Inappropriate ICD Therapies

Raja Selvaraj MD DNB FCE (Toronto)
Professor of Cardiology
JIPMER
Definitions
Sensing
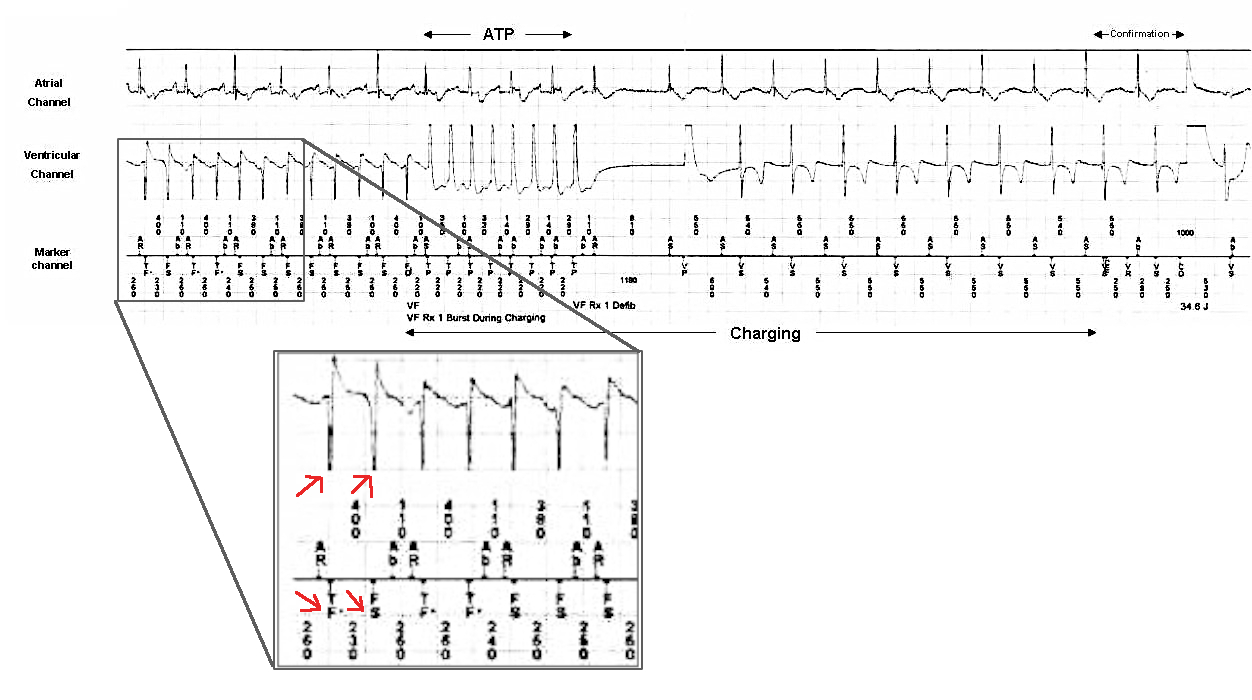
Detection
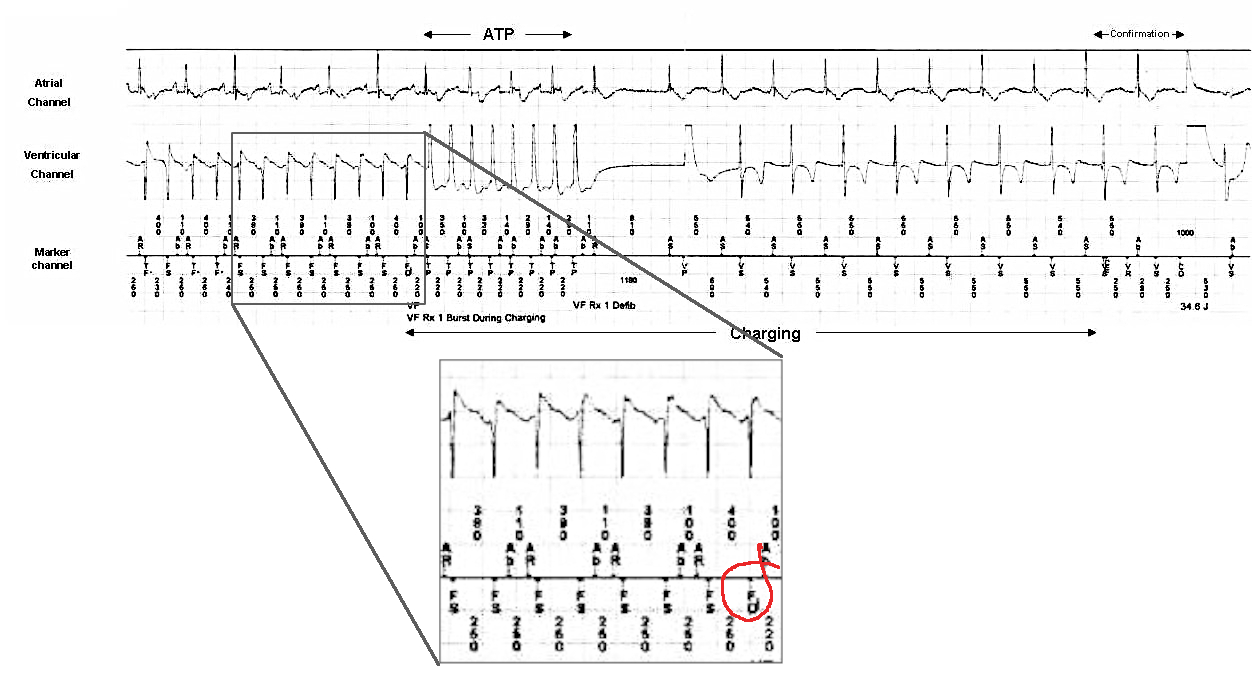
Confirmation
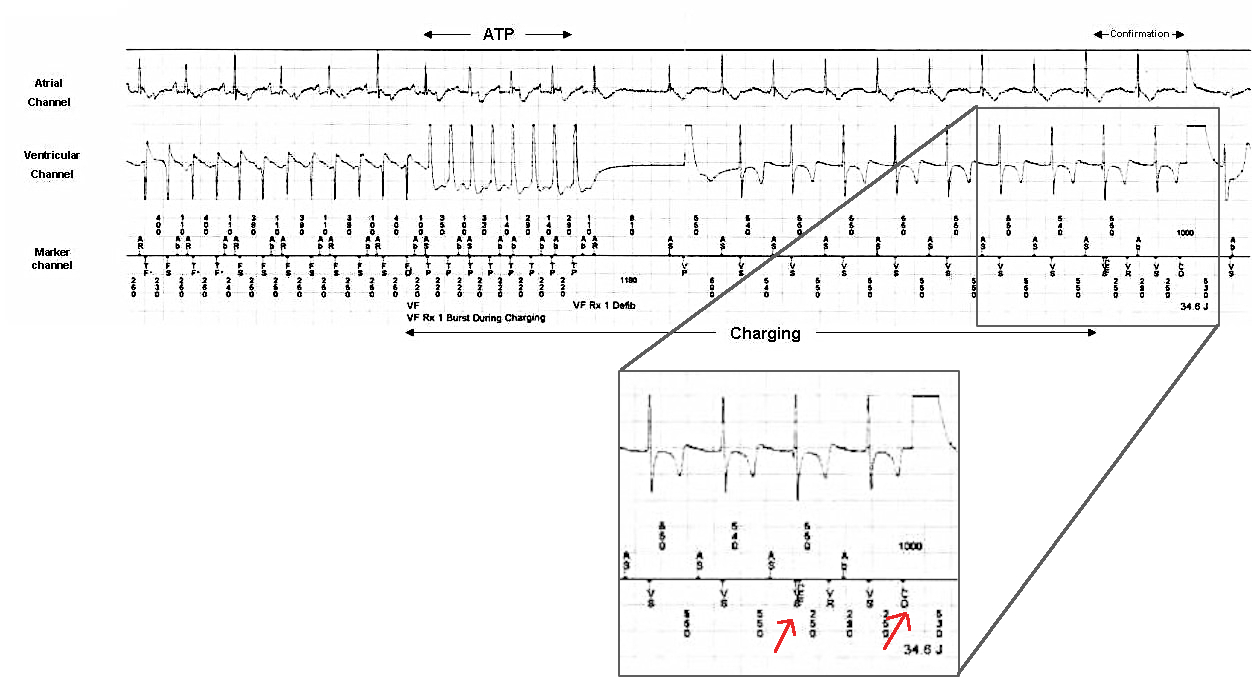
Re-detection
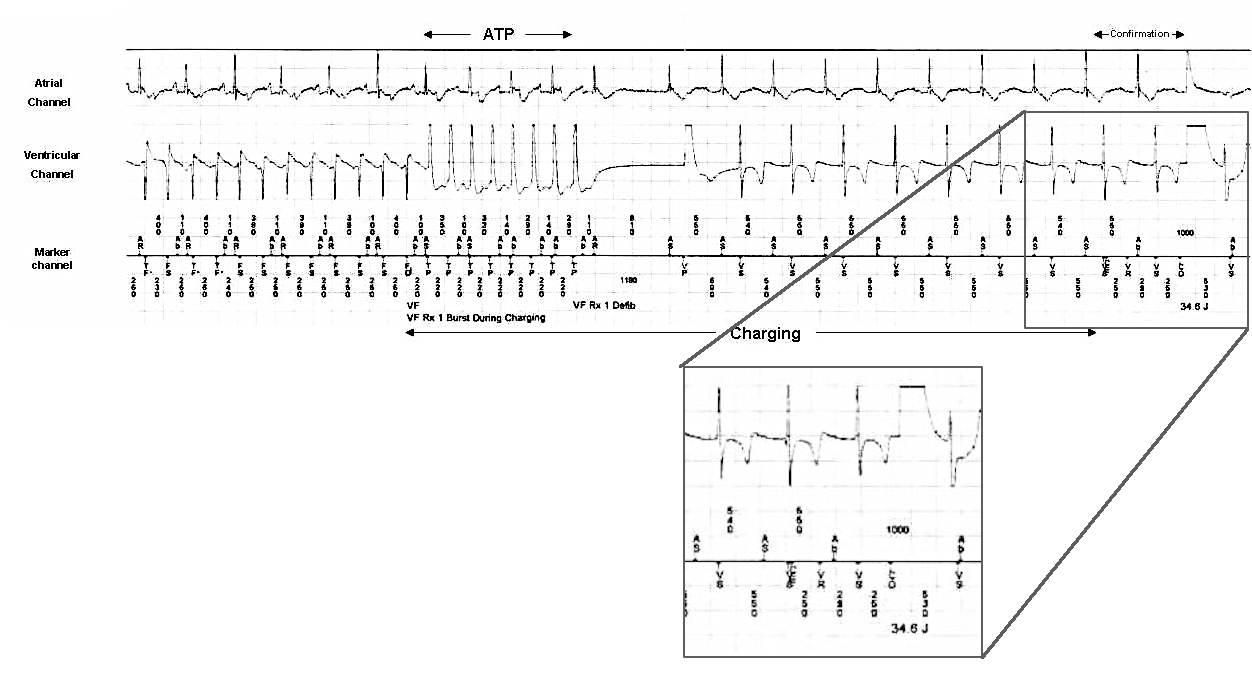
Inappropriate therapy
- Non physiological signals
