Mapping fundamentals, electrograms and entrainment

Raja Selvaraj, JIPMER
Basics of recording electrograms in the lab
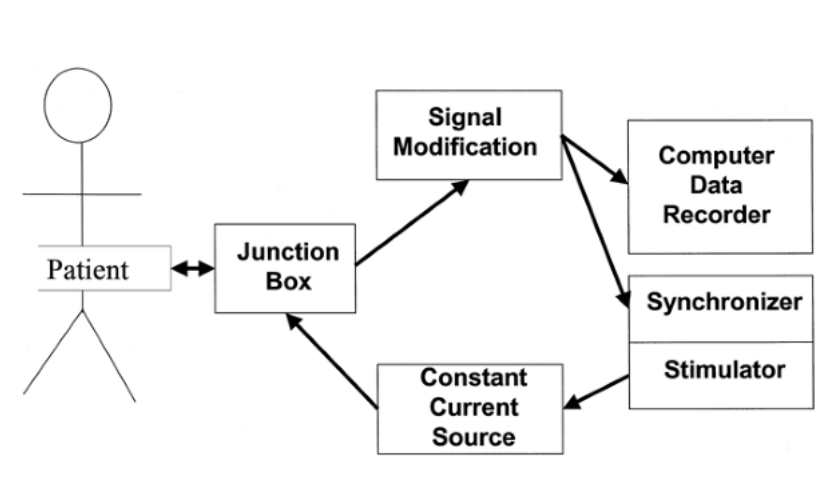
Schematic of EP lab setup
Multi-electrode Catheters
- 2 - 20 electrodes
- Quadripolar
- Decapolar
Decapolar catheter - which is electrode 1 ?
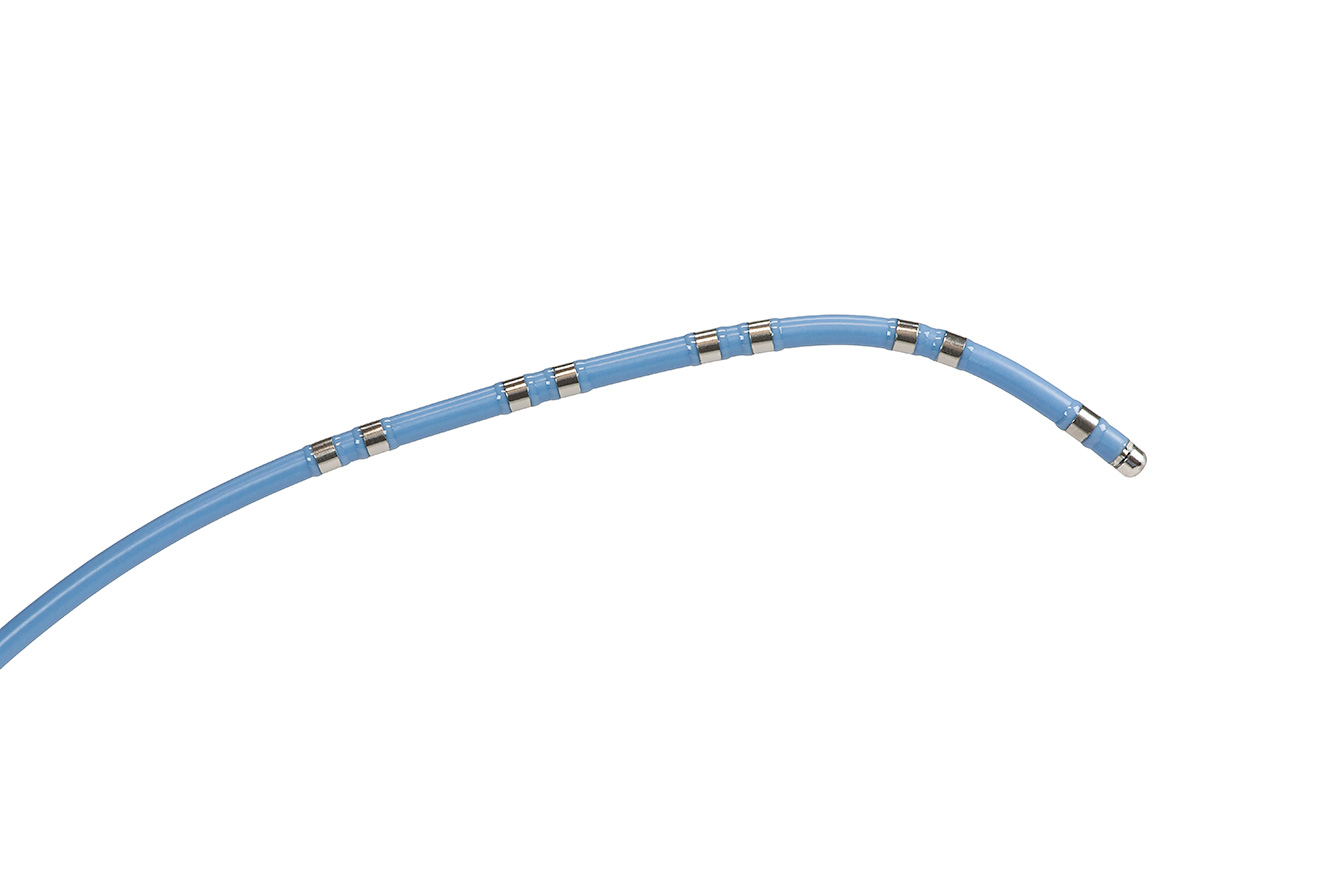
Interelectrode spacing
- Varying inter-electrode distances
- Accurate timing information with 2 or 5 mm distance
- Usually 5 mm between electrode pairs
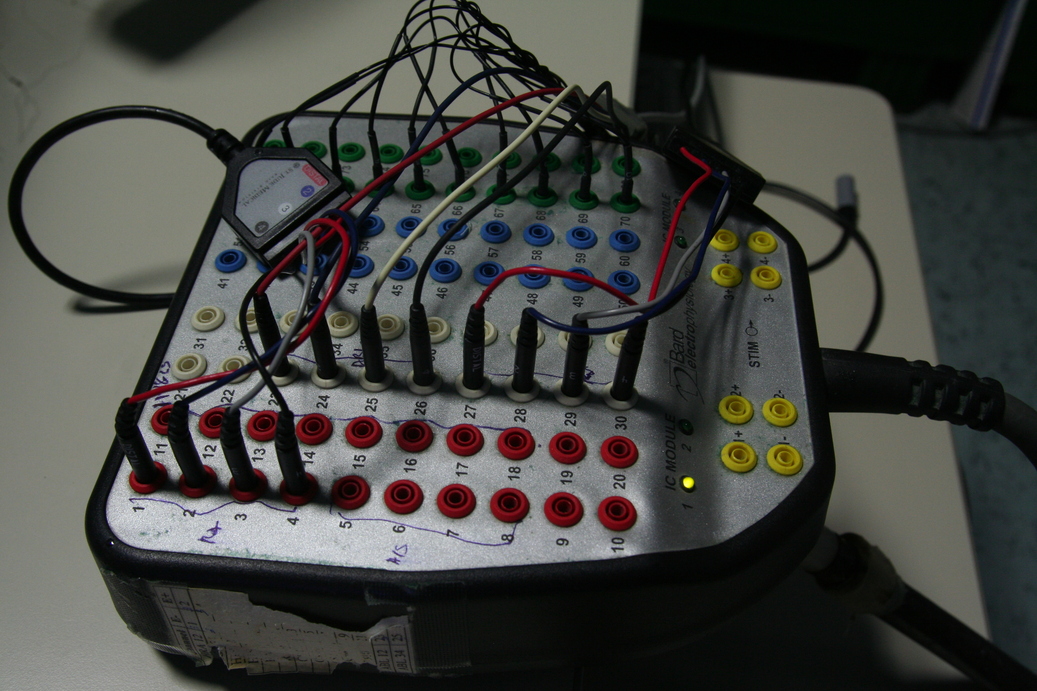
Connector
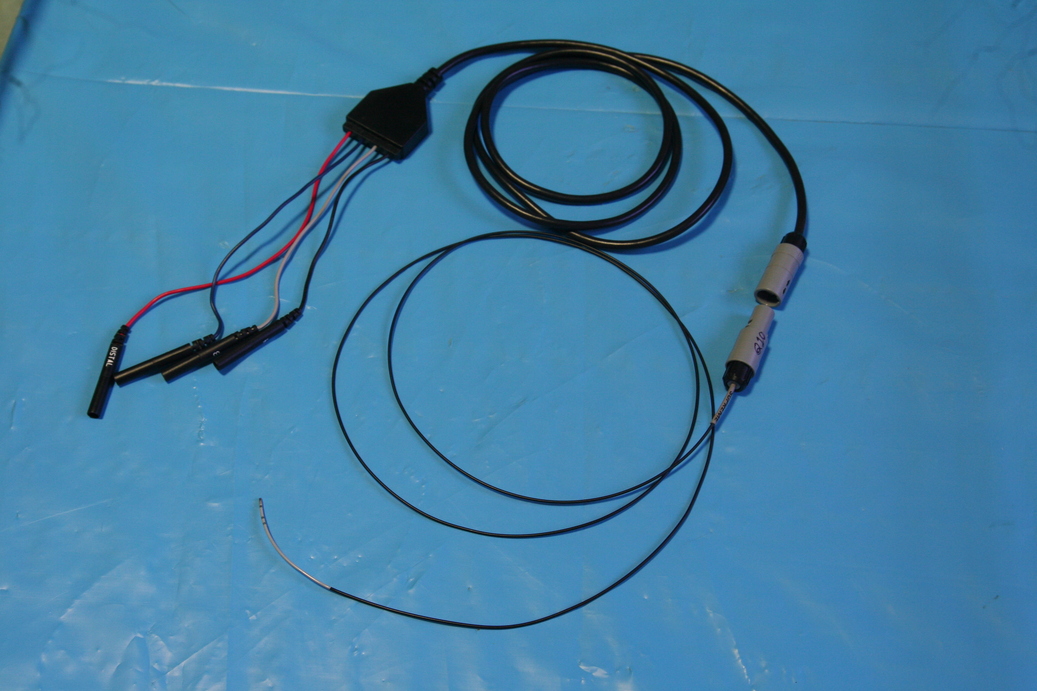

