Pacing indication and patient selection for pacemaker
17-10-2020
Raja Selvaraj, JIPMER
Outline
- Indications for pacing
- Pacing mode selection
References
- ACC/AHA Guidelines for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices (1998)
- ACC / AHA / HRS guideline - Evaluation and management of patients with bradycardia and conduction delay (2018)
- ESC guidelines - Cardiac pacing and CRT (2013)
ACC/AHA Guidelines for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices: Gabriel Gregoratos et al. Circulation 1998;97:1325–1335
2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients With Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay. JACC Volume 74, Issue 7, August 2019 DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.044
Brignole M, et al. 2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014 Jan;67(1):58. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2013.11.003.
Broad Indications
- Bradycardia / Risk of future bradycardia
- Symptoms or risk of death
- Irreversible
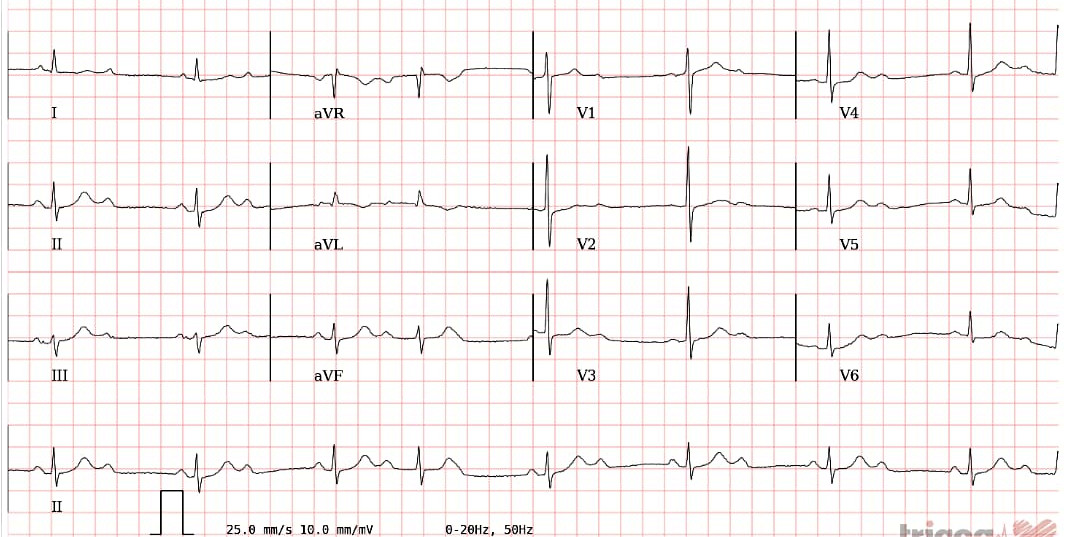
Sinus bradycardia
Class I
- Symptomatic bradycardia
- Symptomatic chronotropic incompetence
Importance of symptoms
- Never need to treat asymptomatic sinus bradycardia
- Presence of symptoms not enough - correlate with bradycardia
Rule out systemic causes
- Physiologic bradycardia
- Hypothyroidism
- Drug therapy (essential drugs which cannot be stopped or whose dose cannot be reduced exempted)
Class IIa
- Sinus bradycardia, rate < 40, association with symptoms unclear
Generally dont pace
- Asymptomatic bradycardia (IIb - Awake HR < 30)
- Symptoms clearly documented to be not related to bradycardia
Holter interpretation
- Correlate with symptoms
- Distinguish awake rate from asleep rate
- Pauses not important
ESC guidelines
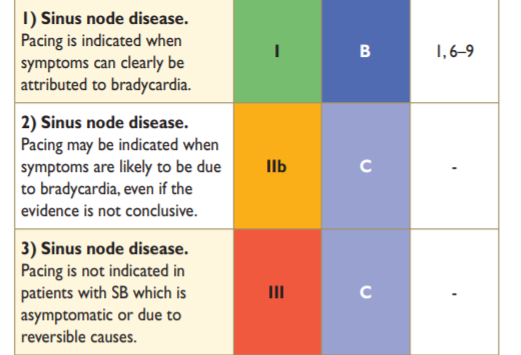
Brignole M, et al. 2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014 Jan;67(1):58. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2013.11.003.
