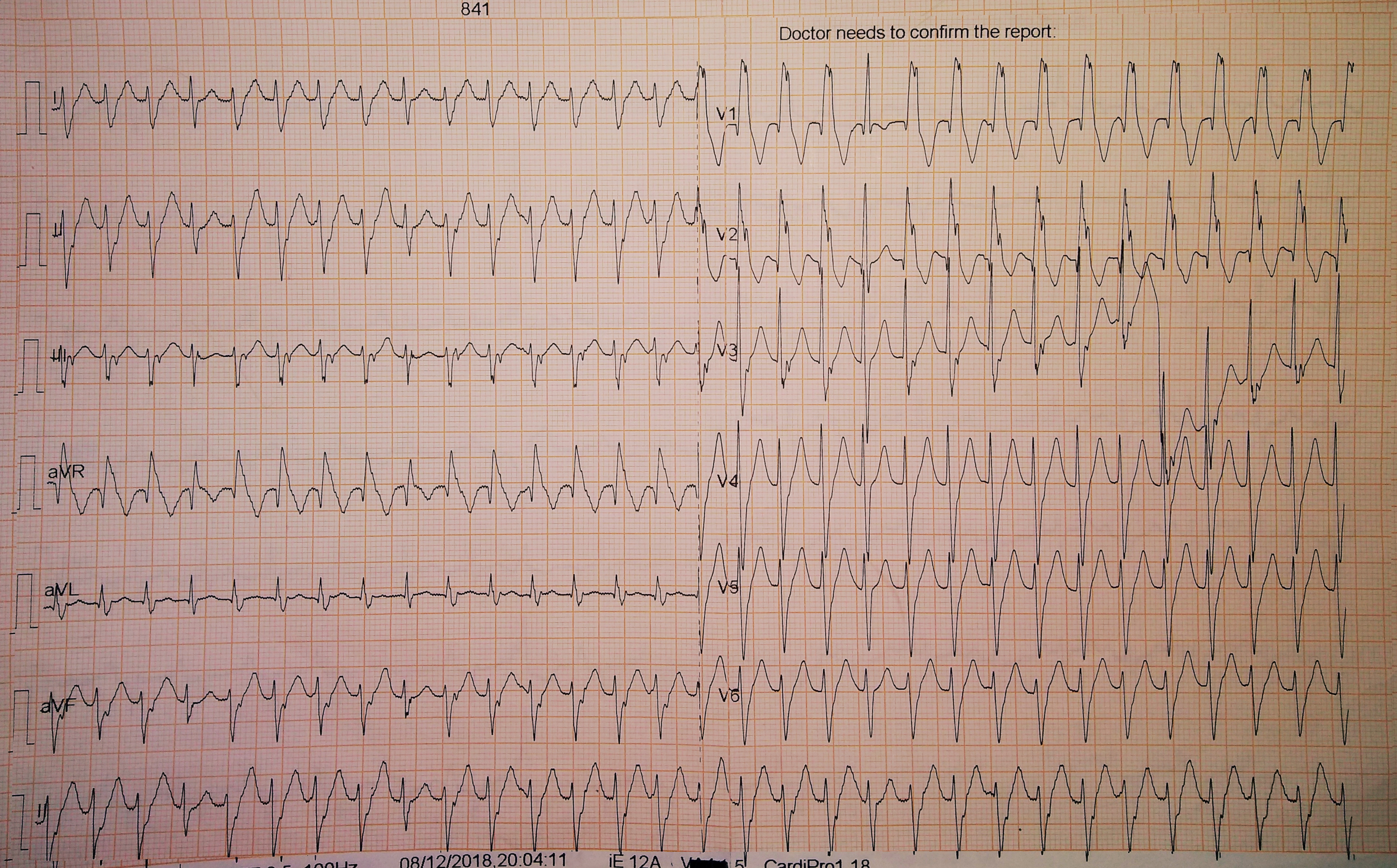
35 M with palpitations
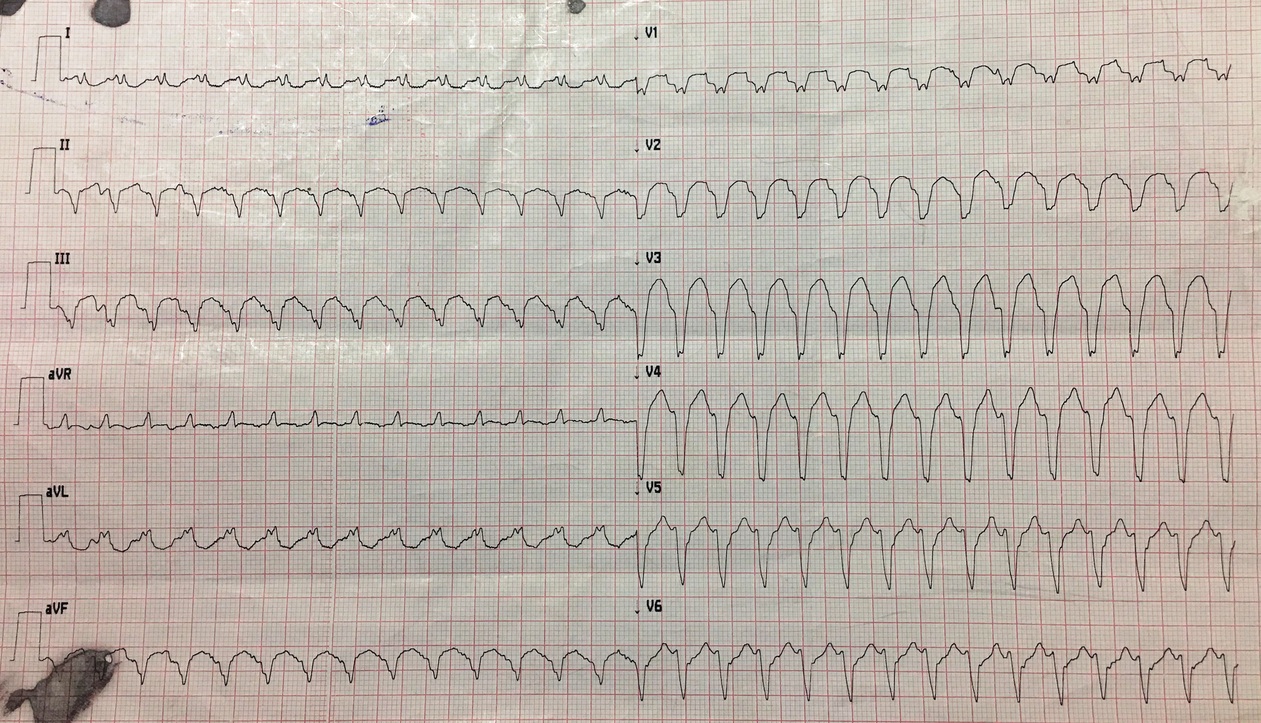
