Arrhythmias in the adult with repaired congenital heart disease

Raja Selvaraj, JIPMER
Introduction
Adults with repaired CHD
- CHD - 1% of population
- Many undergo correction
- With improved care, many of these patients grow up to be adults
- Arrhythmias are an important morbidity
- Complex interplay between arrhythmias and hemodynamics
Mechanisms
- Underlying heart disease
- Chamber enlargement / pressure overload
- Fibrosis - sutures / patches
- Trauma to specialised conduction system
Topics
- Bradyarrhythmias
- Tachyarrhythmias
- Clinical evaluation
- Evaluation - Imaging / ECG
- Pacemaker for brady-arrhythmias
- Medical management of tachyarrhythmias
- Ablation for tachyarrhythmias
- Common arrhythmias (AVNRT, AP)
- Risk stratification
Cover
- Bradyarrhythmias
- Tachyarrhythmias
- Clinical evaluation
- Evaluation - Imaging / ECG
- Pacemaker for brady-arrhythmias
- Medical management of tachyarrhythmias
- Ablation for tachyarrhythmias
- Common arrhythmias (AVNRT, AP)
- Risk stratification
Management
Hemodynamics correction
- Residual shunts
- Tricuspid regurgitation
- Pulmonary regurgitation
- Outflow tract obstruction
Drugs
- Class Ic (Flecainide, Propafenone)
- Class III (Amio, Dofetilide, Sotalol)
- Proarrhythmia / systemic problems
Ablation
- Relatively less efficacious
- But still generally safe, can be very beneficial
Atrial Tachyarrhythmias
- Macroreentrant Atrial tachycardia
- Typical flutter most common
- Atriotomy related
- septal rare
- may be combination
- Focal atrial tachycardia
Flutter Circuits
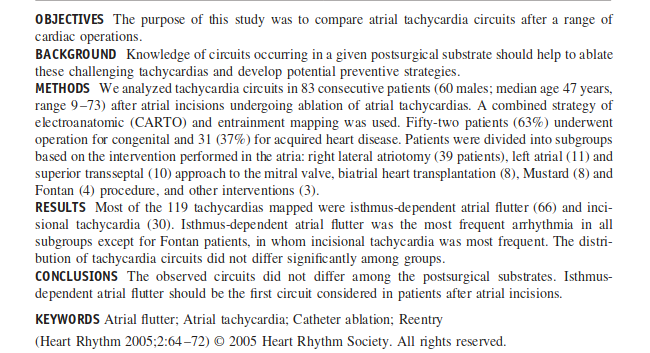
Peter Lukac et al. Ablation of atrial tachycardia after surgery for congenital and acquired heart disease using an electroanatomic mapping system: Which circuits to expect in which substrate?. Heart Rhythm 2005;2(1):64-72
Ventricular arrhythmias
- Monomorphic Ventricular tachycardia
- Macroreentry around ventriculotomy / patches
- Polymorphic Ventricular tachycardia
- LV outflow tract obstruction
- d TGA with atrial switch (systemic RV)
- TOF, poor RV function
Macroreentrant VT in repaired TOF
Zeppenfeld K, Schalij MJ, Bartelings MM, Tedrow UB, Koplan BA, Soejima K, Stevenson WG. Catheter ablation of ventricular tachycardia after repair of congenital heart disease: electroanatomic identification of the critical right ventricular isthmus. Circulation. 2007 Nov 13;116(20):2241-52
Substrate
- ASD
- DORV / TOF
- Ebsteins anomaly
- Mustard / Senning
- Fontan
- almost 50% of classic fontan have arrhythmias
- modern approaches (lateral tunnel / extracardiac) - less arrhythmias, more difficult access
Ablation
- Why
- When
- Who should do
- How
Ablation - Why ?
- Arrhythmias often poorly tolerated
- Rapid VR during flutter because of young age / slower flutters
- Poor response to drugs
- Drug therapy not preferred
- Long term side effects
- Proarrhythmia
- Negative inotropy
Ablation - When
ESC Scientific Document Group; Arrhythmias in congenital heart disease: a position paper of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Working Group on Grown-up Congenital heart disease, endorsed by HRS, PACES, APHRS, and SOLAECE, EP Europace, Mar 2018, https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eux380
Ablation - Who
- Pediatric Electrophysiologist
- ACHD Electrophysiologist
- Electrophysiologist with support of pediatric Cardiologist
Ablation - How
- Understand anatomy
- CHD
- Repair
- Identify conduction barriers
- Identify circuits
- Linear ablation (barriers)
- Confirming block
Procedure planning
- Surgery notes
- Imaging
- Residual shunts
Access issues
- Difficult transseptal
- CHD surgery
- ASD device
- Baffle puncture in Mustard / Senning for CTI line
- Magnetic navigation may allow retrograde route
Access - Venous access
- Iliofemoral occlusions
- Pediatric percutaneous procedures
- IVC interruption
- LSVC
Azygous continuation of IVC
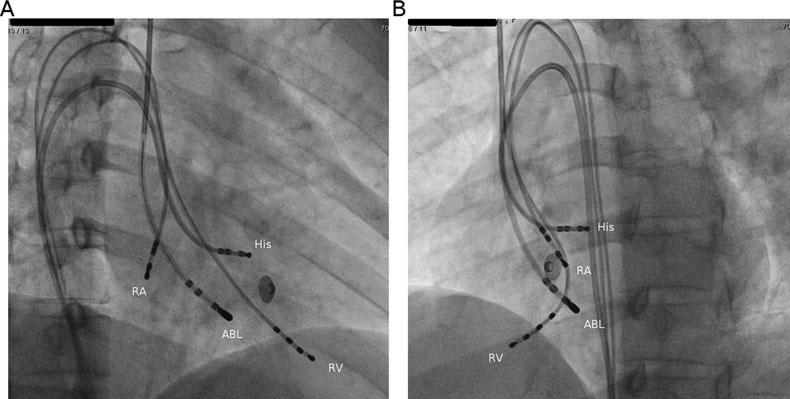
RB Vidhyakar .. Raja Selvaraj. Ablation of atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia using the superior approach in a patient with IVC interruption. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology 2012;23(12):1393-4
Azygous continuation of IVC
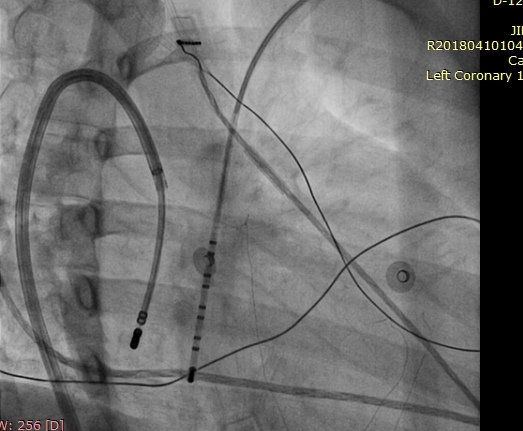
Mapping - Technology
- Use of 3D mapping
- Image integration
- Use of array
- Multielectrode mapping
- Use of magnetic navigation (1)
Ueda A, Suman-Horduna I, Mantziari L, Gujic M, Marchese P, Ho SY, Babu-Narayan SV, Ernst S. Contemporary outcomes of supraventricular tachycardia ablation in congenital heart disease: a single-center experience in 116 patients. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013 Jun;6(3):606-13. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.113.000415.
