Device implant
07-11-2020
Raja Selvaraj, JIPMER
Pre-procedure
Pre-procedure evaluation
- Check indication
- Decide on pacing mode
- Decide on side
- Discuss with patient
Pre-procedure preparation
- Fasting (hydration)
- Ipsilateral venous cannula
- Blood investigations
- Drugs - antiplatelets, anticoagulation
- Chest X-ray
Prep and drape
- Shaving / trimming
- Antiseptic scrub
- Drape
- Skin film
Anaesthesia and Instruments
Local anaesthesia
- Lignocaine
- Additional Bupivacaine
- 0.5 - 2.0 %
- 3-4 mg/kg
Anaesthesia
- Conscious sedation
- Fentanyl + Midazolam
- General anaesthesia
Instruments - 1
- Clamps - Hemostats, Allis, Babcock
- Scissors - Mayo, Metzenbaum
- Forceps - toothed, Adson
Instruments - 2
- Scalpel - #20 blade, #11/15 blade, #3 and #4 handle
- Needle holder
- Retractor - Senn, cats paw, Weitlaner self retaining
Incision and dissection
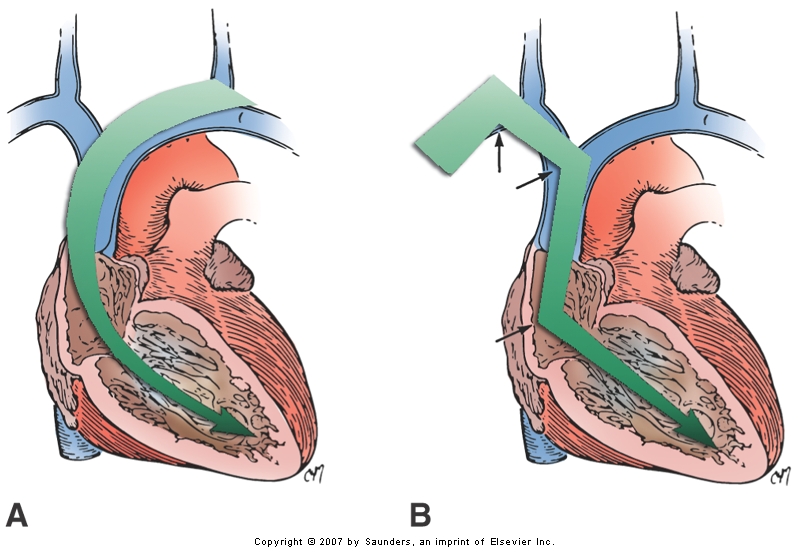
Choosing side
- Profession ?
- Left side - Common, easier route, problems with persistent LSVC
- Right side - Difficulty due to angulation, CRT difficult, ICD problems
Side
Persistent LSVC
Venogram in every patient before incision ?
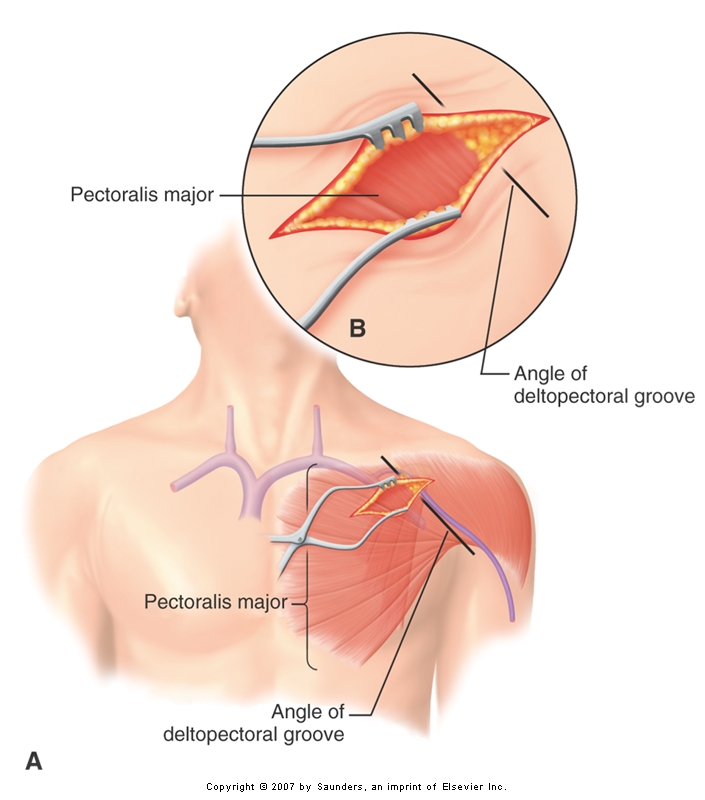
Skin incision
- Horizontal
- Parallel to deltopectoral groove
- Length of incision
- 20 blade
Dissection
- Use self retaining retractor
- Sharp dissection with 11 blade / Cautery
- Upto Deltopectoral fascia
Venous access
Routes
- Cephalic vein
- Subclavian vein
- Axillary vein
- Other, unconventional
Venous access at JIPMER (approx)
- 75% - Cephalic vein (20% assisted)
- 24% - Axillary vein puncture (25% with venogram)
- 1% - Subclavian vein puncture
Anatomy