Acquired adult AV block - Third degree
Class I
- Third degree AV block with symptoms (irrespective of level, rate)
- Third degree AV block without symptoms
- Awake rate < 40
- Awake, pause > 3 seconds
- Post ablation
- Post operative, not expected to resolve
- Neuromuscular diseases
Class IIa
- Asymptomatic, awake rate > 40
Acquired adult AV block - Second degree
Class I
- Second degree AV block with symptomatic bradycardia (irrespective of level, type)
Class II
- Asymptomatic type II
- Asymptomatic intra- or infra-His AV block (incidental at EPS)
ECG identification
ECG identification
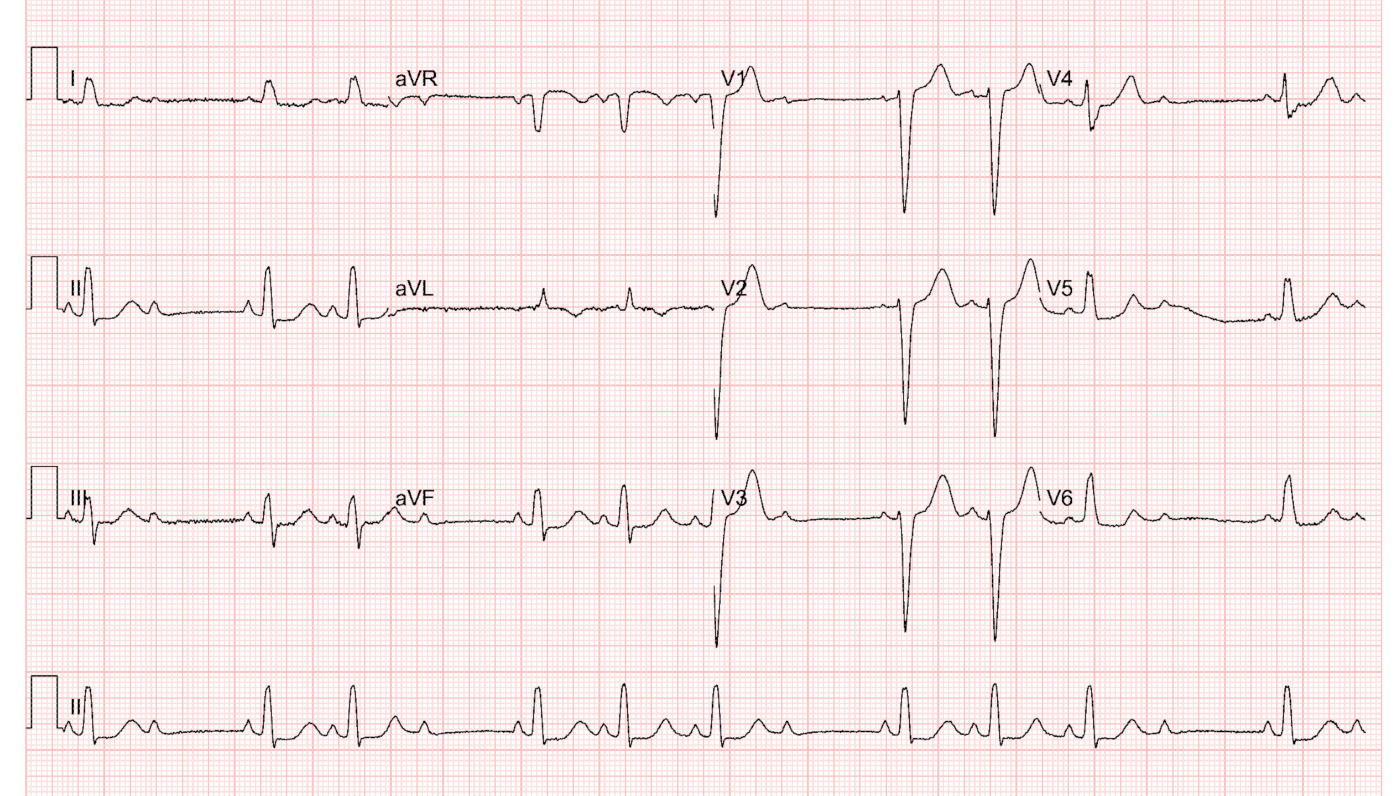
EPS
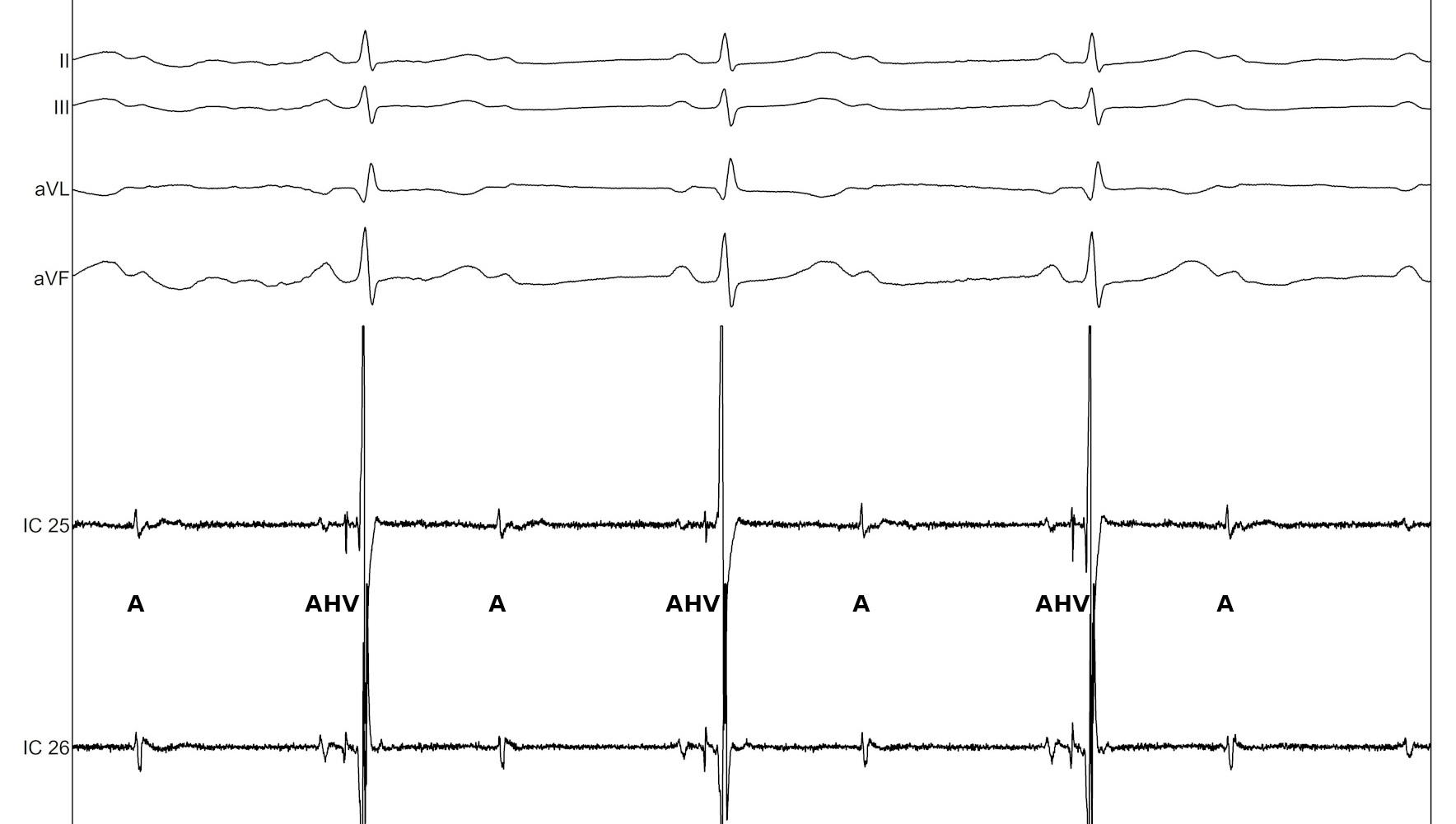
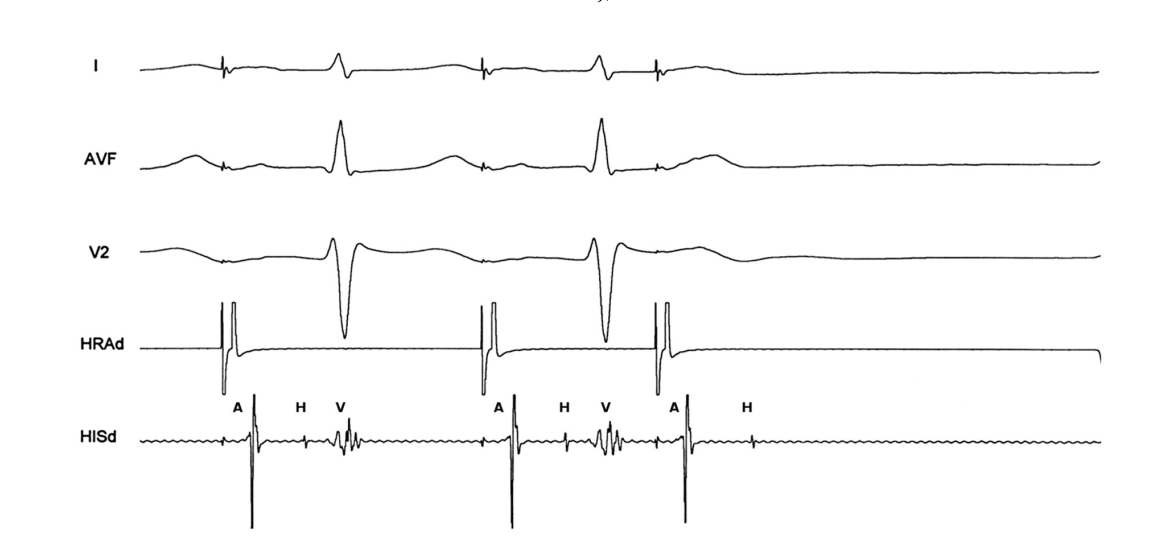
Intra-His AV block
Intra-His AV block