- Physiological, non-arrhythmic signals
- Intracardiac
- T wave (small RR alternation)
- QRS double counting (Na blockers, high heart rate)
- P wave sensing (children, long PR, lead dislodgement)
- Extracardiac
- No relation to cardiac cycle
- Greater signal on widely spaced electrodes
- Lead connector problems - small part of cycle, saturates amplifier
- Intracardiac
- Non ventricular arrhythmias
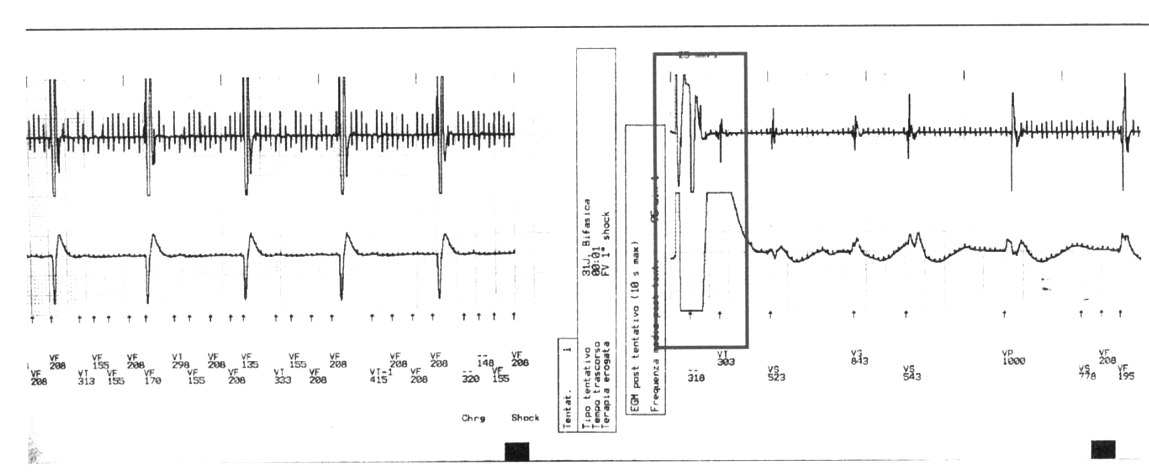
Case 1
Case
- Young female
- Idiopathic DCMP
- Single chamber ICD
- Presented with ICD shock 2 months after implant
Tracing of therapy
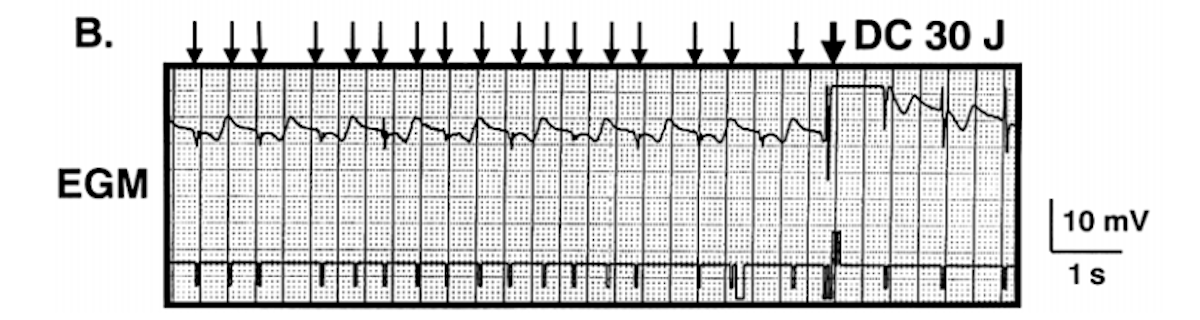
Jpn Circ J 2001; 65: 685 –687
Decrease in R wave amplitude
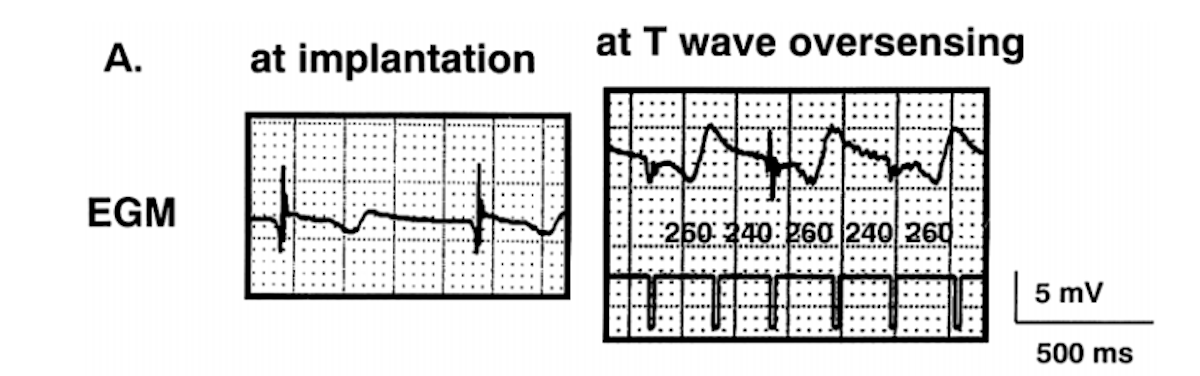
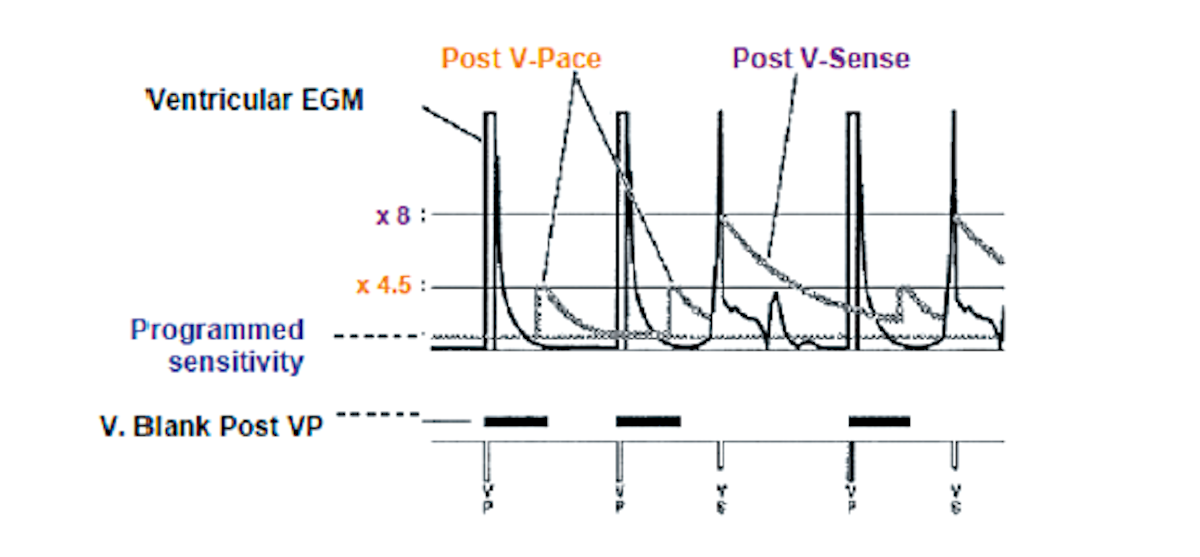