Junction box
- Provides an interface between the catheters and the recording system
- Numbered poles - can be used for setting up channels for recording / stimulation
Junction box
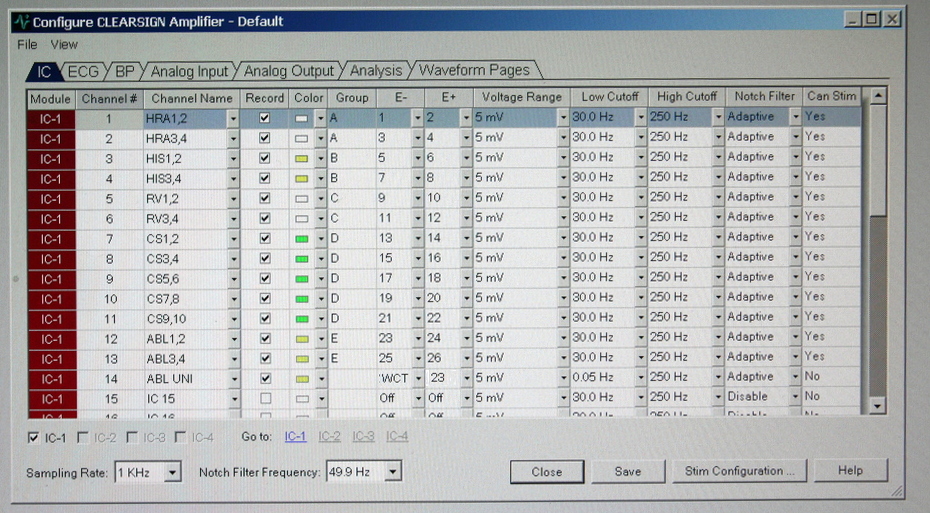
Setting up the amplifier
Amplifier
- Signals are extremely small
- Amplification required
- Digitization
- Filtering
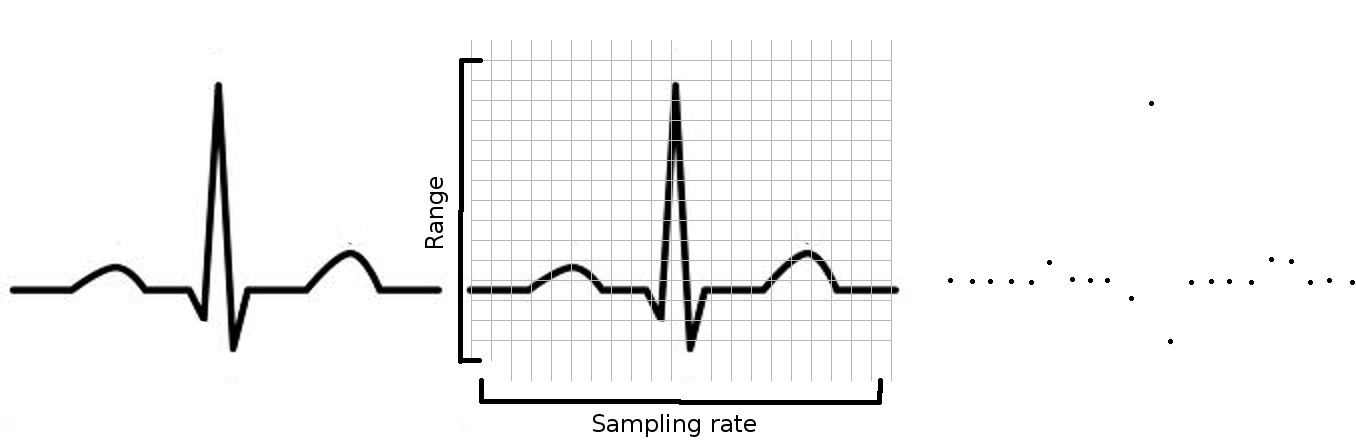
Digitization
- Range (intracardiac signals not more than 10 mV)
- Bit resolution
- Sampling rate
Digitization
Filters
- High pass
- Low pass
- Notch
High pass filter