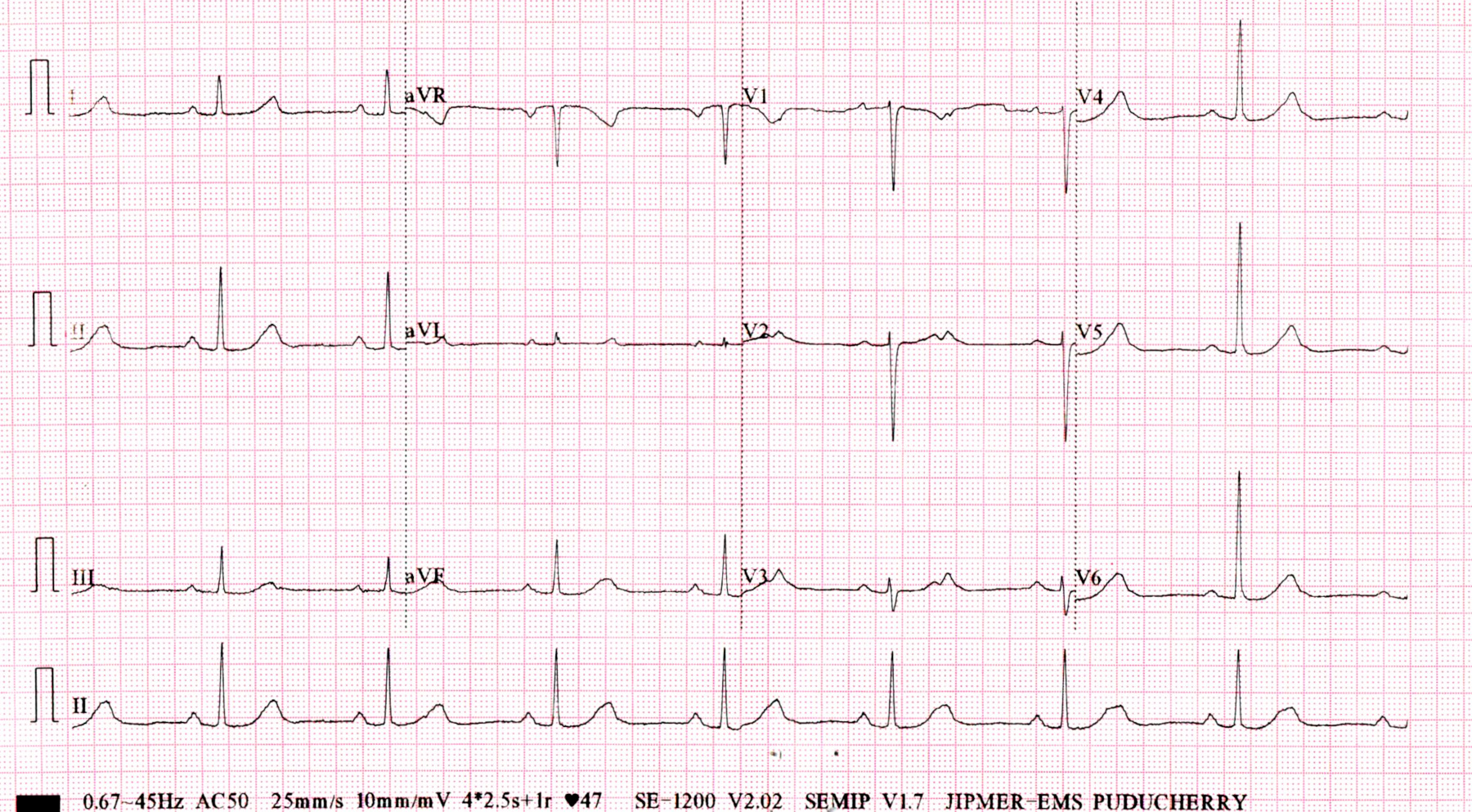
AV block - First degree
Class II a
- Symptoms of pacemaker syndrome, alleviation with temporary pacing
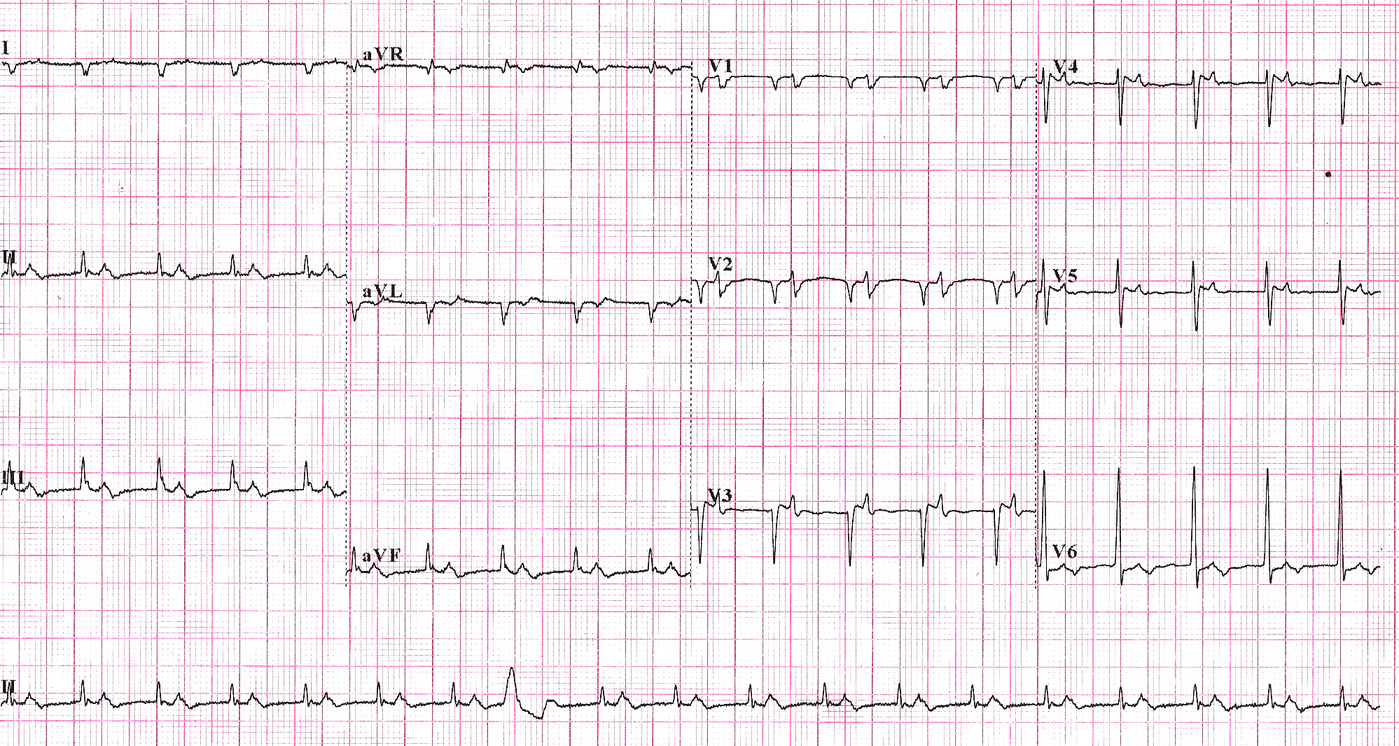
Kandaswamy PK .. Selvaraj RJ. Heart failure and pulsus alternans: an unusual presentation of first-degree heart block. Circ Heart Fail. 2014 Jan;7(1):227-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000945. PMID: 24449815.
