Entrainment, Basic principles of EP maneuvers

Raja Selvaraj
Professor of Cardiology, JIPMER
Entrainment
Basic principles
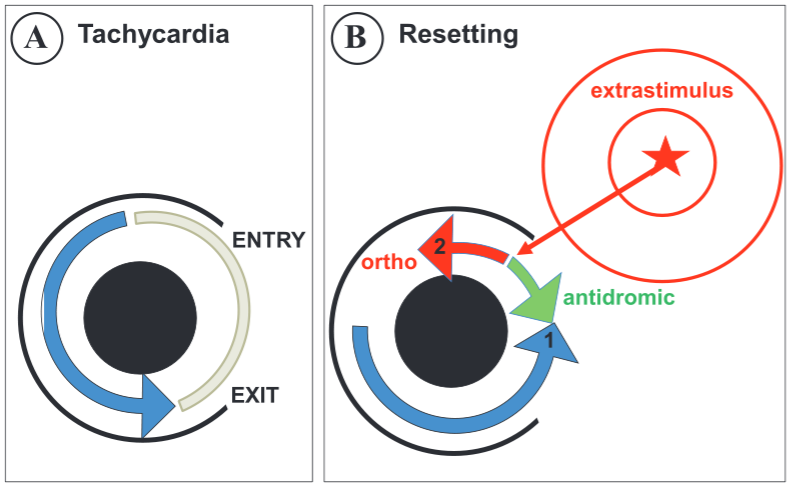
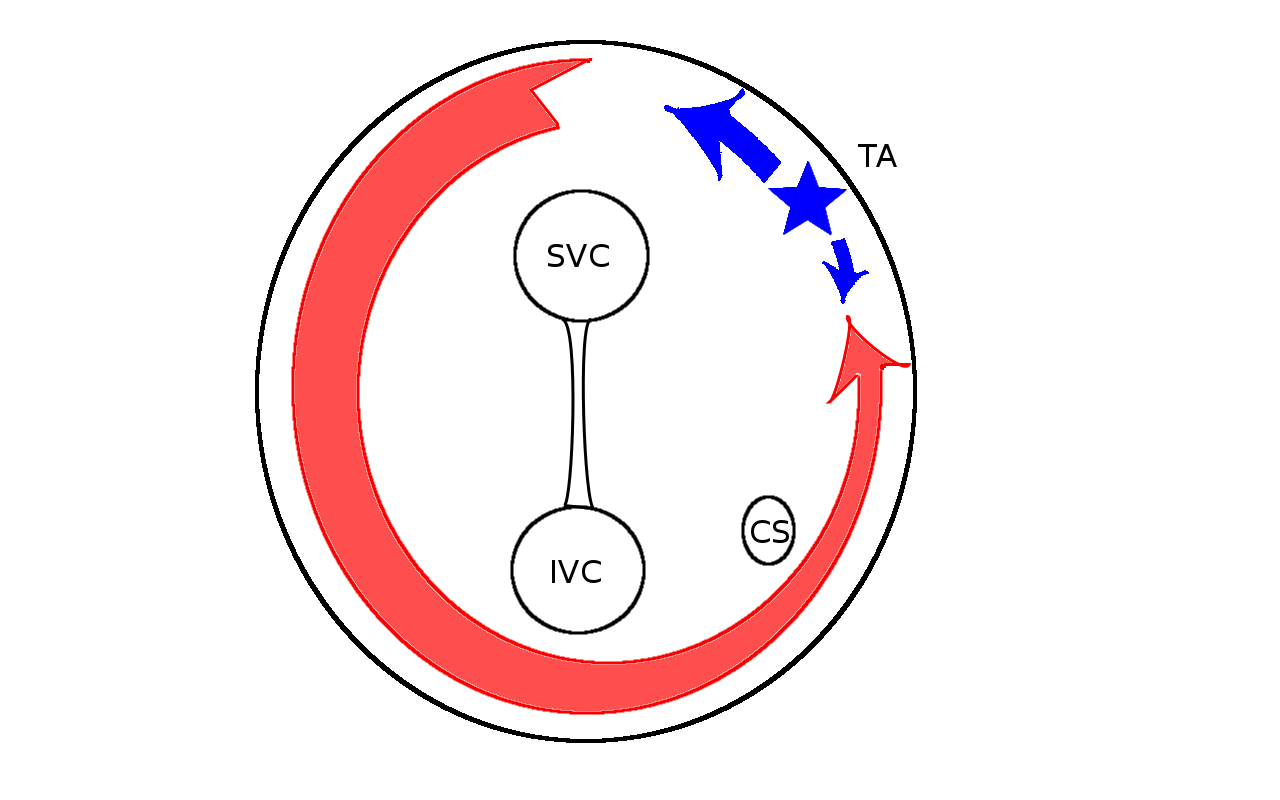
Prerequisites for entrainment
- Reentrant circuit
- Excitable gap
- No entrance block
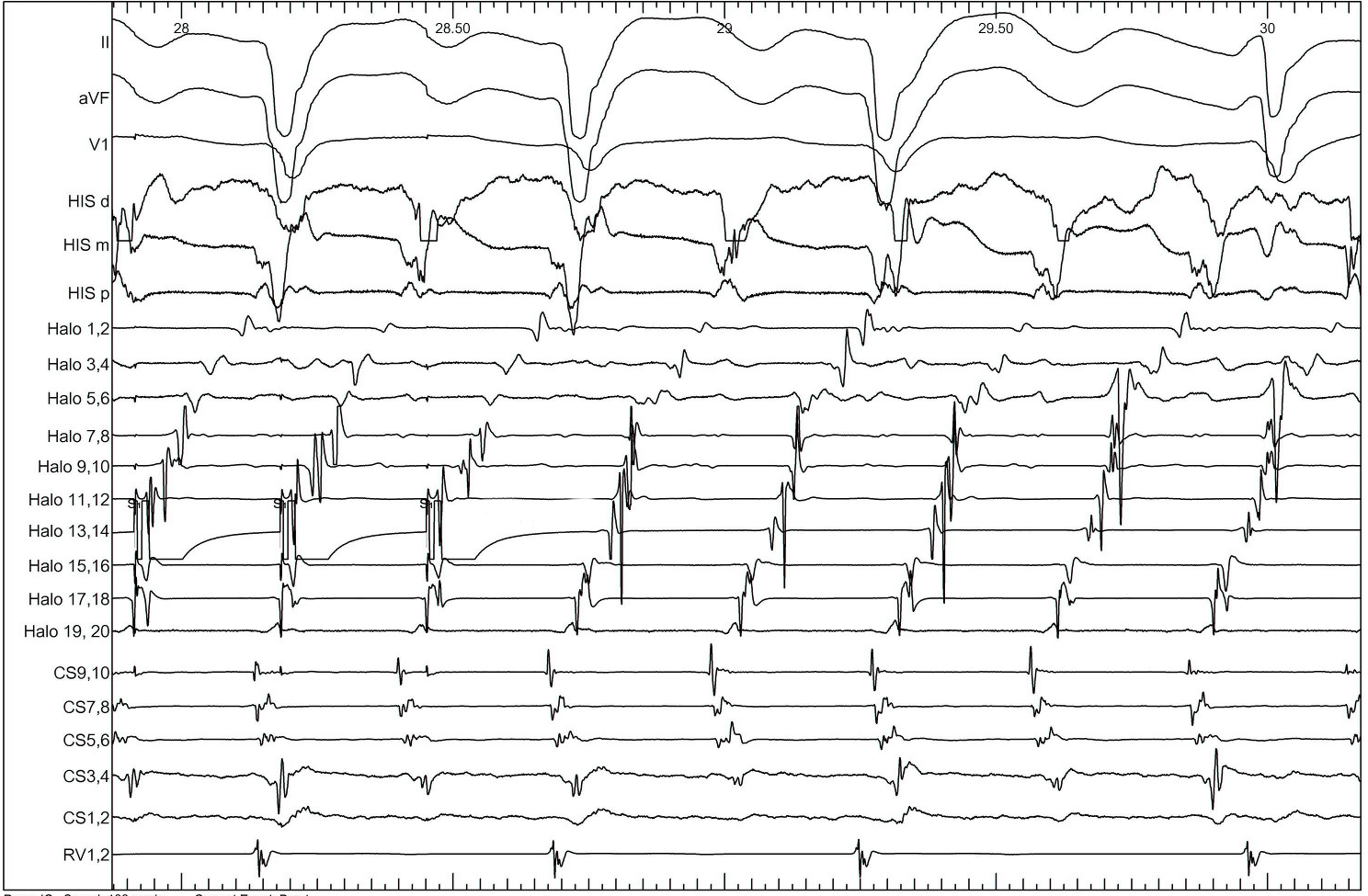
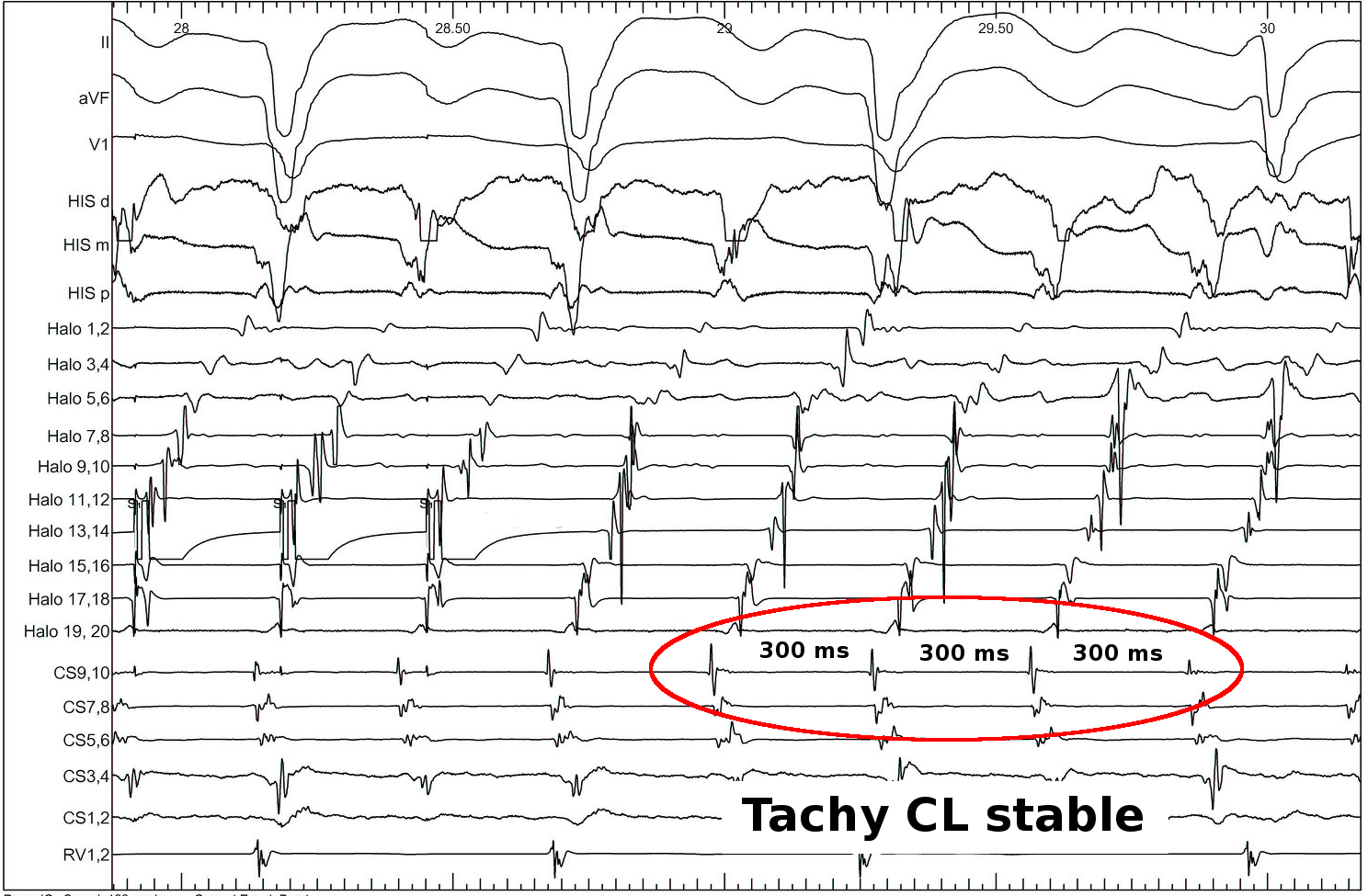
Identifying entrainment