Catheter
- Large tips
- Cooled tips
- Equally effective in producing transmural atrial lesions (1)
McGreevy KS, Hummel JP, Jiangang Z, et al. “Comparison of a saline irrigated cooled-tip catheter to large electrode catheters with single and multiple temperature sensors for creation of large radiofrequency lesions.” J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2005; 14(3): 139-45
Substrate
- Conduction blocks - Atriotomy
- Line of low voltage
- Line of double potentials
- Scarring from pressure overload
- Low voltage regions
- Late potentials
Typical flutter
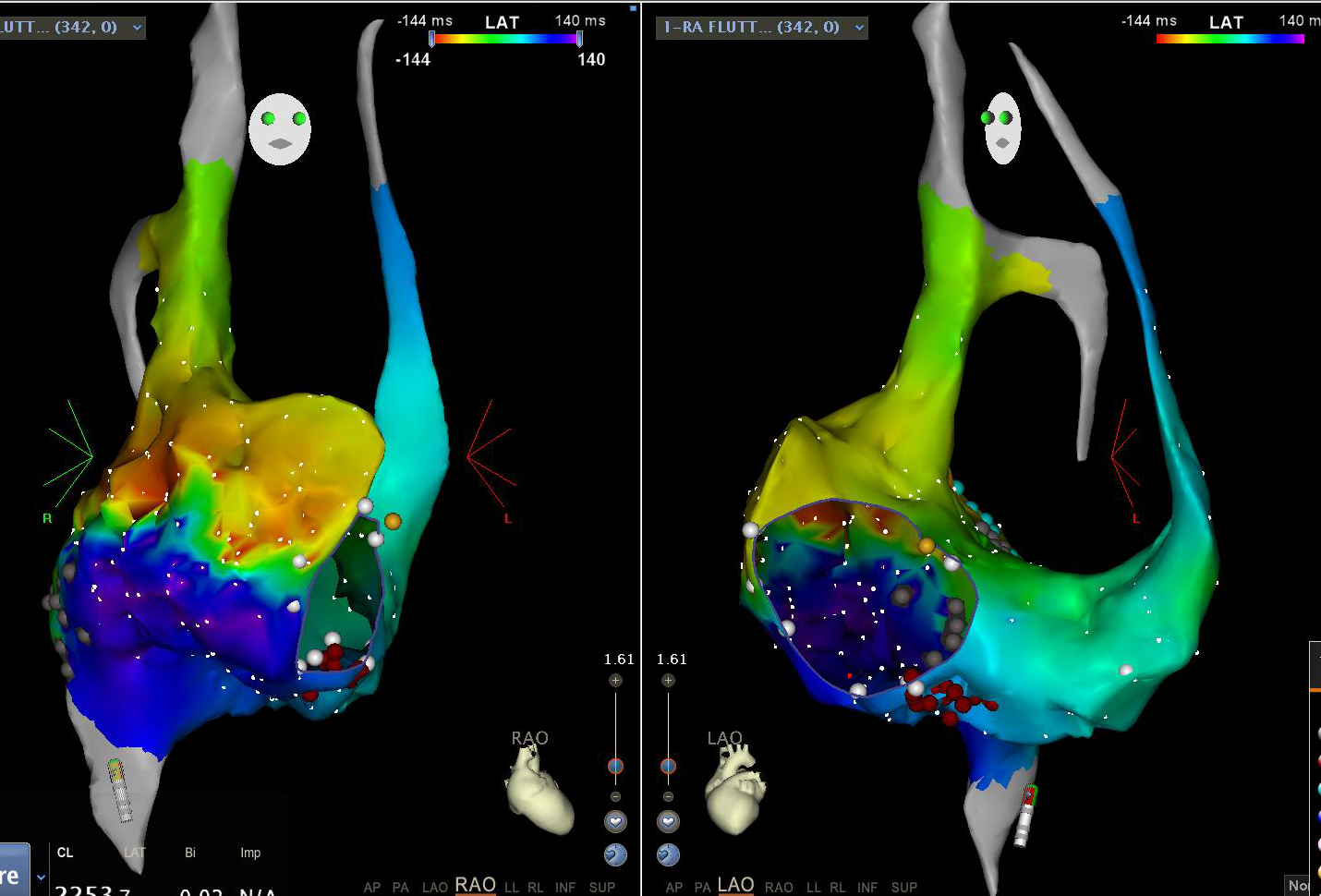
Substrate - Atriotomy
Substrate - Atriotomy
Substrate - Fibrosis / slow conduction
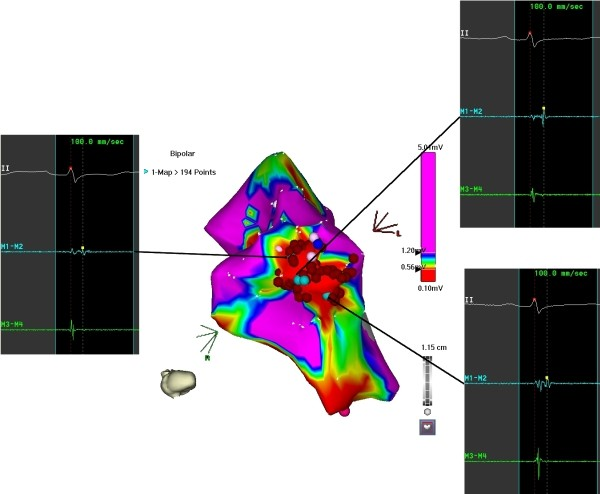
Raja Selvaraj et al. Ventricular tachycardia in repaired double