ECG in sinus
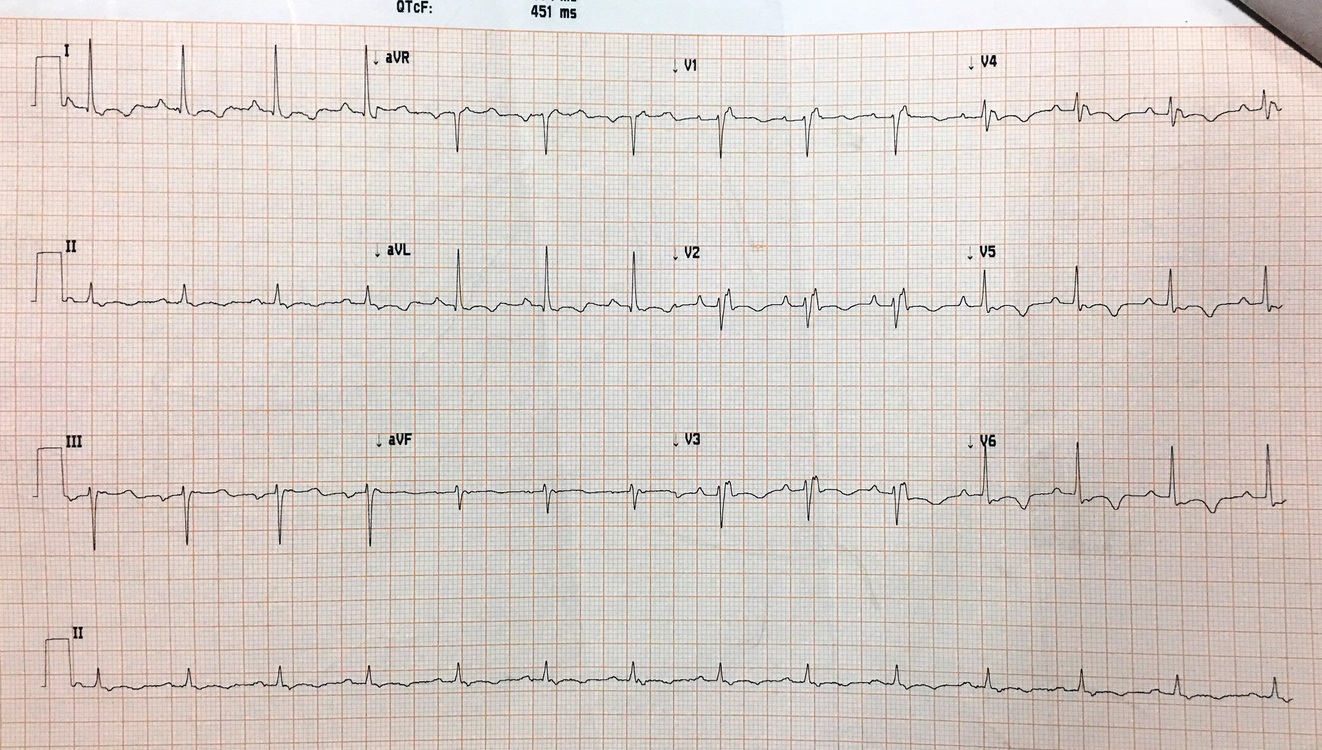
60 M
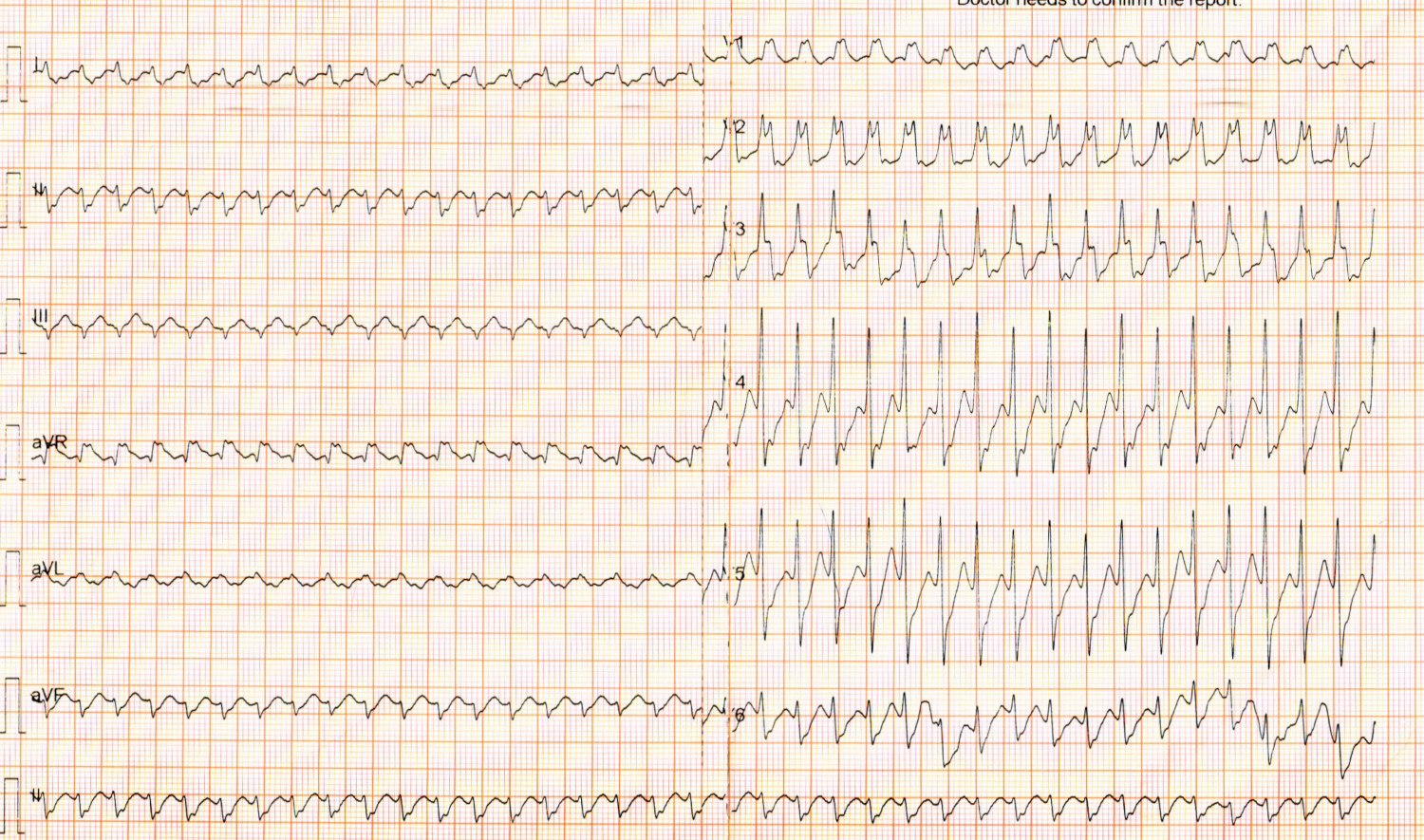
Adenosine