- Constant fusion
- Progressive fusion
Constant fusion
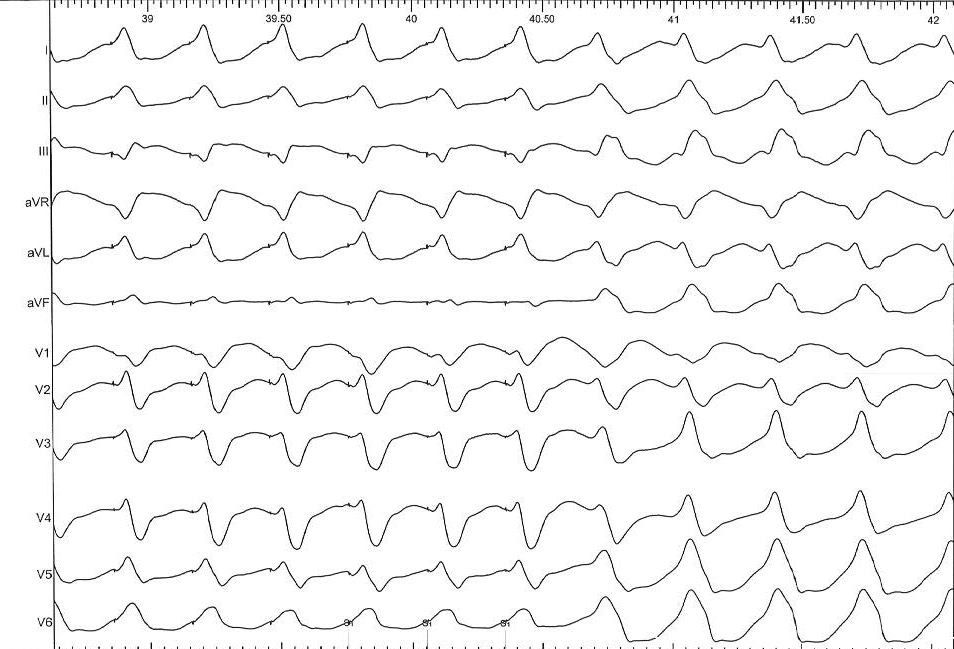
Progressive fusion
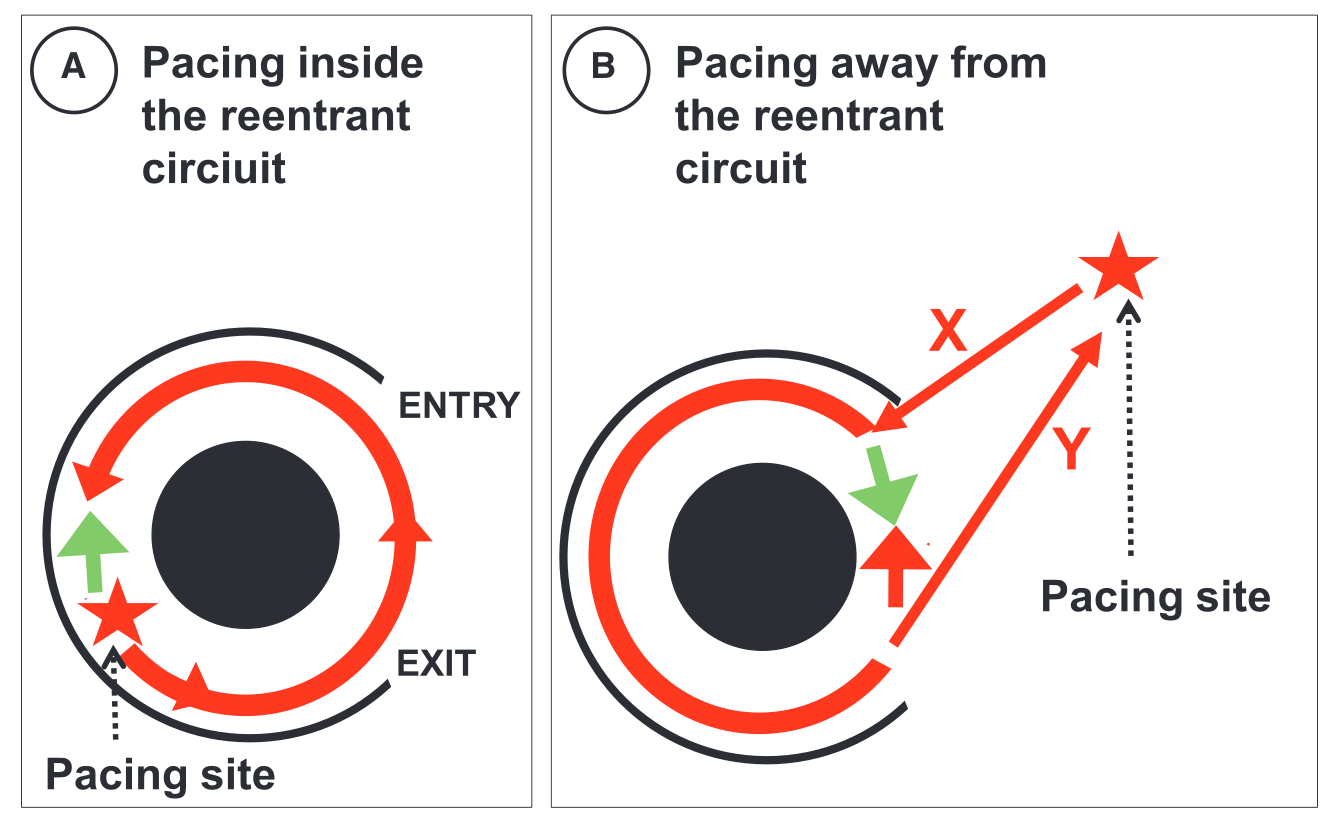
Locate site of pacing in relation to tachycardia circuit
- Deviation from morphology indicates extent of capture by antidromic wavefront
- Deviation from cycle length indicates distance from circuit
PPI
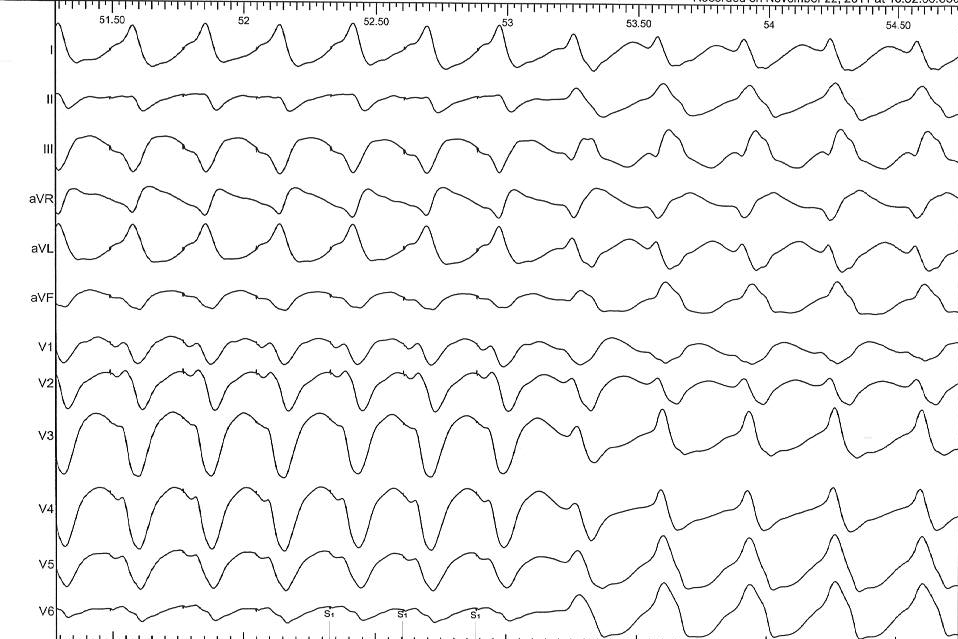