Autogain (sensing threshold)
Learning points
- Dynamic sensing thresholds
- Inappropriate oversensing
- Reduction in signal amplitude
- Increase in "noise" amplitude
- After longer pause
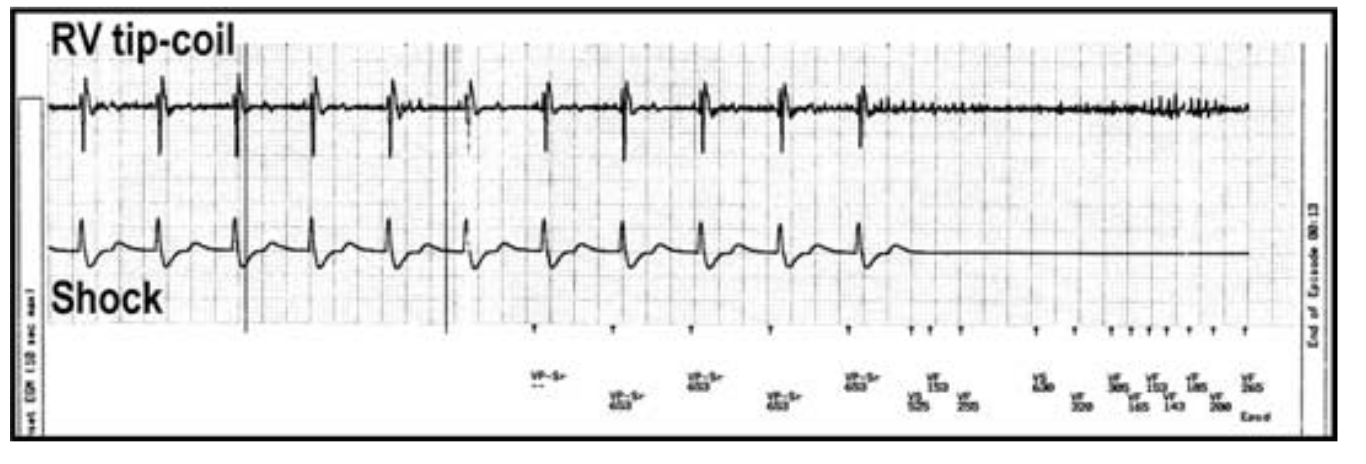
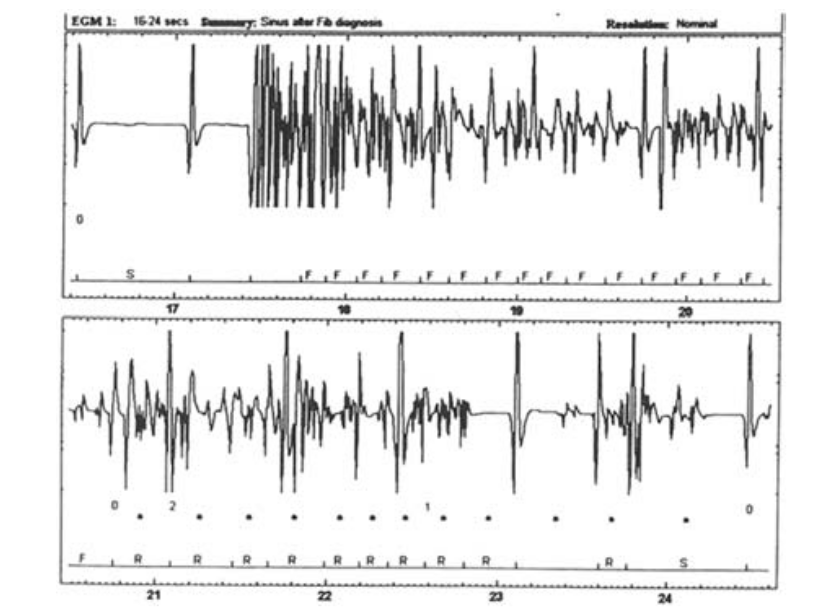
Case 2
Case
- Middle aged male
- Post MI, LV dysfunction, VT
- Dual chamber ICD
- Presented with shock
