WPW Syndrome - How to Read ECG
Raja Selvaraj, JIPMER
Introduction
What is WPW syndrome?
- Constellation of findings in patients with an accessory pathway with bidirectional conduction
- Delta wave and short PR = preexcitation = antegrade conduction
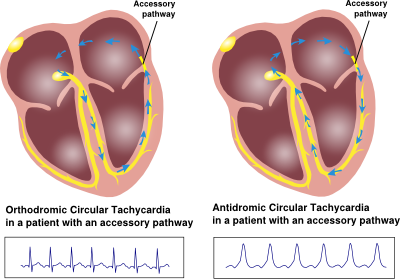
- Palpitations / tachycardia = Orthodromic AVRT = retrograde conduction
- WPW pattern / preexcitation pattern

ECG findings
Main ECG findings
- Short PR interval
- Delta wave
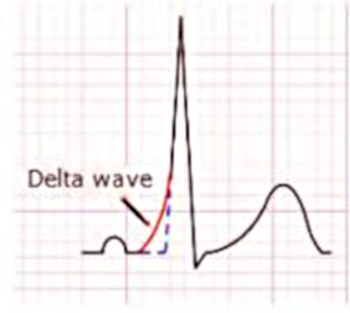
The delta wave
- Slurring of the initial part of the QRS
- Fusion between conduction from pathway and AV conduction system
- May be negative as well as positive