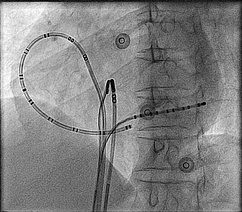
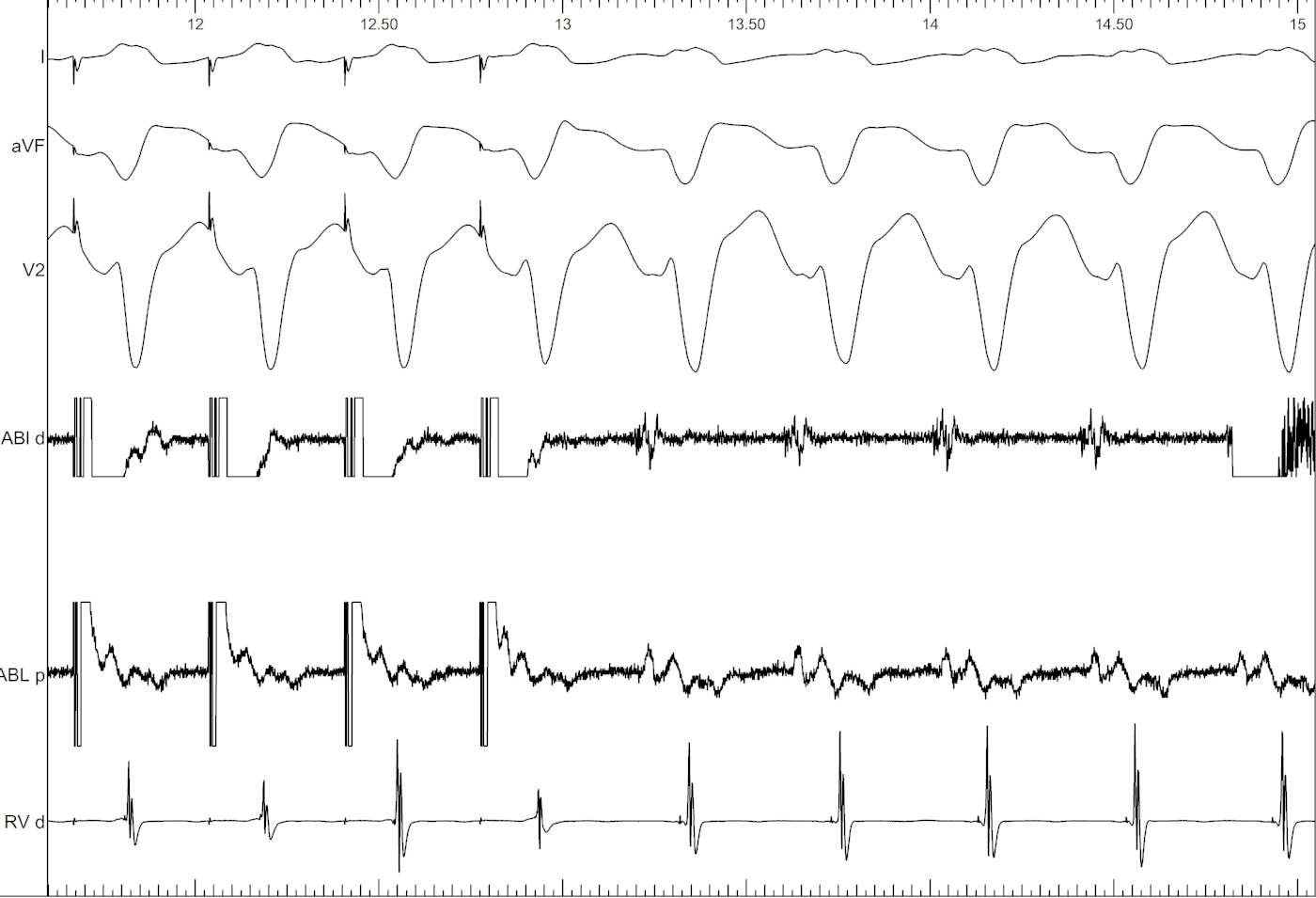
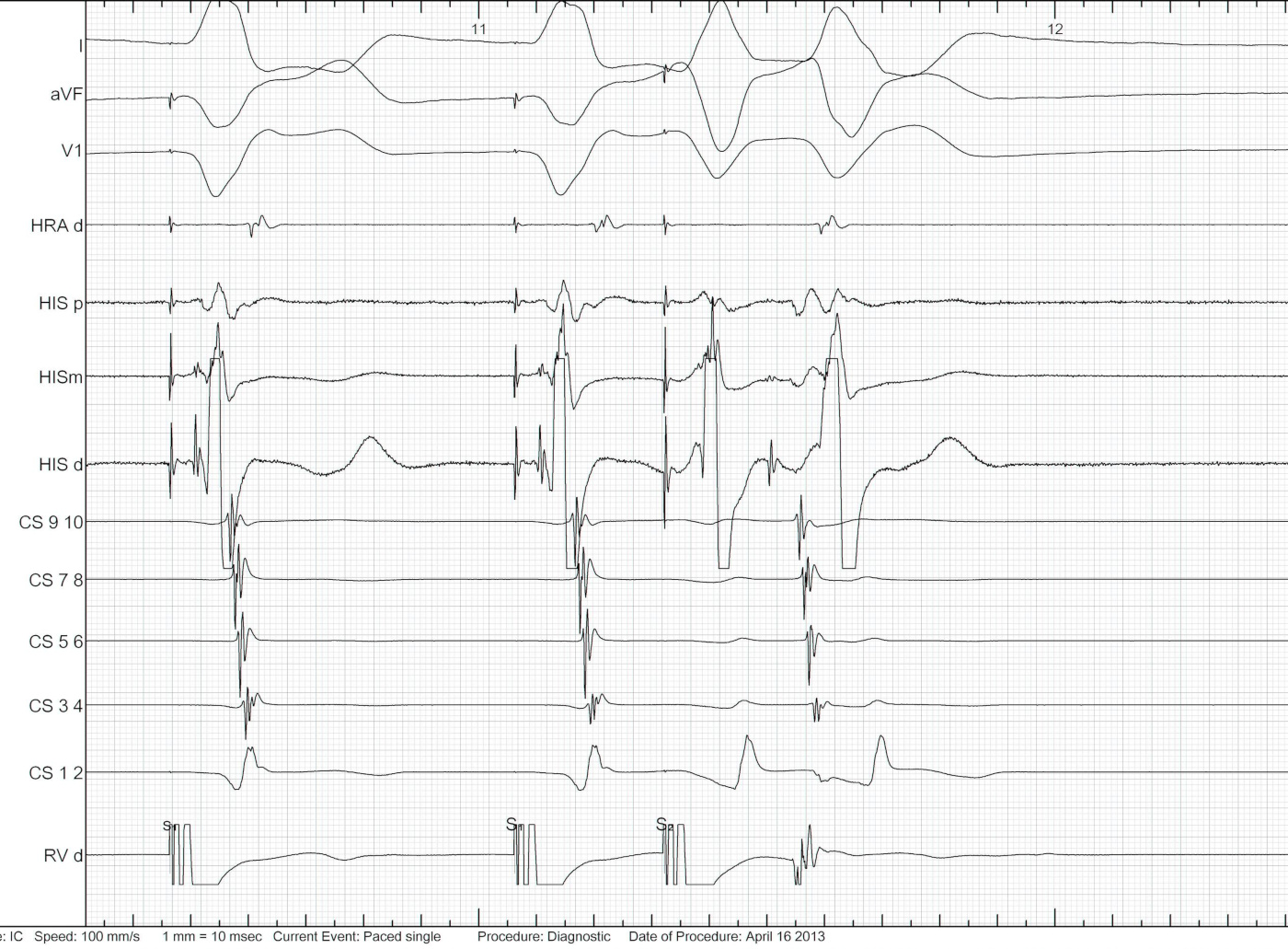
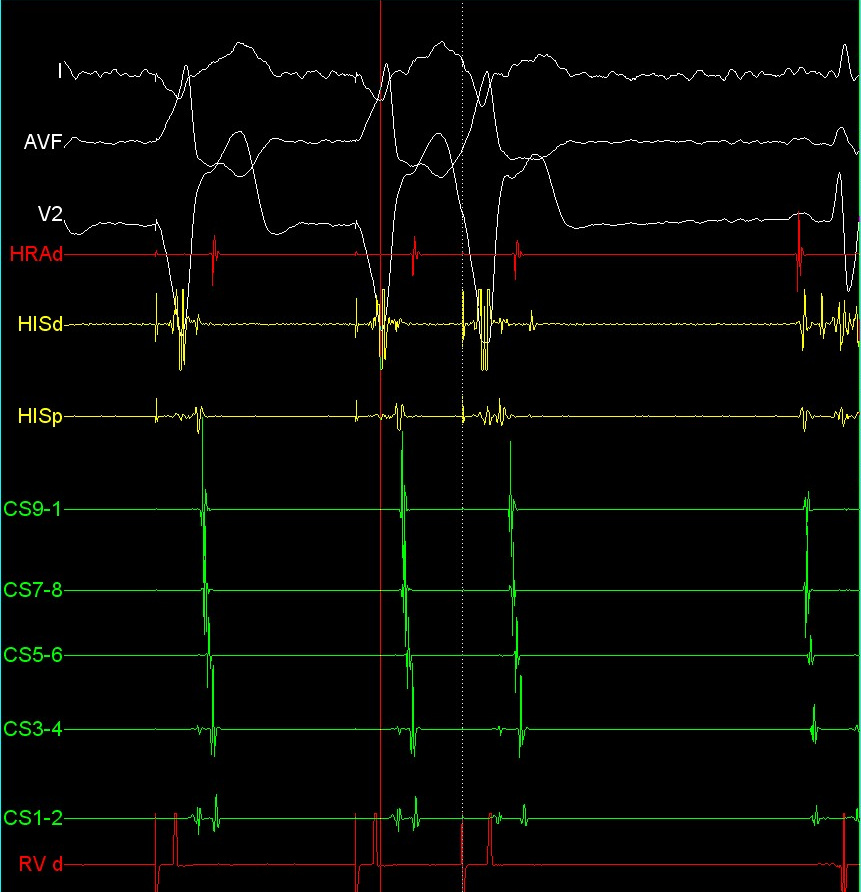
Example - Entrainment in Atrial flutter
Catheters
Entrainment
Pacing from lateral RA
Pacing from lateral RA
Pacing from lateral RA
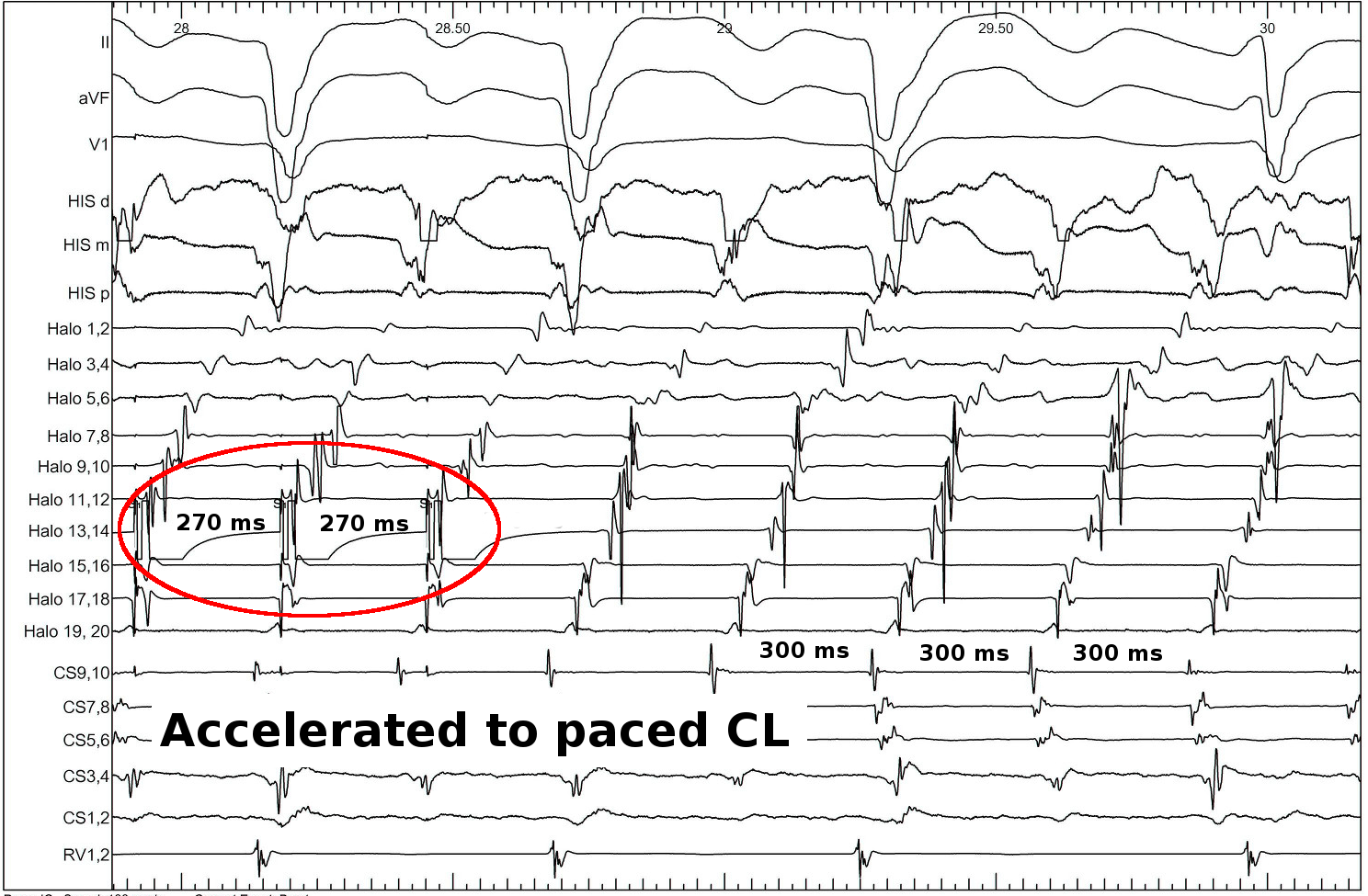
Pacing from lateral RA
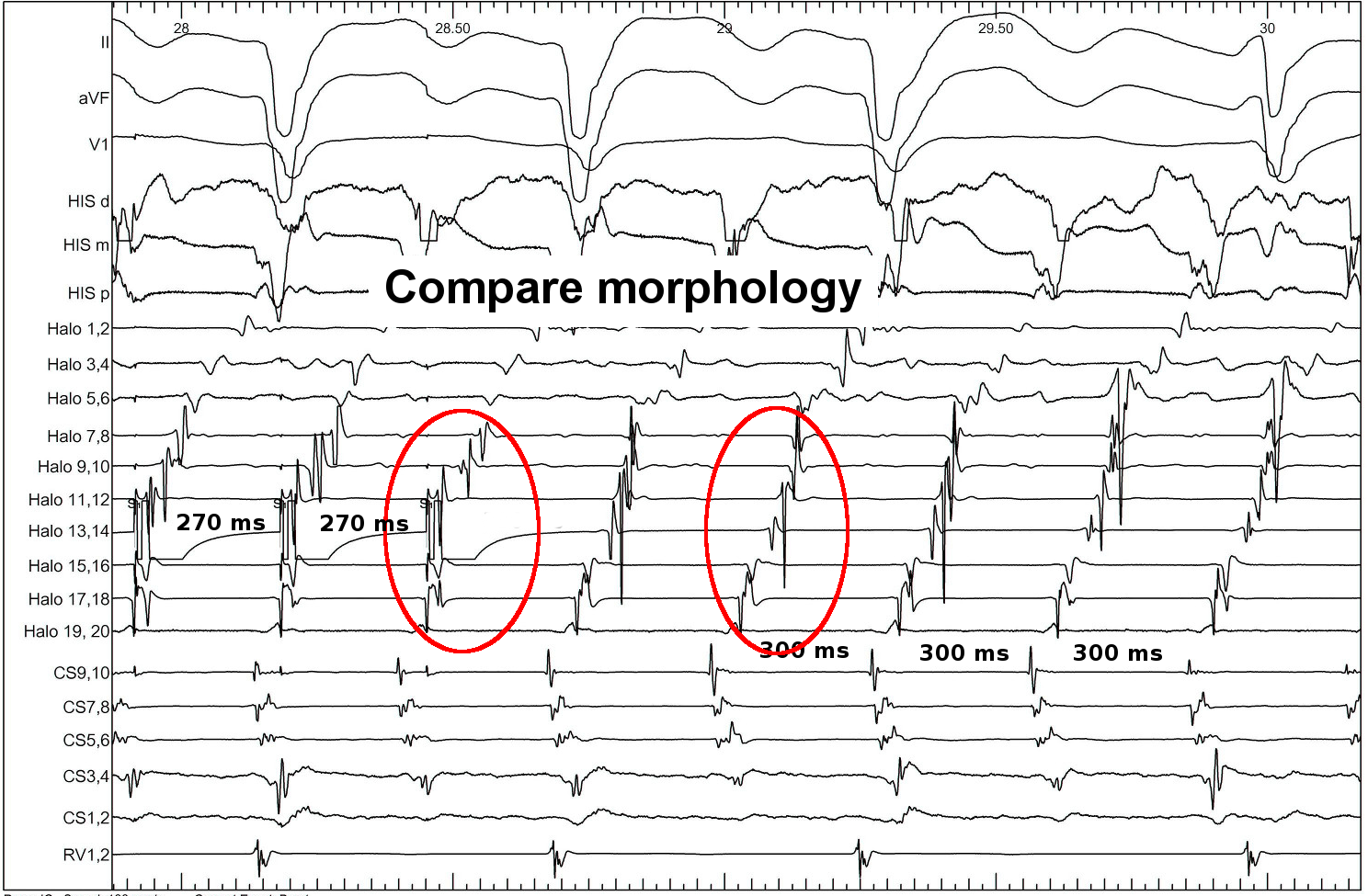
Pacing from lateral RA