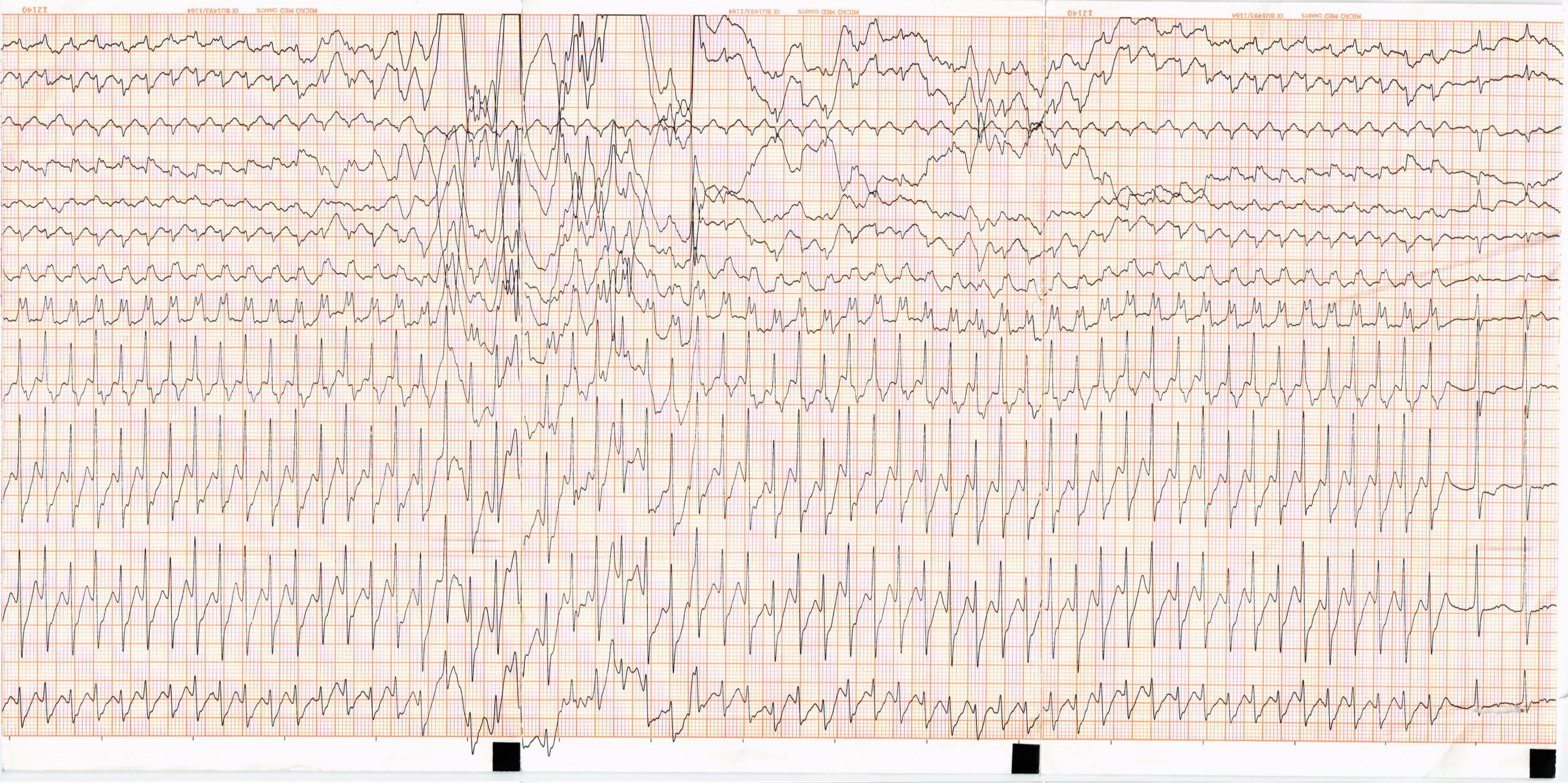
Dilzem
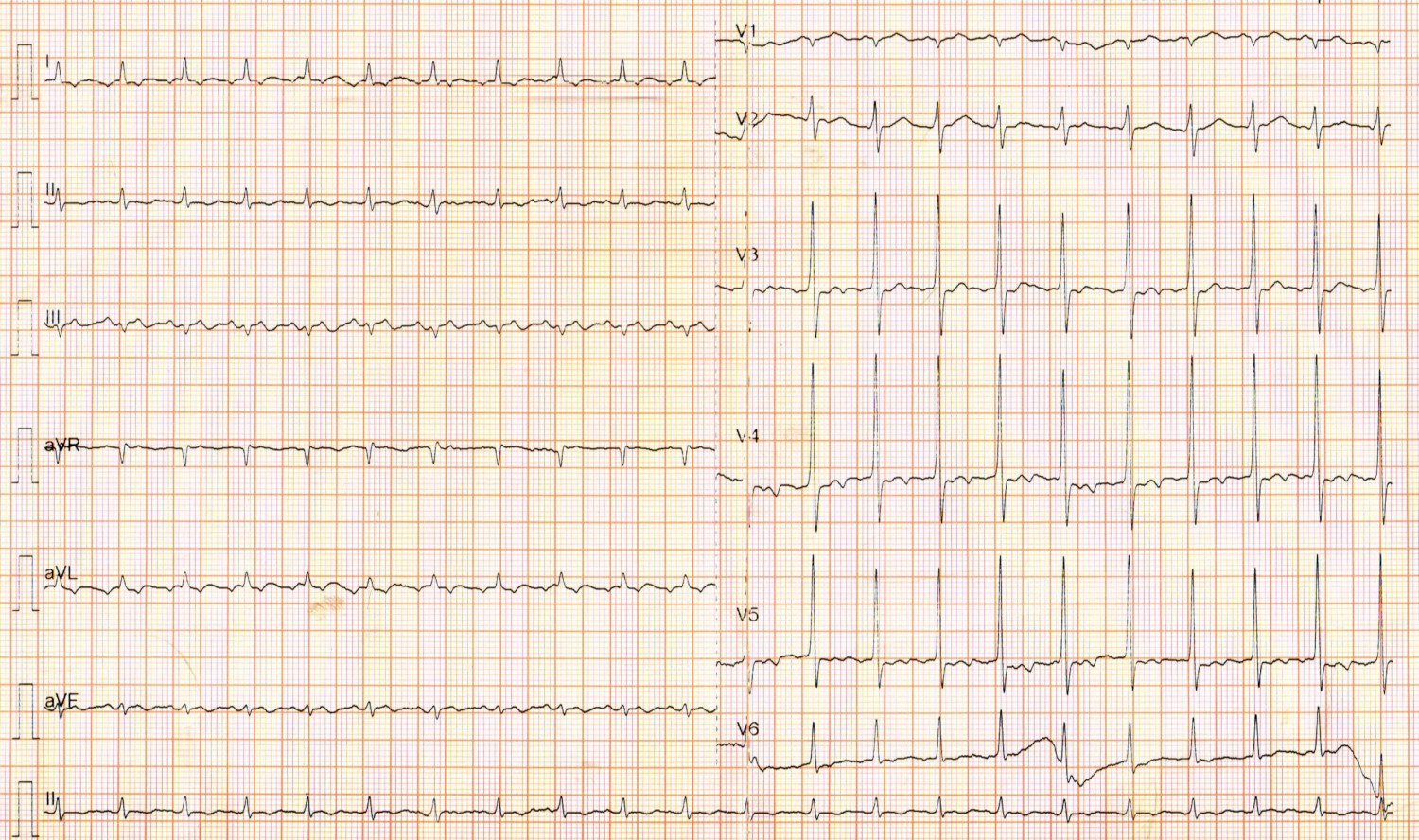
34 F, Palpitations and syncope