- Higher high pass limits view to 'local' events
- Increasing further reduces the energy of recording
- Removes baseline wander and other low frequency noise
Low pass filter
- No significant components beyond about 300 Hz
- Reduces high frequency noise component
Setting up filters
- Frequency content of the signal
- High - content up to 300 Hz
- Low - T waves
- Noise to be avoided
- Electrical interference (50 / 60 Hz)
- Myopotential / high freq artifacts
- Respiration / Baseline wander
ECG
- All 12 leads
- 0.1/0.5 - 50/100 Hz
Bipolar
- Adjacent electrodes
- 30/50 Hz - 300/500 Hz
- Notch filter
Unipolar
- Intracardiac / WCT for reference electrode
- Exploring electrode to positive terminal
- DC/0.05 Hz - 300/500 Hz
Amplifier setting
Setting up the display
Pages
- 12 lead
- IC
- Abl, others
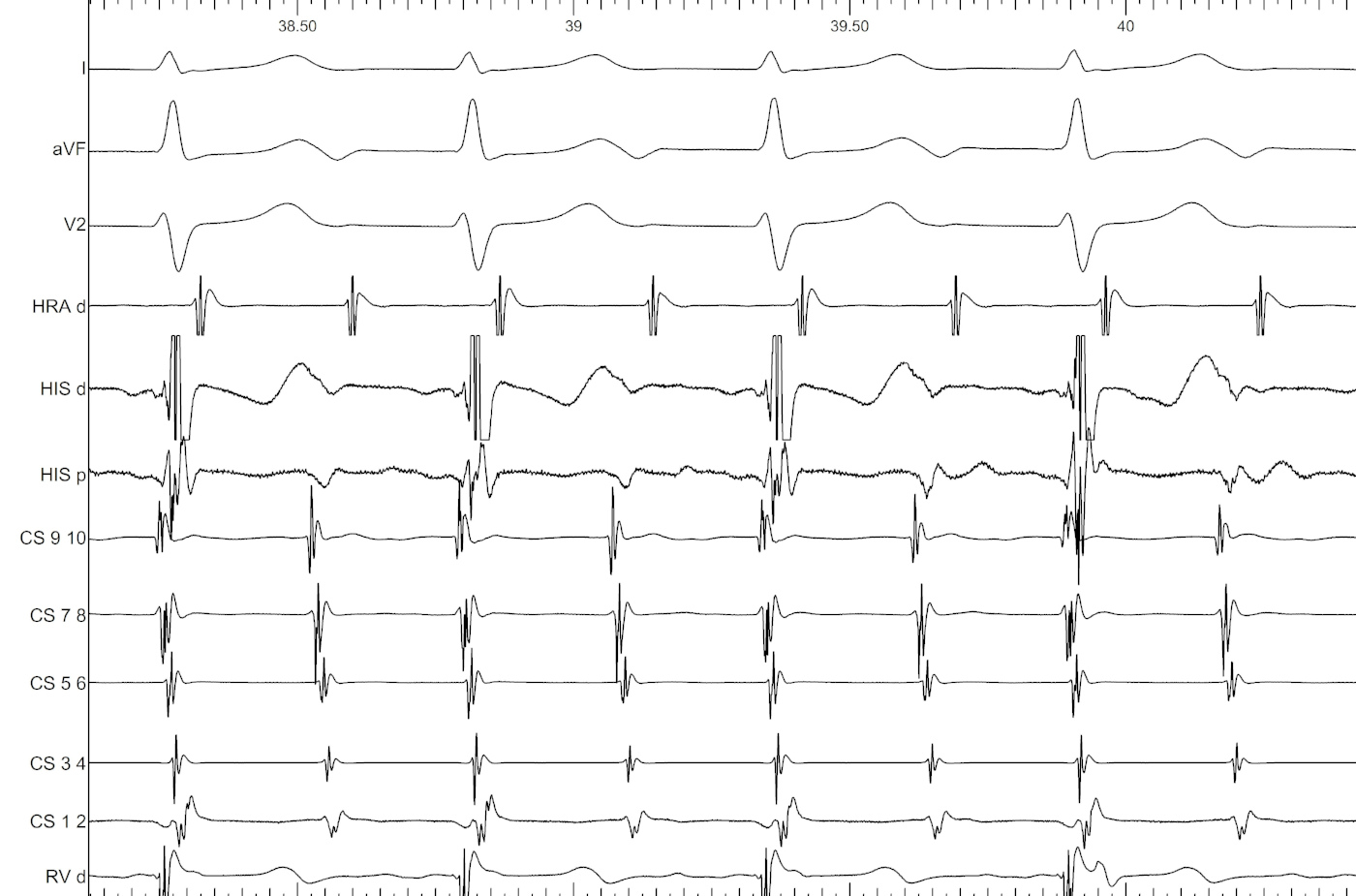
Intracardiac
- 3-4 ECG leads, usually orthogonal
- Intracardiac
- CS display conventions
- Colors
Ablation
- Essential signals only
- Unipolar EGM from mapping catheter
- No clipping of ablation signals
- Equal gain of proximal and distal ablation signals
Electrograms
Bipolar
- Potential difference between two electrodes
