
Narrow QRS Tachycardia in Children
Raja Selvaraj MD DNB FCE (Toronto)
Cardiac Electrophysiologist
Professor of Cardiology
JIPMER
Introduction
Narrow QRS tachycardia in children
- Not a very common presentation
- Can be a challenging scenario
- Step wise approach
- ECG at presentation
- Adenosine
- ECG in sinus rhythm
- Acute management
- Long term management
Case
- 9 year old boy
- Palpitations since 2 hours
- Otherwise comfortable
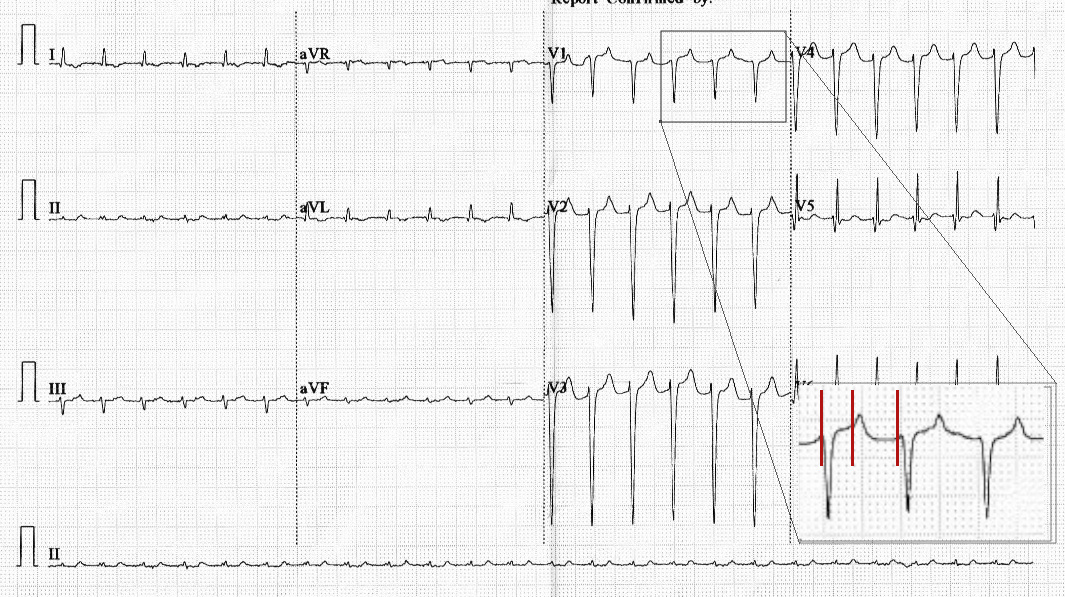