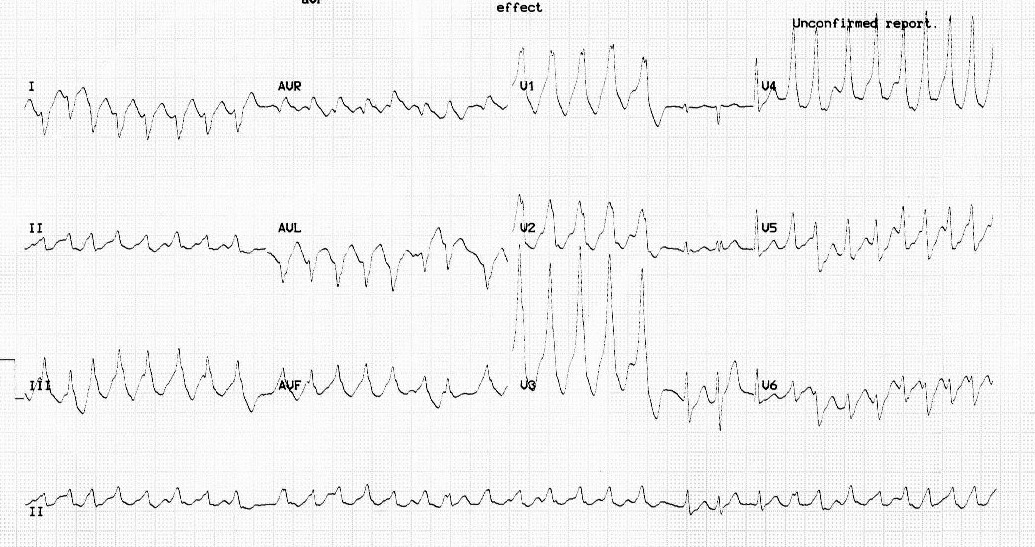
Sinus rhythm
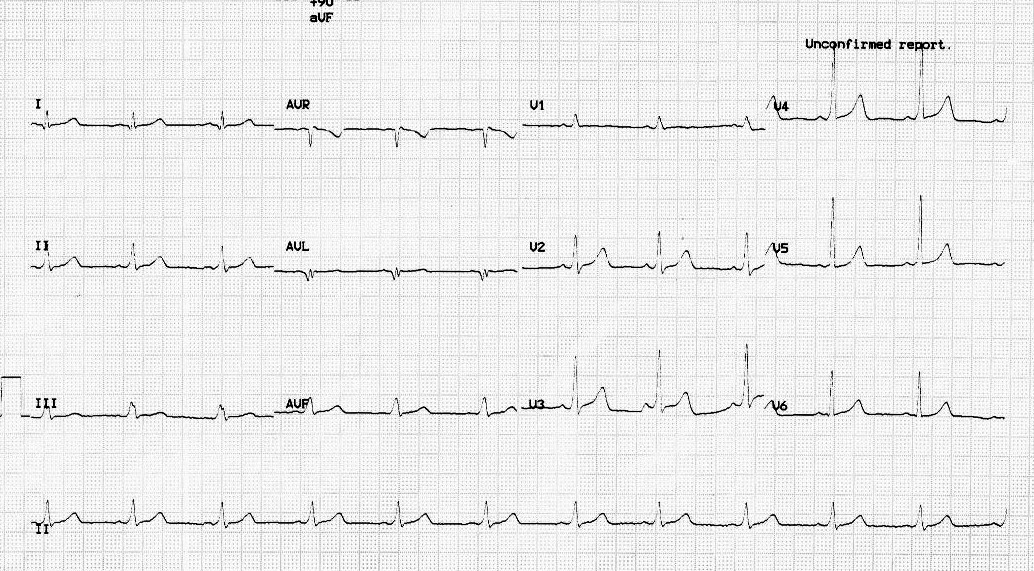