Kandaswamy PK .. Selvaraj RJ. Heart failure and pulsus alternans: an unusual presentation of first-degree heart block. Circ Heart Fail. 2014 Jan;7(1):227-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000945. PMID: 24449815.
Bifascicular / trifascicular block
Class IIa
- Syncope, other causes excluded
- HV > 100 ms (incidental in EPS)
- Pacing induced Infra-His block, not physiological during EPS
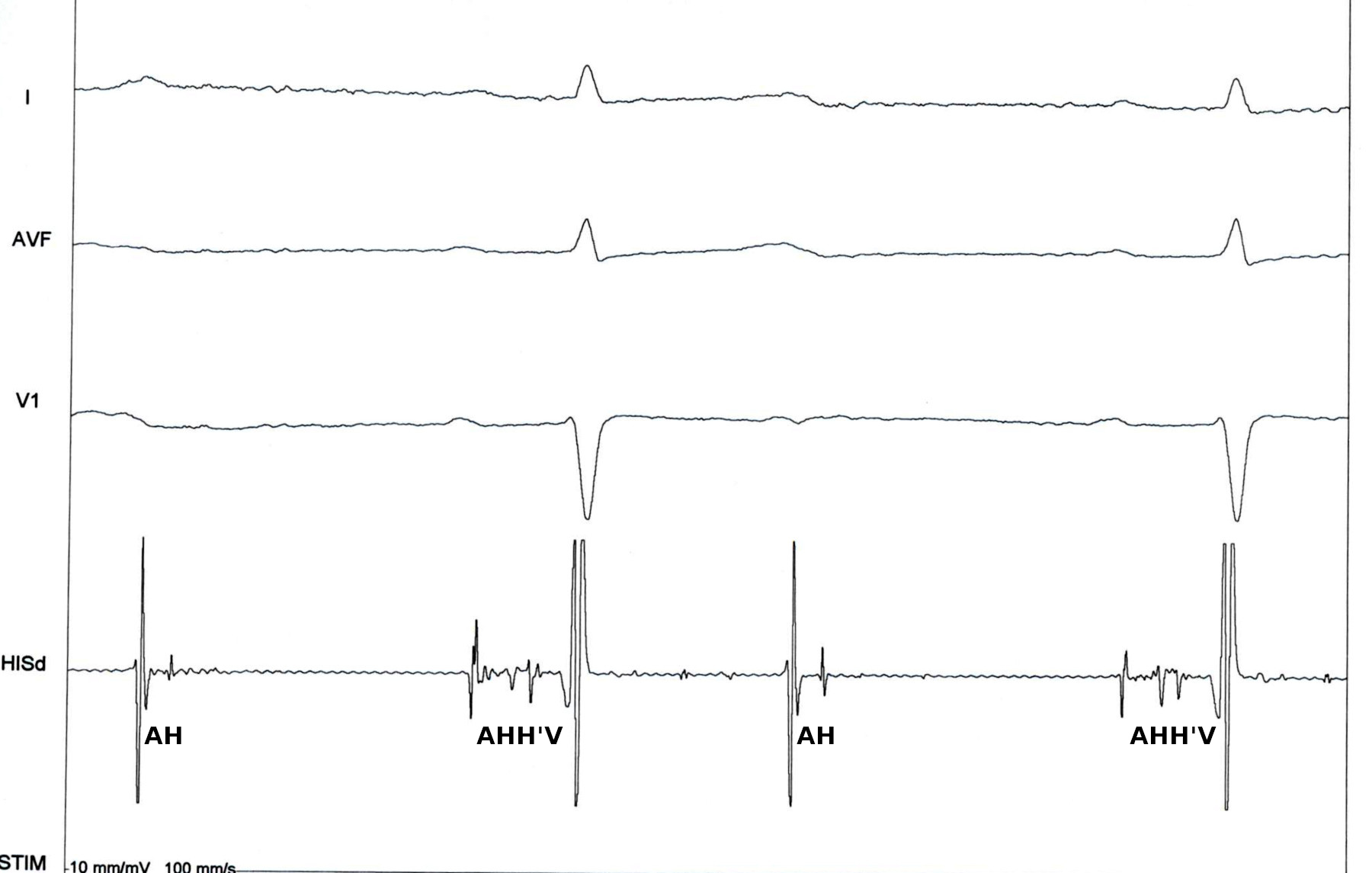
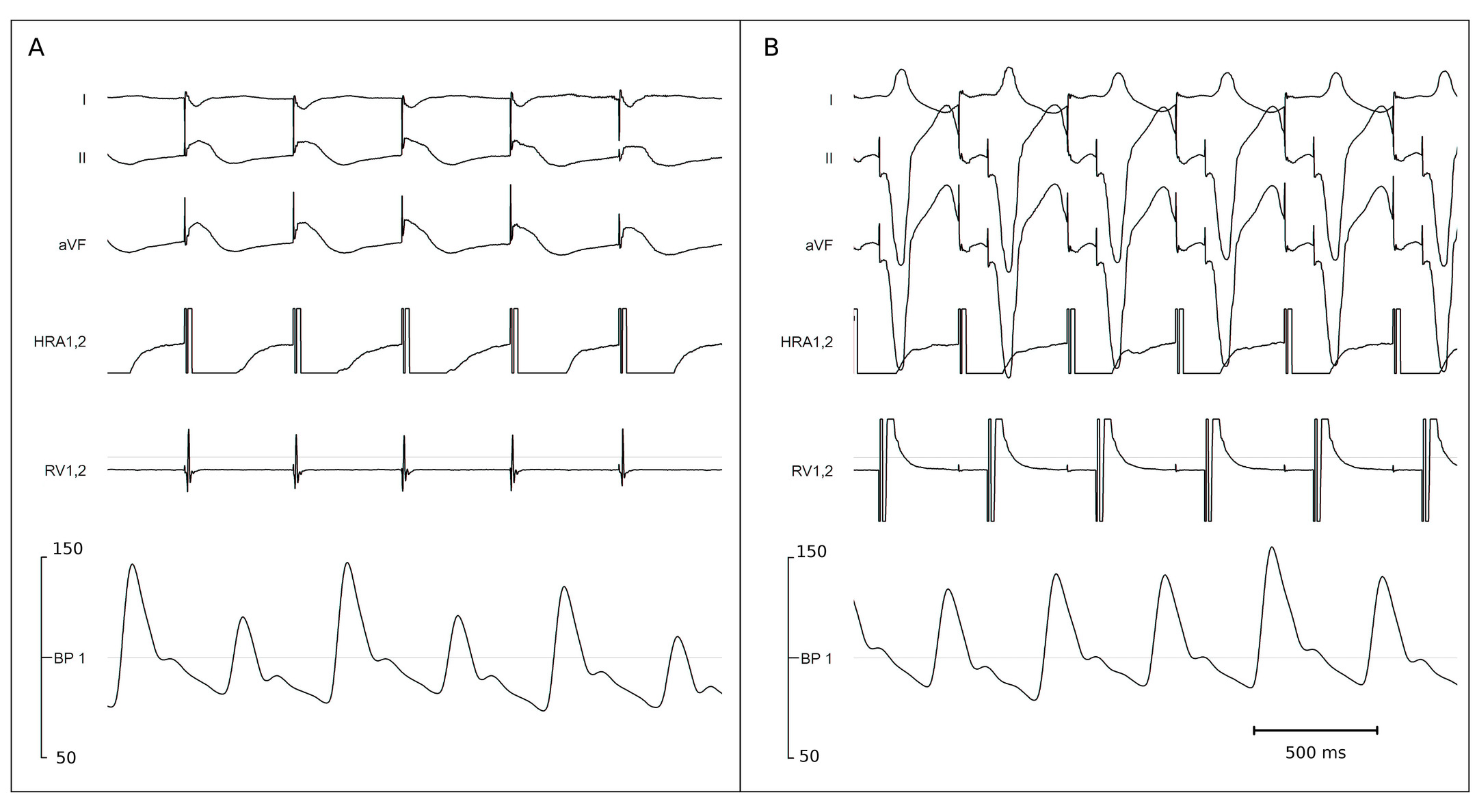
Infra-His block - tracings
Selvaraj RJ, Kumar B, Rangasamy S. Infra-His Block during Atrial Pacing-Functional or Pathological? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2017 Jan;40(1):69-71. doi: 10.1111/pace.13001.