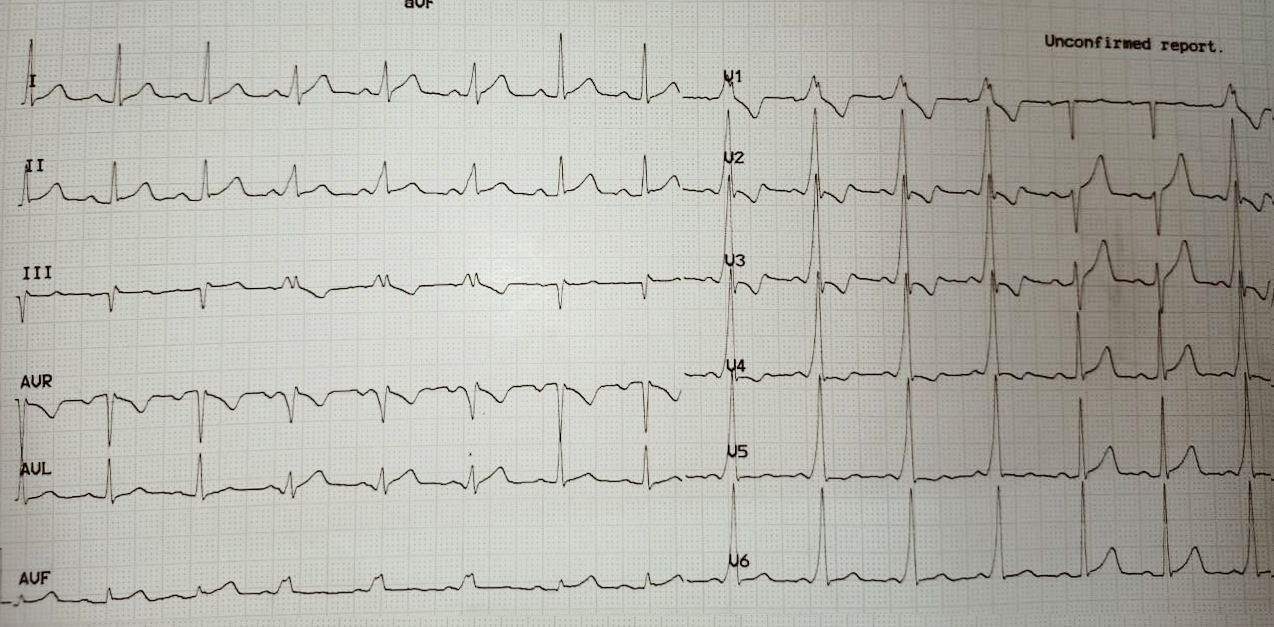
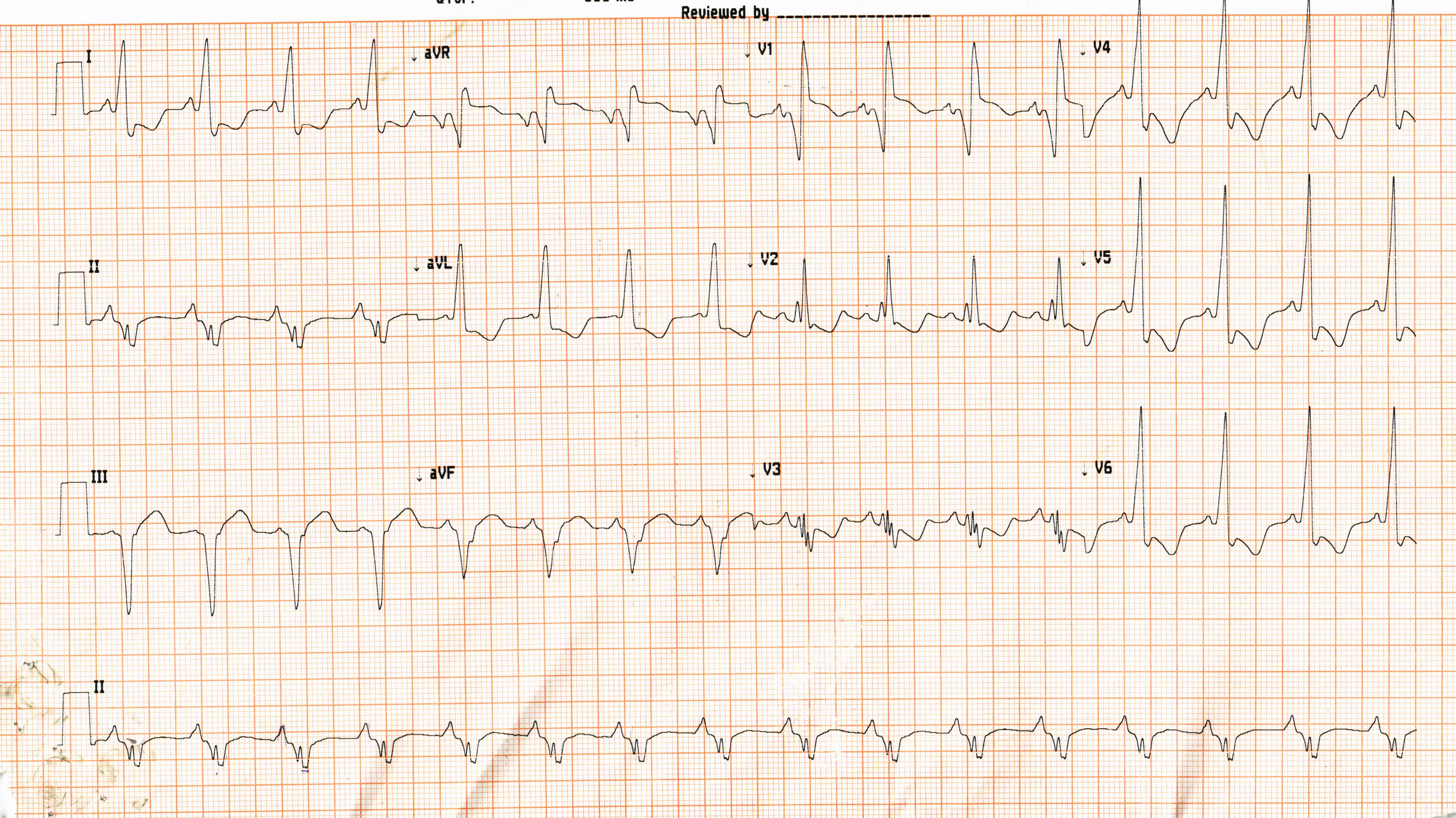
ECG at presentation
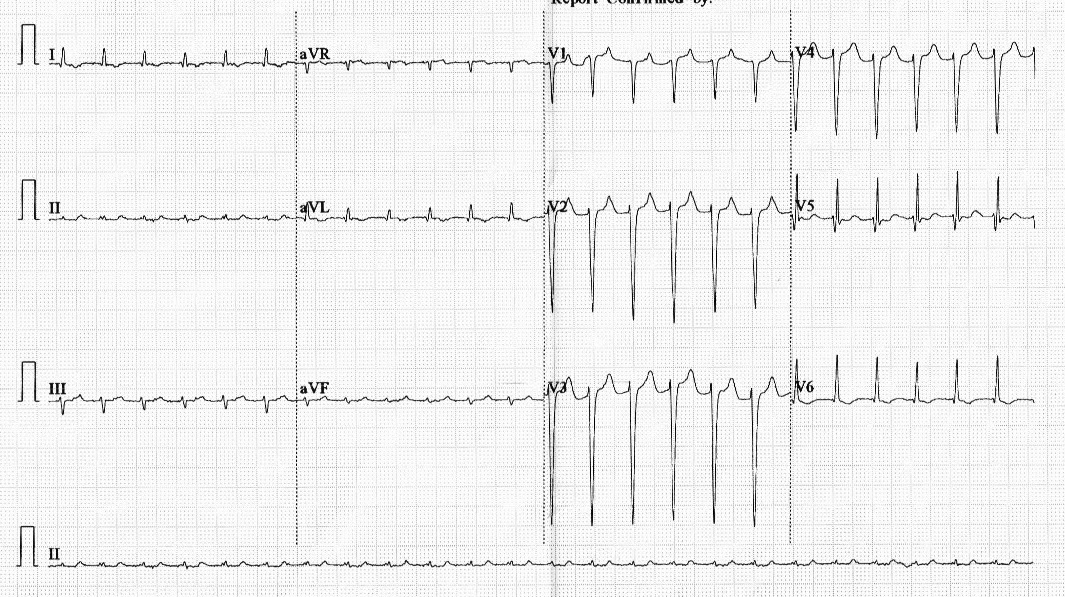
Differential diagnoses
