Primary Prevention of SCD in Heart Failure : Should we look beyond LV EF ?

Raja Selvaraj MD DNB FCE (Toronto)
Cardiac Electrophysiologist
Professor of Cardiology
JIPMER
Introduction
Heart failure is not a homogenous entity
- Ischemic cardiomyopathy (old MI)
- Non ischemic cardiomyopathy (Idiopathic DCMP)
- Others
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Sarcoidosis
- Arrhythmogenic RV Cardiomyopathy
- HFPEF
Concepts in Risk stratification
- To identify patients who will benefit from ICD implantation
- SCD risk is continuous
- Competing risk (risk of non sudden death)
- Find patients with high risk of SCD and low competing risk
Ischemic cardiomyopathy (old MI with LV dysfunction)
Current guidelines - class I indication
- LVEF 40% or less, NSVT, inducible sustained VT
- LVEF 35% or less, 40 d post MI, 90 d post revasc, NYHA class II or III, despite GDMT
- LVEF 30% or less, 40 d post MI, 90 d post revasc, NYHA class I, despite GDMT
Al-Khatib SM et al. 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for Management of Patients With Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2018 Sep 25;138(13):e272-e391. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000549.
MUSTT
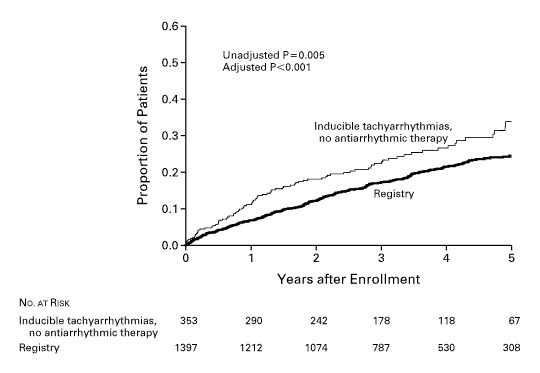
Buxton et al. Electrophysiologic Testing to Identify Patients with Coronary Artery Disease Who Are at Risk for Sudden Death. N Engl J Med 2000; 342:1937-1945
SCD-HeFT - Ischemic
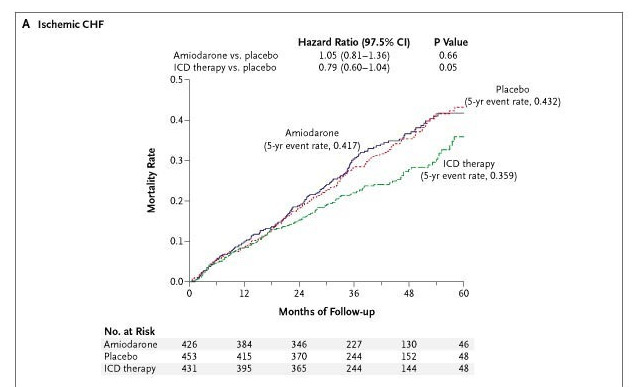
Bardy GH et al. Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial (SCD-HeFT) Investigators. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2005 Jan 20;352(3):225-37. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043399.
MADIT II
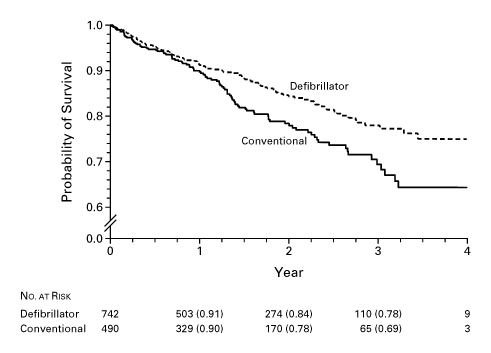
Moss AJ, Zareba W, Hall WJ, et al. Prophylactic implantation of a defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346: 877–88
Summary
- EF strong and best predictor. Base for everything else
- However primarily EF based indication has low sensitivity (NNT - MADIT II 18, SCD-HeFT 13)
- NYHA class, NSVT, Inducible VT
- All others not stood test of time
Prospective study - Previous MI with EF < 40%
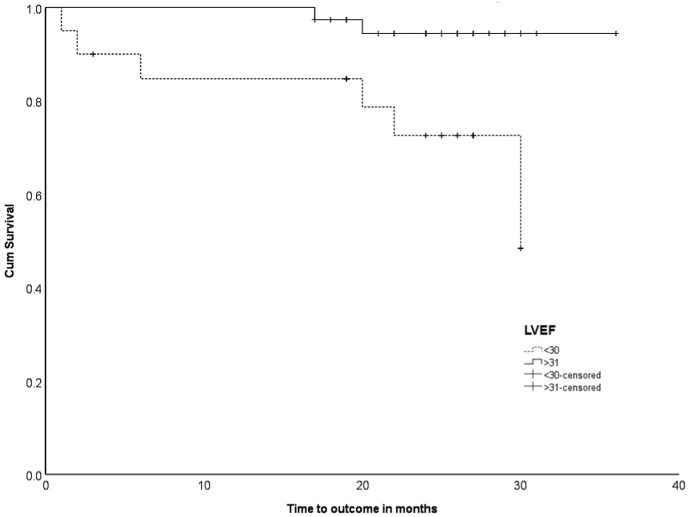
Selvaraj RJ et al. Sudden death and its predictors in myocardial infarction survivors in an Indian population. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2021 Mar-Apr;21(2):82-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ipej.2020.12.002. Epub 2020 Dec 19. PMID: 33352202; PMCID: PMC7952752.