chambered right ventricle – Identification of the substrate and successful ablation. Indian Pacing and Electrophysiology Journal 2012; 12(1):27-31
Substrate - Isthmus for reentrant VT
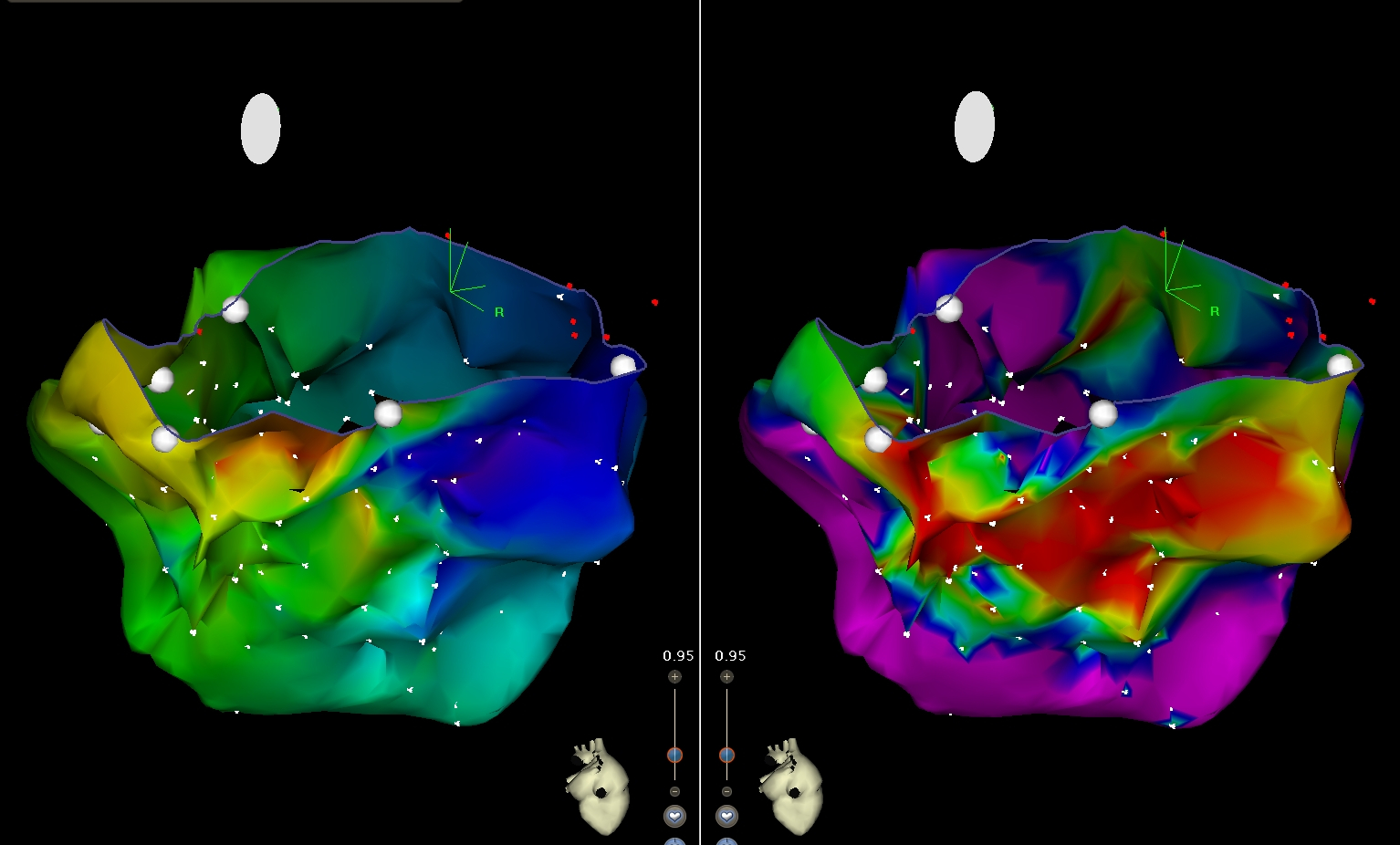
Senthil Kumar.. Raja J Selvaraj. Peritricuspid reentrant ventricular tachycardia in Ebstein's anomaly. Europace 2014;16(11):1633
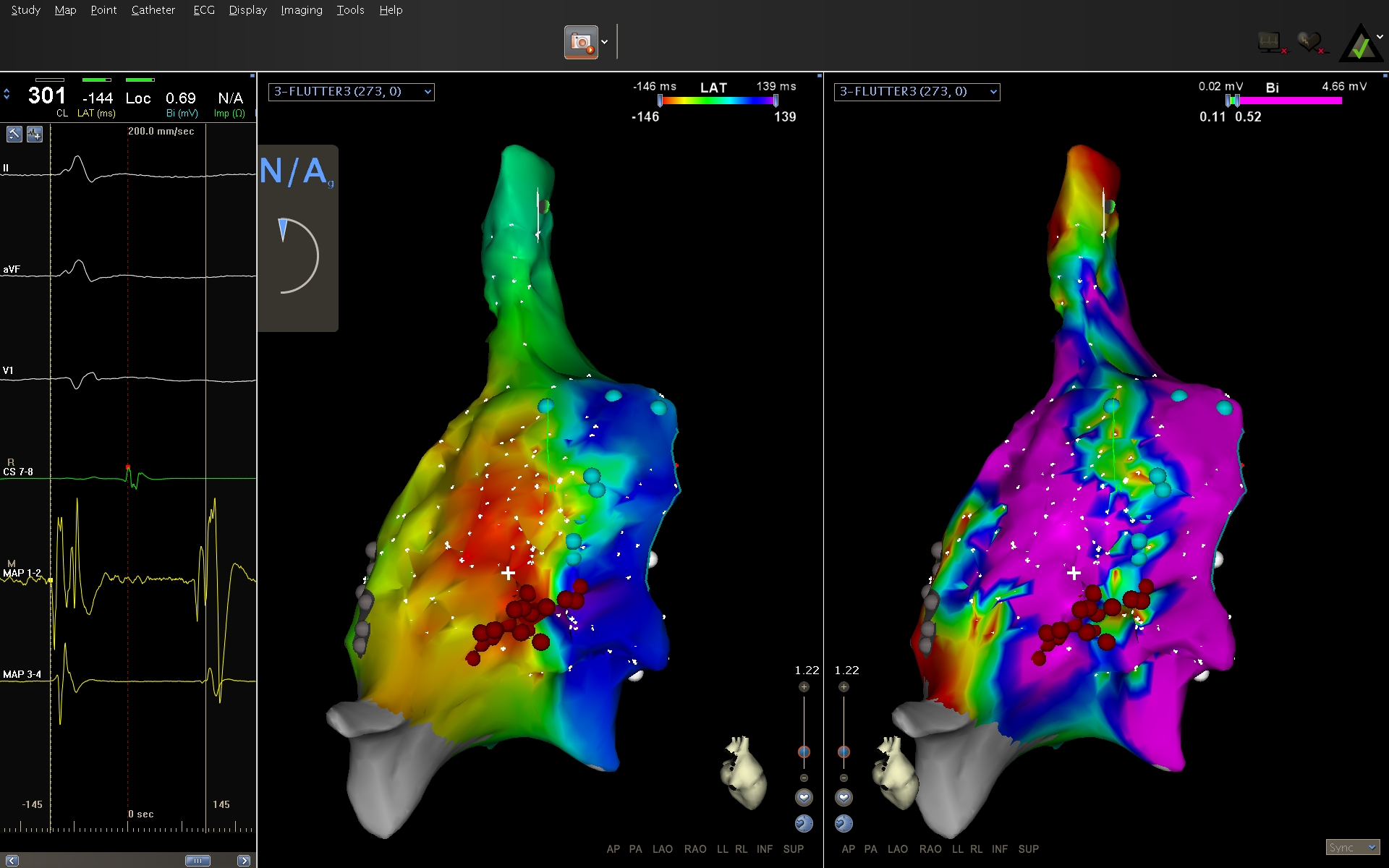