- Atrial tachycardia
- Focal atrial tachycardia
- Atrial flutter
- Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia
- Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia
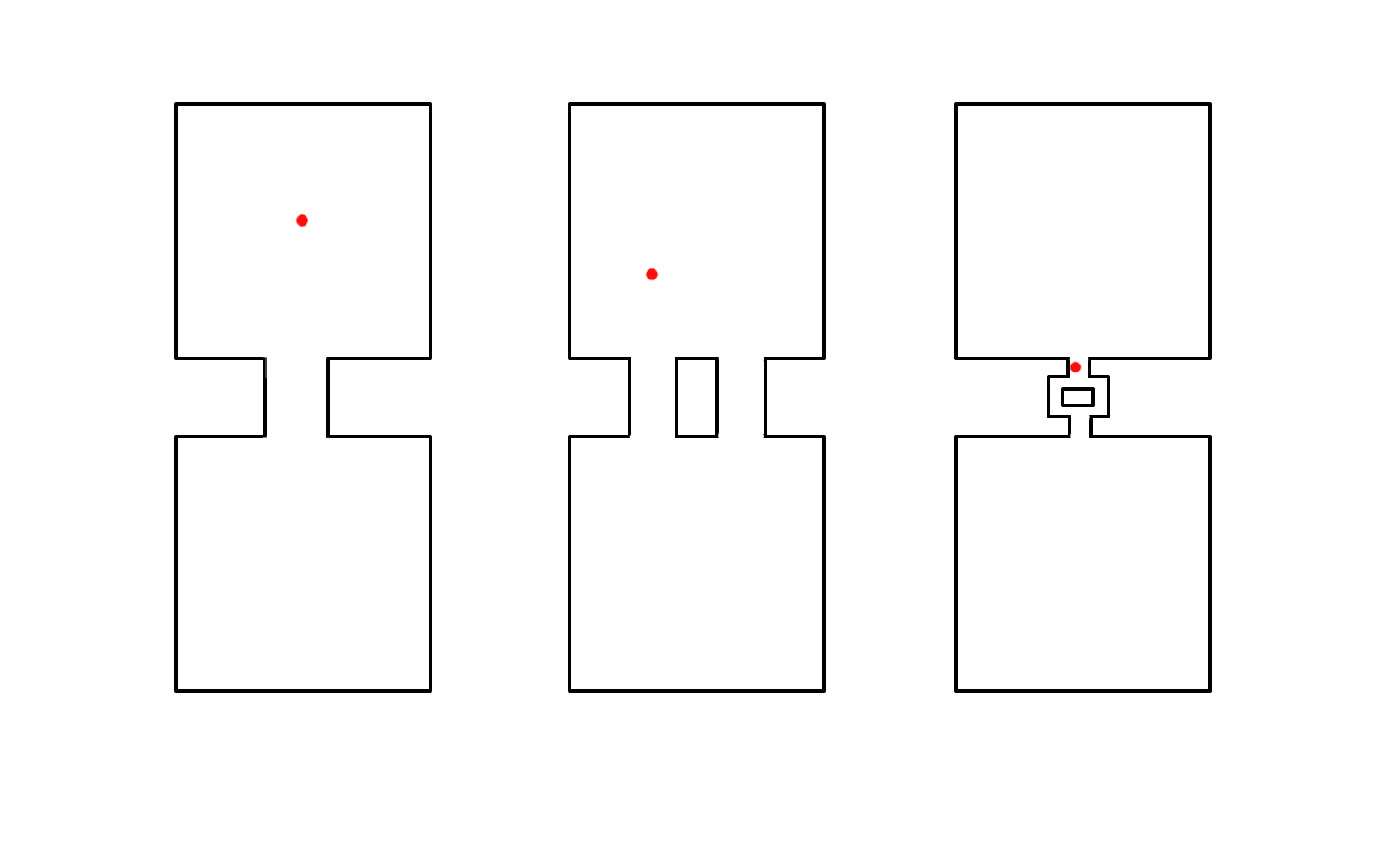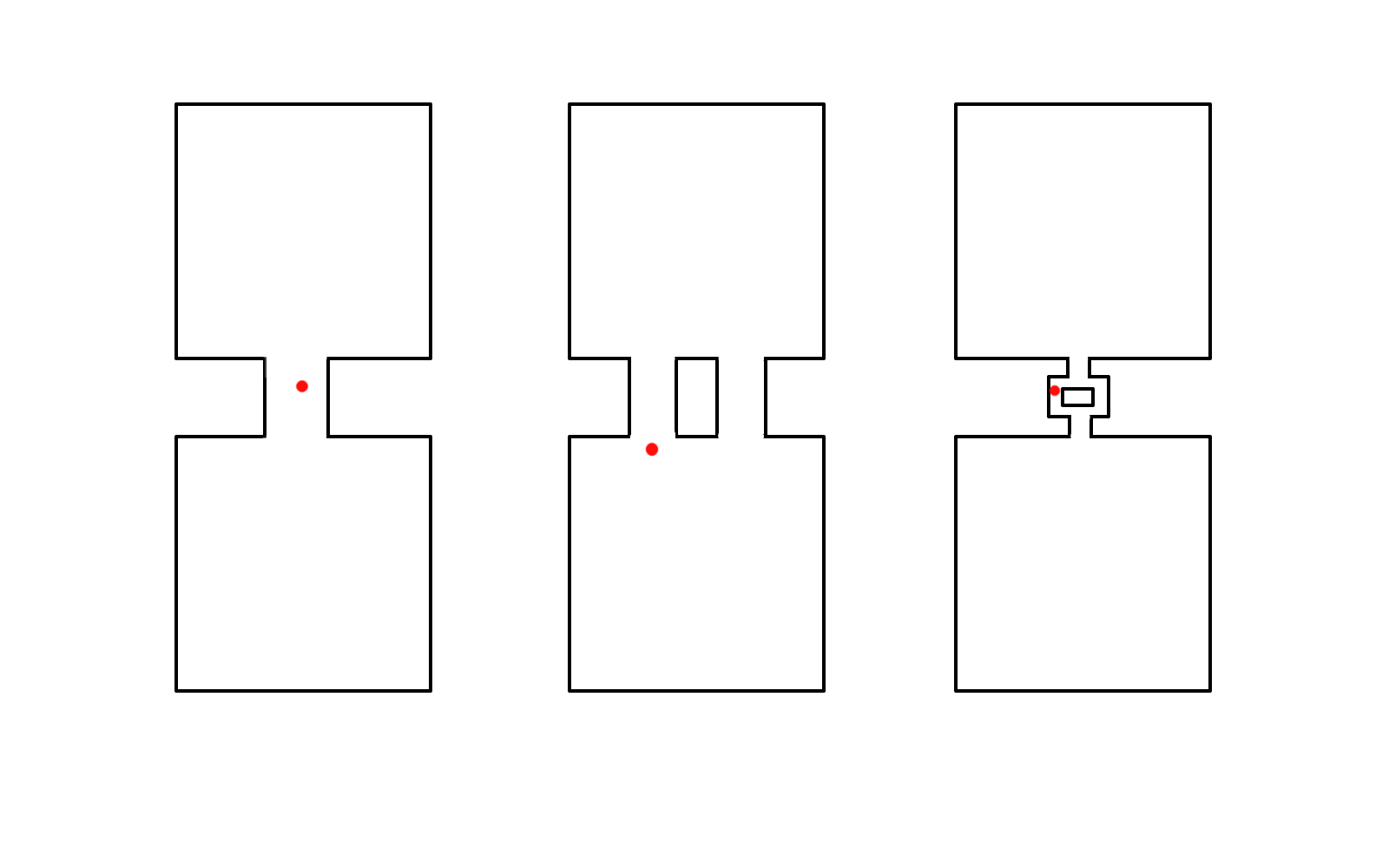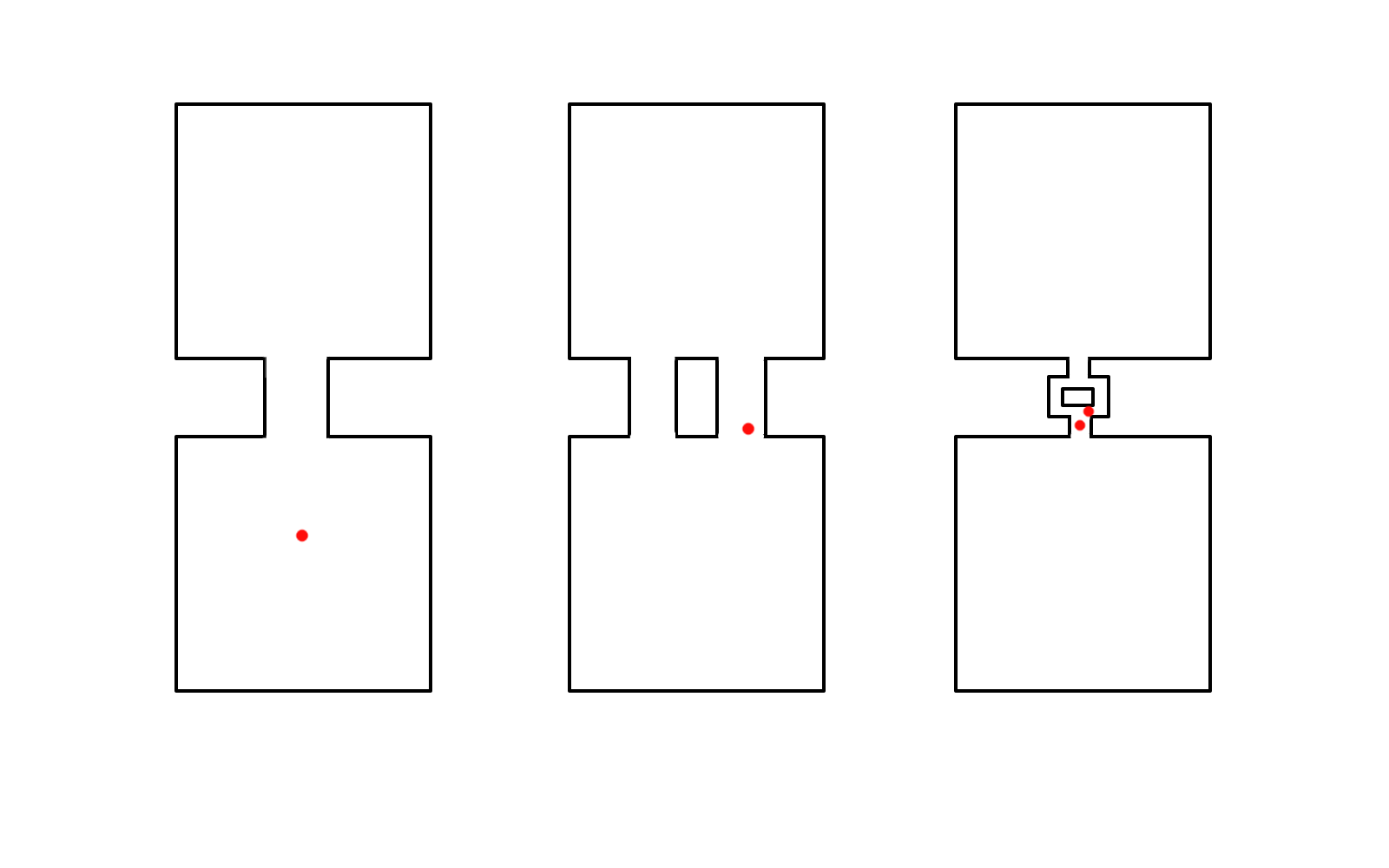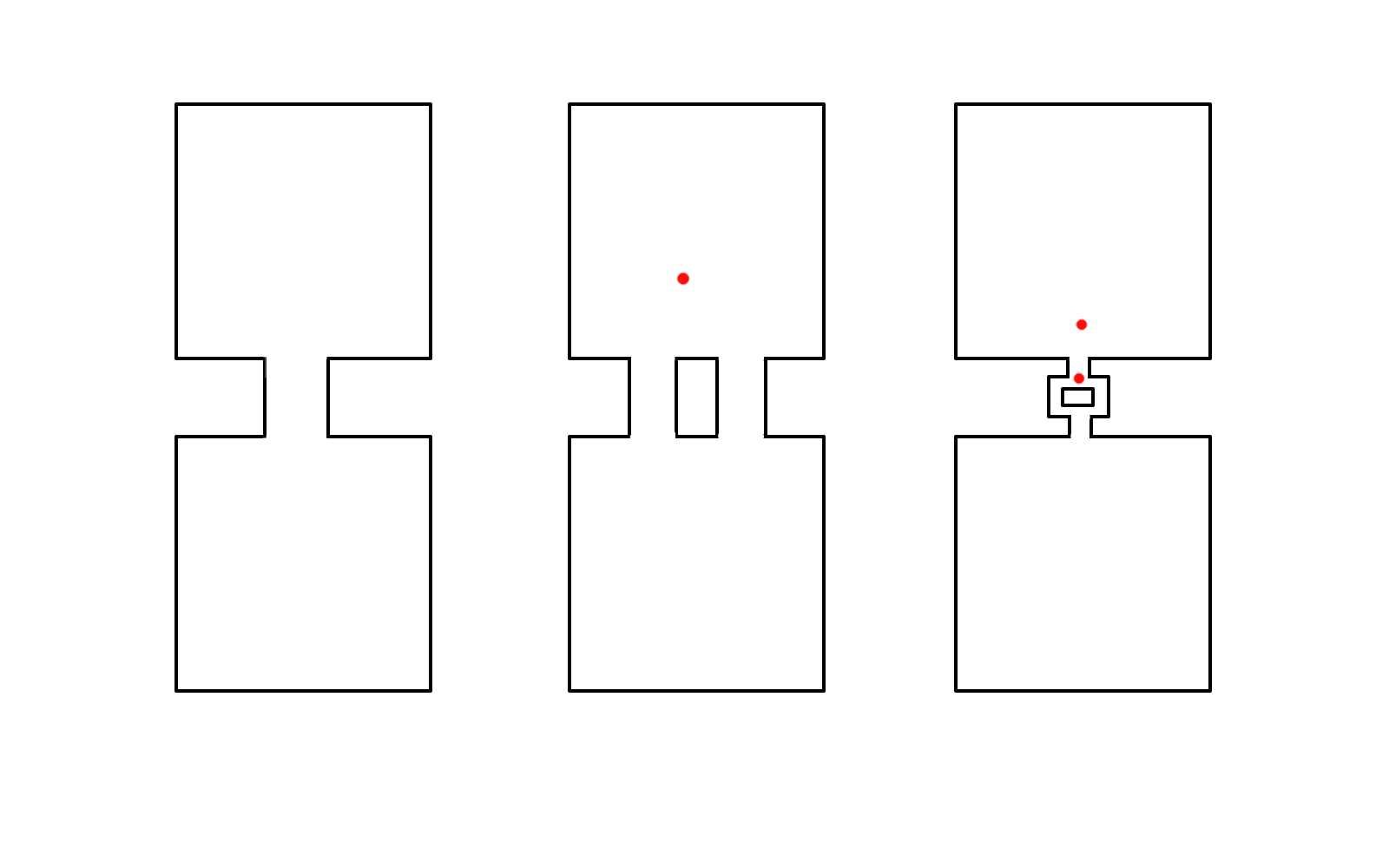