Non Ischemic Cardiomyopathy (Idiopathic DCMP)
Current guidelines
- Class I - LVEF 35% or less, class II or III despite GDMT for at least 3 months
Evidence in NICM
- DEFINITE - Reduces SCD, trend towards reduction in overall mortality
- SCD-HeFT - 27% to 21% mortality at 5 years in NICM group
- DANISH - > 1000 patients, CRT in 58% of the patients, less SCD, no change in mortality
SCD-HeFT - Non-Ischemic
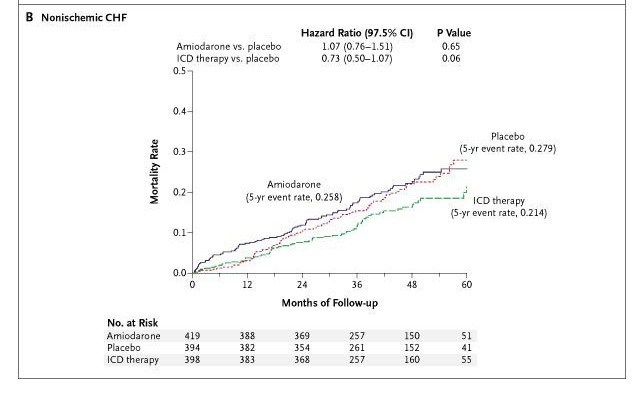
Bardy GH et al. Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial (SCD-HeFT) Investigators. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2005 Jan 20;352(3):225-37. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043399.
Danish trial
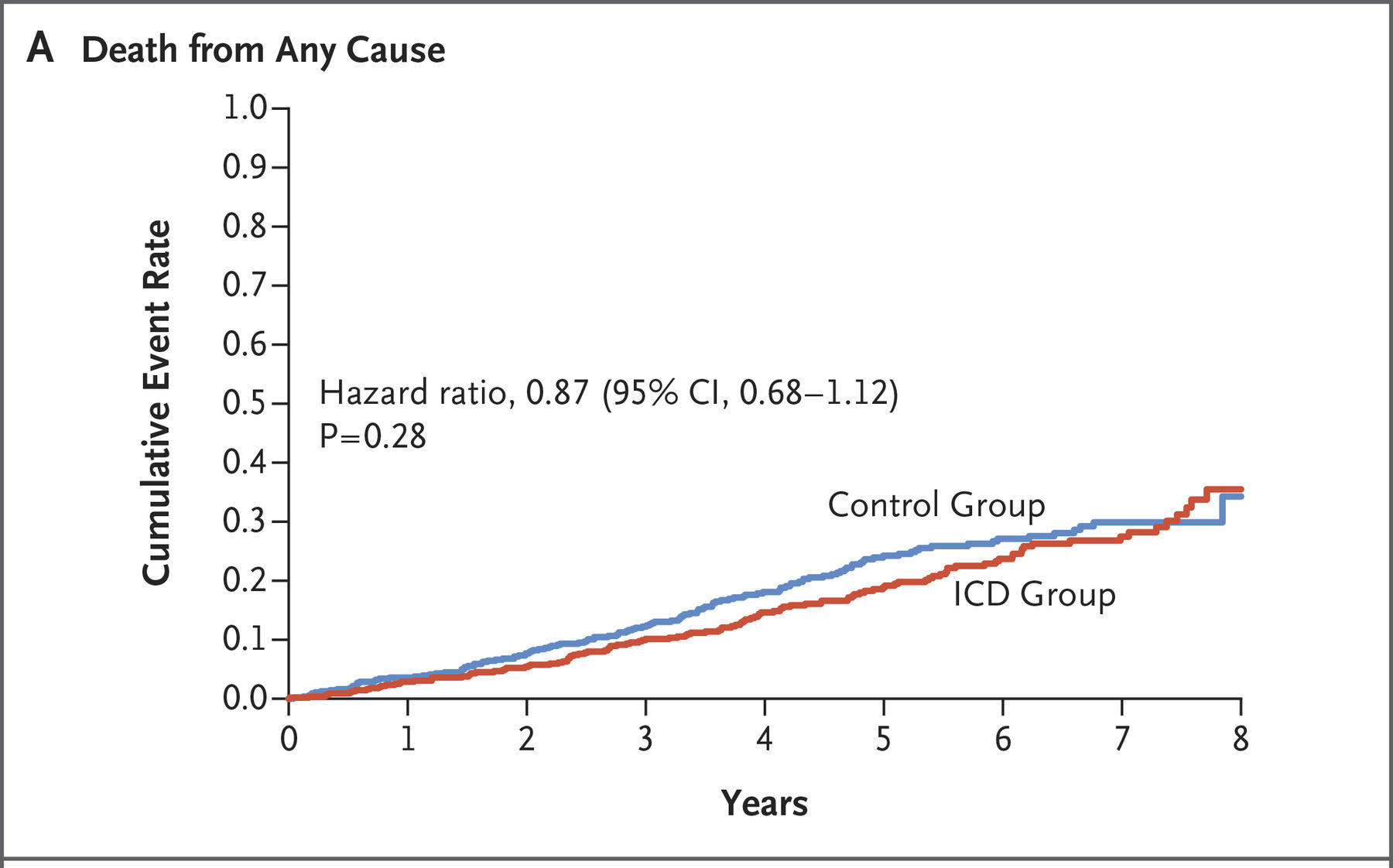