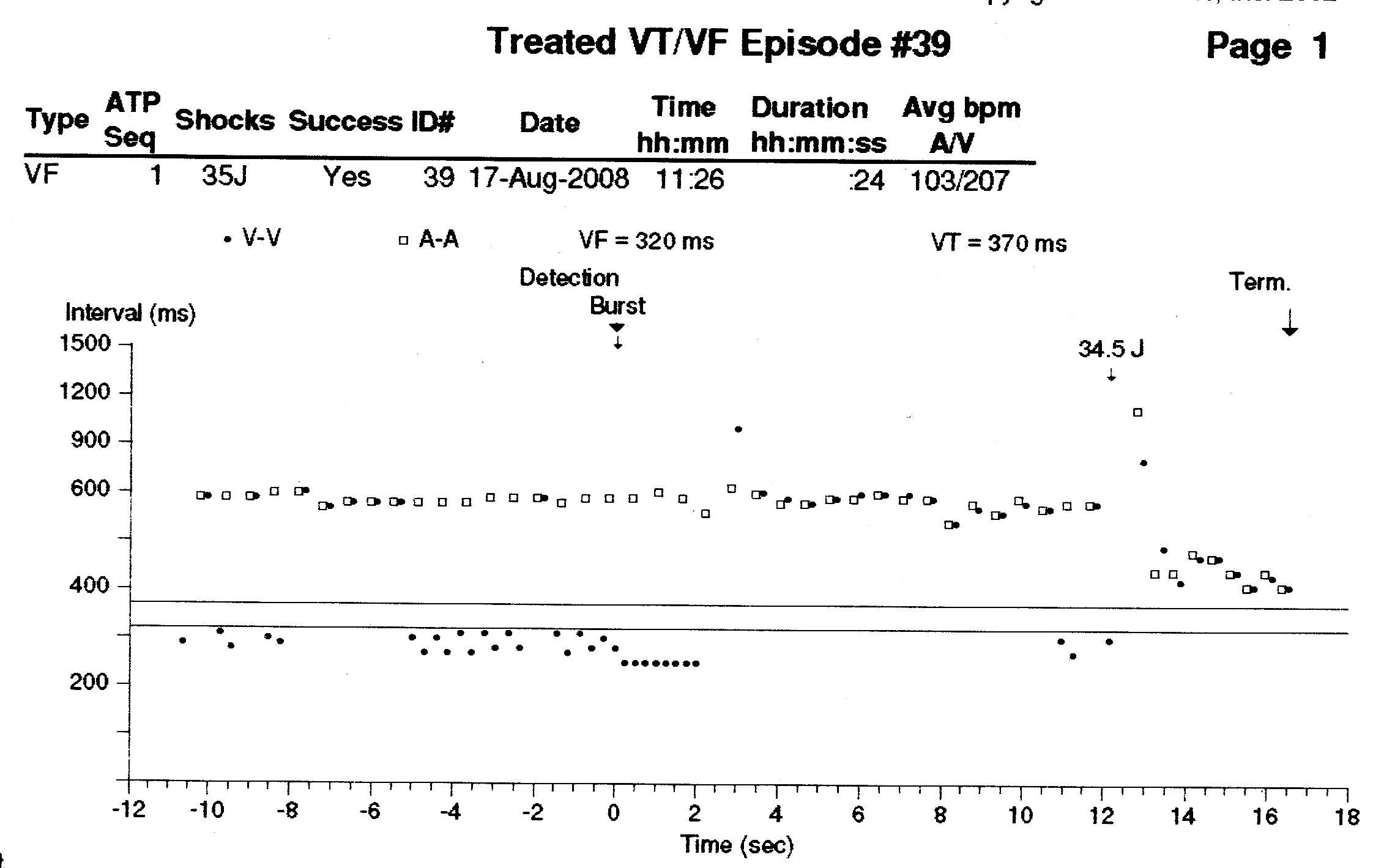
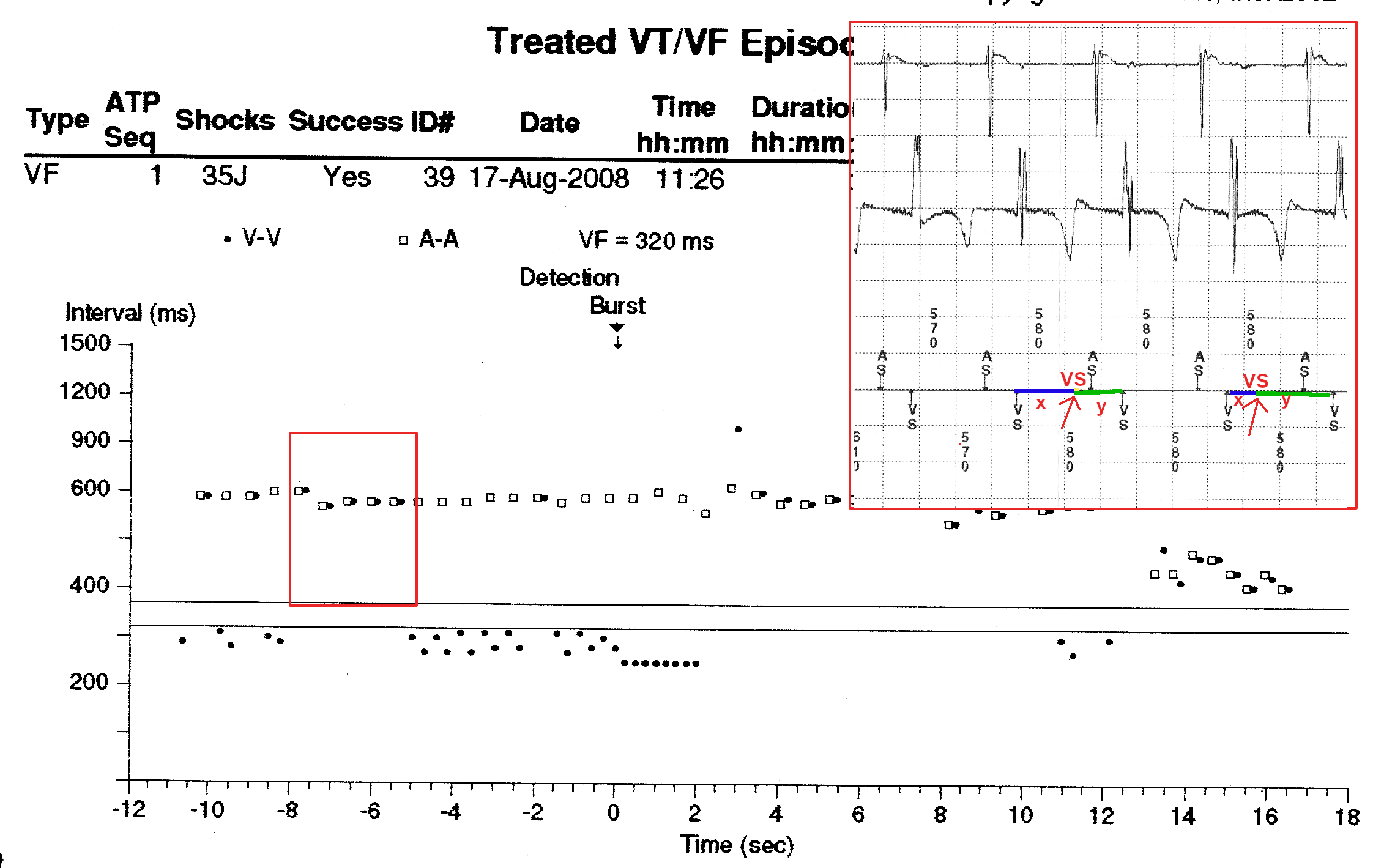
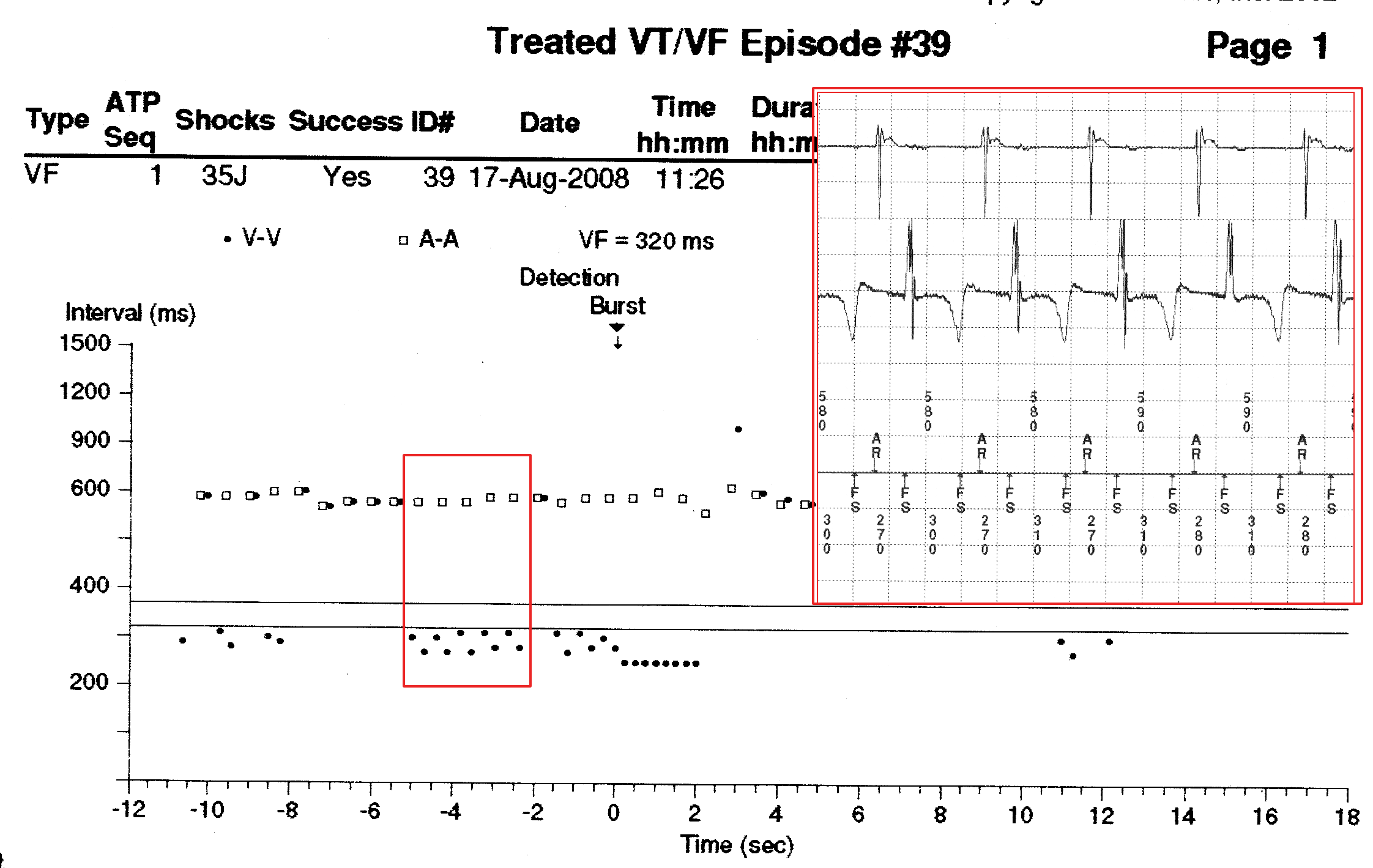
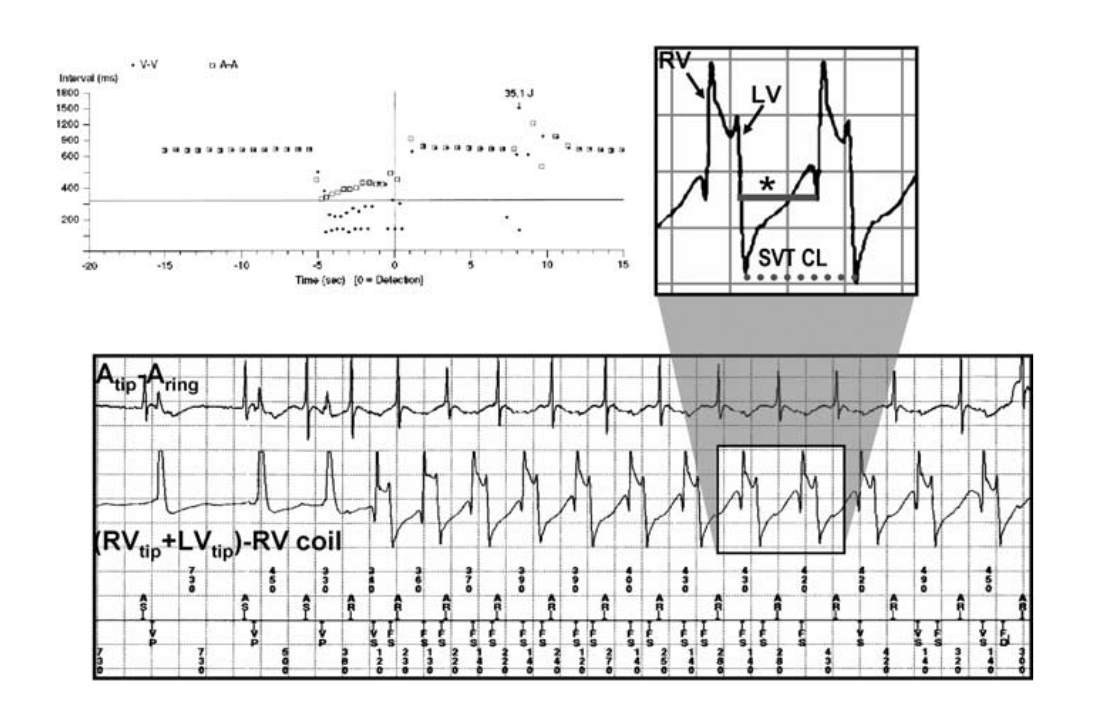
Dot plot - Illustration

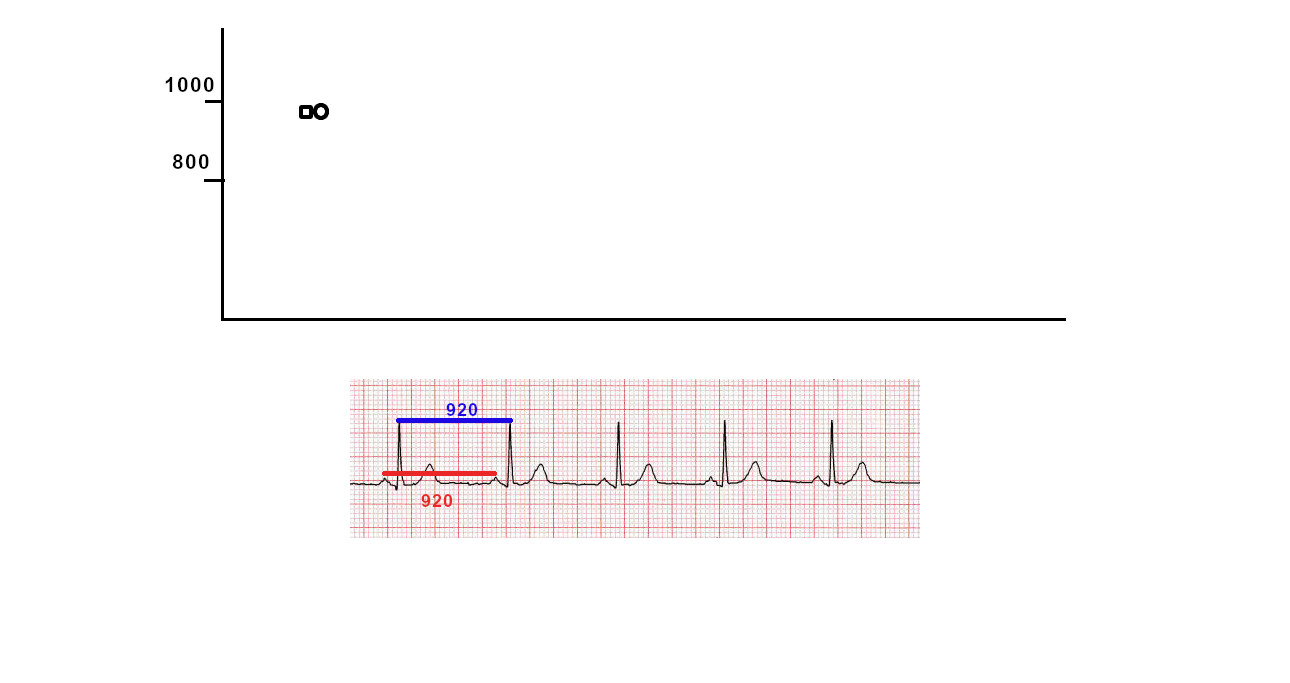
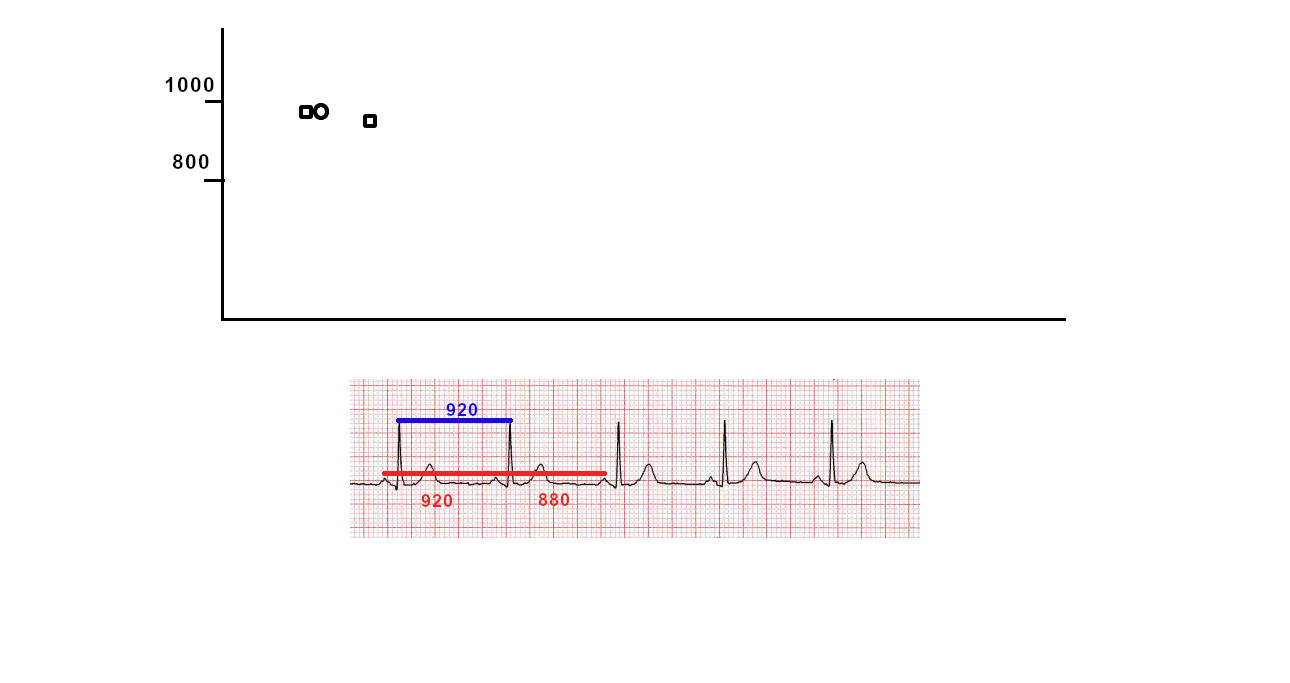
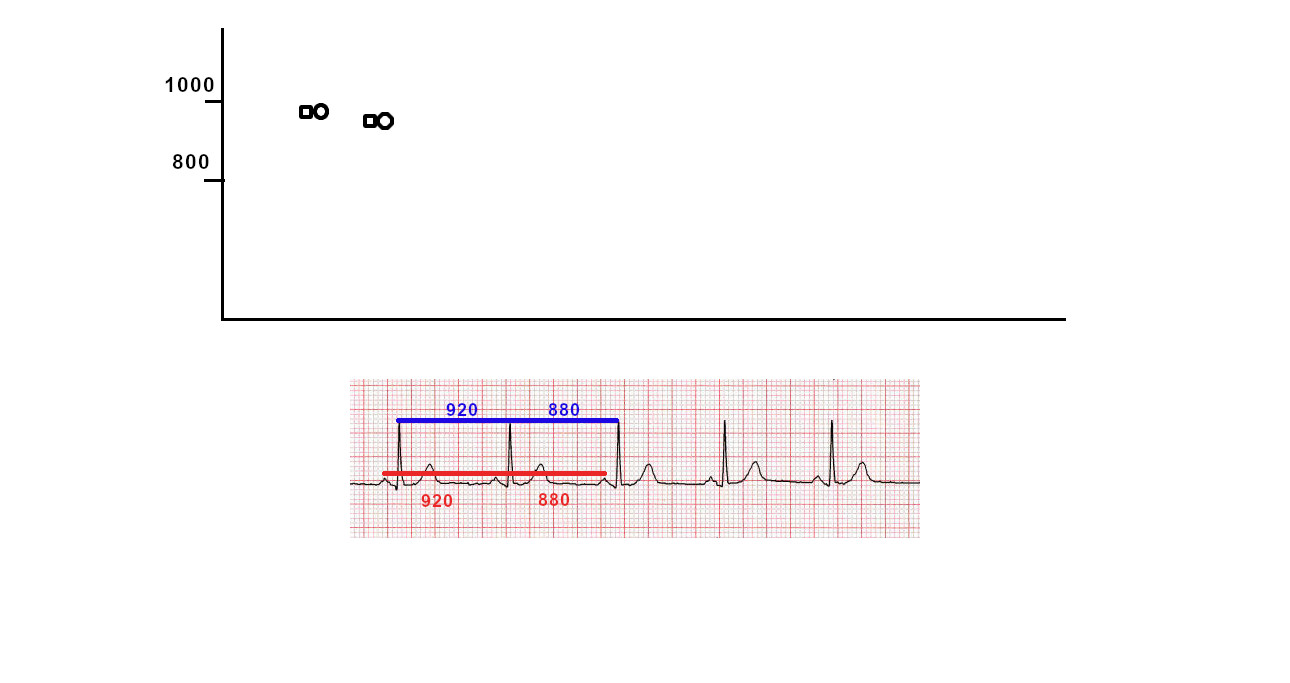
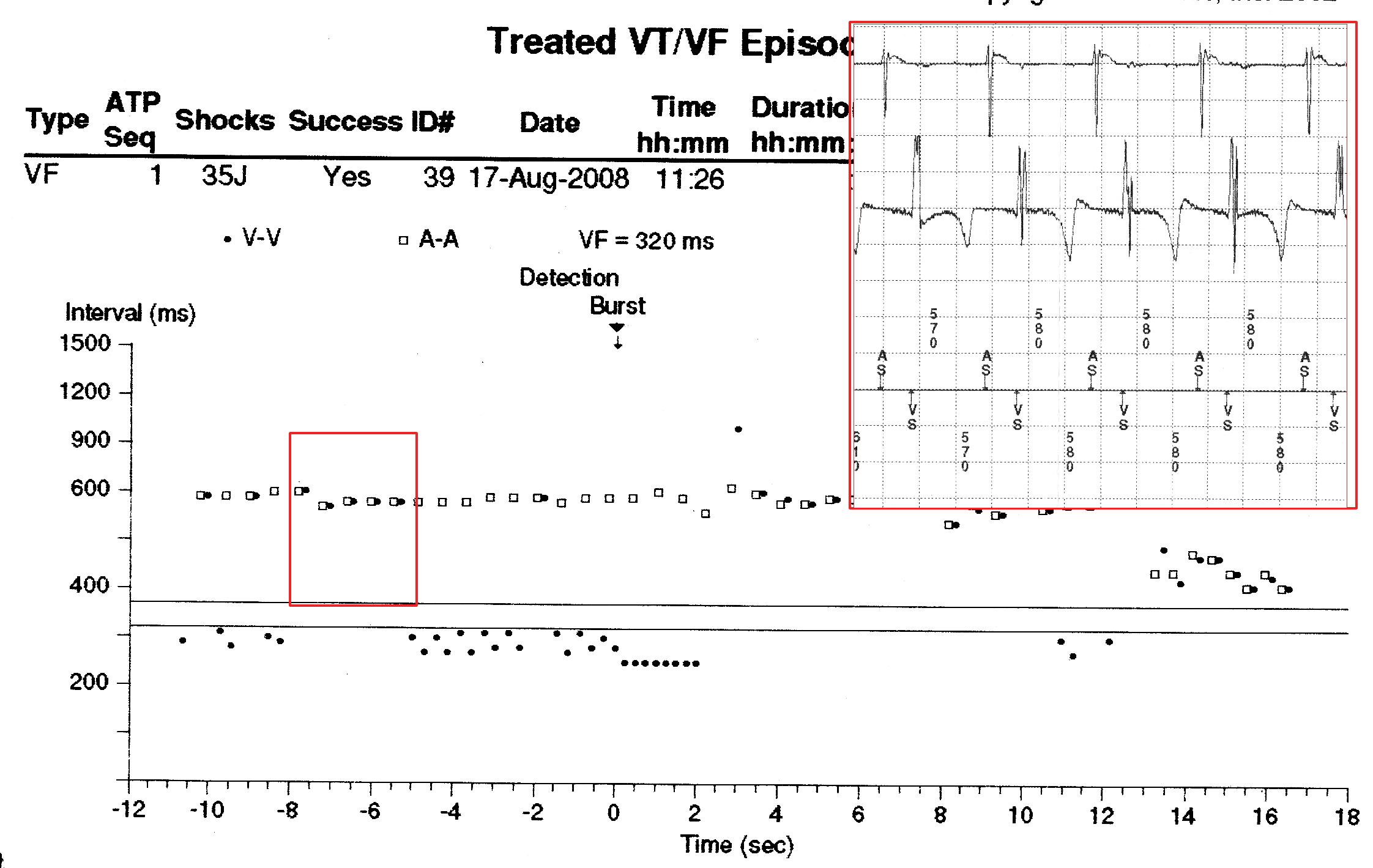
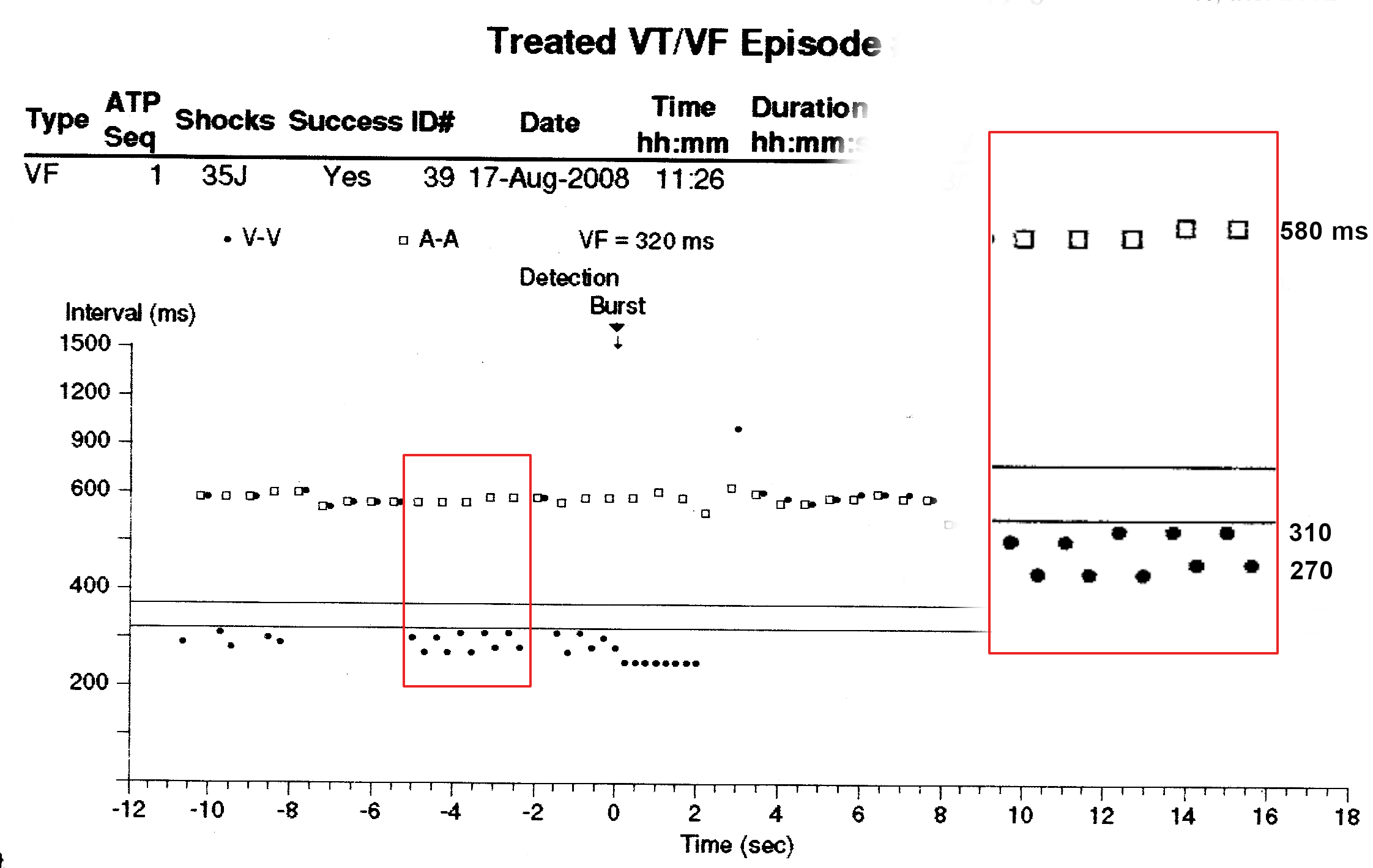