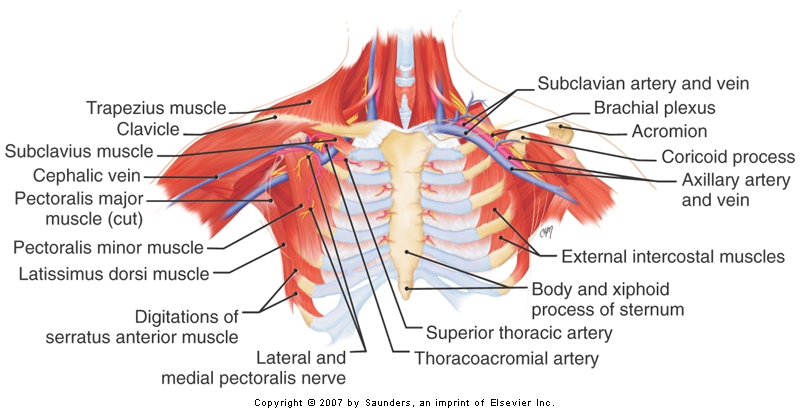
Cephalic vein
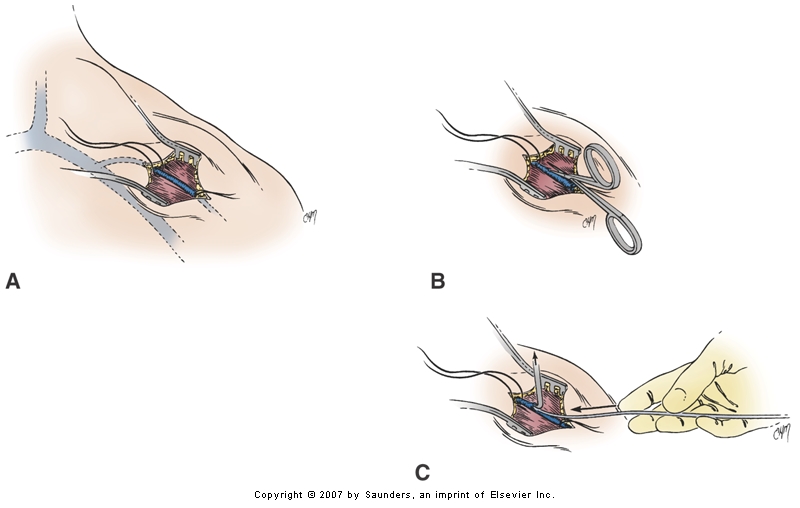
Cephalic vein dissection
- Sharp dissection up to pectoral fascia
- Identify pad of fat in deltopectoral groove
- Vein is within pad of fat
- Separate from fascia, distal tie, open and pass lead
Cephalic vein dissection
Cephalic vein dissection
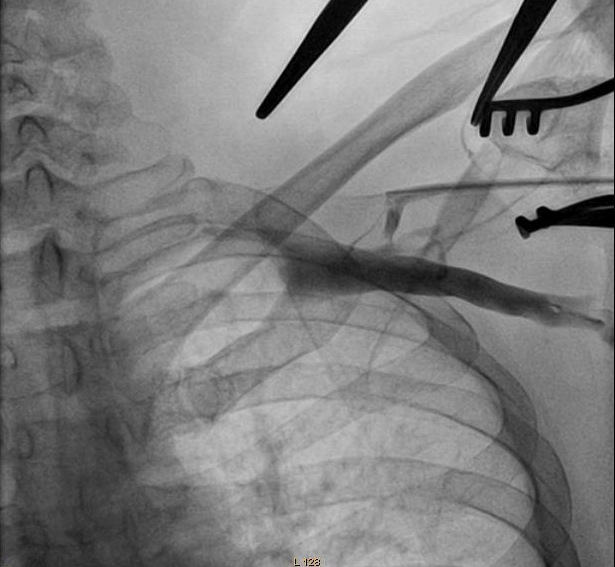
Assisted cephalic vein access
- Wire and lead
- Wire and peel-away
- 0.014 wire -> 5F -> exchange for 0.035 -> 7F
Cephalic vein
Cephalic vein
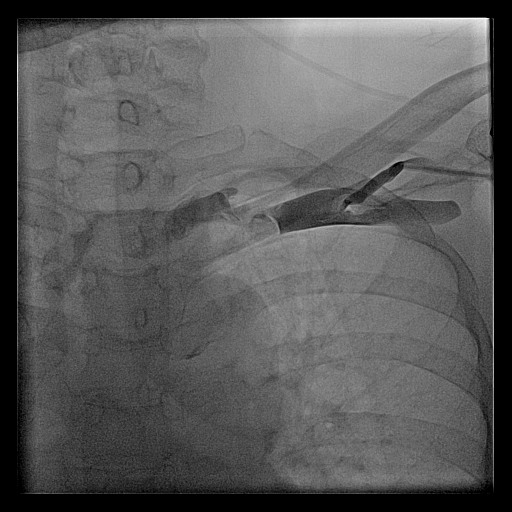
Cephalic venogram
Cephalic vein - pros and cons
- ( - ) Learning curve
- ( - ) Time
- ( - ) Painful
- ( - ) May not take multiple leads
- ( + ) No pneumothorax
- ( + ) No lead crush
Axillary vein
Axillary vein puncture
- Fluoro guided
- Junction of clavicle and first rib