Køber L et al. DANISH Investigators. Defibrillator Implantation in Patients with Nonischemic Systolic Heart Failure. N Engl J Med. 2016 Sep 29;375(13):1221-30. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1608029. Epub 2016 Aug 27. PMID: 27571011.
NICM - A different kettle of fish
- Heterogenous population, overall lower risk of sudden death
- Risk of sudden death has reduced with time
- Benefit definitely lesser compared to ICMP (is there a benefit at all ?)
- CRT eligible vs CRT ineligible
Multiparametric assessment
- History - Family history of SCD, unexplained syncope
- ECG - fQRS, anterolateral T inversion, Tp-Te
- Holter - PVCs, NSVT
- Echo - LVEF, RV function, Global longitudinal strain
Cardiac MRI
- LGE seen in about 30-45%
- These patients at higher risk of arrhythmias
- Distribution and extent of LGE may carry prognostic information
- Interstitial fibrosis - may not show LGE, but associated with arrhythmias
Meta analysis
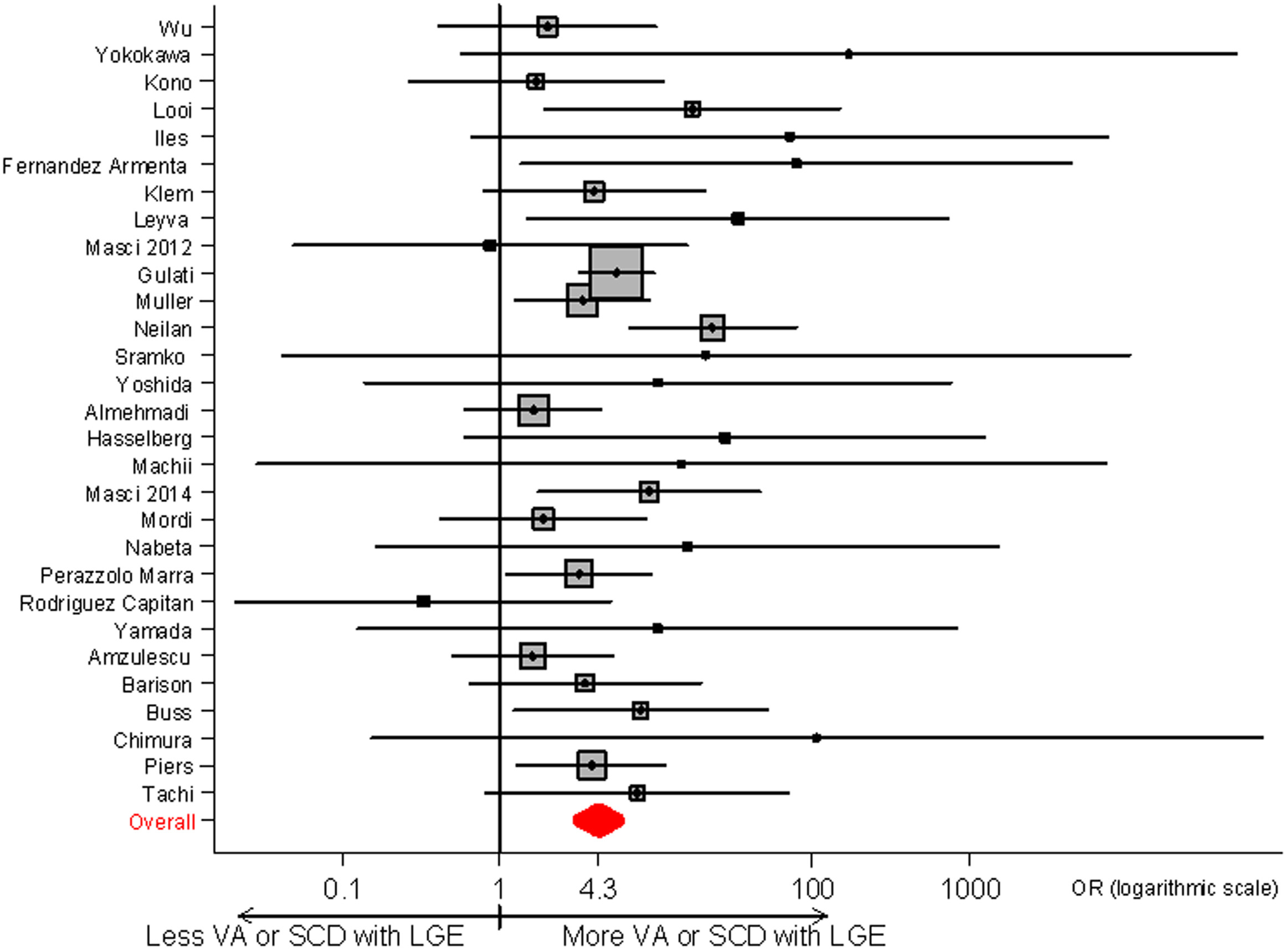
Andrea Di Marco et al. Late Gadolinium Enhancement and the Risk for Ventricular Arrhythmias or Sudden Death in Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JACC: Heart Failure Volume 5, Issue 1, January 2017, Pages 28-38
Genetic testing
- Specific mutations associated with higher risk
- Risk may be high despite absence of significant LV dysfunction
- LMNA mutations, truncating FLNC variants
Lamin A/C mutations
- LVEF < 45%
- Male sex
- NSVT
Van Rijsingen et al. Risk Factors for Malignant Ventricular Arrhythmias in Lamin A/C Mutation Carriers: A European Cohort Study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology Volume 59, Issue 5, 31 January 2012, Pages 493-500
