Arrhythmias in Acute MI

Raja Selvaraj, JIPMER
Pathophysiology
Acute ischemia
- ATP deficiency -> Anaerobic glycolysis -> Acidosis -> Increased extracellular K
- Reduced AP duration
- Reduced resting membrane potential
- Reduced conduction velocity
- Mechanism - Reentry
Reperfusion
- Intracellular Ca overload -> EAD / DAD
- Mechanism - Triggered activity
Susceptible groups
- Late presenters
- Incomplete revascularization
- Prior myocardial damage
Arrhythmias
- Prognostic implications - short term and long term
- Acute management
- Long term management
Complete Heart block
Mechanisms
- Autonomic imbalance
- Ischemia / necrosis of conduction system
- 2-3 fold higher incidence in IWMI
Blood supply
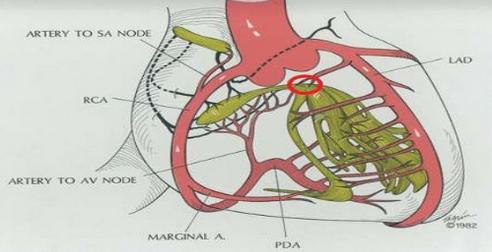
AV block in IWMI
- Block is above His usually
- Good escape
- Transient block
- Low mortality risk
AV block in AWMI
- Usually below the node
- Extensive myocardial necrosis
- Multivessel disease
- Usually significant hemodynamic problems
Prognosis
- Depends on extent of myocardial damage
- Worse in AWMI
AV block in primary PCI era
- Incidence 3.2%
- Most within 48 hours
- 91% resolved
Uffe Jakob Ortved Gang et al. High-degree atrioventricular block complicating ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in the era of primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Europace (2012) 14, 1639–1645
AV block in primary PCI era
- Predictors
- RCA occlusion