- Contribution to QRS dependent on degree of fusion
Delta wave
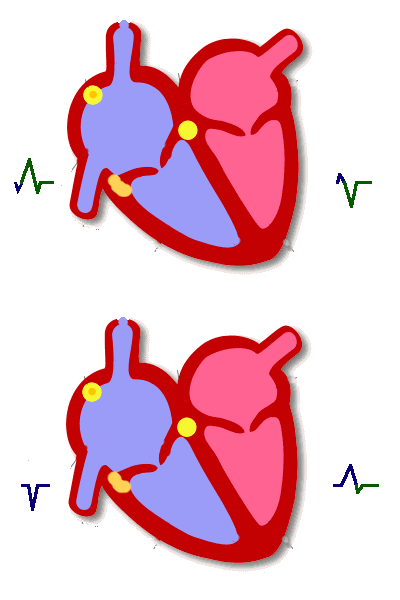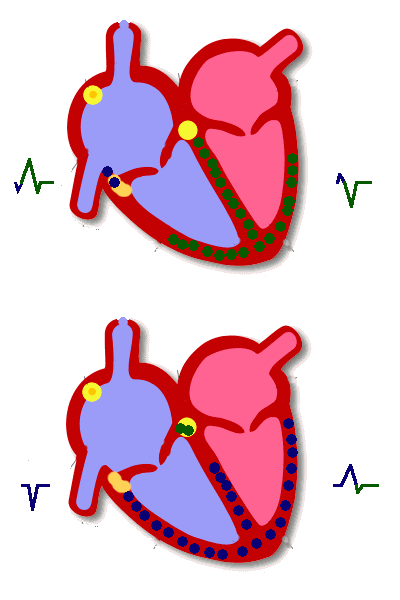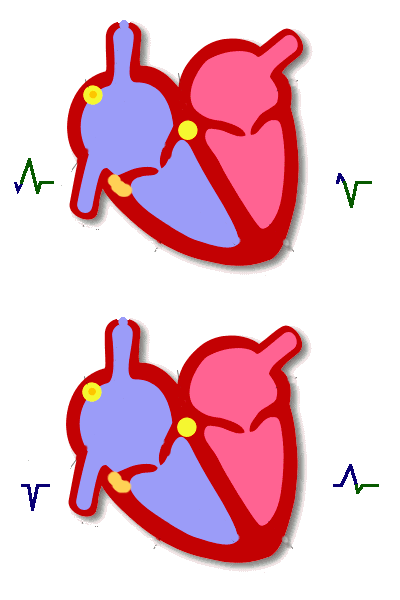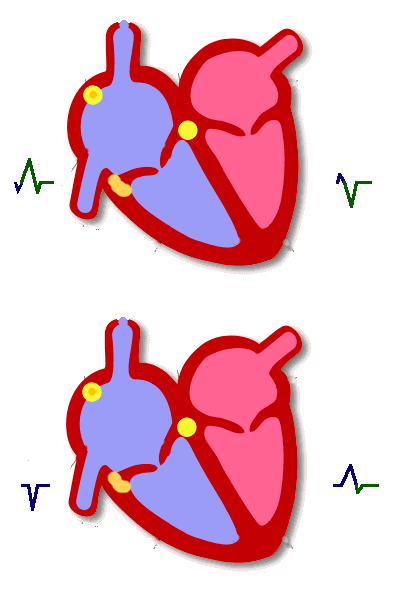
Localization - Not important
- V1 delta = ventricle of origin
- Inferior leads = superior / inferior
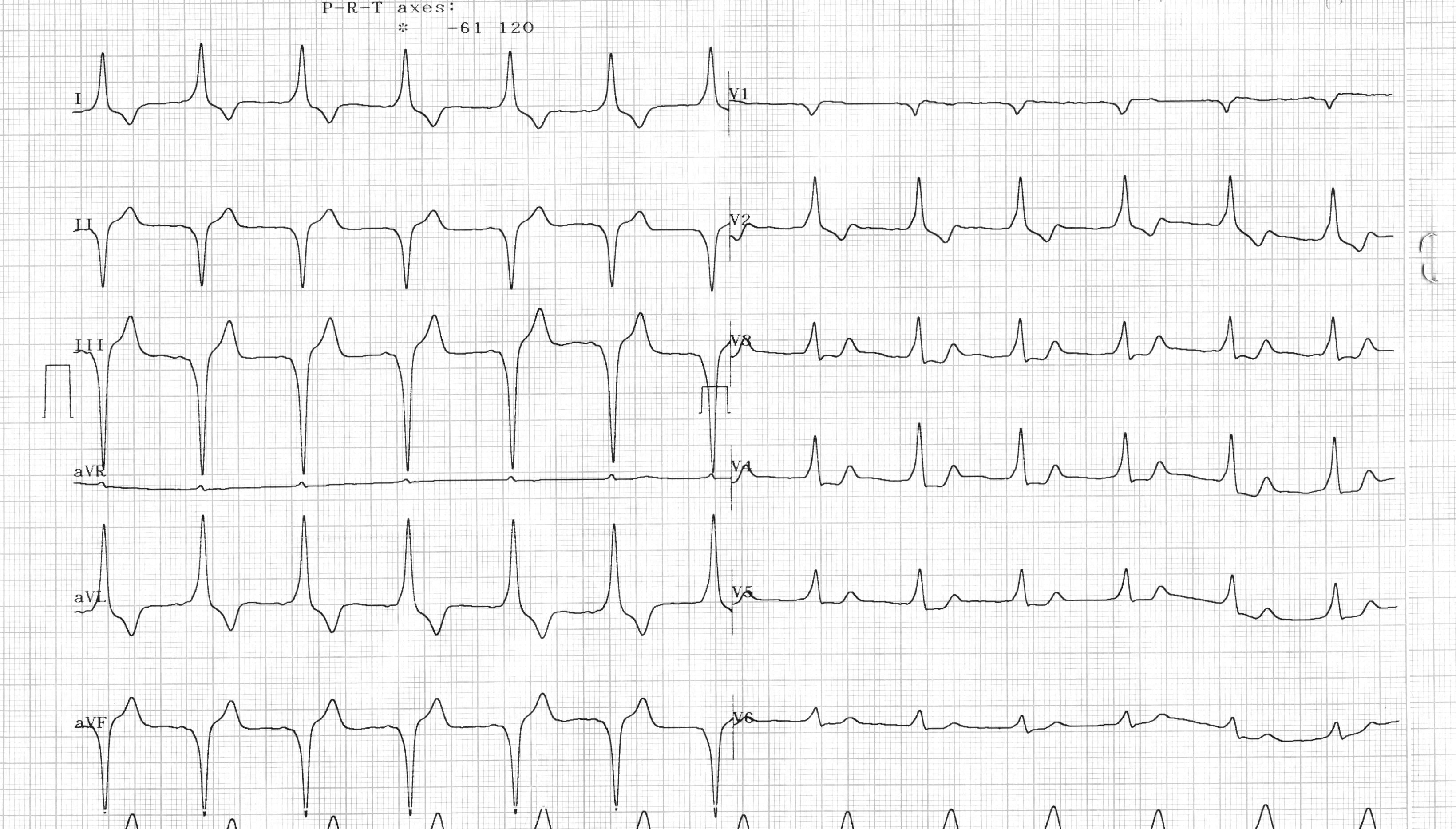