Lamin A/C mutations
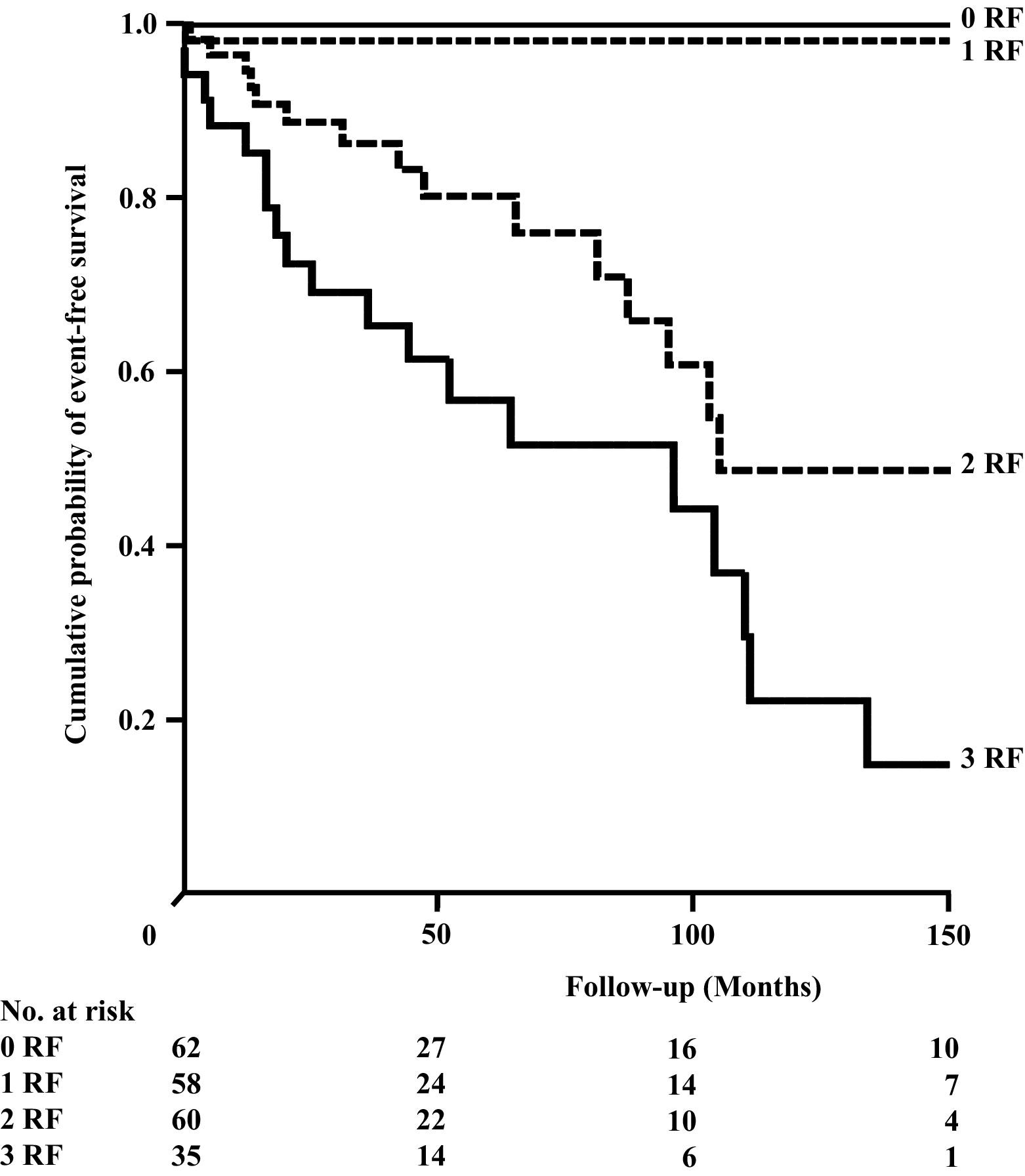
LV reverse remodeling
- Occurs in 40%, associated with better prognosis
- Those unlikely to remodel may be chosen for early ICD implant
- Larger ventricle, longer QRS duration, intolerance to beta blockers may be predictors
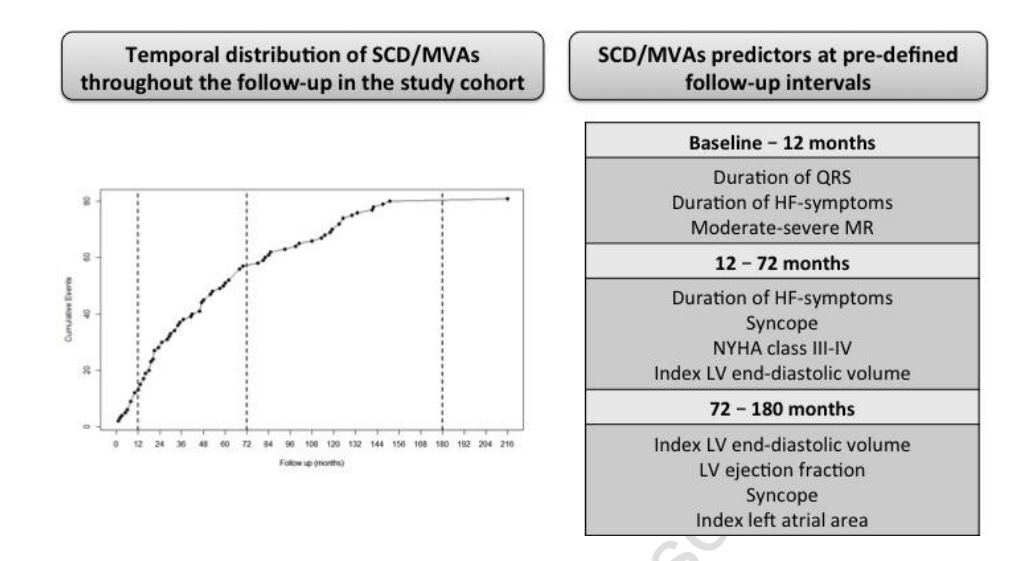
Stolfo et al. Arrhythmic Risk Stratification in Patients With Idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. AJC 2018;121:1601-1609
An integrated approach
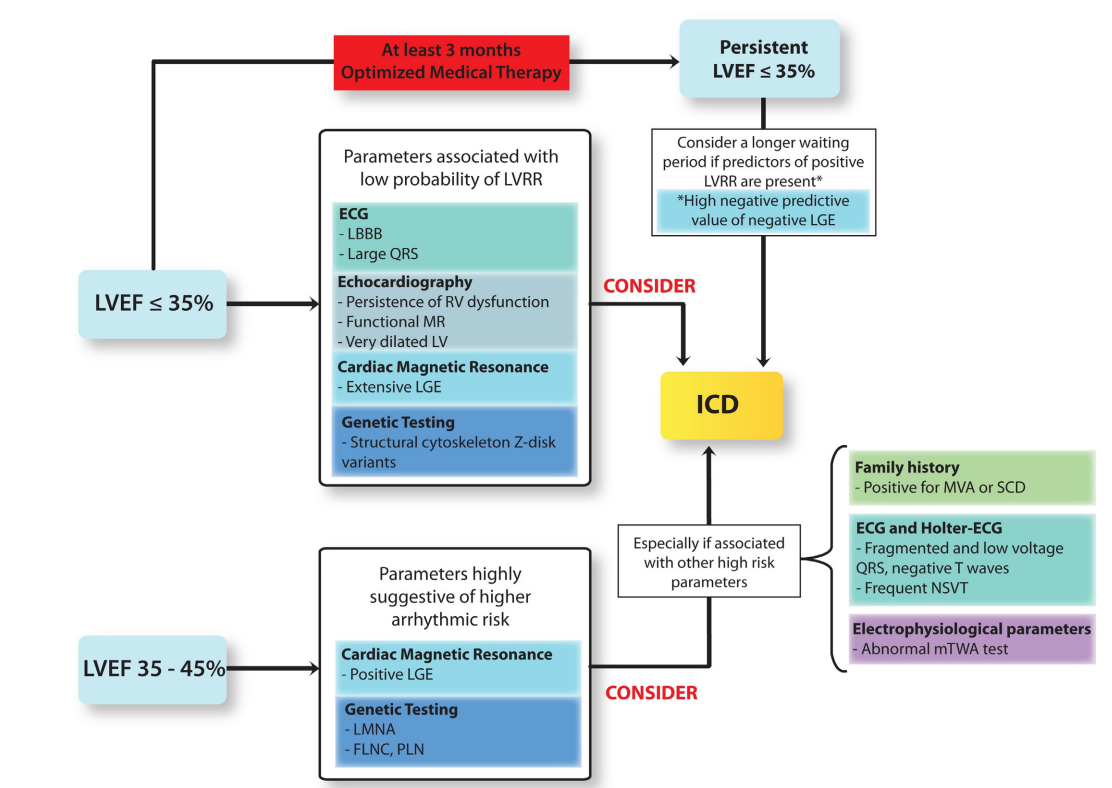
Cannata et al. Arrhythmic risk stratification in non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy beyond ejection fraction. Heart 2020;0:1–9. 10.1136/heartjnl-2019-315942
Special populations
Listed for transplant
- Not eligible by standard guidelines
- However, they become eligible if they are listed for transplant
- Improves survival
- Wearable defibrillator is an option
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)
- Lower risk of SCD compared to HFrEF
- Still comprises nearly a quarter of all deaths
- No consistent risk factors identified
Others
- ECG / AI
- Biomarkers
- Genetic studies
Summary
- SCD is a definite issue in patients with heart failure
- ICD is an effective treatment but carries significant cost considerations and morbidity
- Need understanding SCD risks and competing risks to utlise ICD efficiently
- EF still remains the basis for risk assessment
- Additional parameters may help improve risk stratification, area of ongoing study
- In general ICDs for ICMP, CRT for NICMP
- Don't forget optimal medical management