Activation mapping - Identify circuit
- Careful mapping with density
- Entrainment
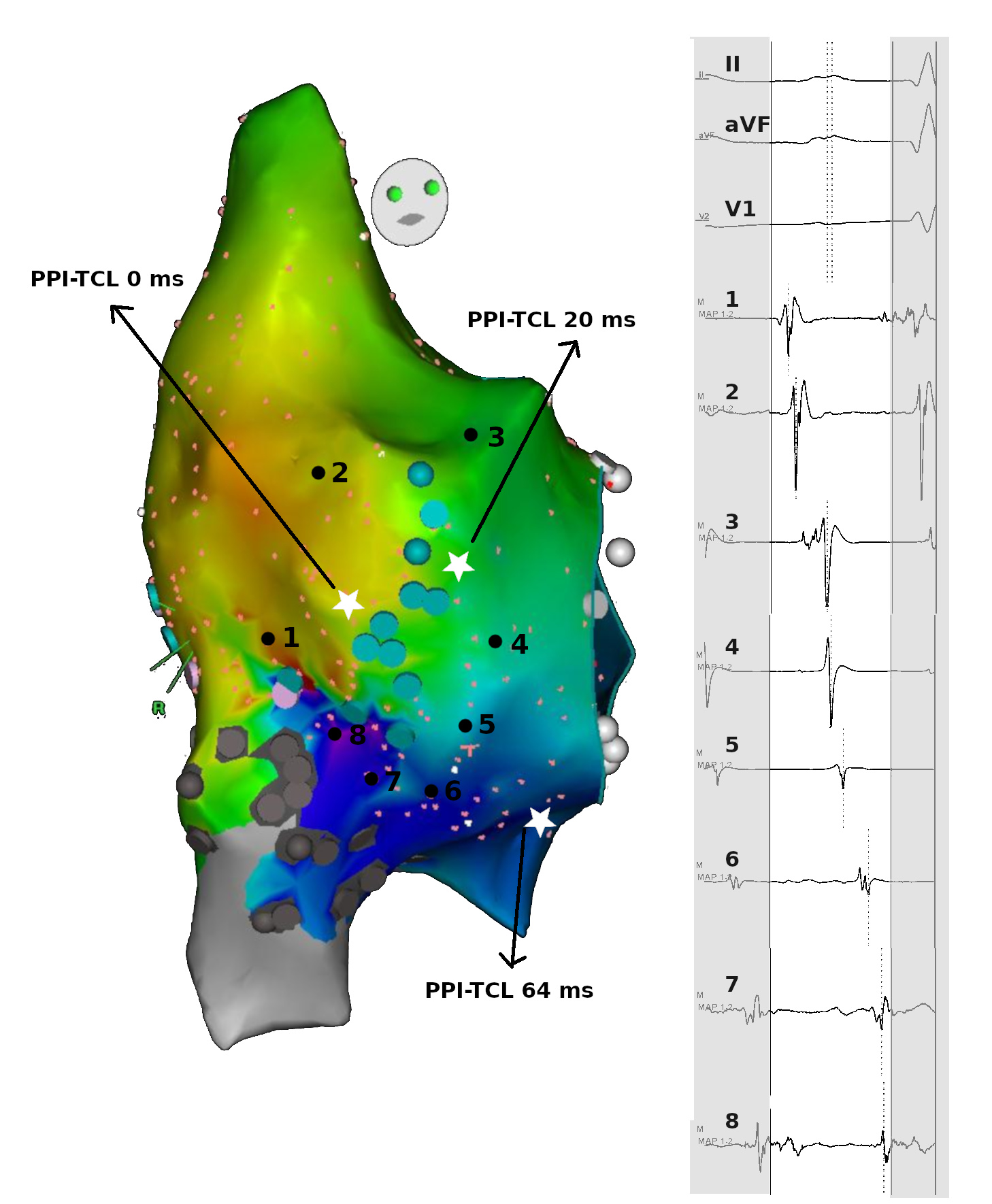
Activation and entrainment
Activation mapping - Basics
- Selecting a good reference electrogram - Stable and reliable
- Setting WOI
- Consistent activation time marking
Atrial activation reference
WOI - focal /reentry
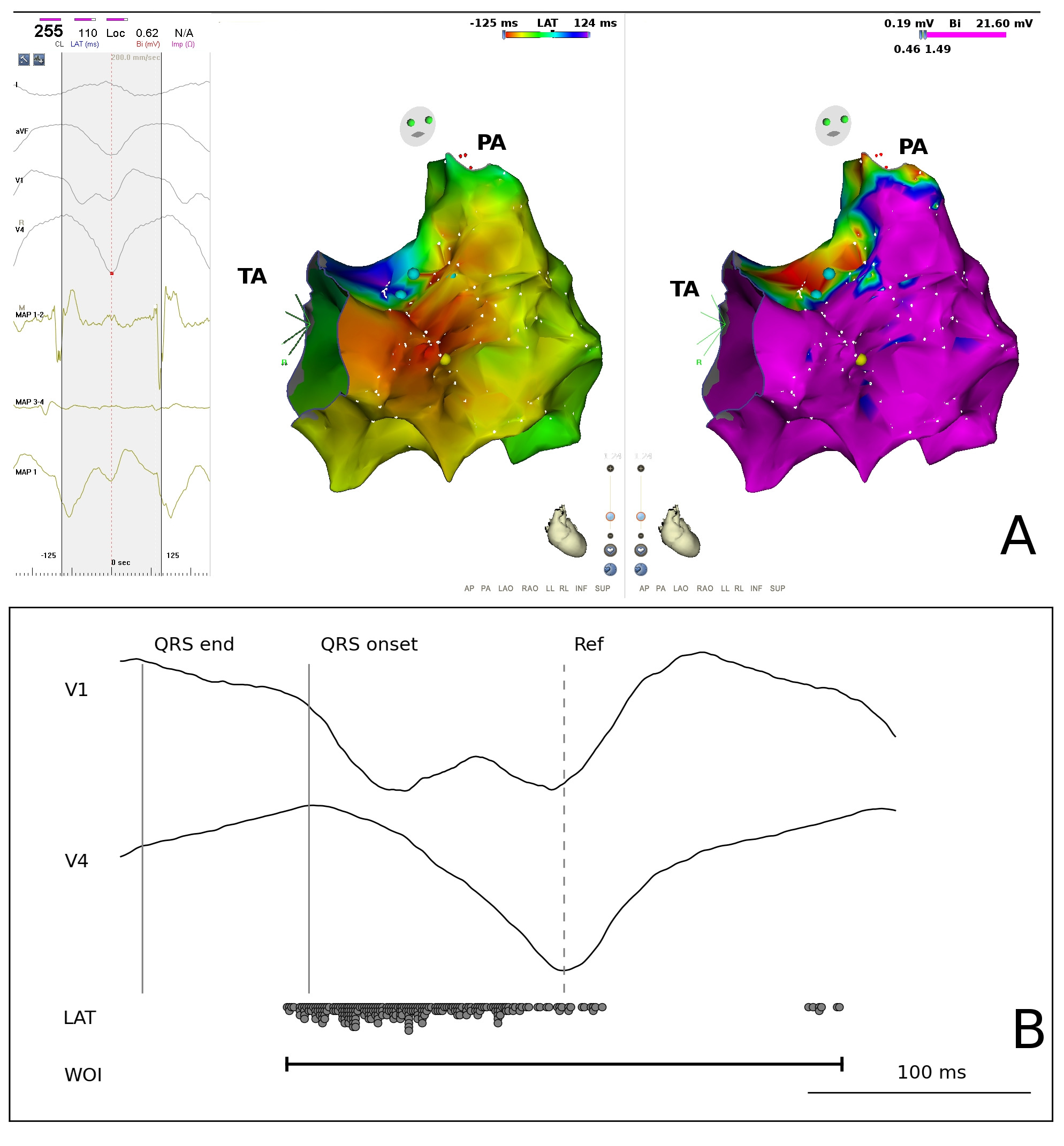
WOI - focal /reentry