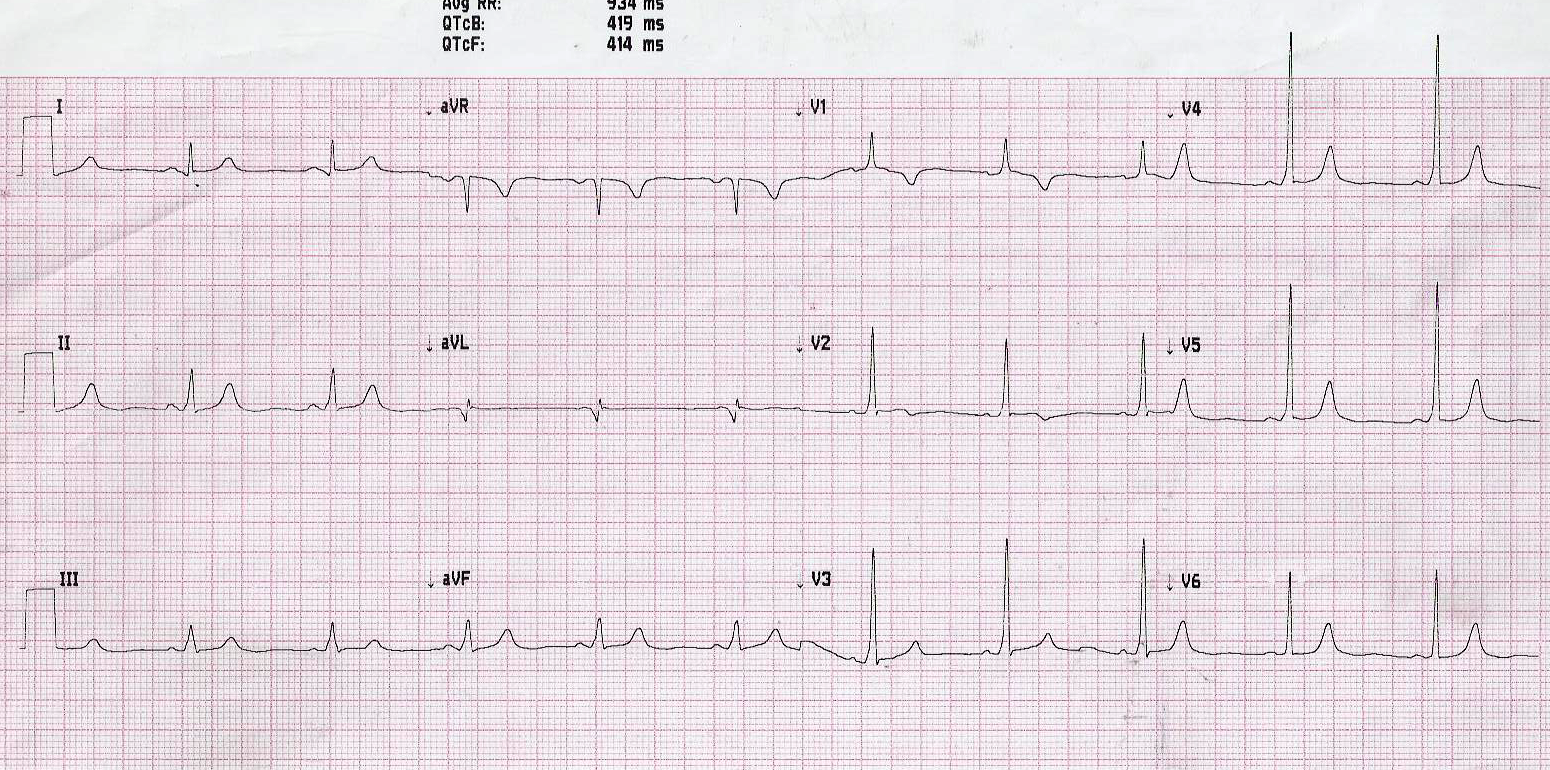
Differentiate delta wave from others
- Short PR
- Old MI
- Slurring
Middle aged male with Rheumatic MS
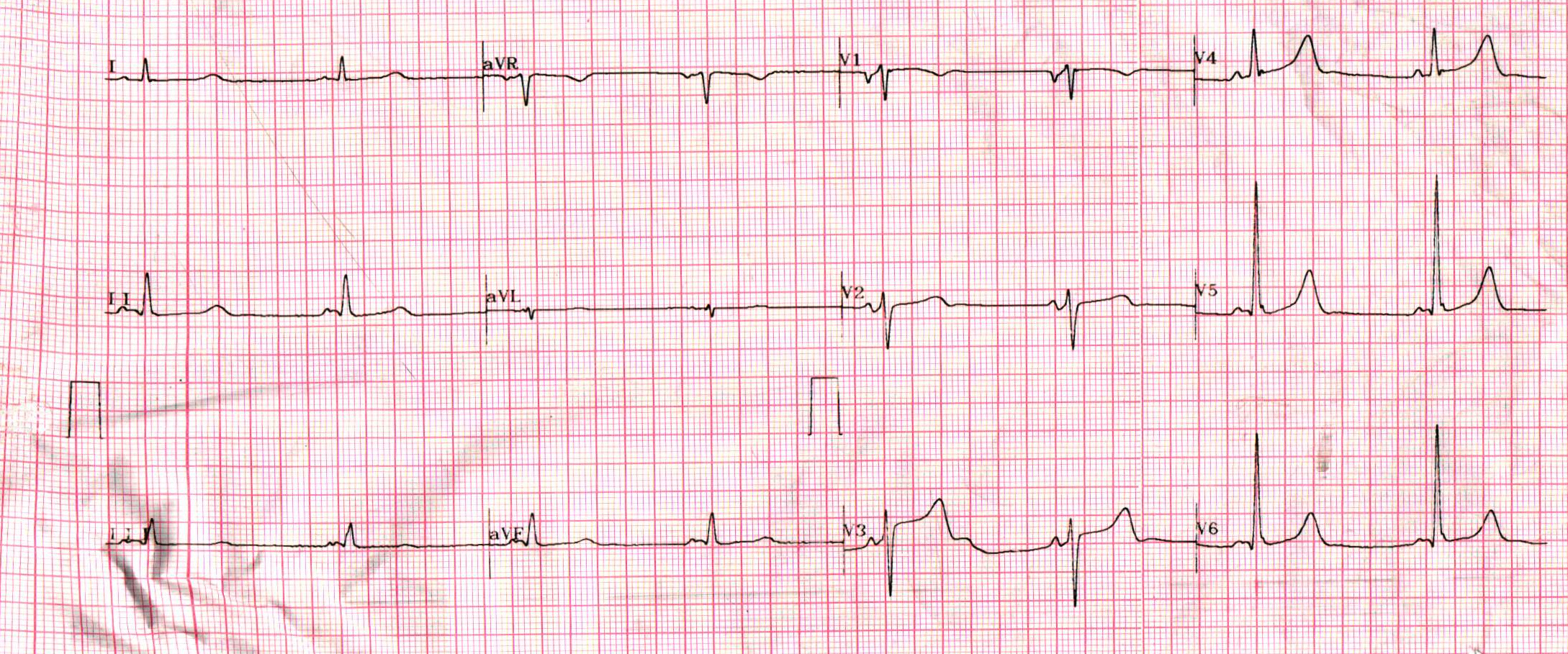
Management
Problems
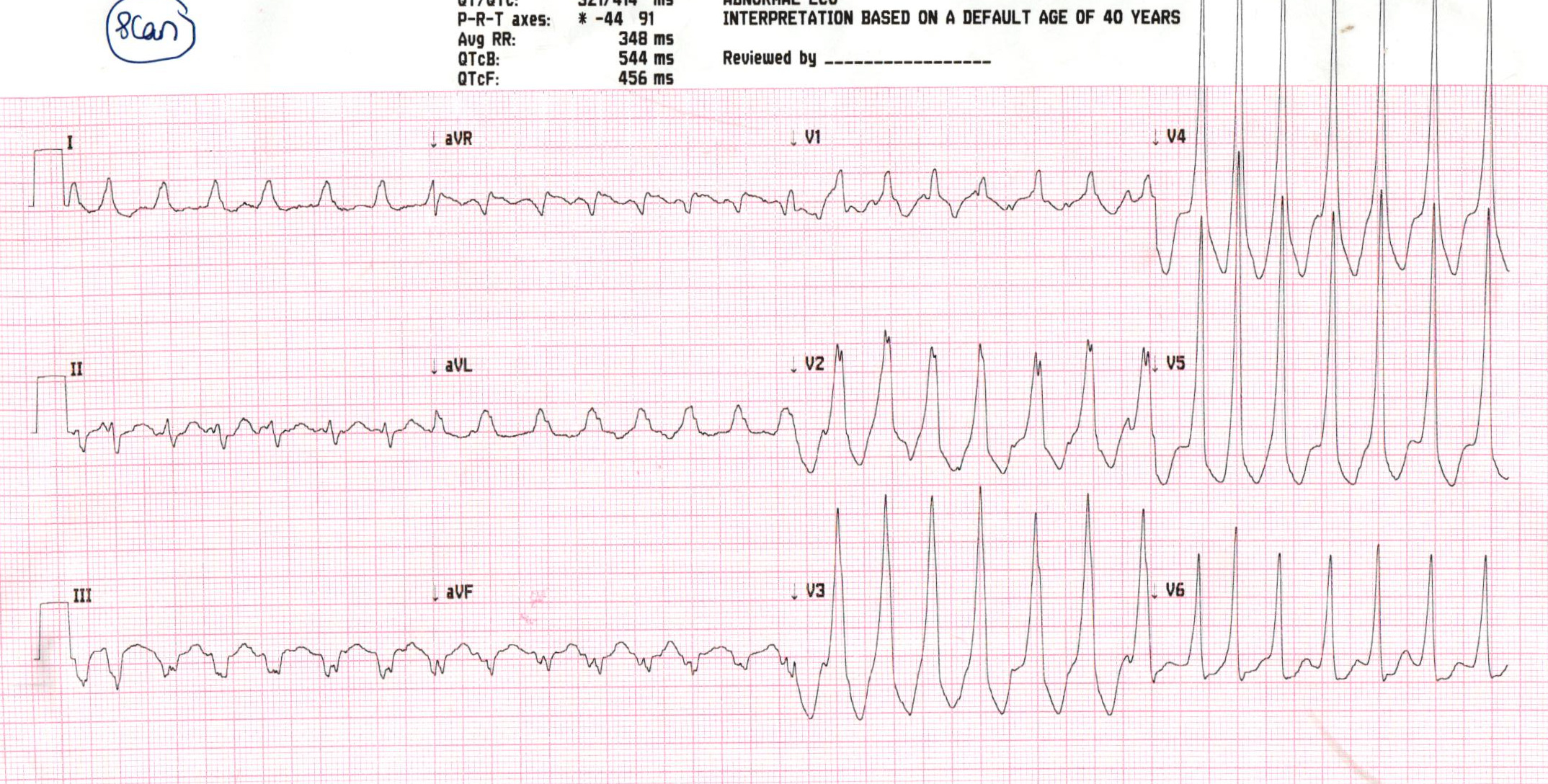
Risk of sudden death
- Rapid ventricular rate during atrial arrhythmias
- AV node behaves as natural defense