- Both in contact with myocardium
- Usually closely spaced
Bipolar
- Rapid, high frequency
- Reflects "local" events
Unipolar
- Potential difference between "exploring" and "indifferent" electrodes
- Exploring electrode is in contact with heart
- Indifferent electrode is at distance
- WCT
- Electrode in IVC
Unipolar
- Records both local and distant events
- Inverse square law
- Frequency higher for local events
Local activation time
- Bipolar electrogram
- Intrinsic deflection
- Zero crossing
- No indication of timing in relation to origin
- Unipolar electrogram
- Maximum negative dV/dt
Electrograms - accessory pathway
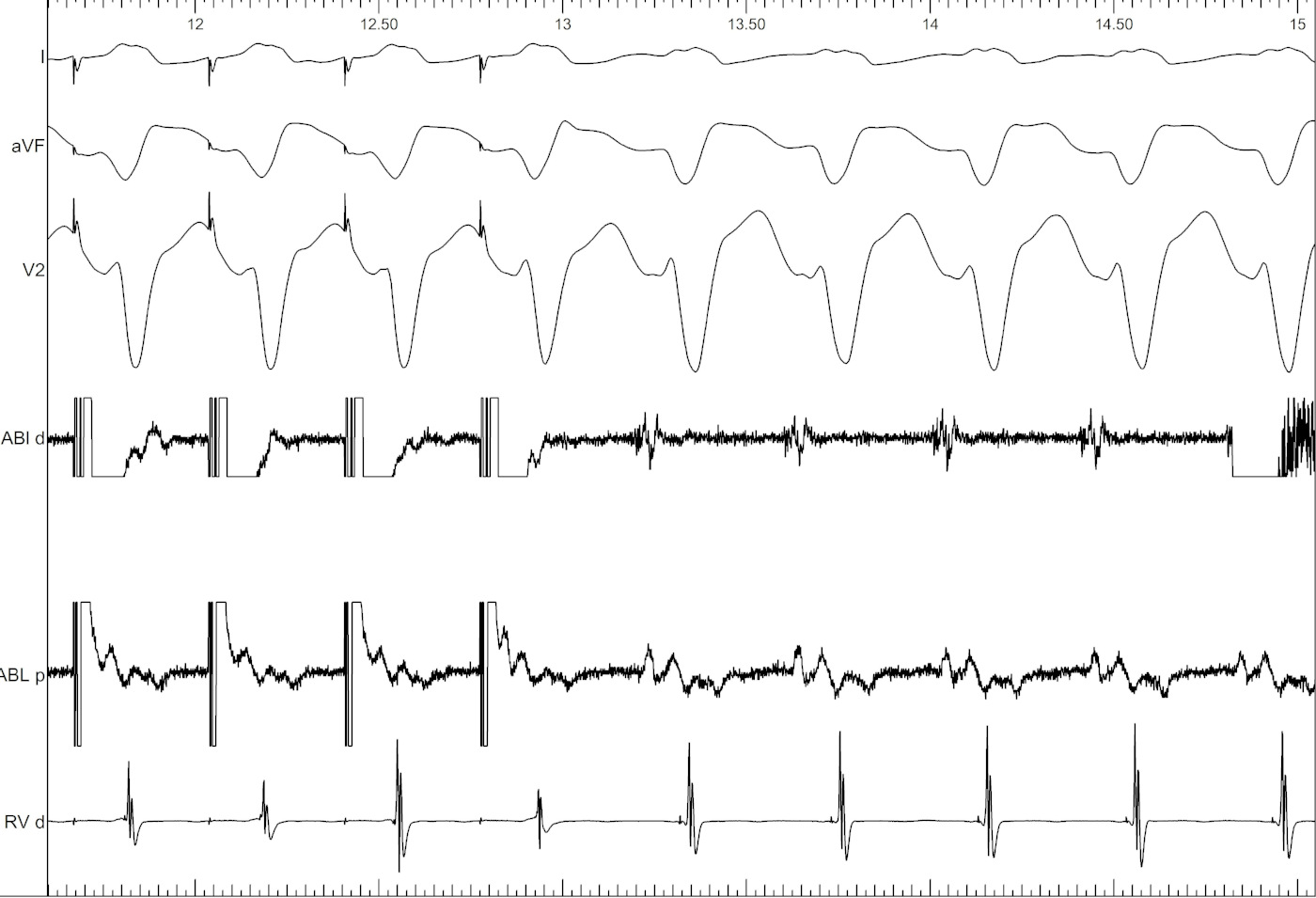
Electrograms - VT
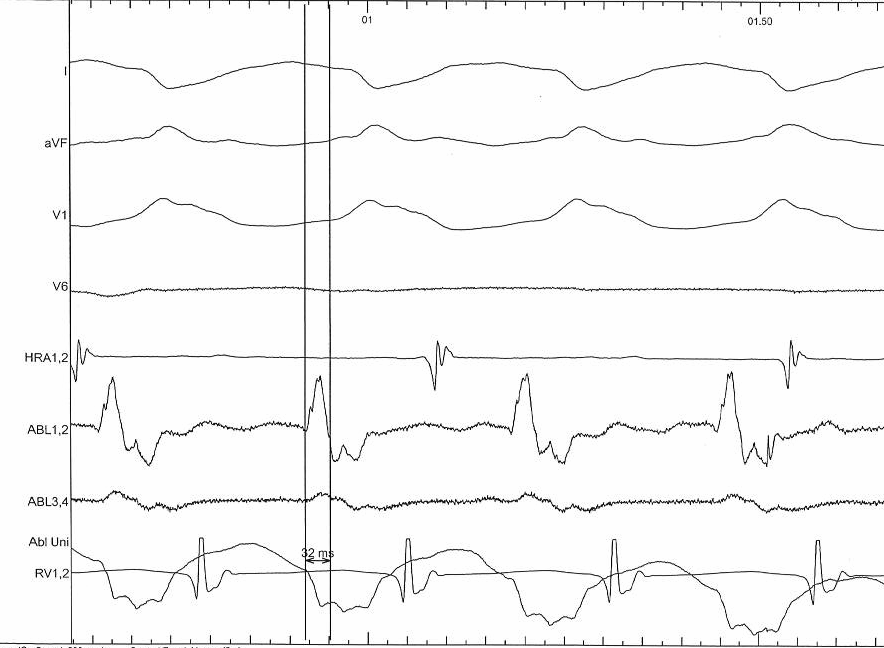
Entrainment
Basic principles
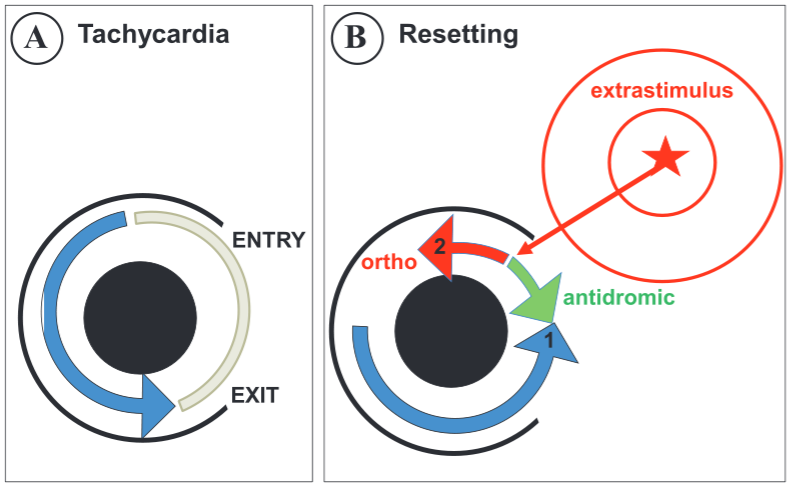
Prerequisites for entrainment
- Reentrant circuit
- Excitable gap
- No entrance block
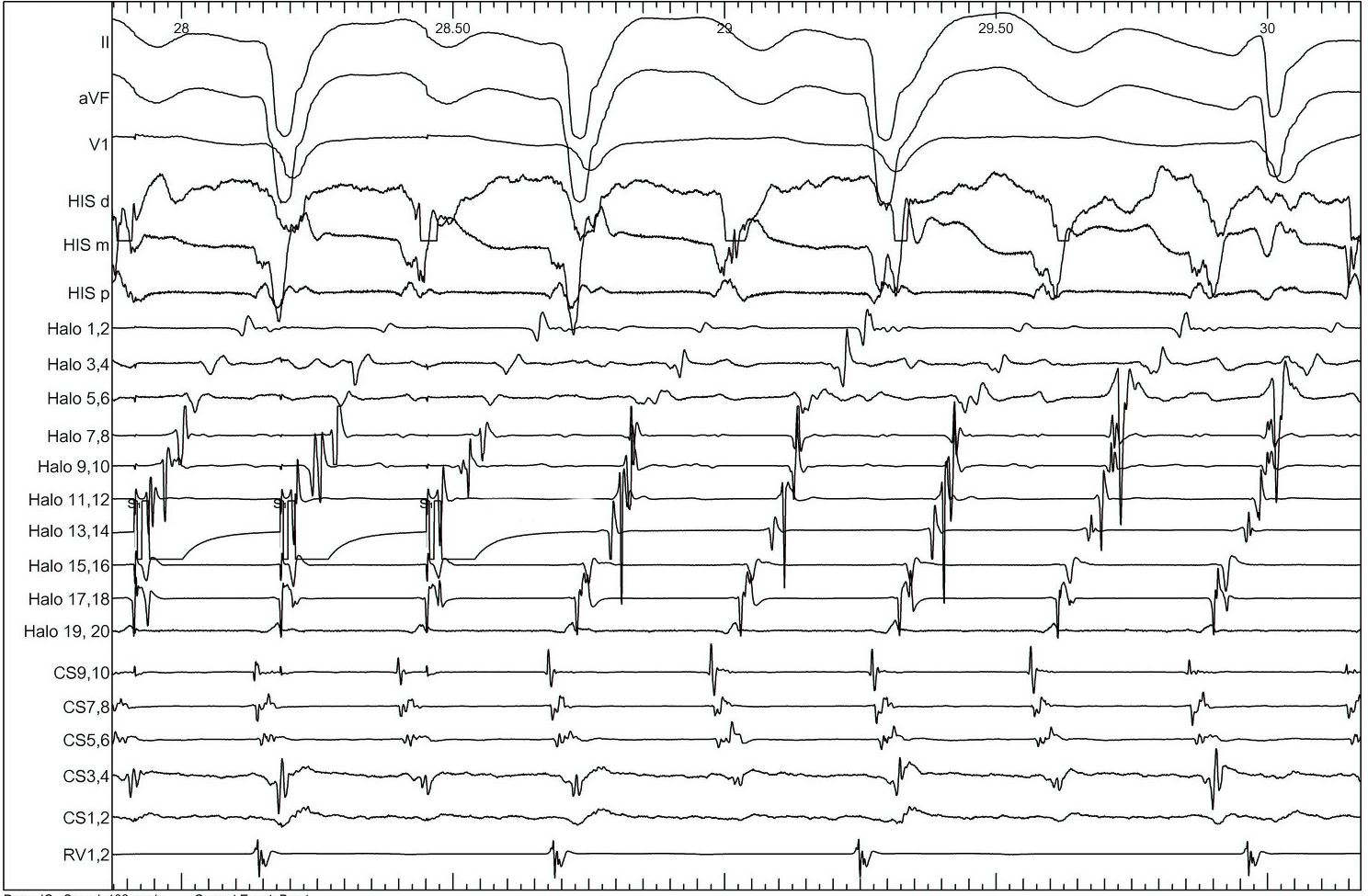
Identifying entrainment
- Constant fusion
- Progressive fusion
- Only two criteria originally described by Waldo
- Sometimes probabilistic
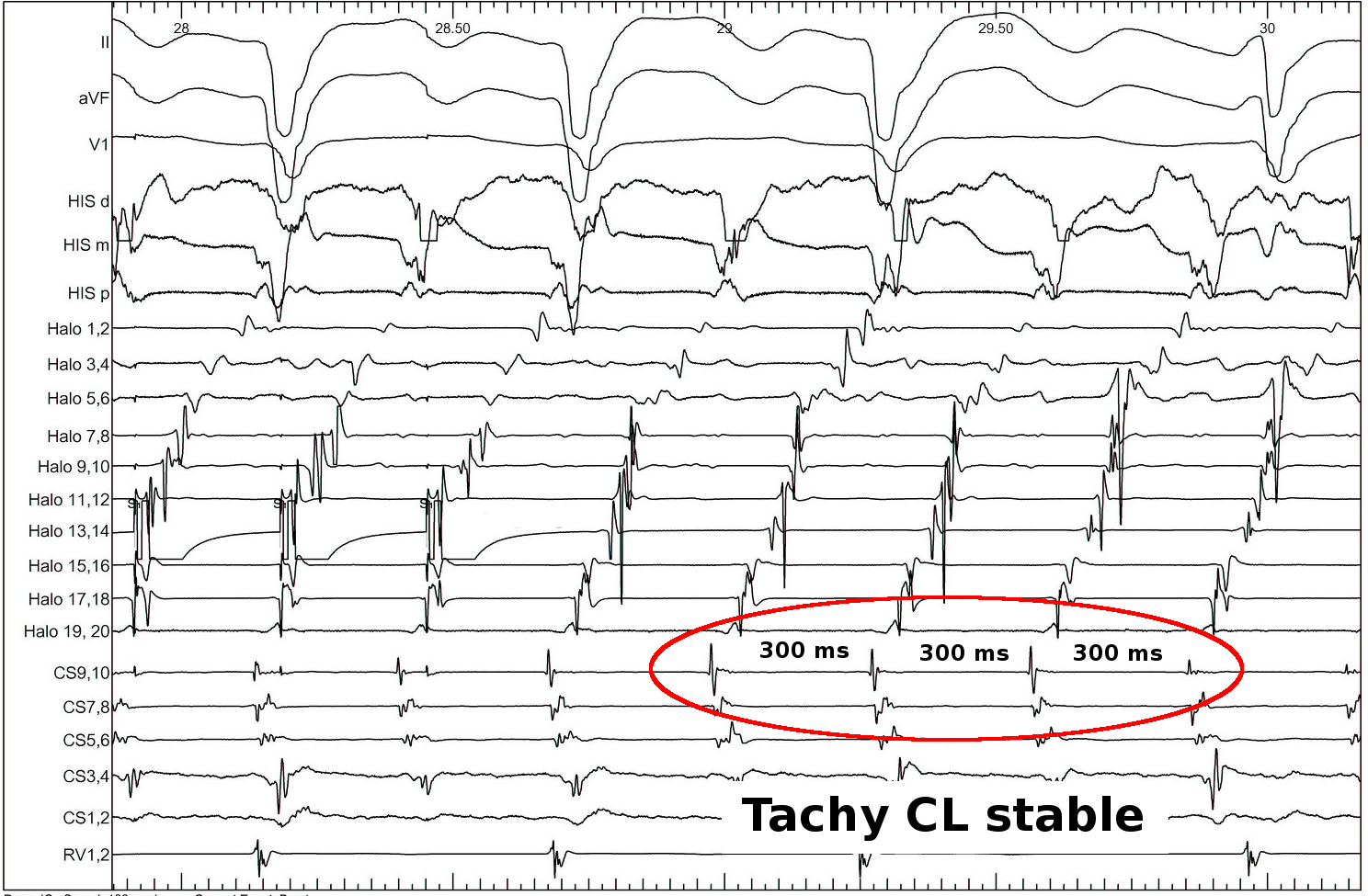
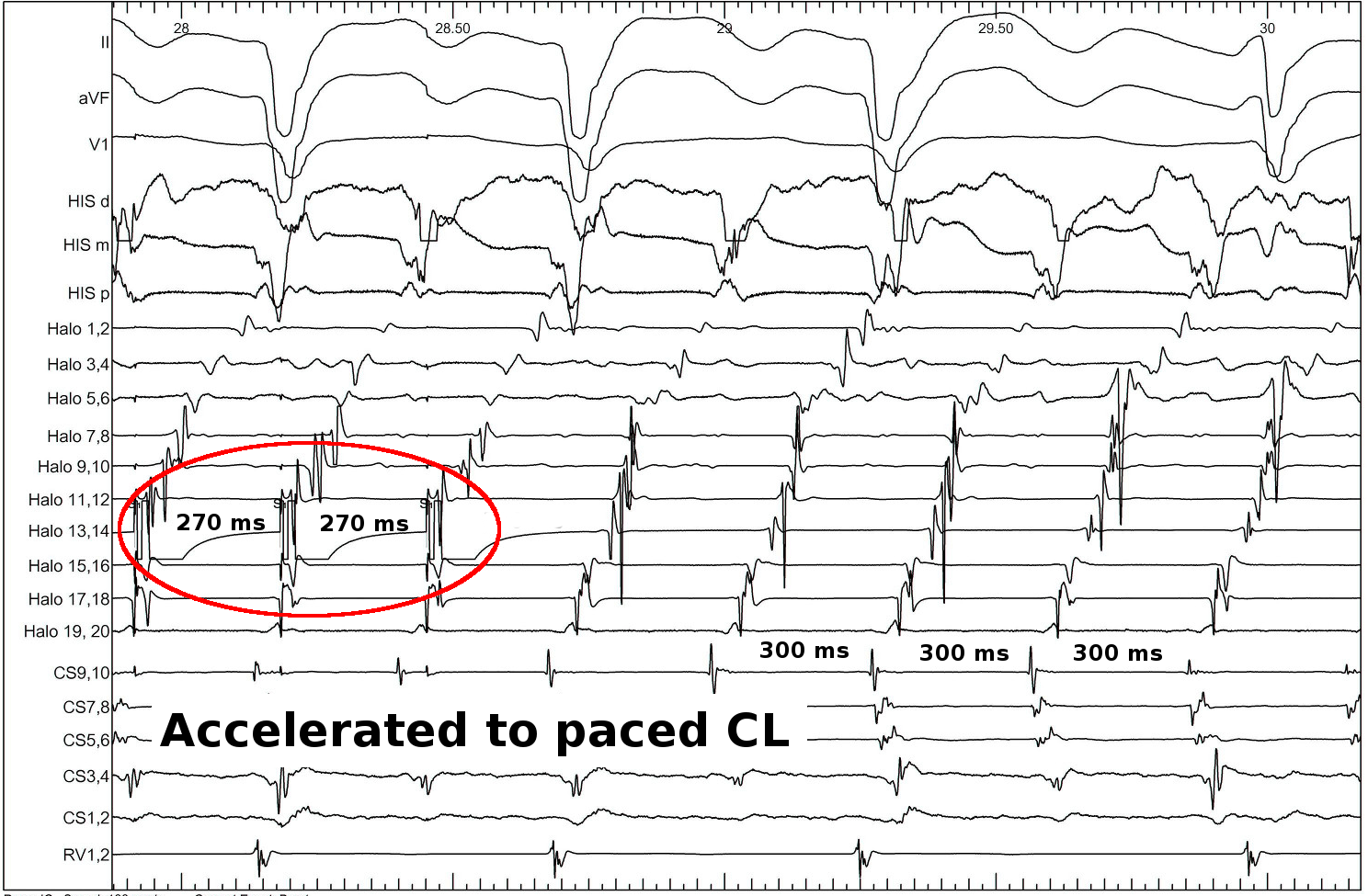