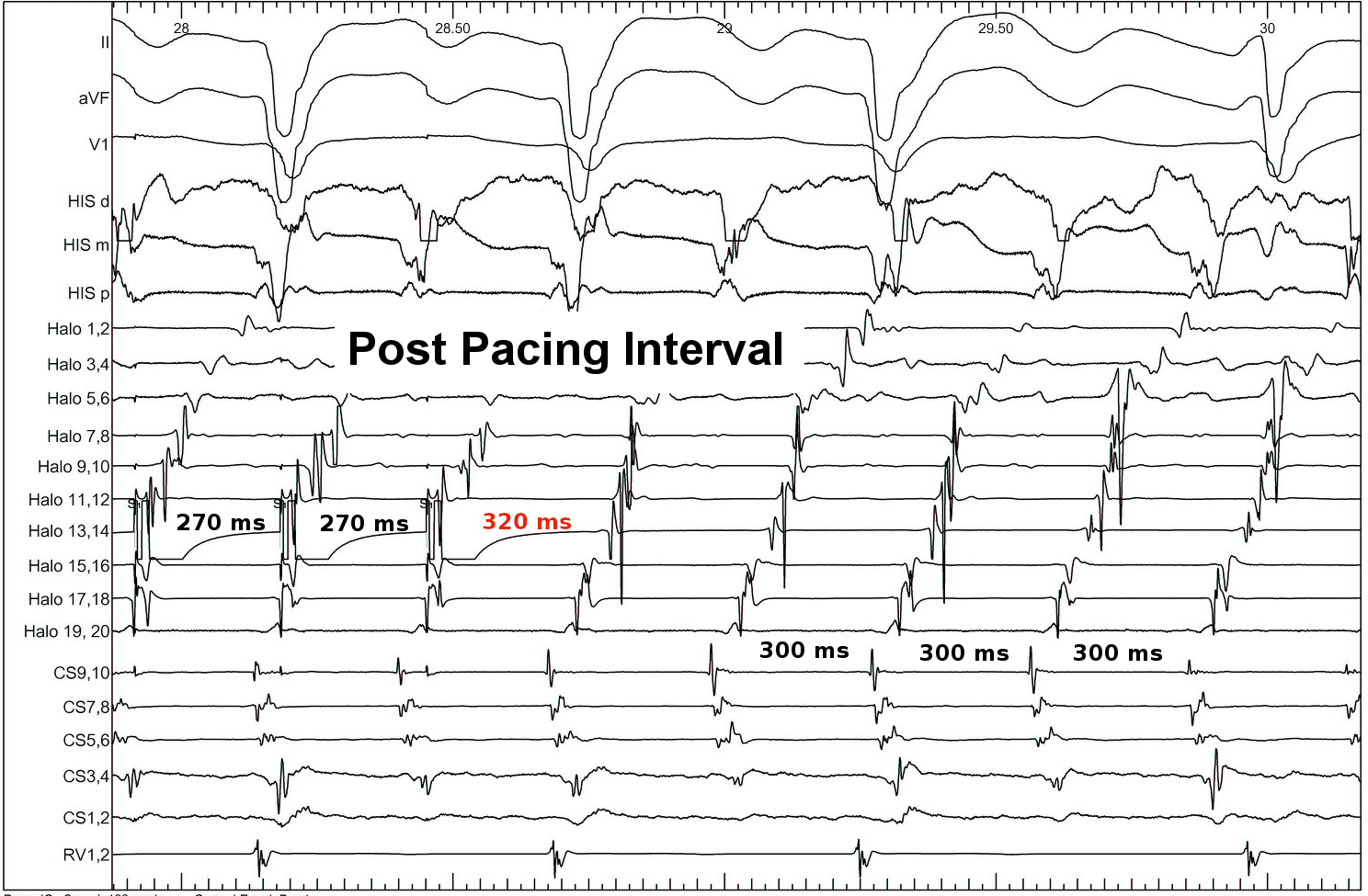
Pacing from lateral Isthmus
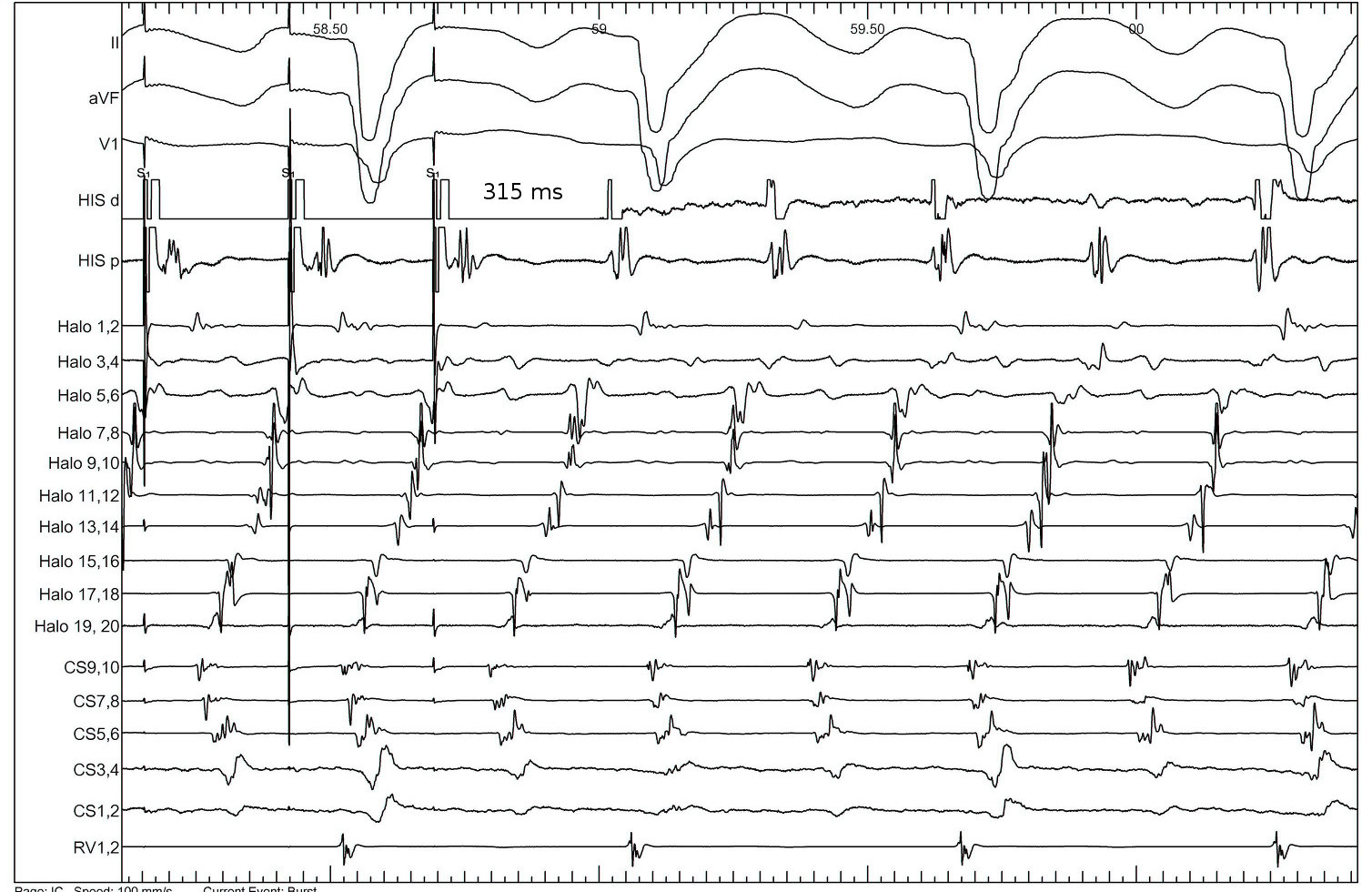
Ventricular tachycardia
Example
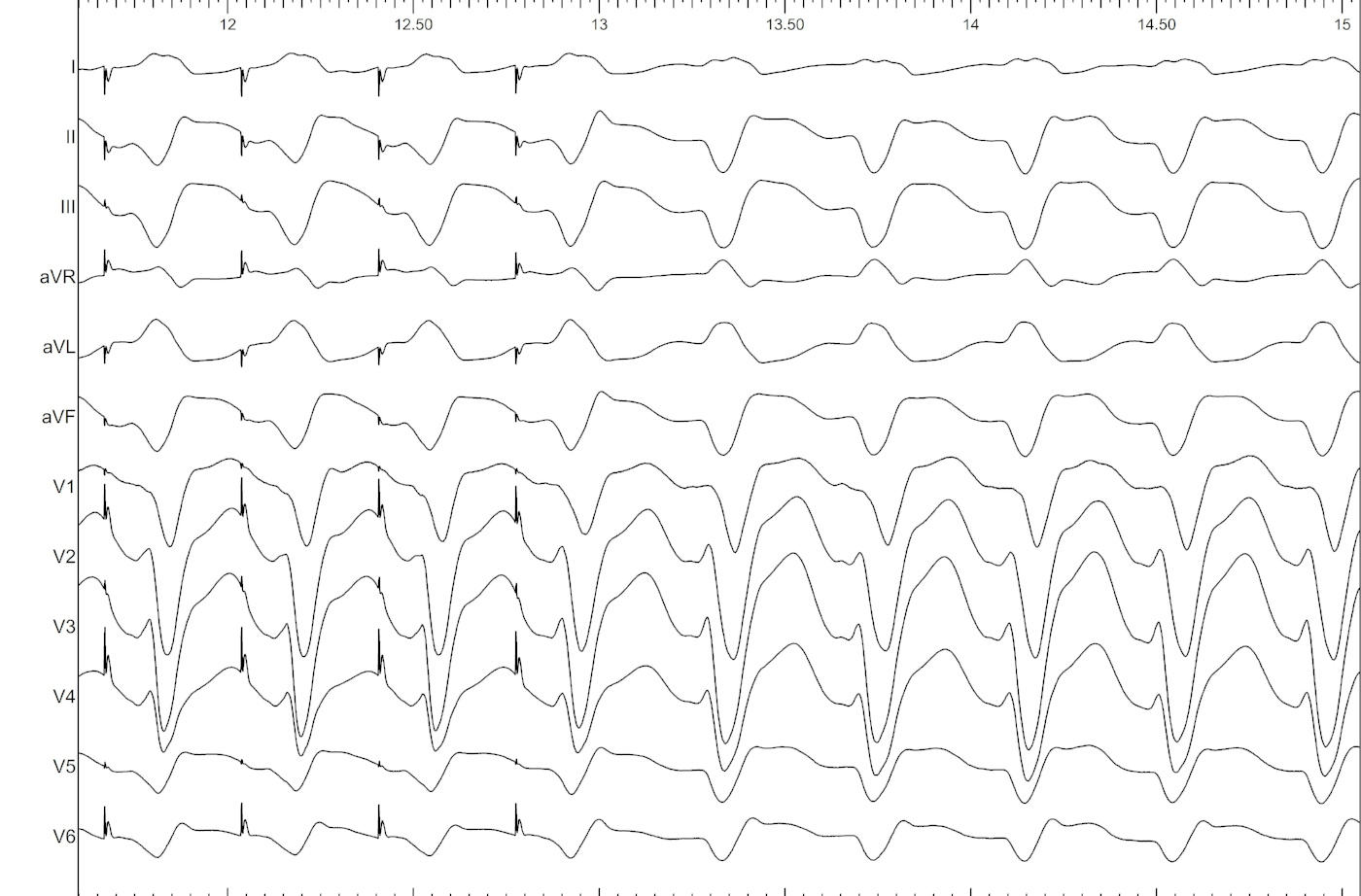
Example
Basic principles of EP maneuvers
Basic principles
- Understand principles rather than rote learn maneuvers
- Understand multiple analogous situations from single principles
- Visual understanding
Start right !