- Walk along first rib
Axillary vein - pros and cons
- ( - ) Small learning curve
- ( - ) Needs fluoroscopy
- ( - ) Needs venogram (myth !)
- ( + ) Very low risk of pneumothorax
- ( + ) No lead crush
Subclavian vein
Subclavian vein puncture
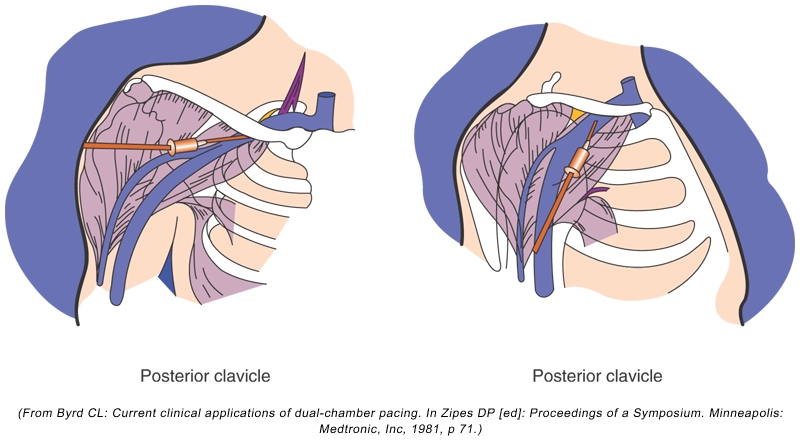
Subclavian vein - pros and cons
- ( + ) More people are familiar
- ( + ) Anatomical landmarks sufficient
- ( - ) Risk of pneumothorax
- ( - ) Risk of lead crush
Lead crush
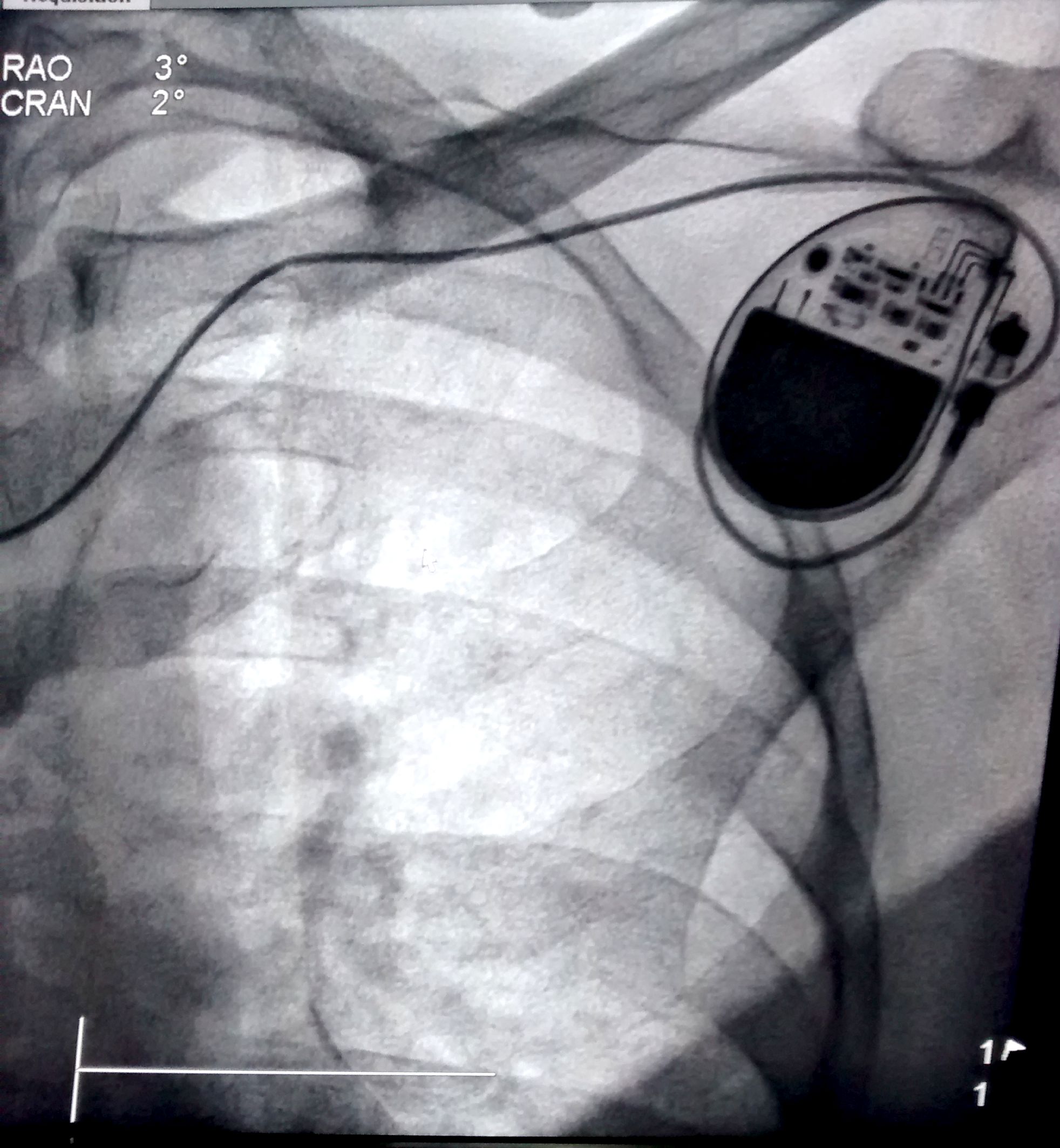
Single versus separate punctures
- In case of difficult punctures
- Routinely ?
- Retained guidewire technique
- Double wire technique
Tips
Axillary vein / subclavian puncture - tips
- Lignocaine in syringe
- No roll under shoulders
- Trendelenburg or elevate legs
- Verify venous access (IVC)
Avoiding air embolism
- Adequate hydration !