- Age > 65
- Female gender
- HT and DM
- Increased 30 day mortality (HR 3.14)
Uffe Jakob Ortved Gang et al. High-degree atrioventricular block complicating ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in the era of primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Europace (2012) 14, 1639–1645
Management
- Reperfusion
- Temporary pacing
- when AVB with significant bradycardia persists after reperfusion
- Only as last resort
- Tamponade in 3/53, lethal in 1 (prev ref)
- Permanent pacing when AVB does not resolve after acute period
Atrial fibrillation
Mechanisms
- Atrial ischemia / infarction
- Hypokalemia / Hypoxia
- Pericardial inflammation
- Increased left atrial pressure
- Autonomic imbalance
Prognosis
- Excess mortality - in hospital, short term, mid term and long term
- Independent of other clinical factors
- Increased risk of recurrent AF, ischemic stroke
Jabre P et al. Mortality associated with atrial fibrillation in patients with myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2011 Apr 19;123(15):1587-93
Management
- Rate control
- Beta blockers
- Amiodarone
- Digoxin
- Rhythm control
- DCCV
- Amiodarone
- Anticoagulation depending on CHADS score
- Triple therapy for short period
- Clopidogrel + OAC
AF with need for DAPT
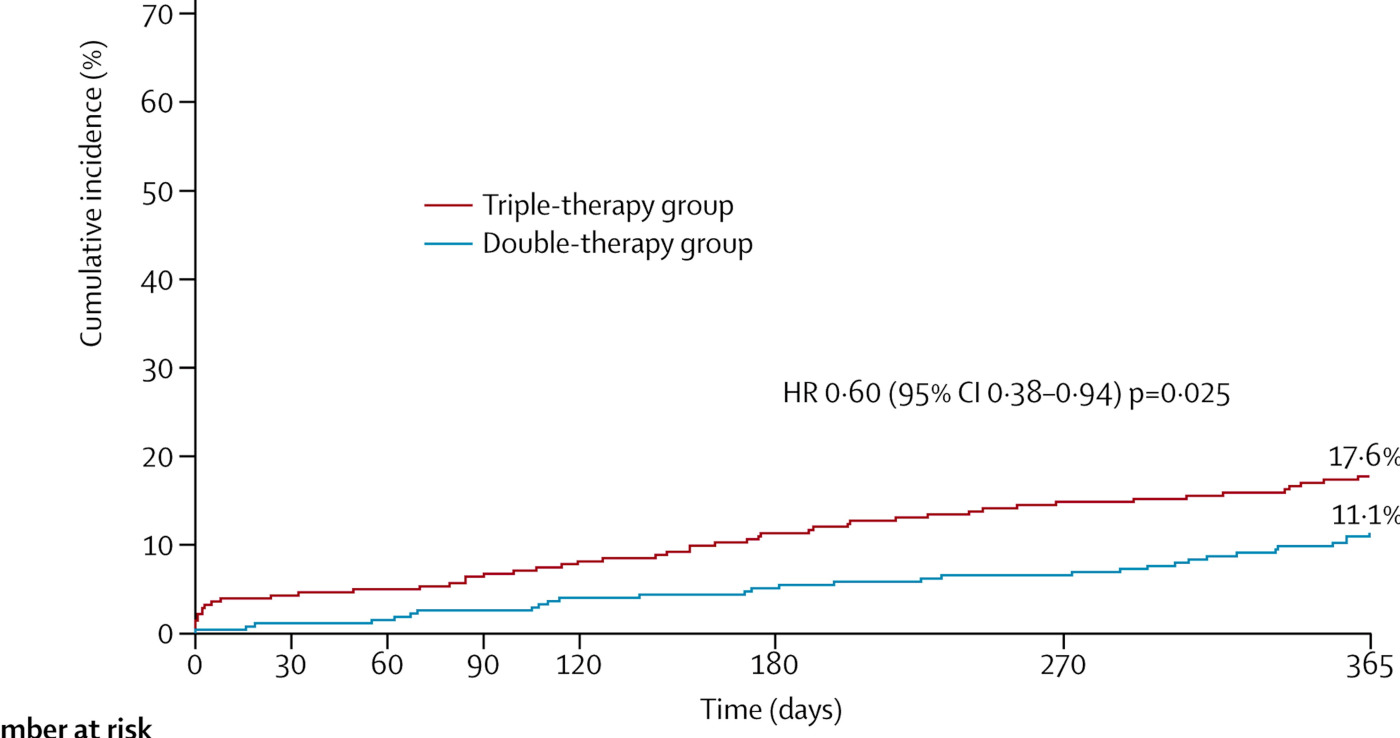