- Learn to use the stimulator
- Learn to set up sync
- Learn to measure
- Repeatedly use early in career
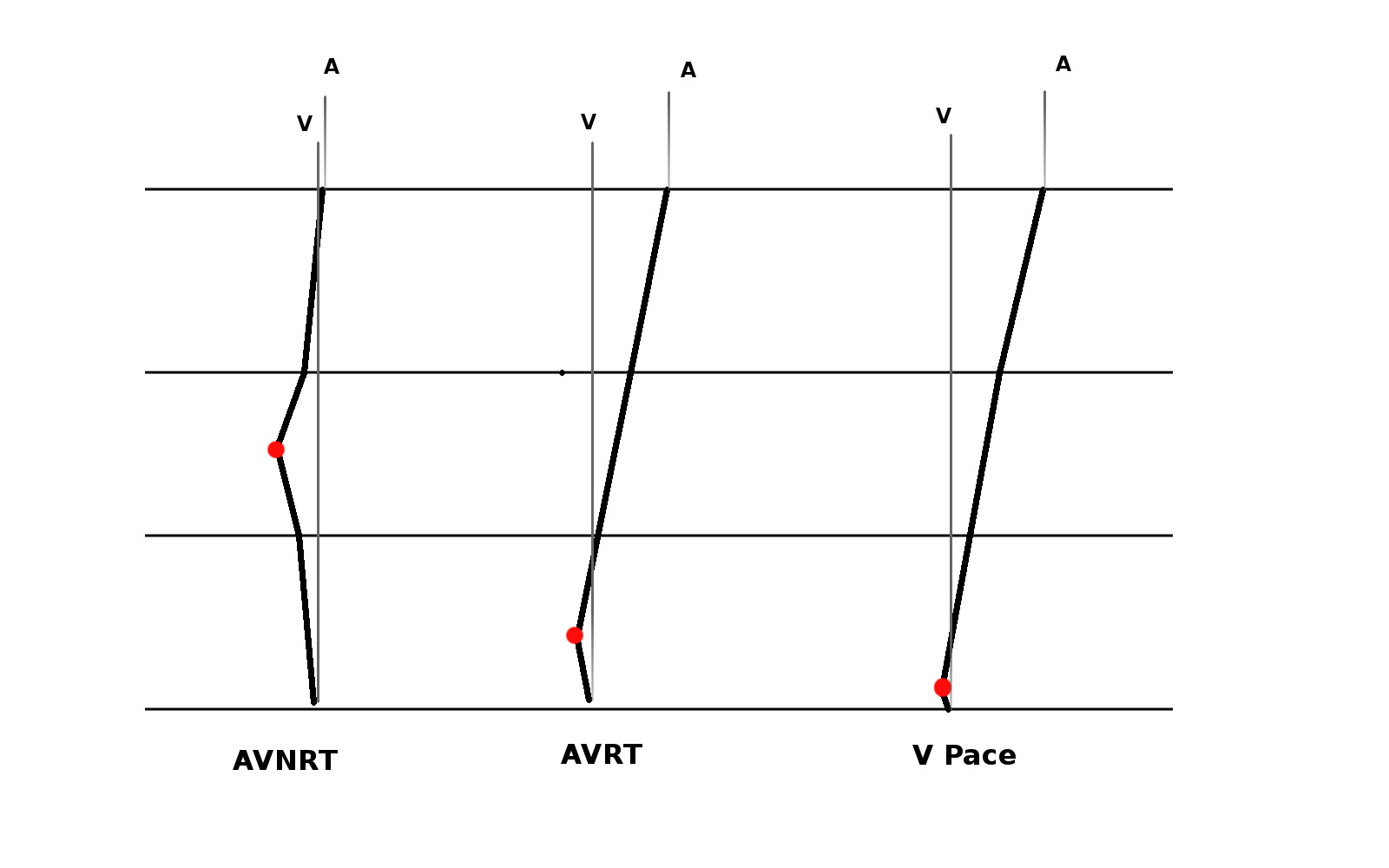
Three diagnoses
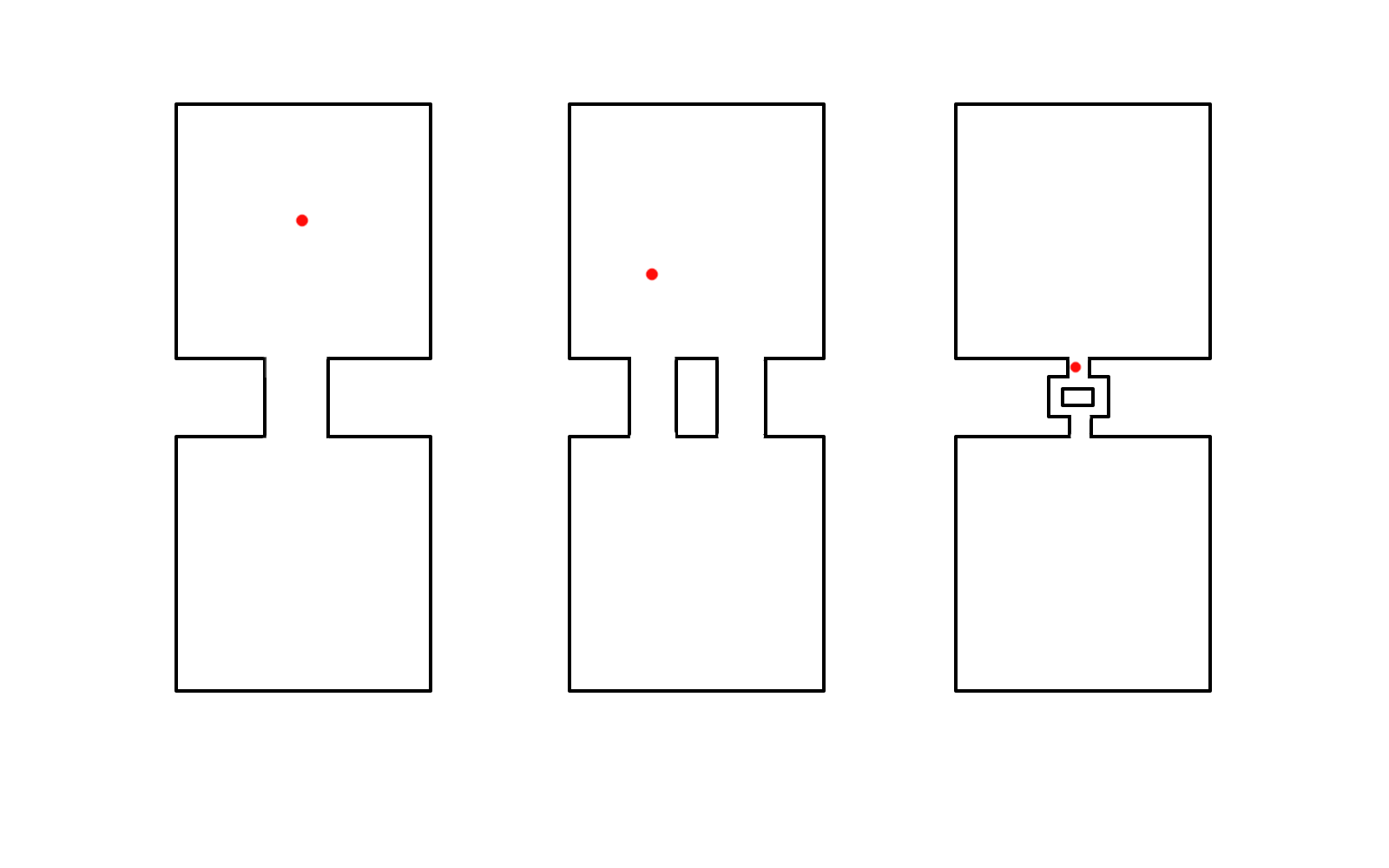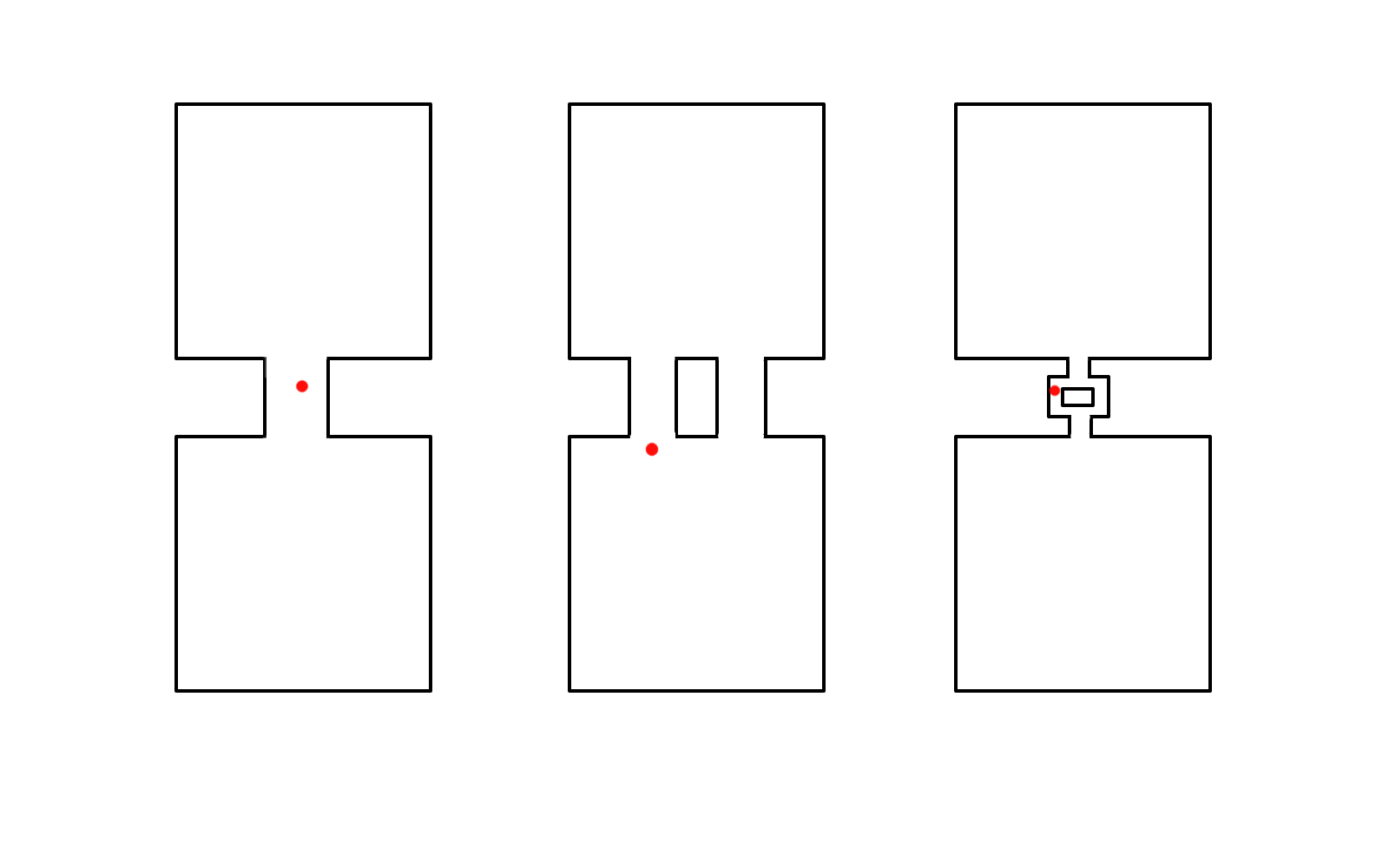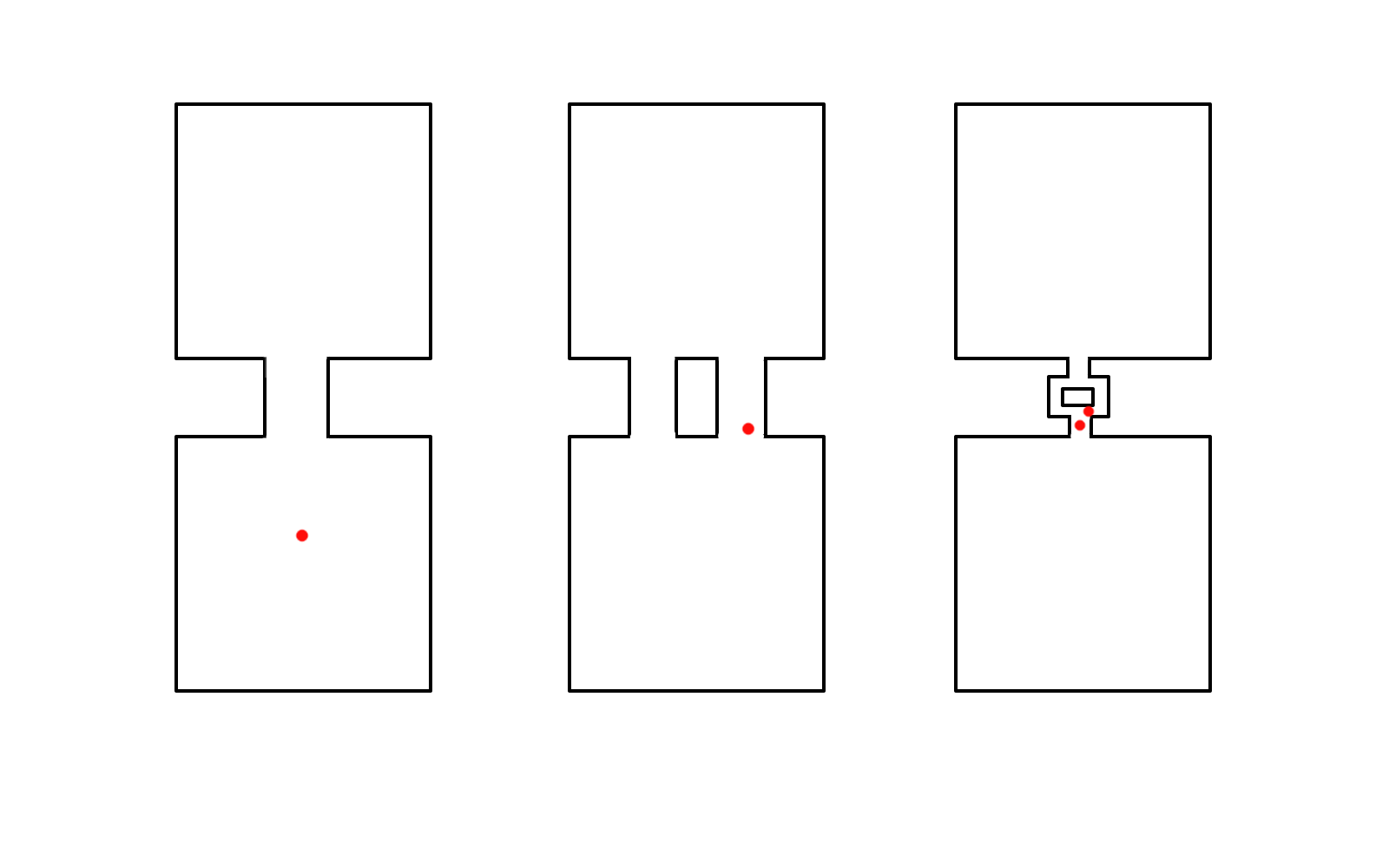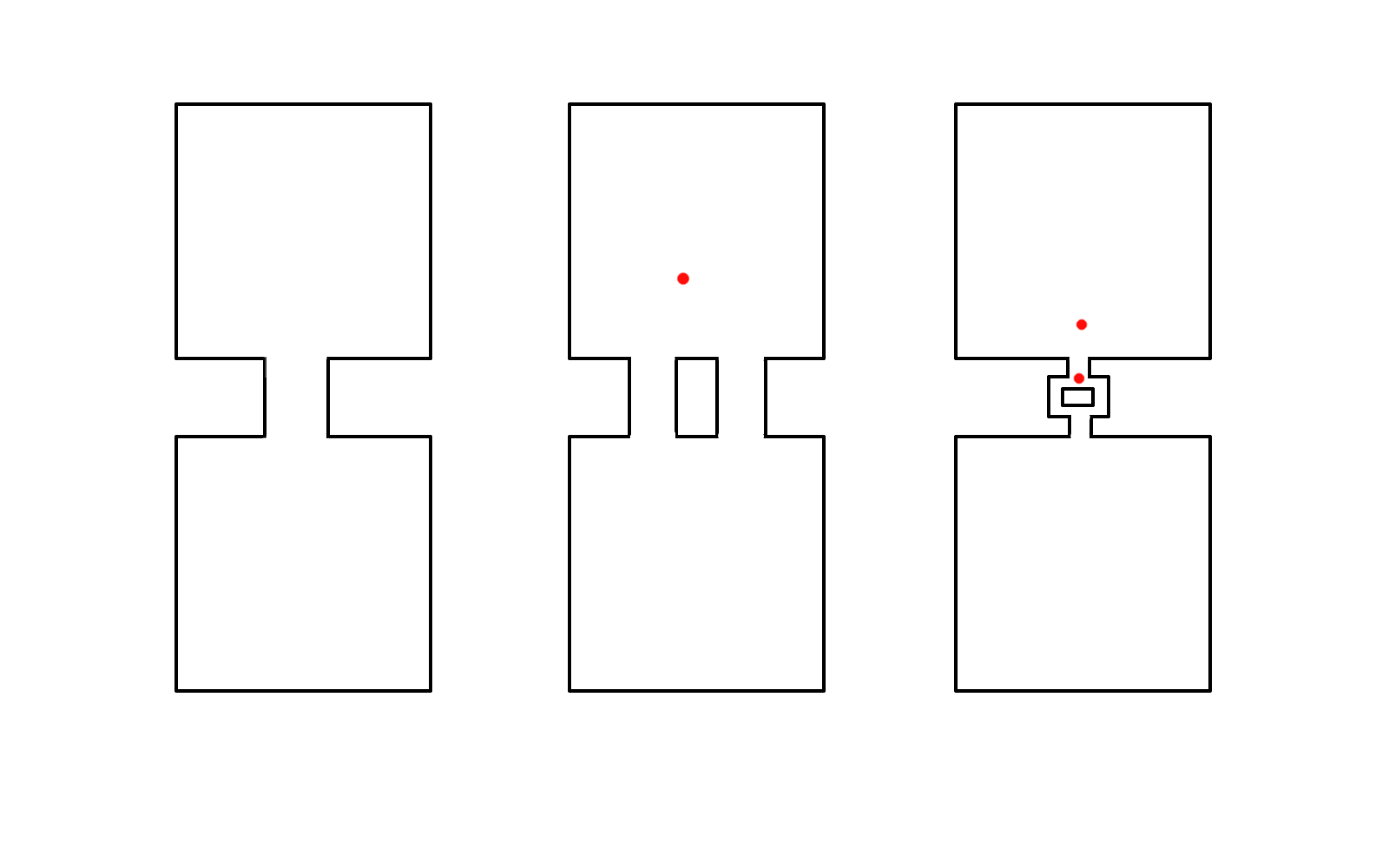
Critical parts of circuit
- AT