- Trendelenberg / Leg elevation
- Pinch sheath
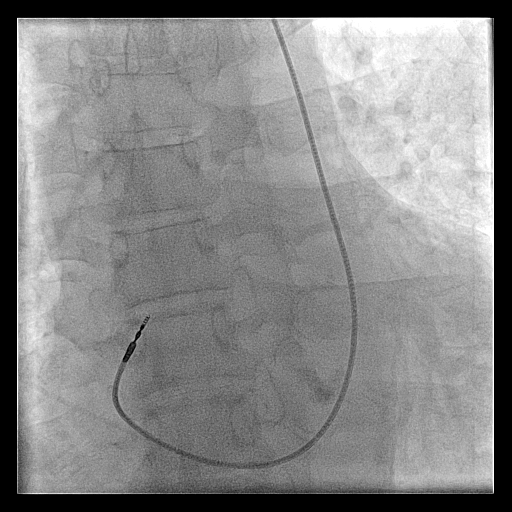
Venogram
- Difficult puncture
- Pre-existing leads
- 10-15 ml of contrast from ipsilateral arm
- Management of stenosis
Puncture with venogram
Unconventional access
- Internal jugular vein
- Femoral vein
Ventricular lead placement
Choosing a lead
- Active or passive
- Length
RVA position - The mimics (AP view)
- RA -> PFO -> LA -> LV
- RA -> CS -> lateral vein
- RA -> Hepatic vein
RVA placement
- Gently curved stylet
- Straight stylet
- RVOT -> RVA
RVA
RVA
RVOT pacing
- Active fixation lead
- Stylet shaping
RVOT pacing
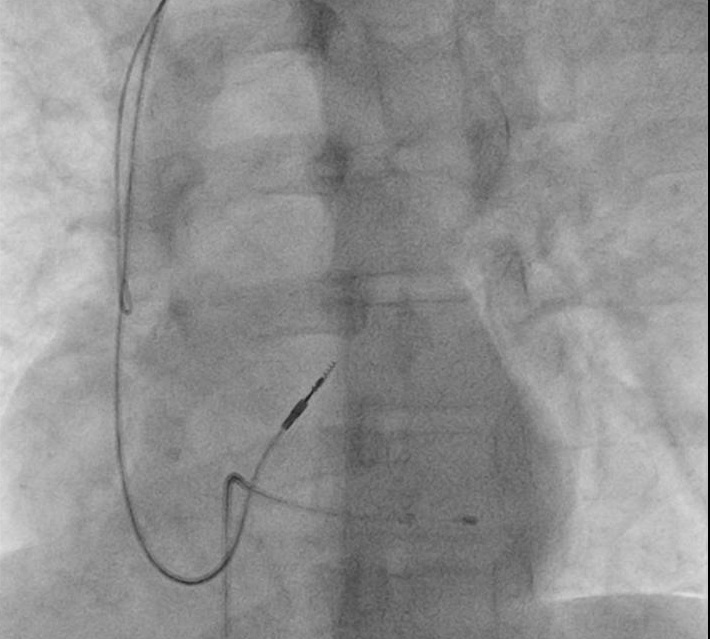
RVOT pacing
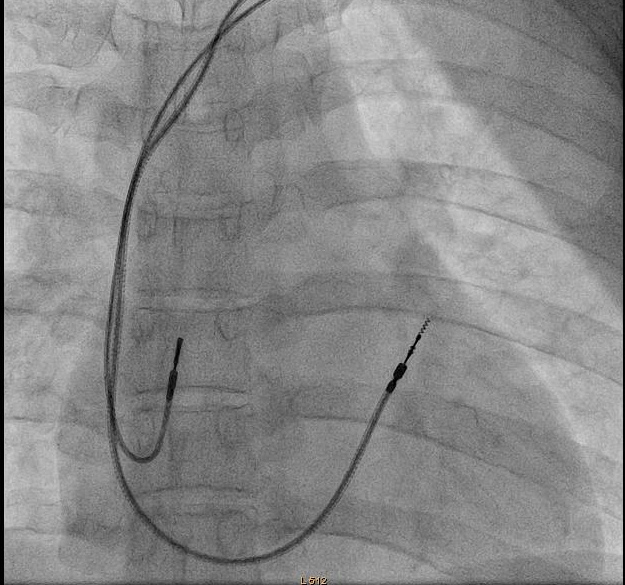
RVOT pacing
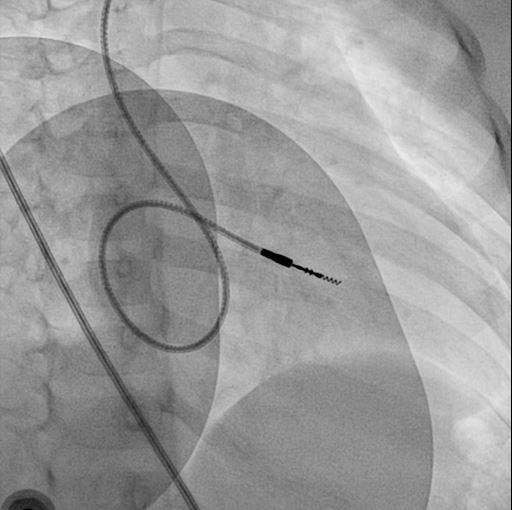
Extra loop
Atrial lead placement
Atrial appendage
- Pre-formed J
- J shaped stylet
- Recognize appendage position
Other atrial locations
- Active fixation lead
- Lateral wall
- Septum
VDD lead
VDD lead placement
- Similar to RVA lead
- Inter-electrode distance
- Position the bipole
Fix and connect
Fixing lead
- Use a suture sleeve
- Fixing to fascia / muscle
Attaching PG
- Connector pin position
- Dynamometric wrench - stops and signals when desired torque is achieved
- Tug to test
Pocket creation
- Sharp dissection to define fascial plane
- Controlled blunt dissection
- Medially oriented
Subpectoral pocket
- Indications
- Between heads of pectoralis major
- Split pectoralis major
Closure
Closure
- Subcutaneous- Vicryl 2-0 in two layers
- Skin - Vicryl 3-0 subcuticular
- Skin - Prolene 3-0 mattress
Post implant
Post procedure care
- Immobilisation / bed rest ?