Infra-His block - tracings
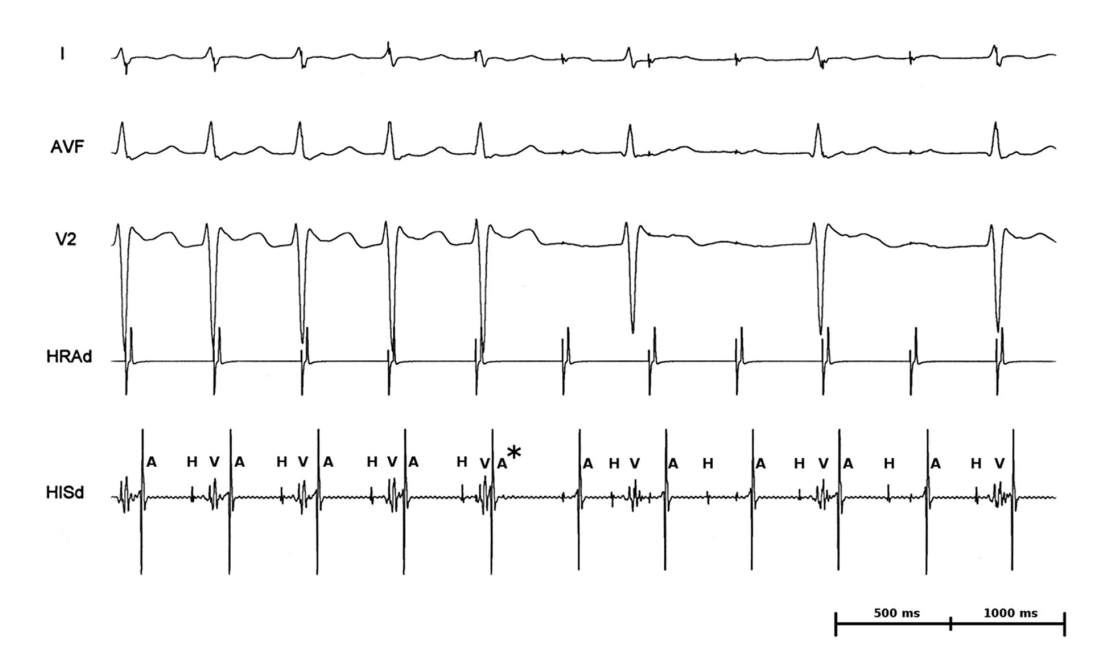
Selvaraj RJ, Kumar B, Rangasamy S. Infra-His Block during Atrial Pacing-Functional or Pathological? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2017 Jan;40(1):69-71. doi: 10.1111/pace.13001.
Post MI AV block
- Persistent, symptomatic second or third degree AV block
- Persistent second or third degree AV block - infranodal
- Transient infranodal block with bundle branch block
ESC guidelines
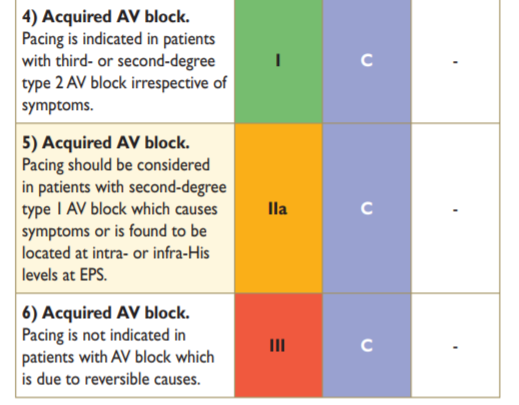
Brignole M, et al. 2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014 Jan;67(1):58. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2013.11.003.
Miscellaneous
Neurocardiogenic syncope
- Carotid sinus hypersensitivity - reproducible - Class I
- Carotid sinus hypersensitive response and recurrent syncope - class IIa
- Neurally mediated syncope with significant bradycardia during HUTT - class IIb
ESC - Reflex syncope

Brignole M, et al. 2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014 Jan;67(1):58. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2013.11.003.