- constant PPI at different pacing rates
Interpretation
- Deviation from morphology indicates extent of capture by antidromic wavefront
- Deviation from cycle length indicates distance from circuit
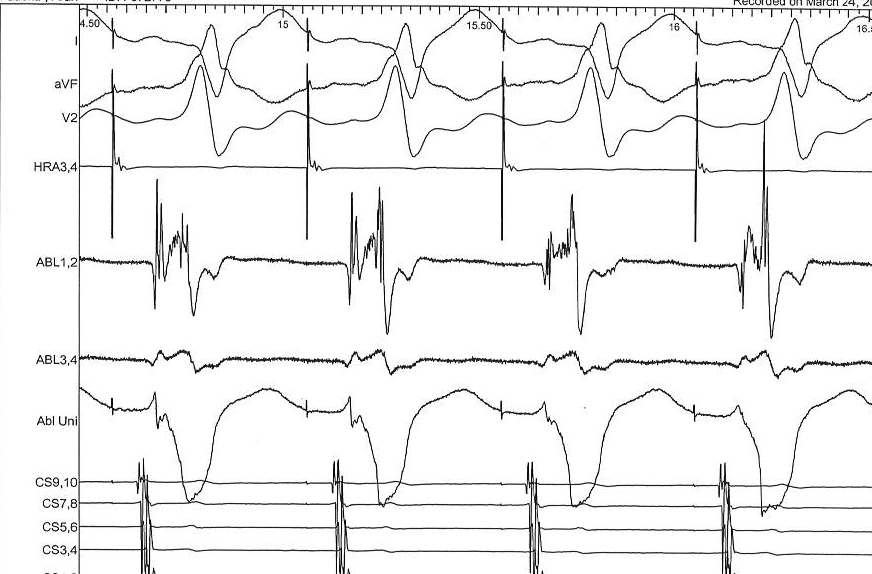
PPI
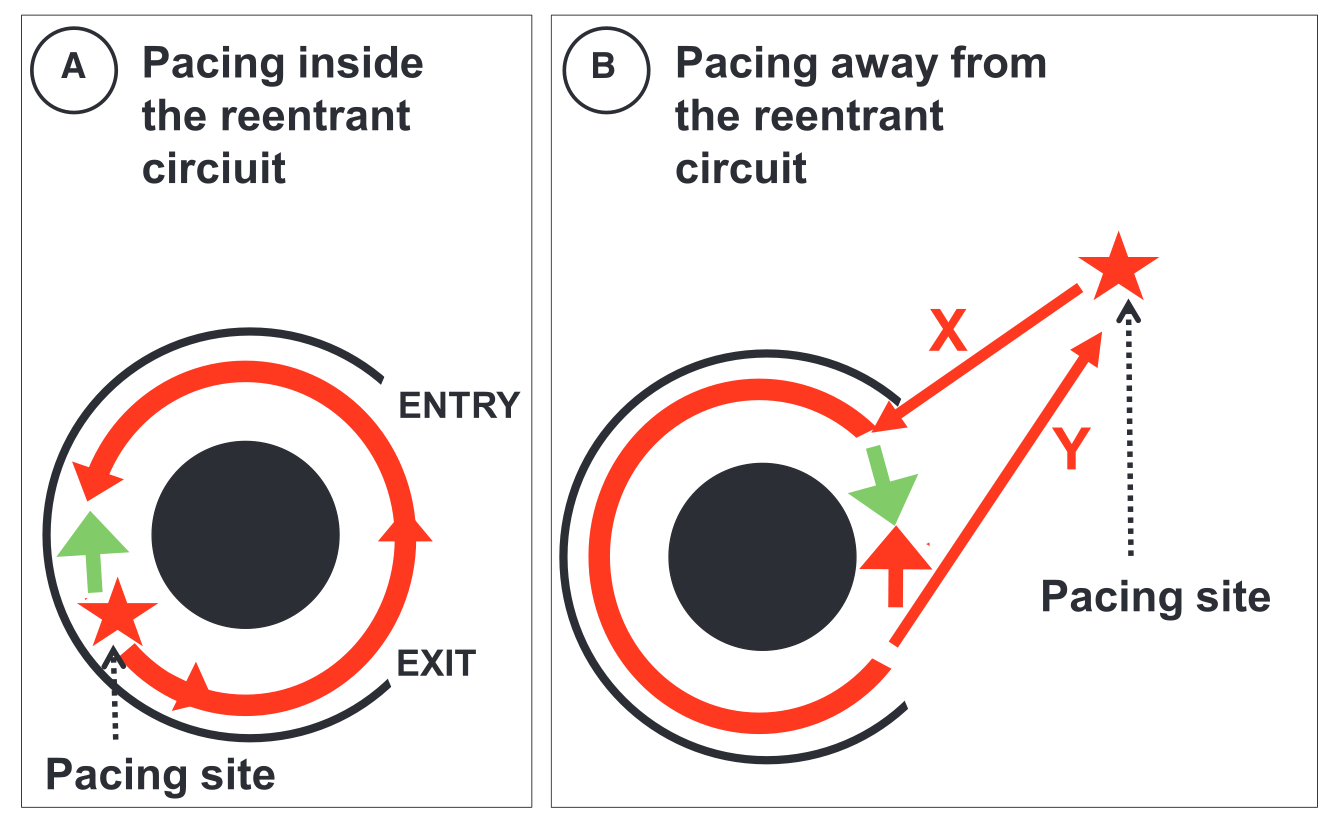
Scenario 1 - Atrial flutter
Pacing CL
- Pace at 20-30 ms shorter than TCL
- Faster - decrement
- Slower - difficult to measure
How to do
- Stim set up
- Atrial activation sequence
- PPI
Interpretation
- Identify circuit
- Quick locate flutter
- Identify isthmus
Catheters