"Tram track" pattern
Patient with CRTD device
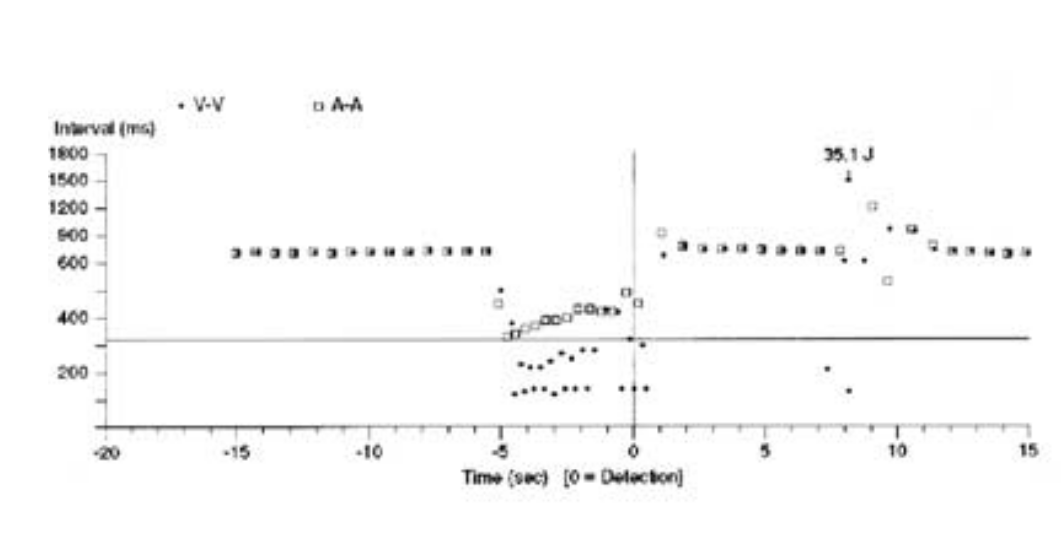
PACE 2005;28:1322–1346
Atrial tachycardia and "double counting"
Learning points
- How to use dot plot
- Tram track appearance - Physiological signal oversensing
- Distance between tracks, sum of tracks
Case series 3 - Extracardiac noise
Diaphragmatic myopotentials