Dewilde WJ … WOEST study investigators. Use of clopidogrel with or without aspirin in patients taking oral aanticoagulant therapy and undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: an open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 2013 Mar 30;381(9872):1107-15
Sustained Ventricular arrhythmias
Incidence
- Historically, decrease in incidence
- 6% today
Management - VT
- Reperfusion if ischemia
- Beta blockers
- K and Mg correction
- Statins ? (1)
He XZ et al. The effect of early and intensive statin therapy on ventricular premature beat or non-sustained ventricular tachycardia in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Cardiol J. 2010;17(4):381-5
Management - VT
- Cardioversion
- AAD last resort
- Class I drugs may be harmful (1)
- Lidocaine does not affect mortality, effective in ischemia (2)
- Amiodarone
- Catheter ablation - purkinje ectopy
- The Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST) Investigators Preliminary report: effect of encainide and flecainide on mortality in a randomized trial of arrhythmia suppression after myocardial infarction , N Engl J Med, 1989, vol. 321 (pg. 406-12)
- Wyman et al. Prevention of primary ventricular fibrillation in acute myocardial infarction with prophylactic lidocaine , Am J Cardiol, 2004, vol. 94 (pg. 545-51)
Amiodarone
- Safest with heart disease
- More mortality compared to lidocaine ? (1)
- No long term benefit (EMIAT / CAMIAT)