- Atrium
- AVRT
- Atrium and ventricle
- AVNRT
- None
Distance gives perspective
- Narrow QRS tachycardia
- Ventricular overdrive pacing
- PVCs
- Wide QRS tachycardia
- Atrial overdrive pacing
- PACs
Waypoint
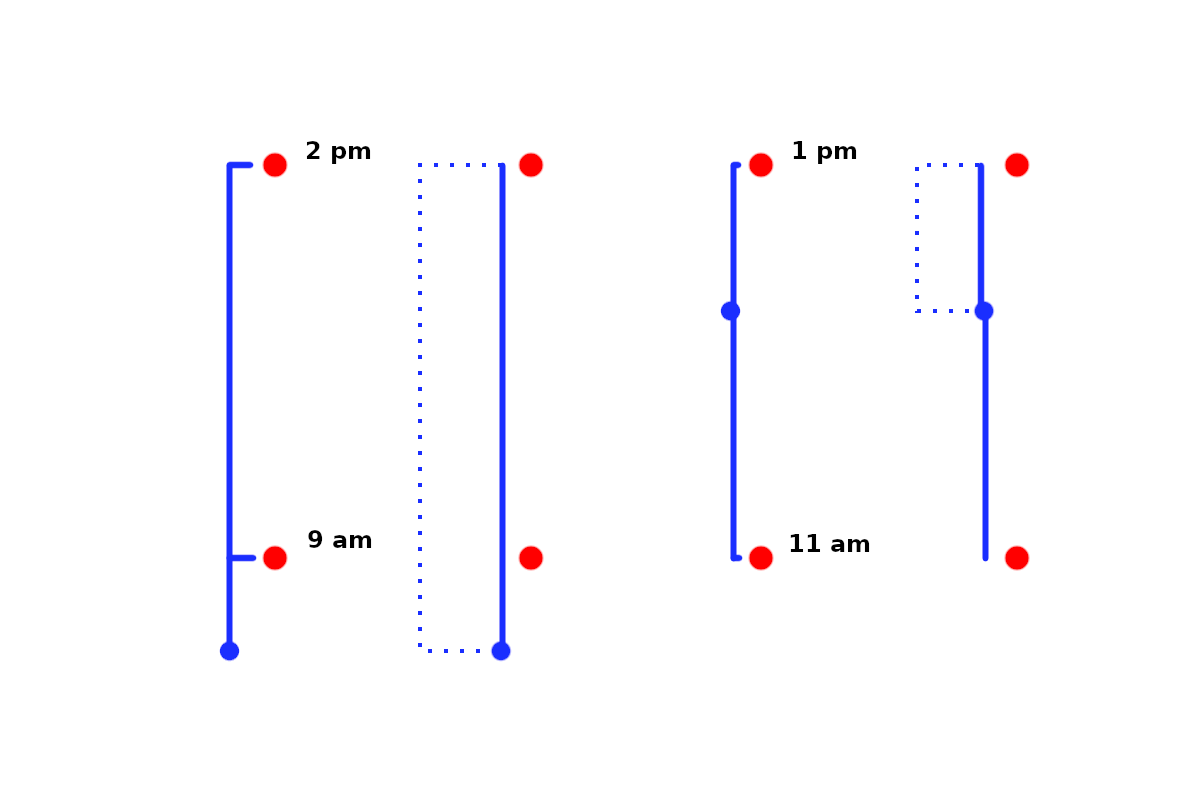
Courier delivery
Courier delivery
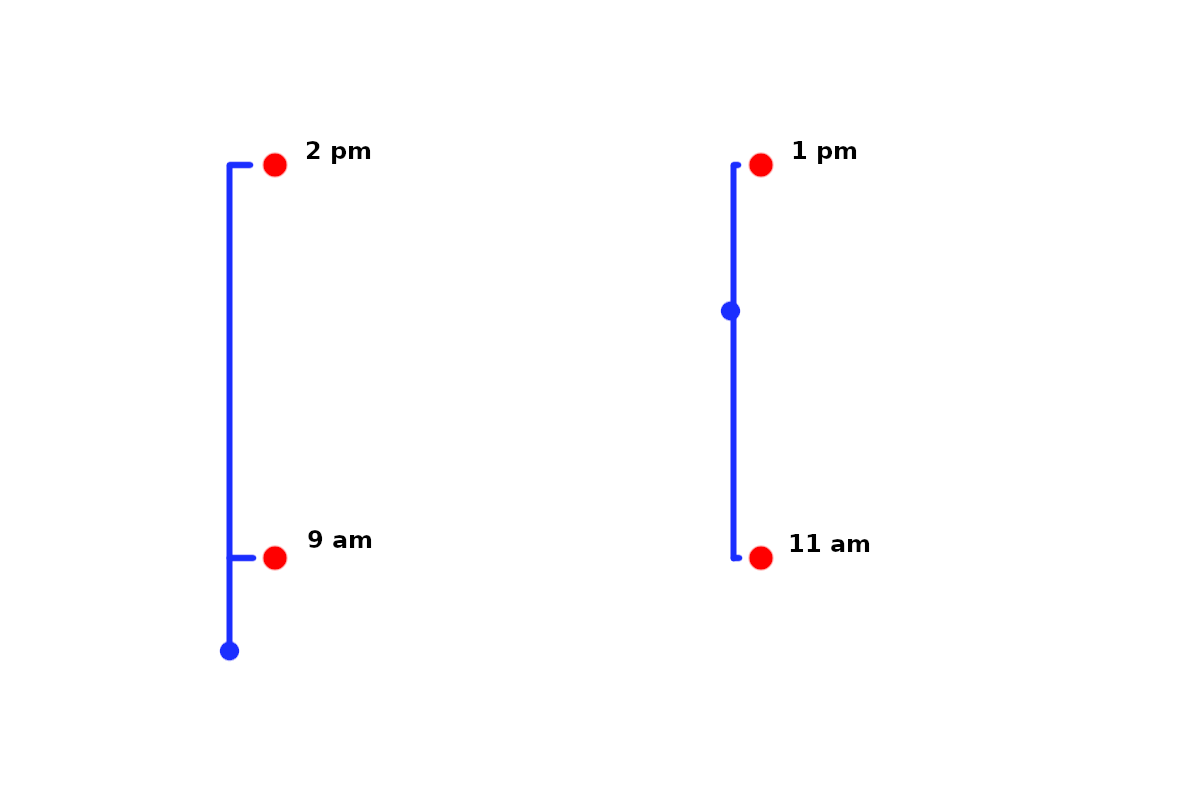
Courier delivery
Sequential vs parallel