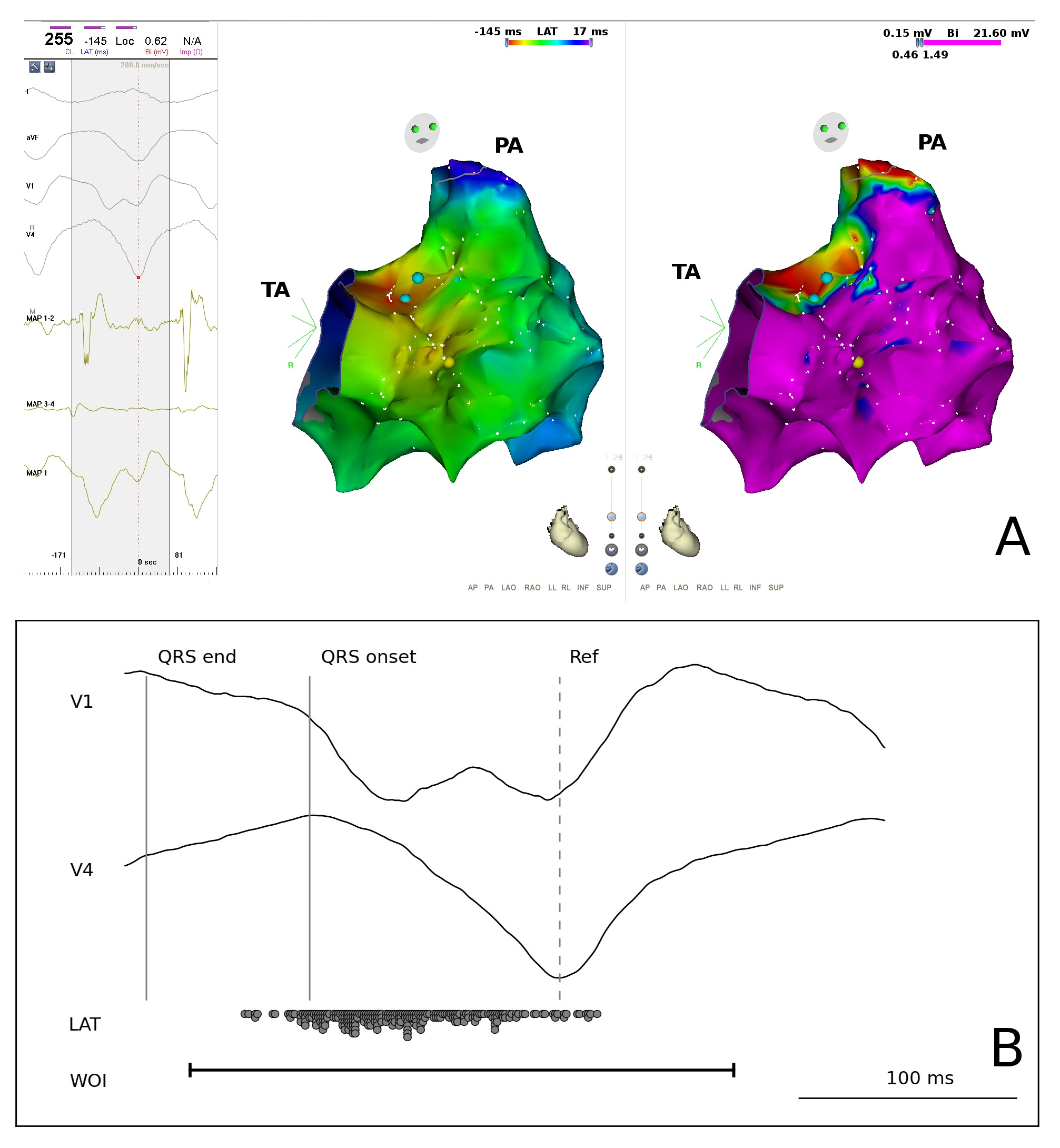
Raja J. Selvaraj et al. Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology. 2014;7:553-556
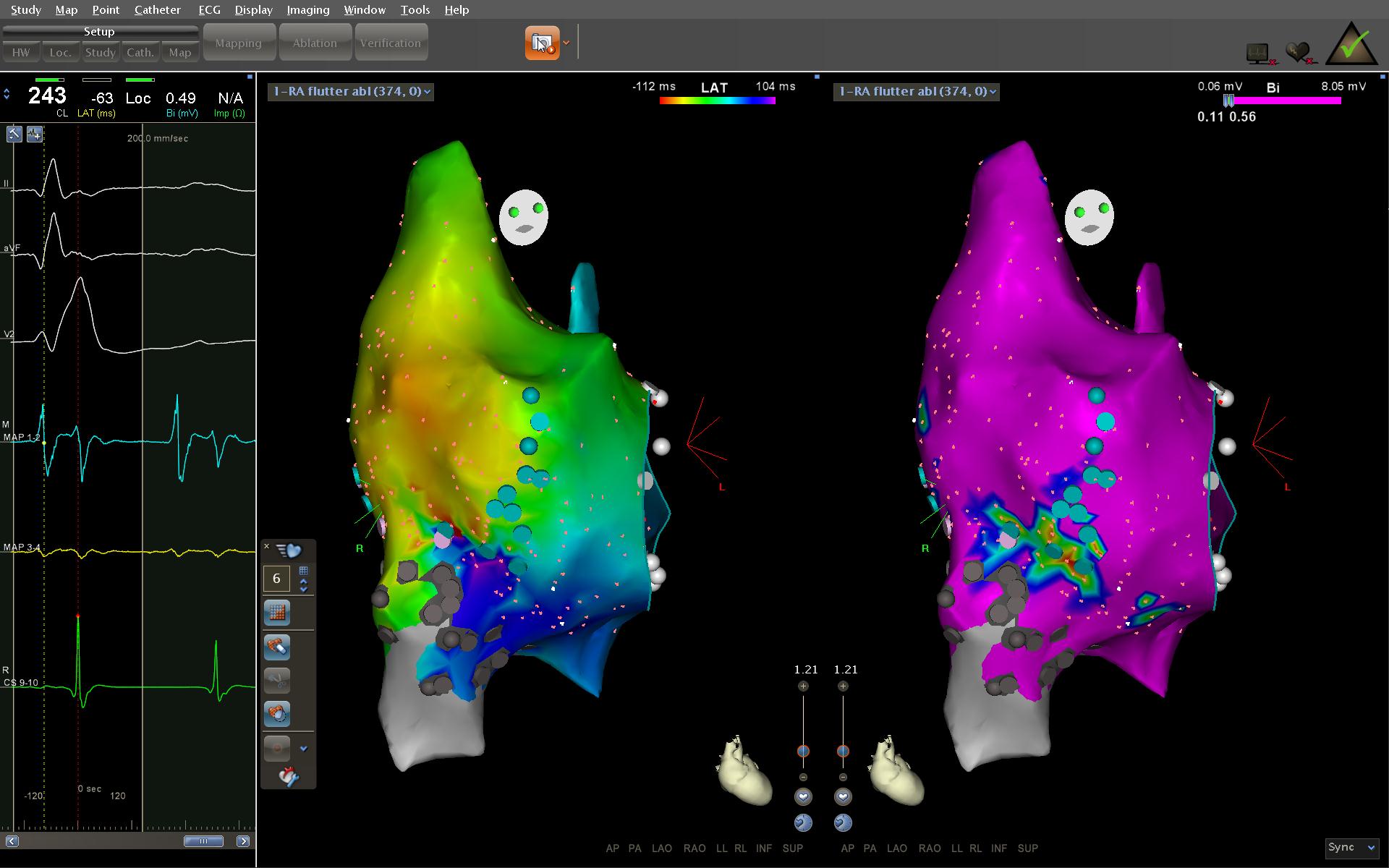
Ablation - Identify isthmus
- Narrow
- Slow conduction
- Easy to ablate
Isthmus
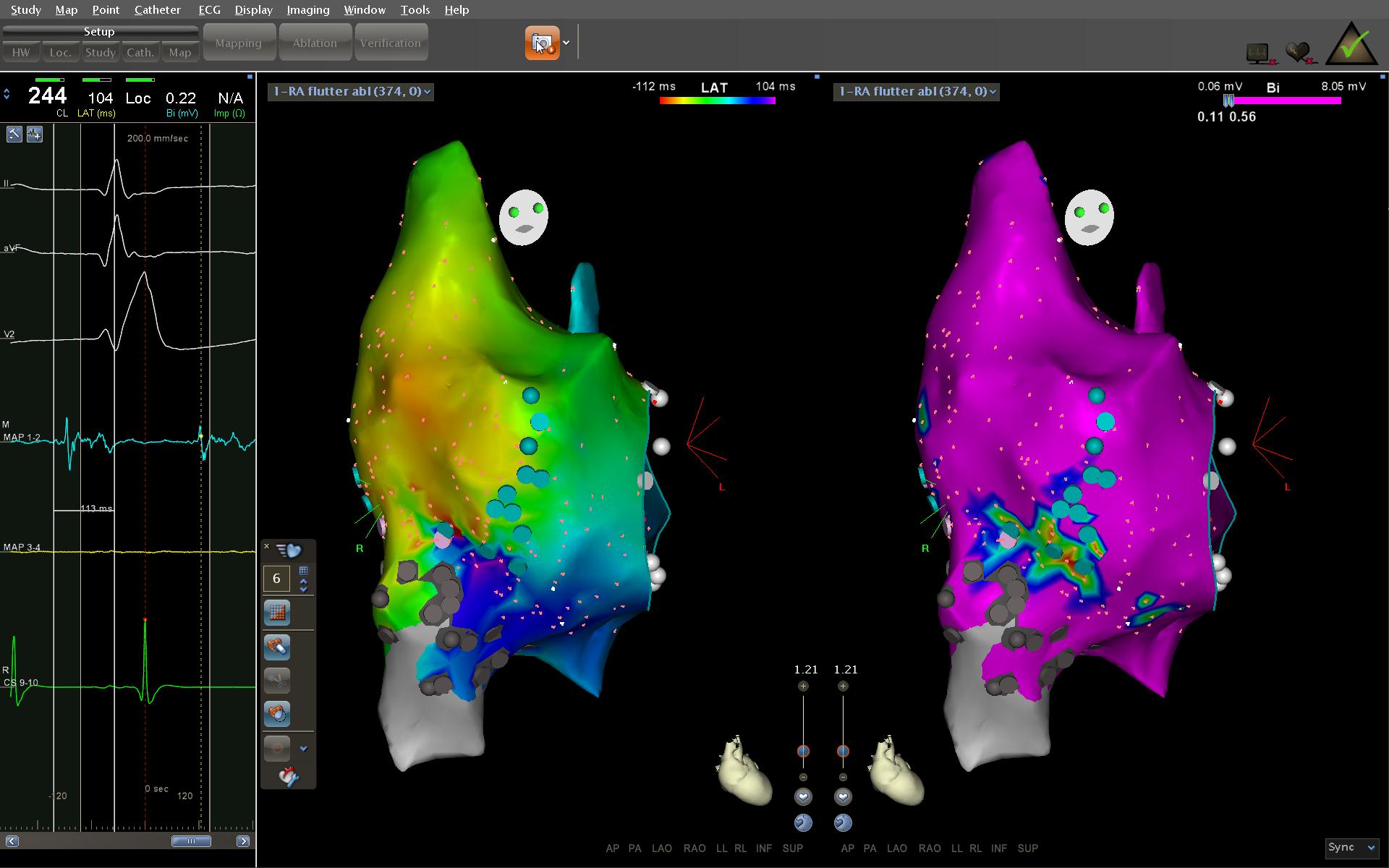
Ablation - Confirm block
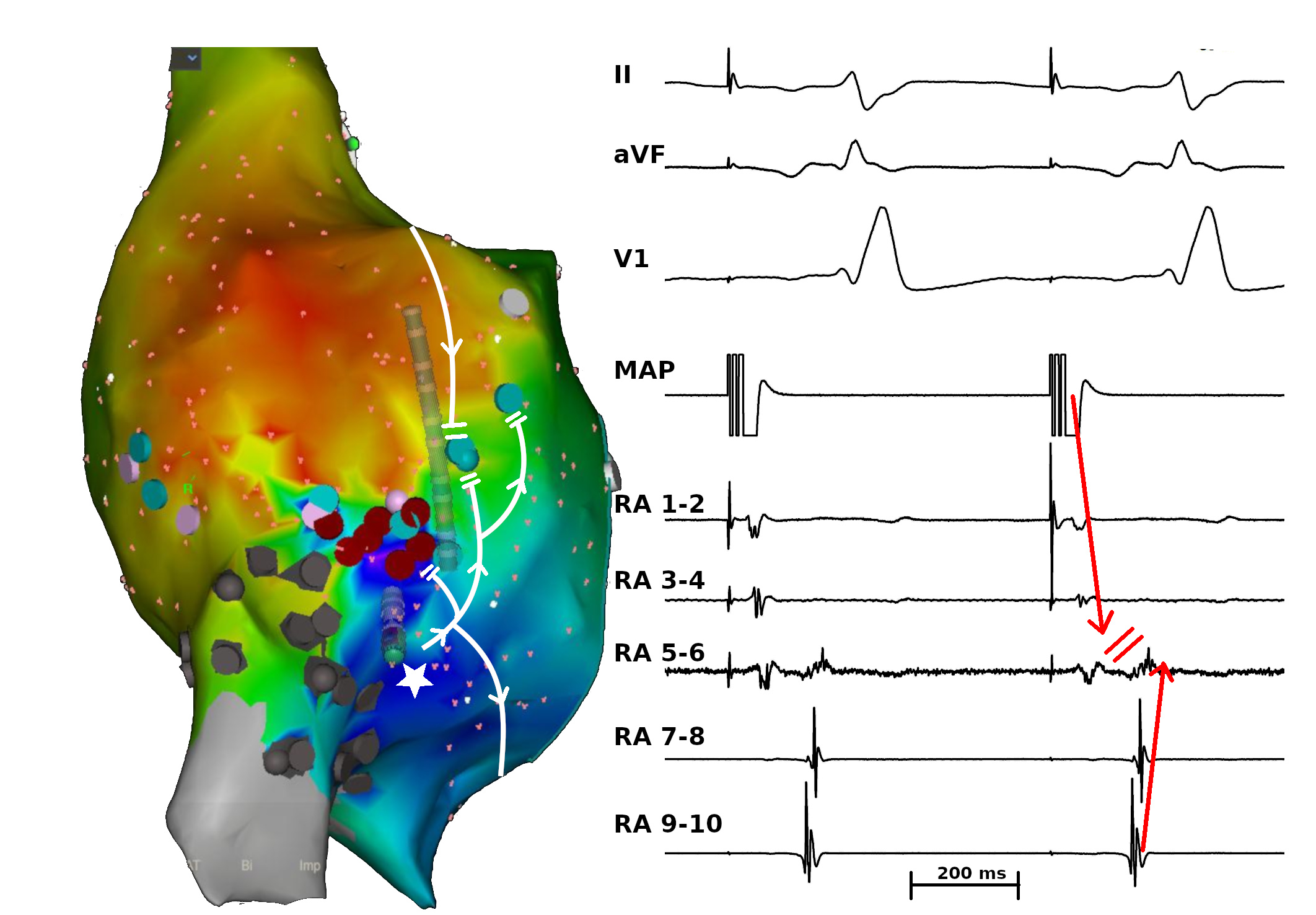
Sudden death in CHD
- 25 to 100 times risk of sudden death compared to age matched controls (1)
- AS, CoA, TOF
- Arrhythmia / Circulatory - Embolic, aneurysm / Heart failure
Silka MJ, Hardy BG, Menashe VD, Morris CD. A population-based prospective evaluation of risk of sudden cardiac death after operation for common congenital heart defects. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998 Jul;32(1):245-51. PubMed PMID: 9669277.