Piccini JP et al. Antiarrhythmic drug therapy for sustained ventricular arrhythmias complicating acute myocardial infarction. Crit Care Med. 2011 Jan;39(1):78-83
Electrical storm
- 3 or more episodes of VT / VF in 24 h
- PVT rather than MMVT - acute ischemia
Management - Storm
- Cardioversion / defibrillation
- Overdrive pacing
- Complete revascularization
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Beta blockade - drugs / neuraxial modulation
- Sedation
- Amiodarone / Lignocaine
- Ablation
- LVAD
Long term prognosis
- Sustained VA > 48 h - higher risk of sudden death long term
- Indication for ICD implantation
Sustained ventricular arrhythmias < 48 h
Early ventricular arrhythmias (VT / VF < 48 hours)
- AIVR benign
- Primary VF - ICD implantation not indicated
- Primary VF - 3 fold higher risk of mortality at 90 days (1)
Mehta et al, APEX AMI Investigators. Incidence of and outcomes associated with ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. JAMA. 2009 May 6;301(17):1779-89
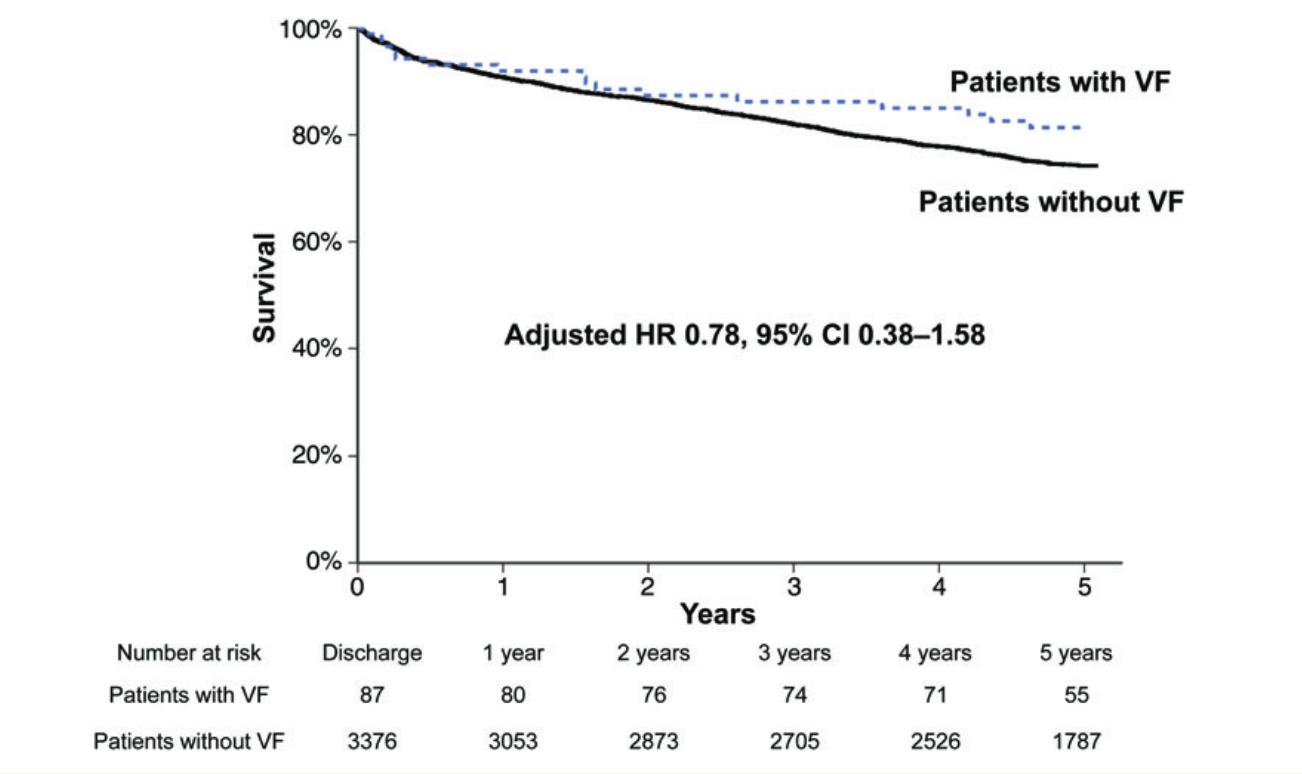
Fast MI registry - 5 year analysis of outcomes
Higher early mortality
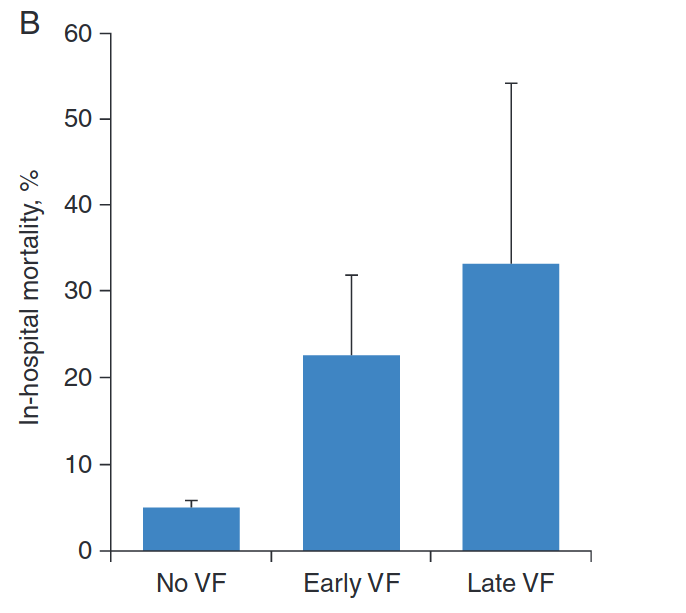
Long term outcome not affected
Appropriate use criteria
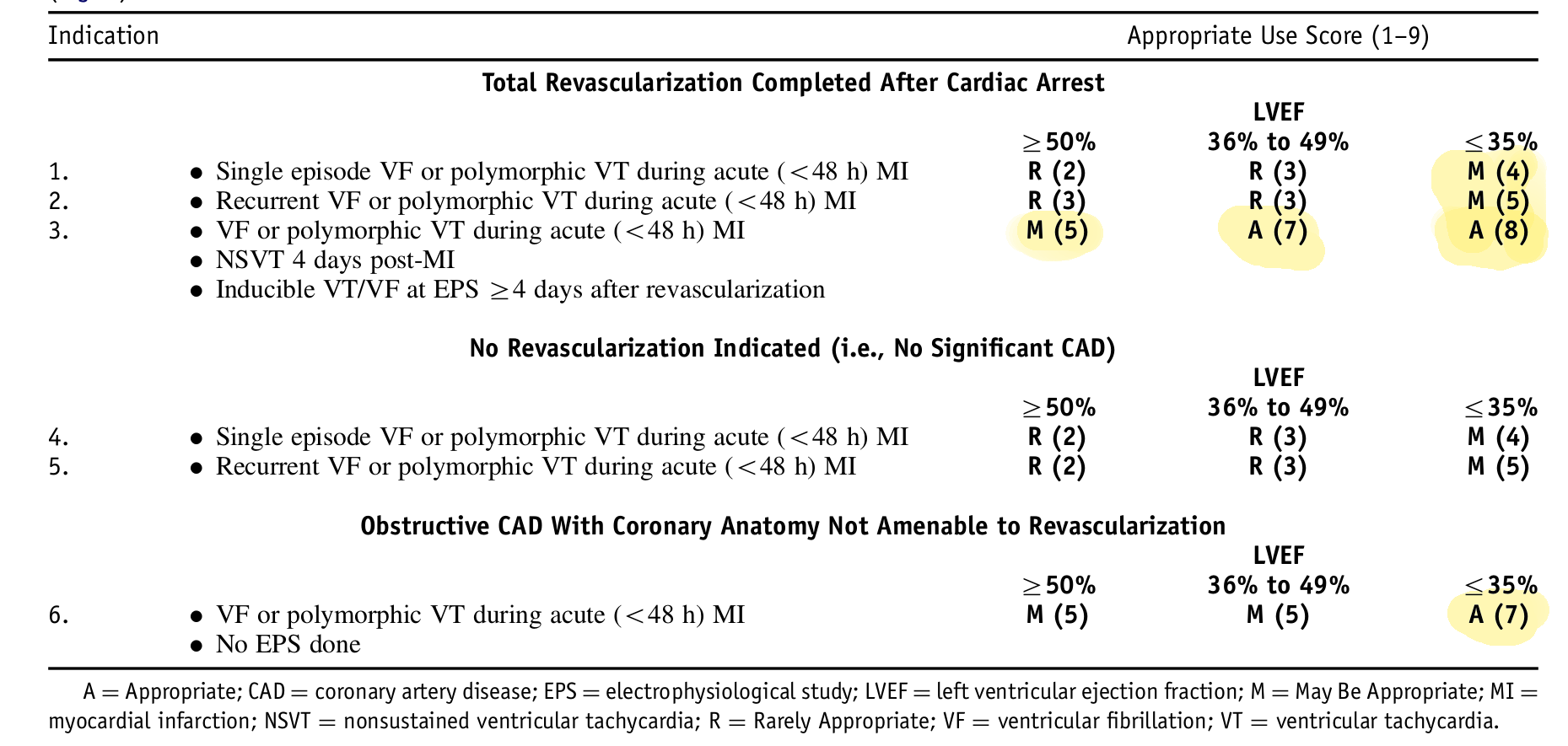
ACCF / AHA / HRS Appropriate use criteria 2013
Summary
- Arrhythmias often associated with poor short and long term outcomes in AMI
- Need prompt and aggressive treatment
- Reperfusion is key
- Beta blockers for tachyarrhythmias