Passing through a closed door

Passing through closed door
Last man standing
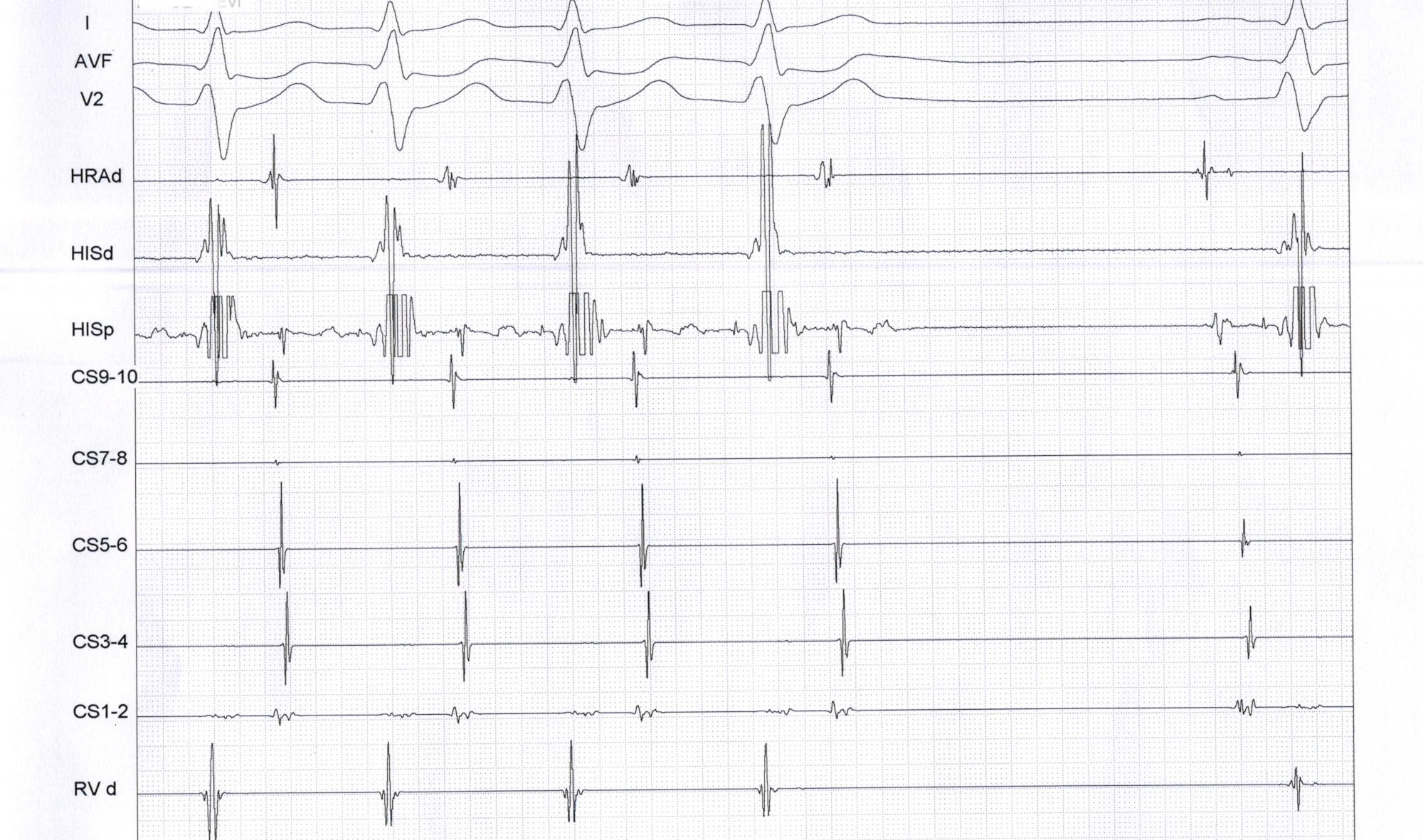
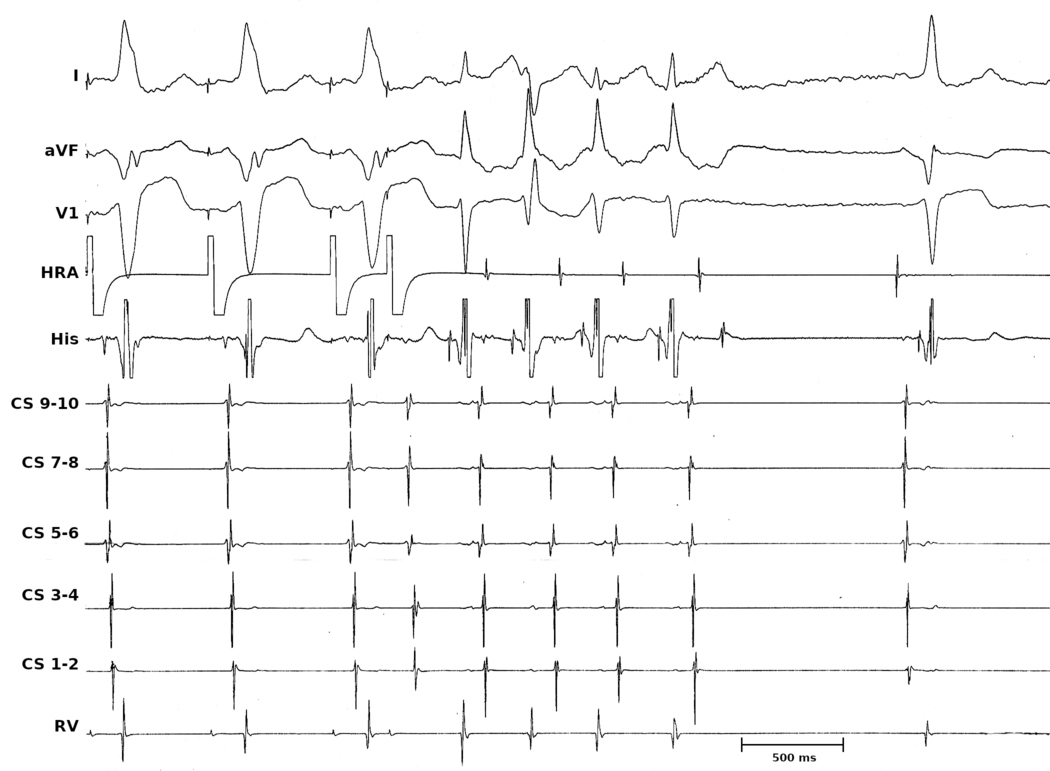
Through the looking glass
- Principles can be applied in reverse direction
- Very useful to remember in WQRST
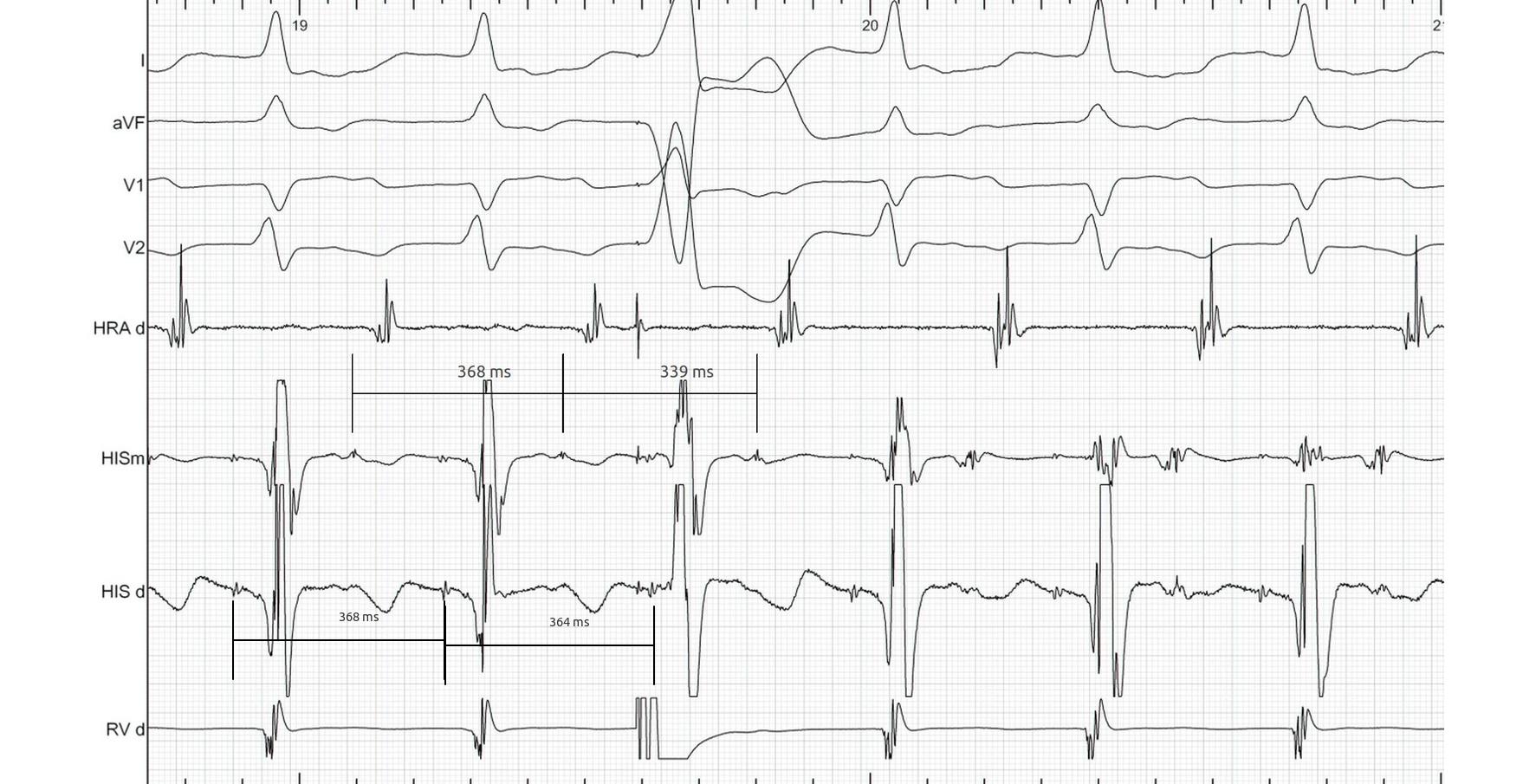
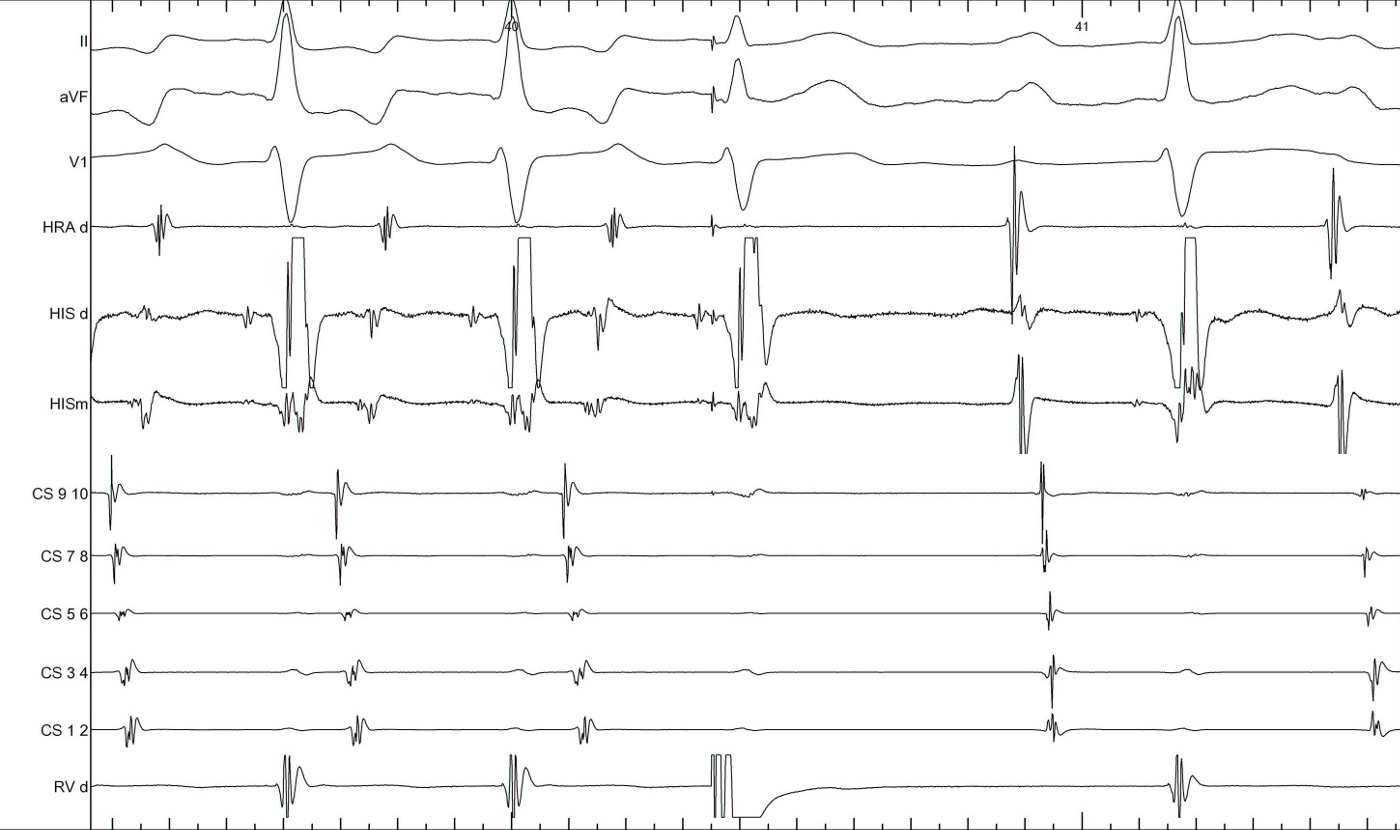