TOF - Ventricular arrhythmias and Sudden death
- Multicenter study - 793 patients
- Mean 20 yrs after repair
- Outcomes
- Sustained VT - 33
- Sudden death - 16
- Atrial arrhythmias - 29
- Same substrate for VT and sudden death
- Pulmonary regurgitation
- QRS widening
Gatzoulis MA, Balaji S, Webber SA, Siu SC, Hokanson JS, Poile C, Rosenthal M, Nakazawa M, Moller JH, Gillette PC, Webb GD, Redington AN. Risk factors for arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death late after repair of tetralogy of Fallot: a multicentre study. Lancet. 2000 Sep 16;356(9234):975-81. PubMed PMID: 11041398.
ICDs in ACHD
- Difficult anatomy
- Inappropriate shocks
- Need for multiple surgeries
- Poor quality of life
Czosek et al. Impact of Cardiac Devices on the Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients. Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology. 2012;5:1064-1072
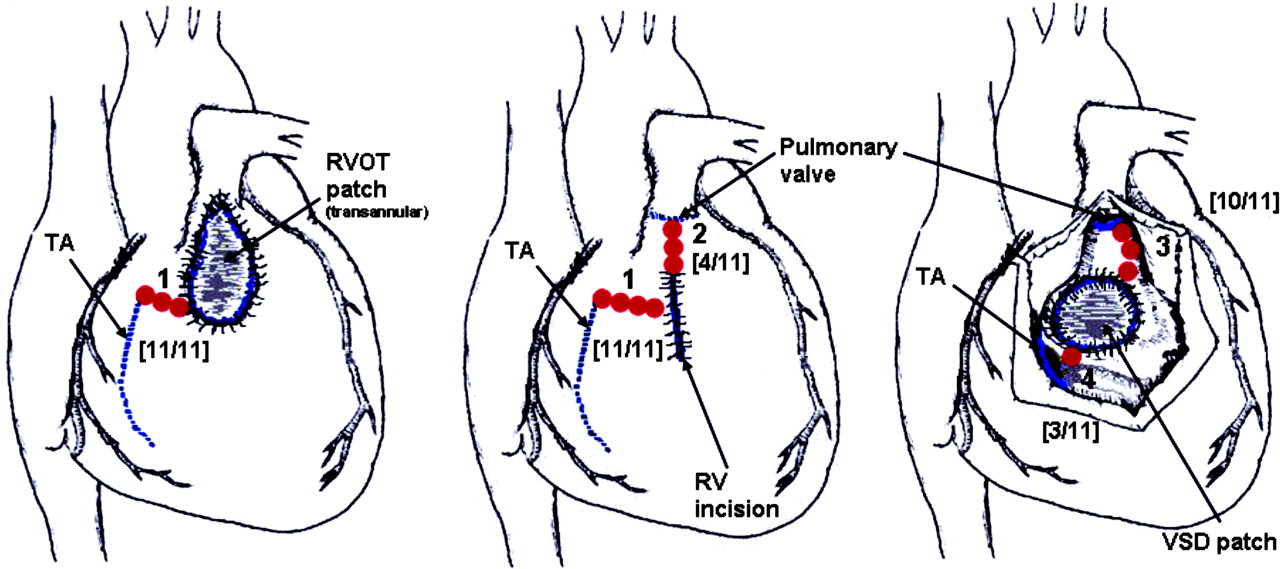
Recommendation
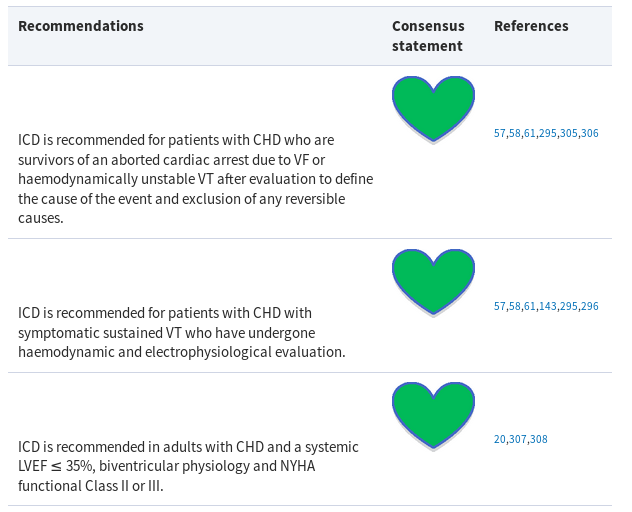
ESC Scientific Document Group; Arrhythmias in congenital heart disease: a position paper of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Working Group on Grown-up Congenital heart disease, endorsed by HRS, PACES, APHRS, and SOLAECE, EP Europace, Mar 2018, https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eux380