- AP - short refractory period, rapid conduction
Middle aged male with MS
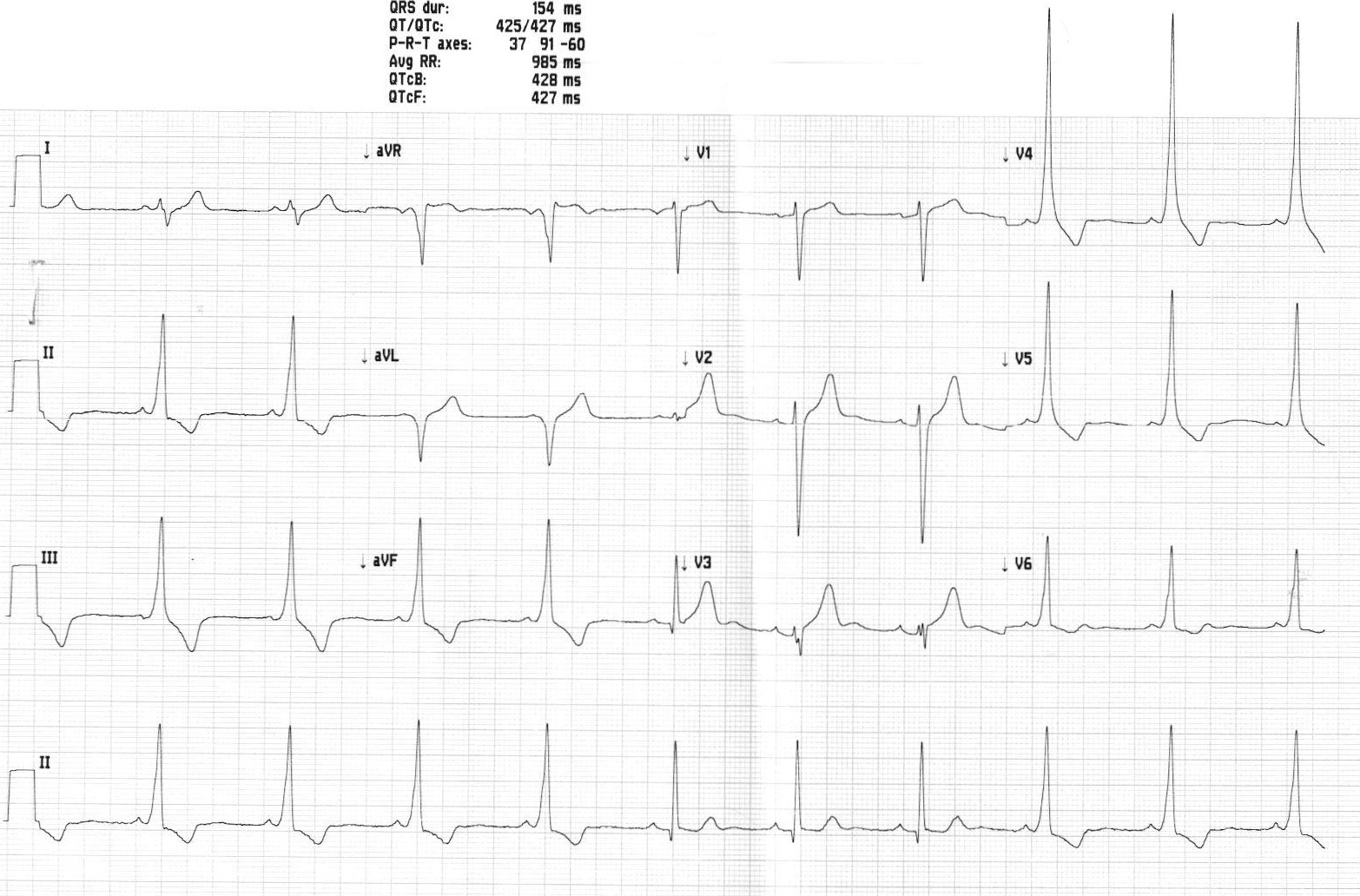
The low risk patient
When to refer ?
- Any patient with suspect / obvious preexcitation
- Especially when history of palpitations
- Urgently if there is history of syncope / preexcited AF
Management of ORT
- Adenosine
- Other AV nodal blocking drugs
Management of preexcited AF
- Adenosine / beta blockers / calcium channel blockers should not be given
- Amiodarone - (not considered safe)
- Procainamide
- DC cardioversion
Ablation
- Curative treatment for pathways in all locations
- Success rate > 95% with low recurrence rate
- Low risk of complications