Entrainment
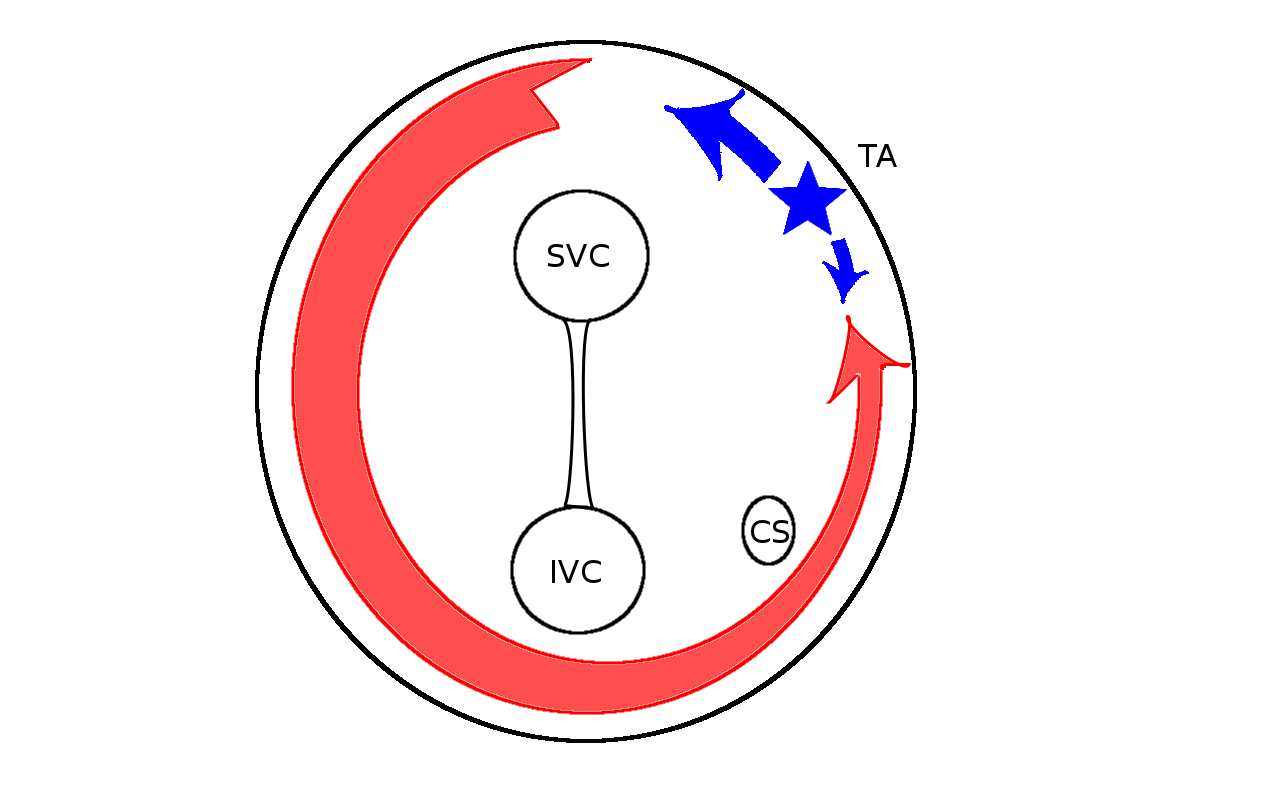
Pacing from lateral RA
Pacing from lateral RA
Pacing from lateral RA
Pacing from lateral RA
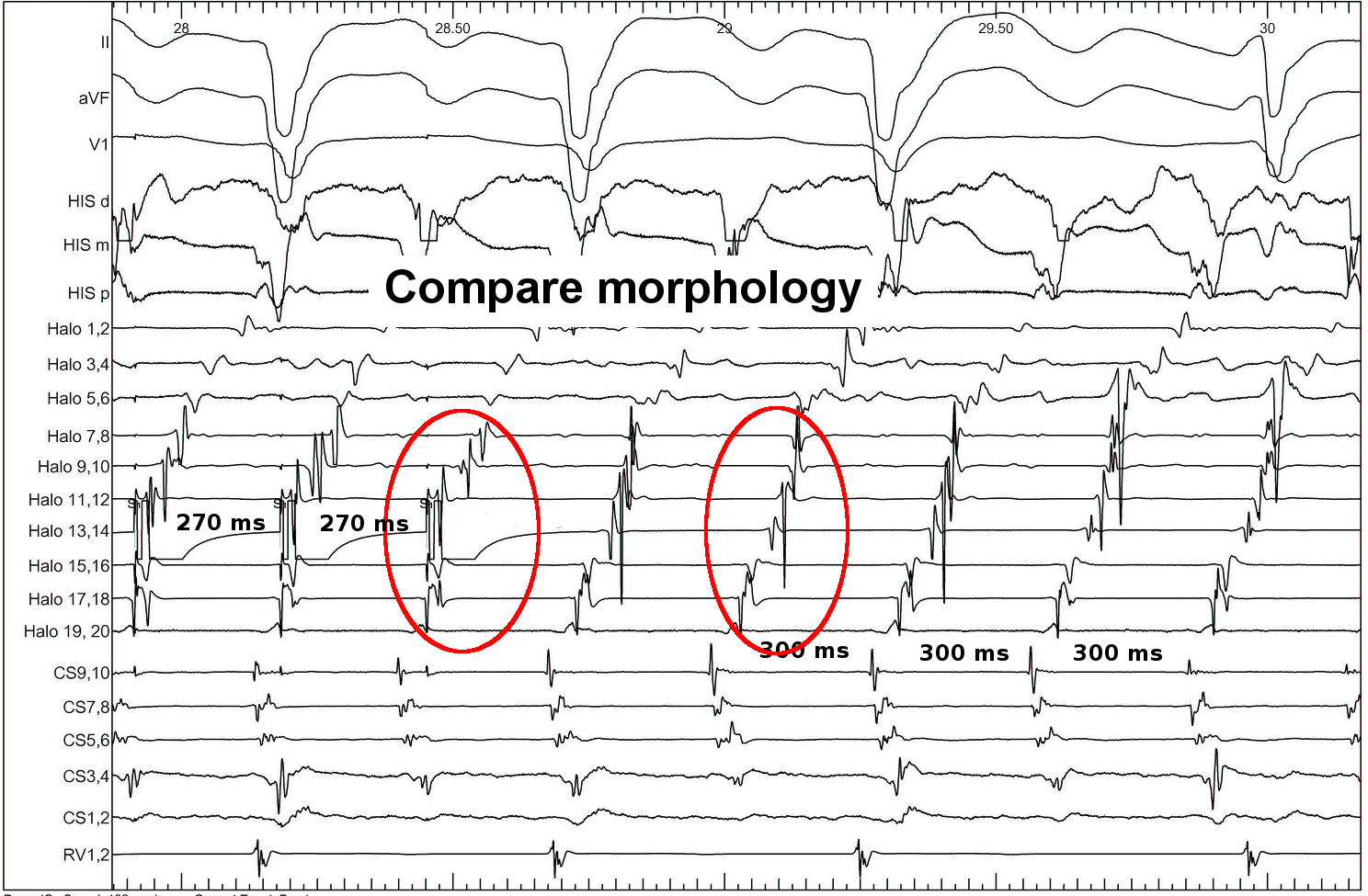
Pacing from lateral RA
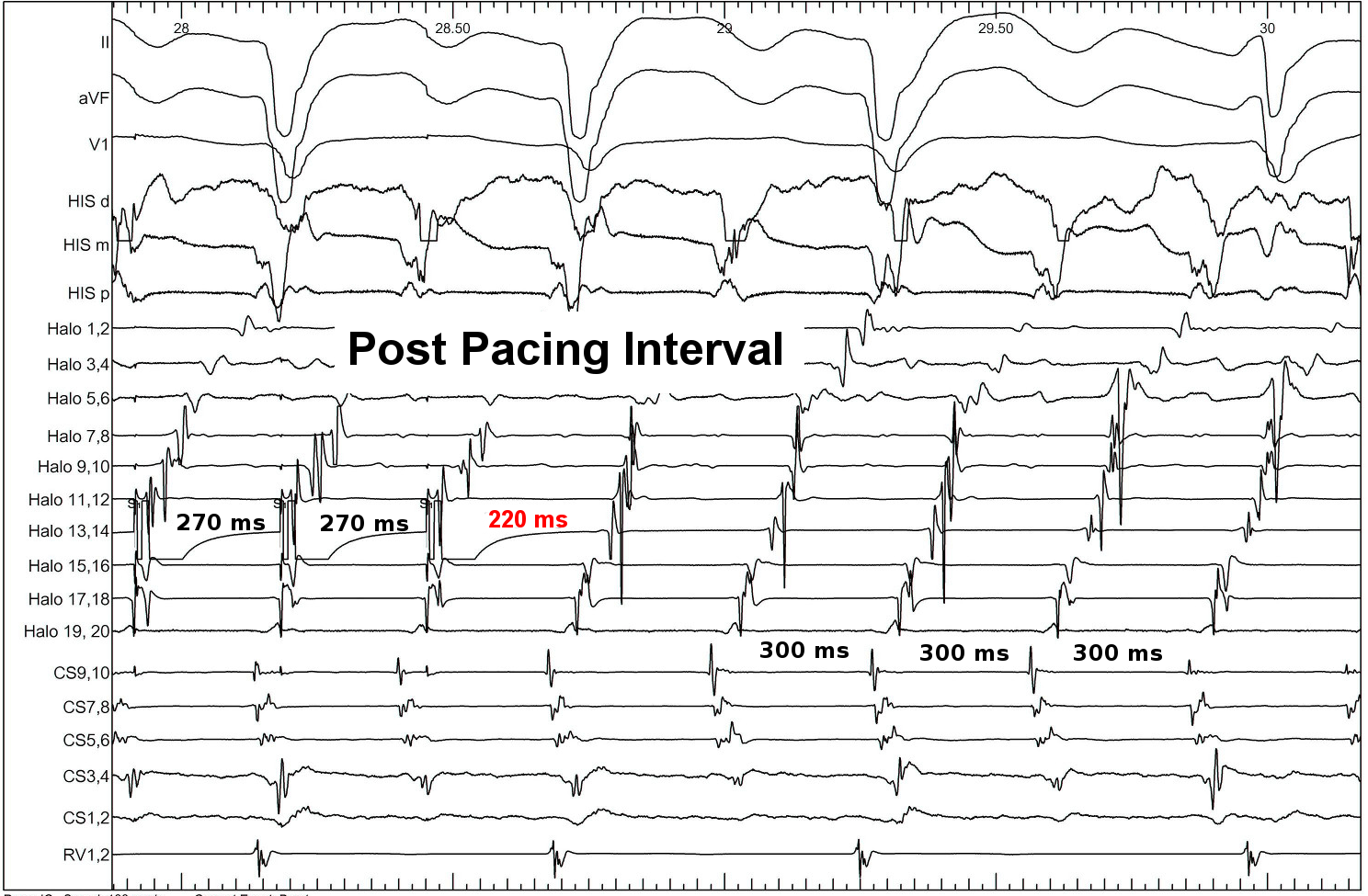
Pacing from lateral Isthmus
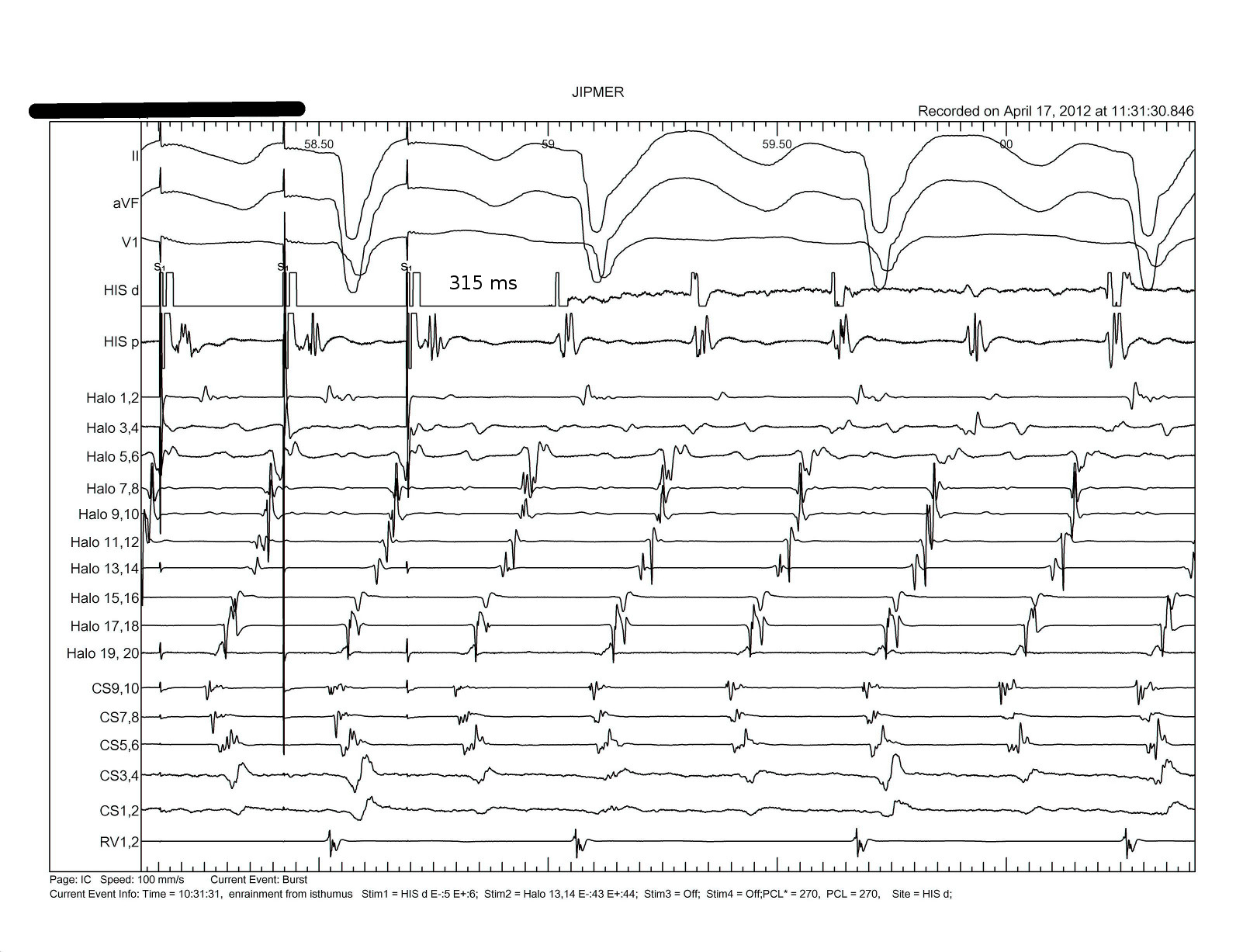
Ventricular tachycardia
Same concept
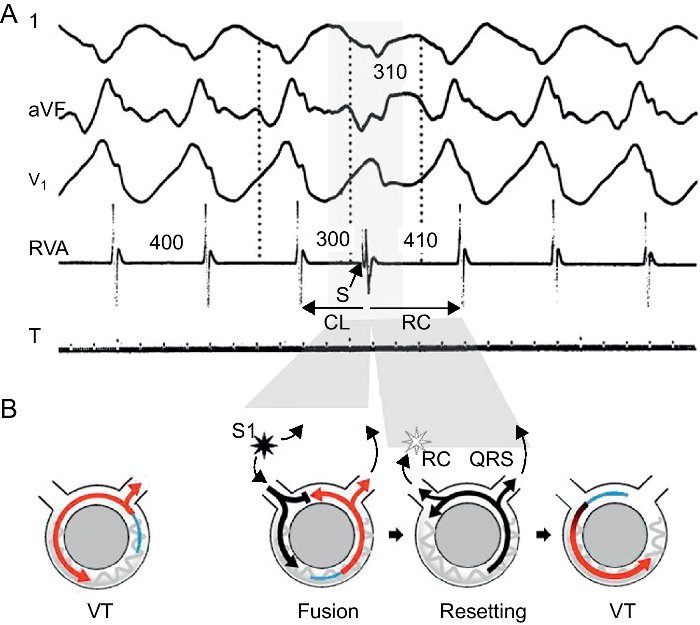
Constant fusion
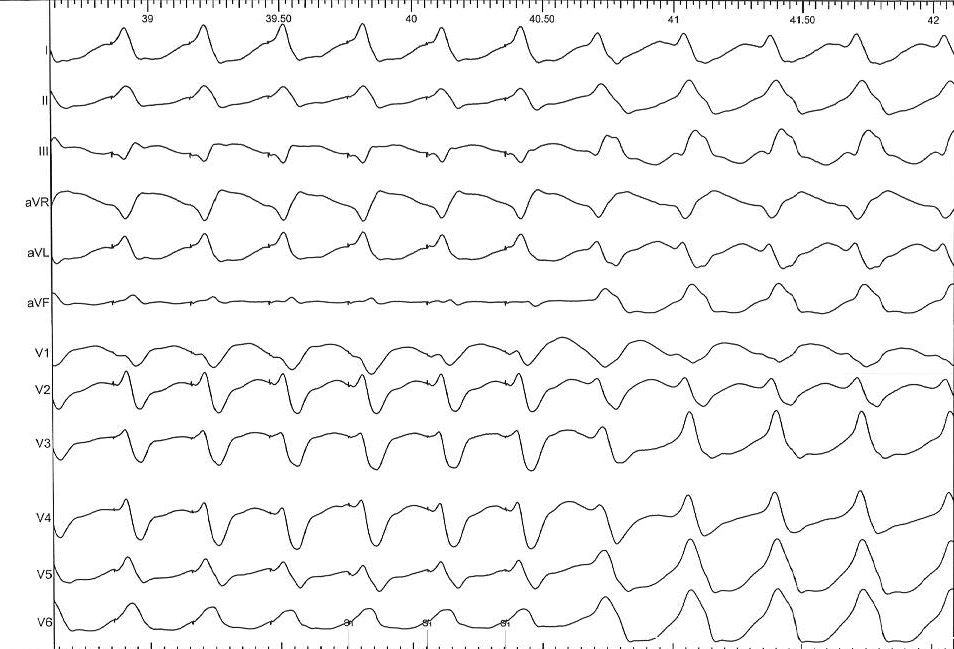
Progressive fusion
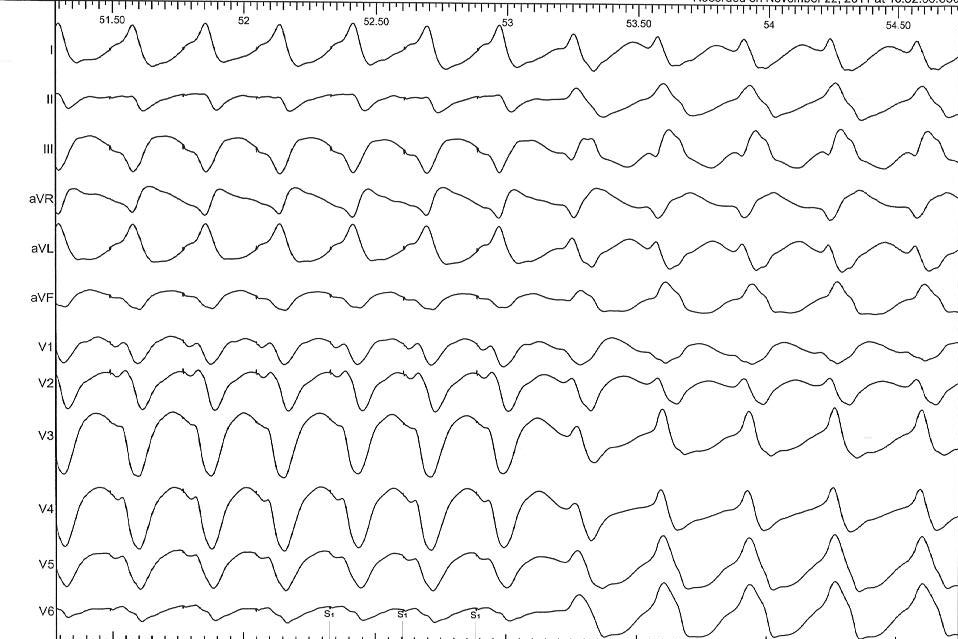
Example
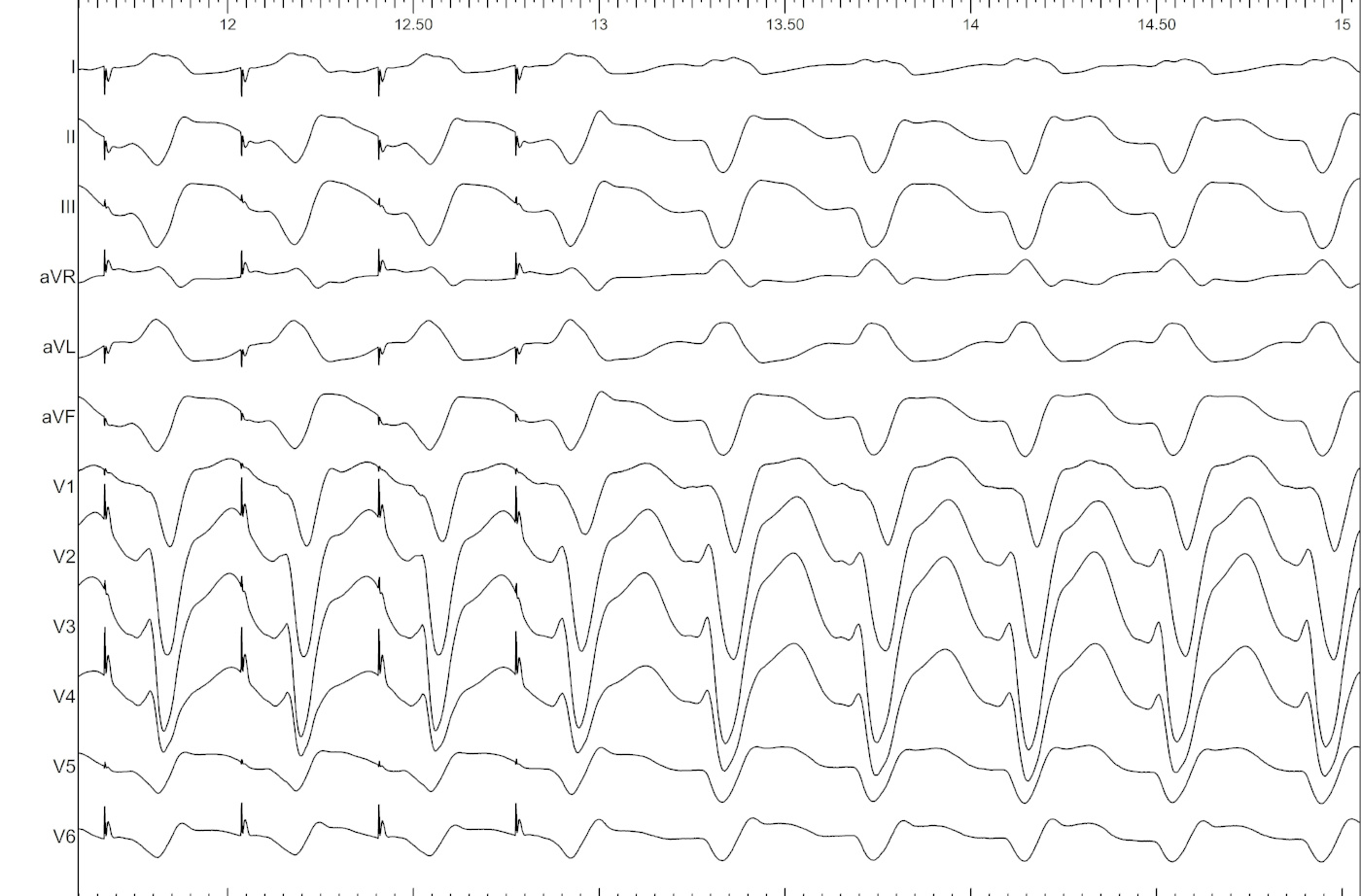
Example