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
Car Alternator
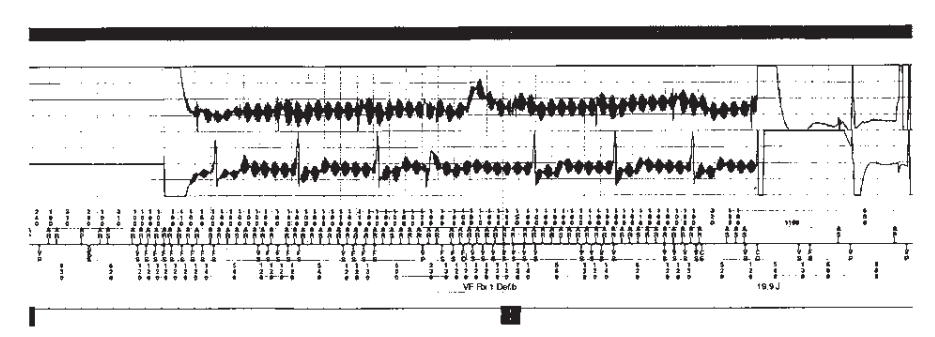
Lead Fracture
Learning Points
- External noise usually seen in all leads
- Not related to cardiac cycle
- High amplitudes with amplifier saturation - Lead fracture
- History of surroundings and activity at time of therapy
Inappropriate therapy
- Non physiological signals
- Physiological, non-arrhythmic signals
- Intracardiac
- T wave (small RR alternation)
- QRS double counting (Na blockers, high heart rate)
- P wave sensing (children, long PR, lead dislodgement)
- Extracardiac
- No relation to cardiac cycle
- Greater signal on widely spaced electrodes
- Lead connector problems - small part of cycle, saturates amplifier
- Intracardiac
- Non ventricular arrhythmias