His refr PVC in NQRST
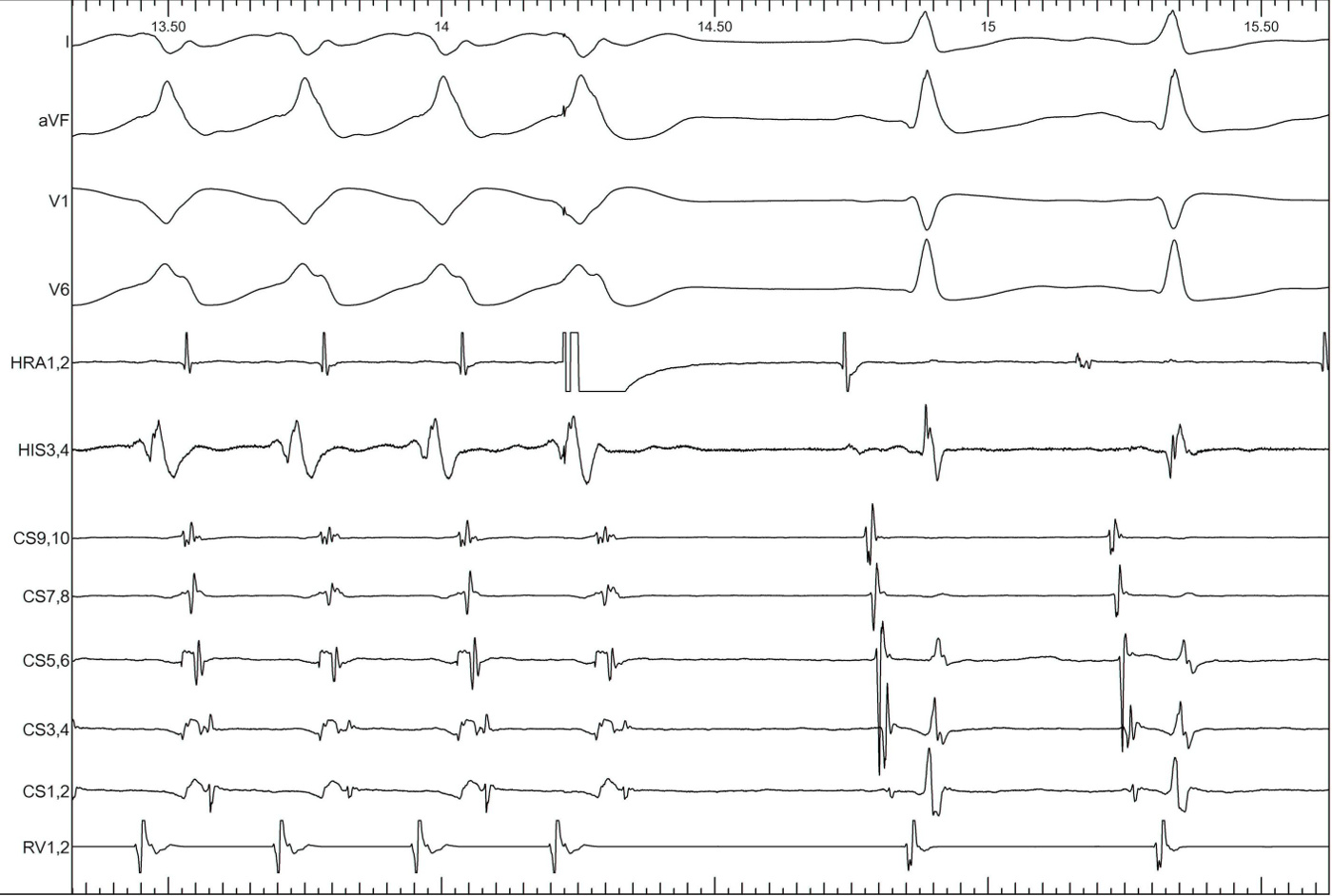
Septal refr PAC in WQRST
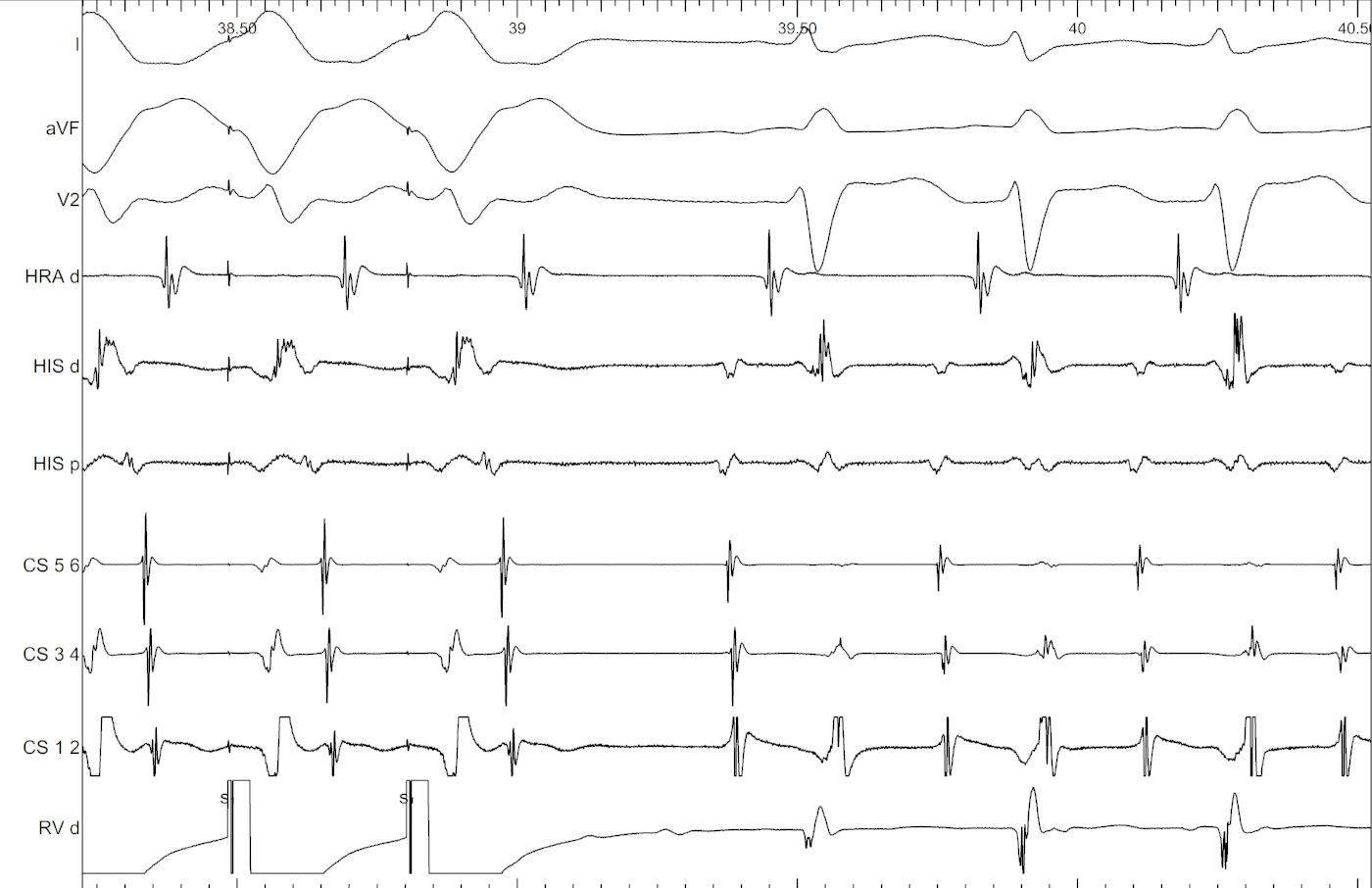
Spontaneous termination of NQRST with 1:1 VA

VOP in narrow QRS tachycardia with 1:1 VA
Summary
- Understand principles rather than rules
- Visualisation of principles
- Ability to apply maneuvers in "reverse" makes it easier in WQRST