54 M, known CAD - old AWMI
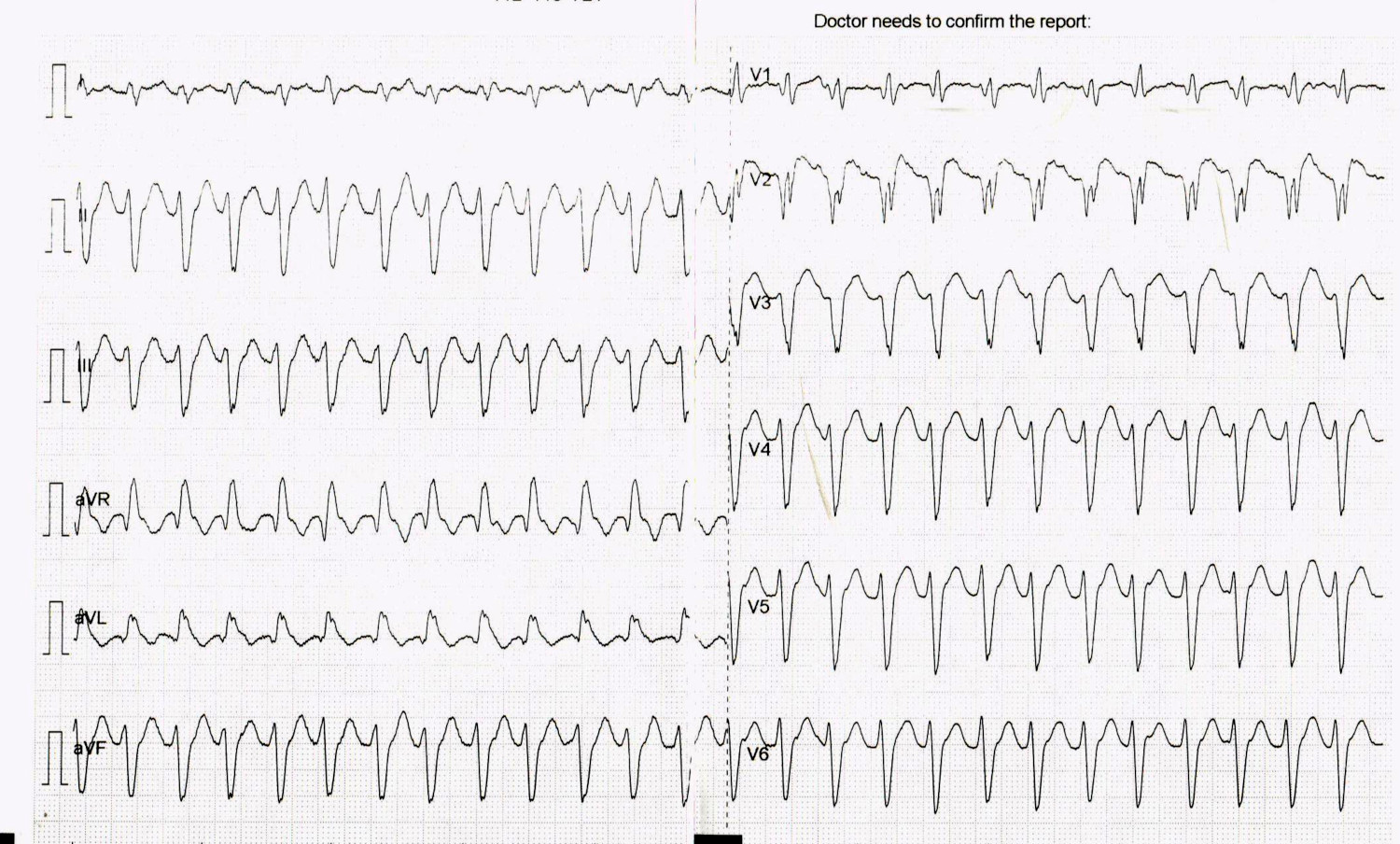
60 M, old AWMI

Adenosine

Elderly male