Congenital heart block
- Symptoms - Class I
- Ventricular dysfunction - Class I
- Wide QRS escape - Class I
- Rate < 50-55 in infant, < 70 with congenital heart disease
- Rate < 50 beyond infancy - Class IIa
- LQTS with AV block
LQTS with AV block
Mode selection
Sinus bradycardia - Recommendations (1)
- Atrial based pacing recommended over single chamber ventricular pacing - Class I
- Without AV conduction abnormalities, dual chamber pacing or single chamber atrial pacing - Class I
- Program dual chamber pacing to minmize ventricular pacing
2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients With Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay. JACC 2018; 74(7), DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.044
AV block
- VVI reasonable if frequent ventricular pacing not expected or multiple comorbodities - Class I
- EF < 50% and expected pacing > 40%, consider pacing with more physiologic activation - Class IIa
ESC - VVI vs DDD
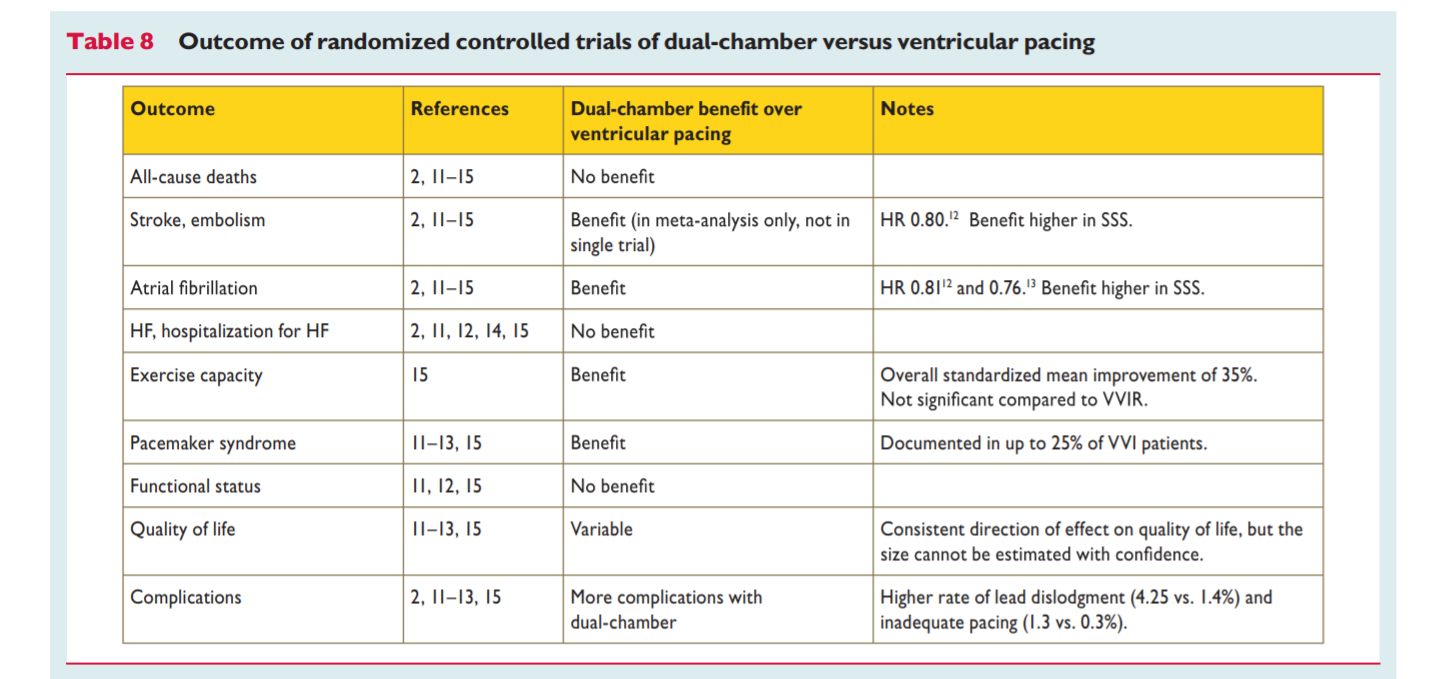
Brignole M, et al. 2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014 Jan;67(1):58. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2013.11.003.
Rate response
- Sinus node dysfunction - Randomized to DDD vs DDDR
- No difference in exercise time, activity scale or QOL at 6 mths and 1 year
Lamas G.A., Knight J.D., Sweeney M.O., et al. (2007) Impact of rate-modulated pacing on quality of life and exercise capacity–evidence from the Advanced Elements of Pacing Randomized Controlled Trial (ADEPT). Heart Rhythm 4:1125–1132
Rate response summary
- Useful in single chamber pacing (VVIR for CHB, AAIR for SND)
- Not shown better in DDD
Summary
- In SND pace only when symptomatic
- In AVB, pace if symptomatic, or block below node
- In SND, DDD superior to VVI, may be better than AAI in selected patients
- In AVB, DDD may be slightly better than VVIR
References
- ACC/AHA Guidelines for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices (1998)
- ACC / AHA / HRS guideline - Evaluation and management of patients with bradycardia and conduction delay (2018)
- ESC guidelines - Cardiac pacing and CRT (2013)
ACC/AHA Guidelines for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices: Gabriel Gregoratos et al. Circulation 1998;97:1325–1335 https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.97.13.1325Circulation.
2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients With Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay. JACC Volume 74, Issue 7, August 2019 DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.044
#+beginreference Brignole M, et al. 2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014 Jan;67(1):58. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2013.11.003.