- Analgesia
- Chest X ray after 4-6 hours
Post procedure care
- ECG / Pacemaker check
- Antibiotics ?
- Shower ?
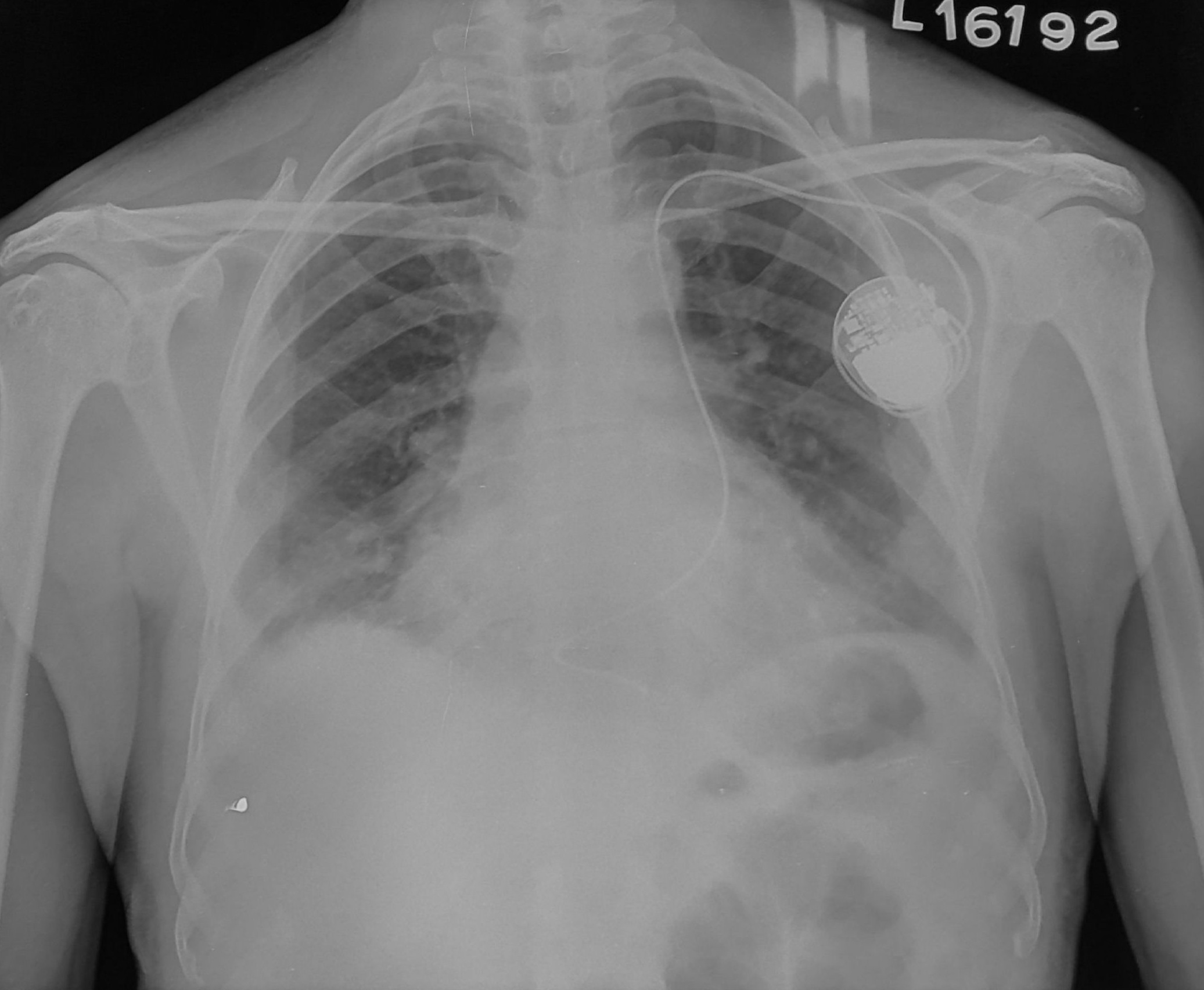
Post procedure CXR
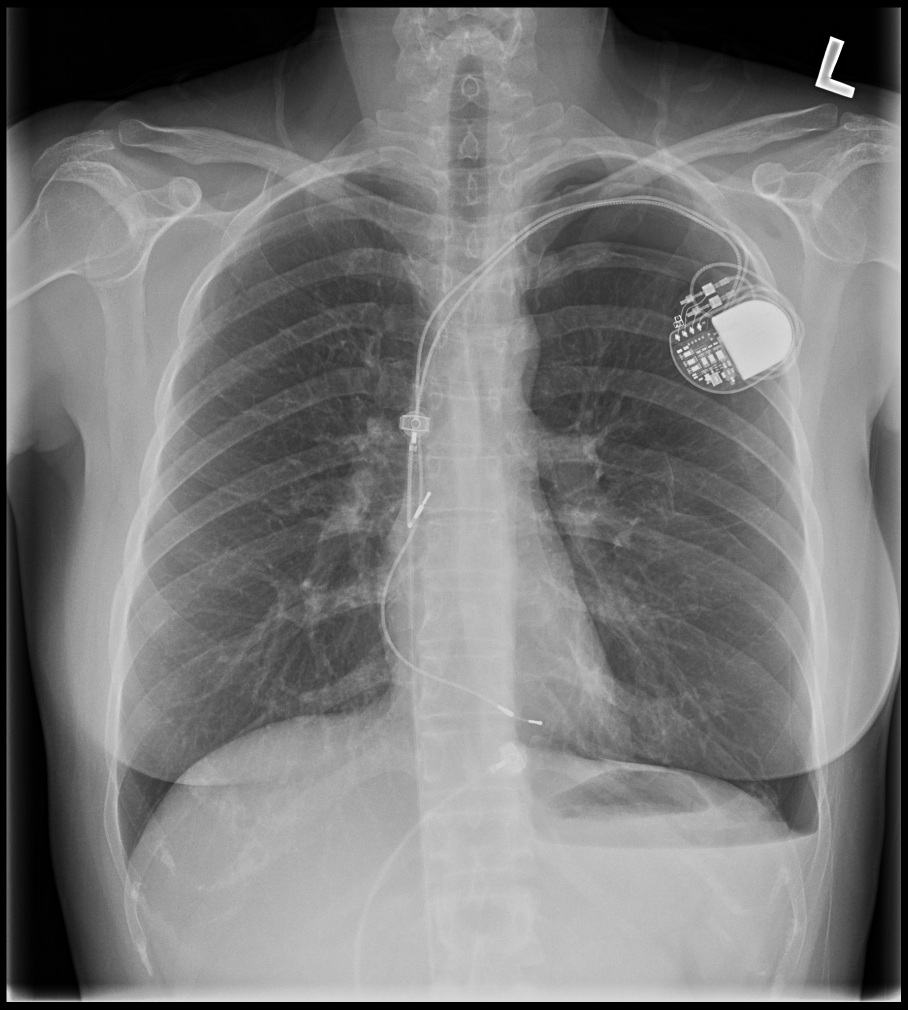
Complications and How to avoid
Infection
- Asepsis
- Antibiotics are not an solution!
- Reduce use of TPI
- Optimise blood sugar control
- Reduce procedure time
- Avoid lead dislodgement
- Correct pocket placement
Lead dislodgement
- Active fixation
- Ensure good myocardial contact
- Current of injury
- Fixation sleeve
Perforation
- Vulnerable patient population
- Vulnerable locations
- Lead stiffness with stylet
Hematoma
- Antiplatelets
- Anticoagulants
- Sharp dissection
- Cautery