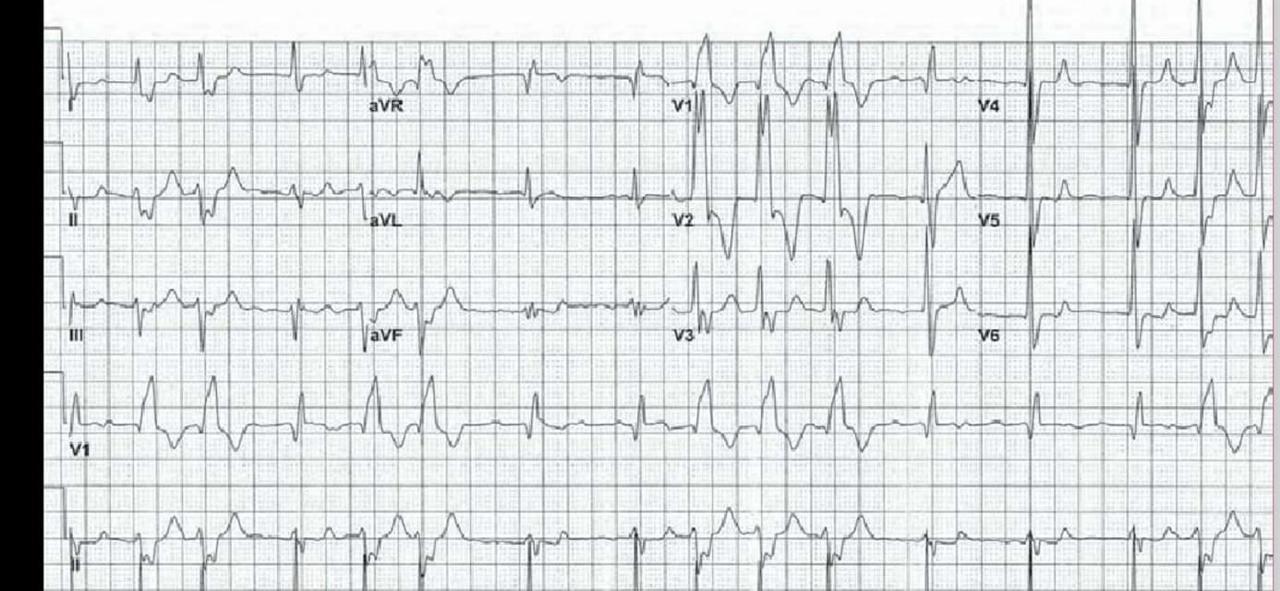
30 F with paroxysmal palpitations
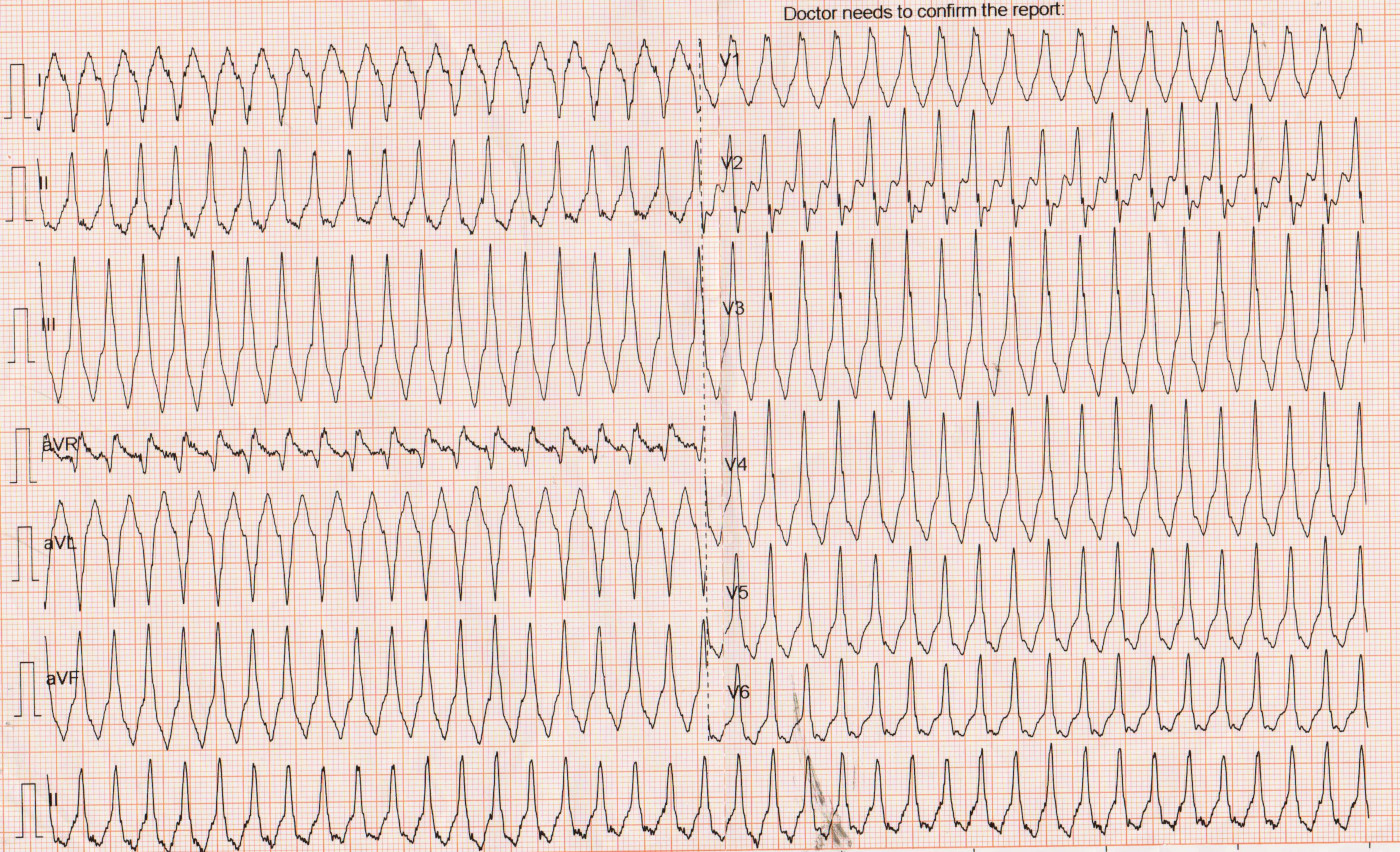
Sinus ECG
Summary
- WQRST - Can be VT or SVT
- Atrial activation is key - A < V in VT, A > V is SVT
- Morphology when A = V, but not very reliable
- Learn in terms of concepts more than rules
- Adenosine in stable tachycardia