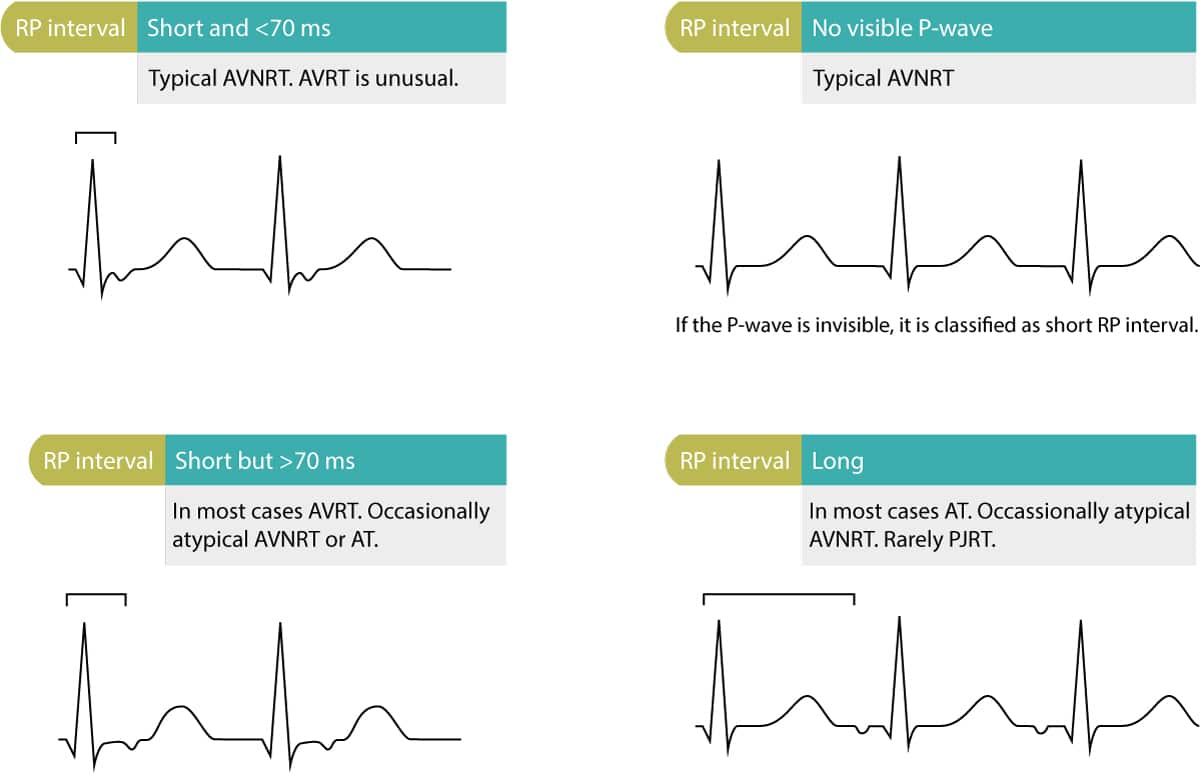
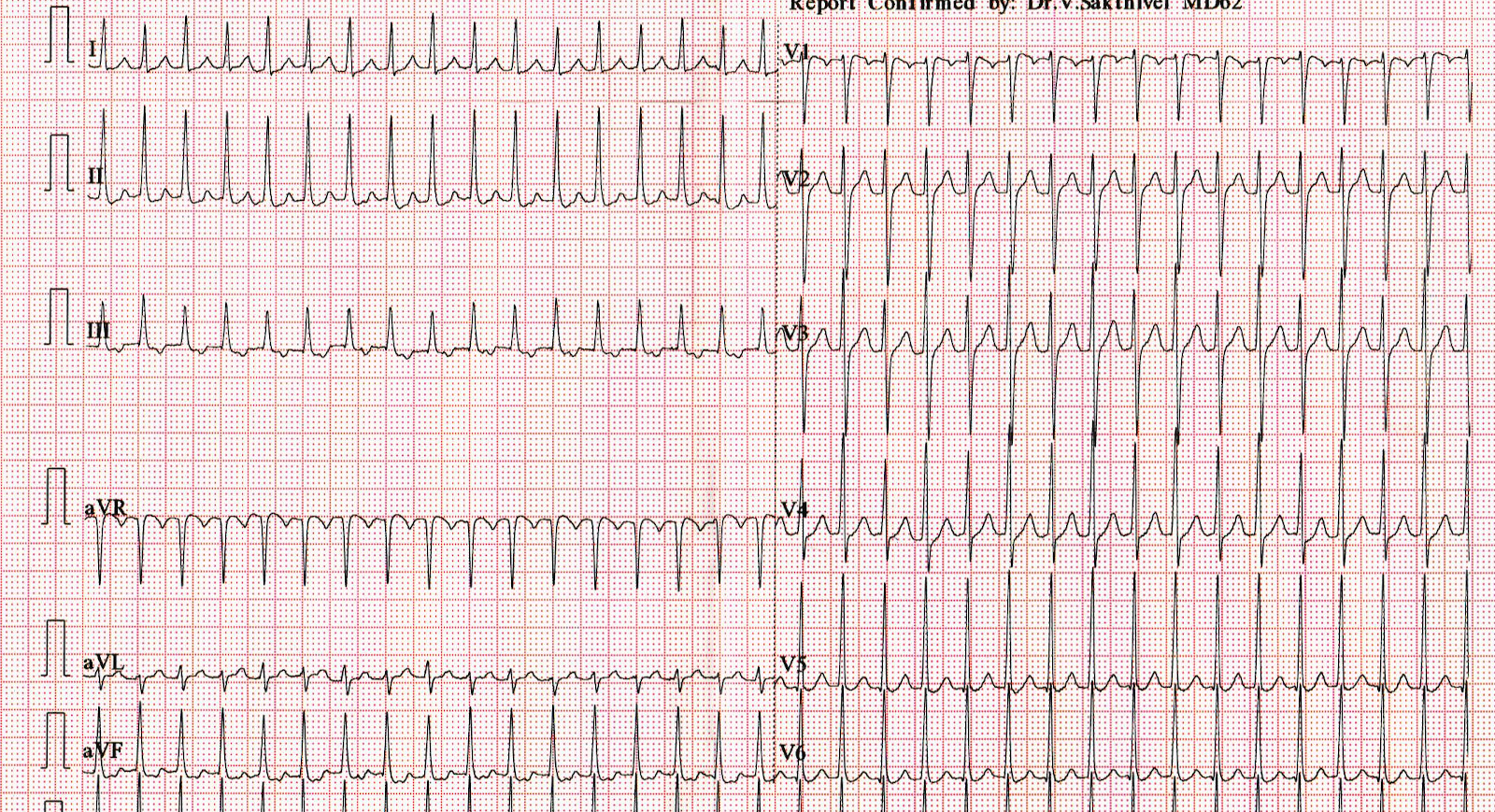
So how do we proceed ?
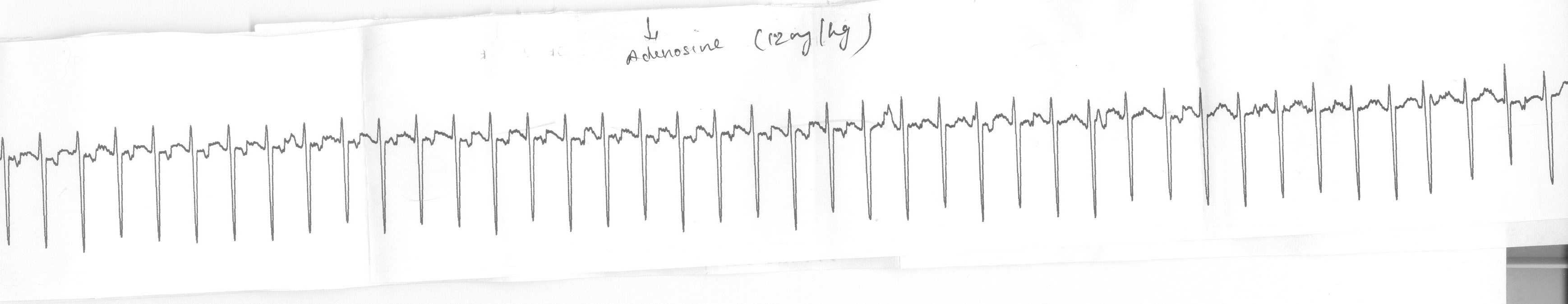
- Should be initial drug of choice in most patients with NQRST (and also WQRST)
- May terminate tachycardia
- Reponse provides information on mechanism of tachycardia
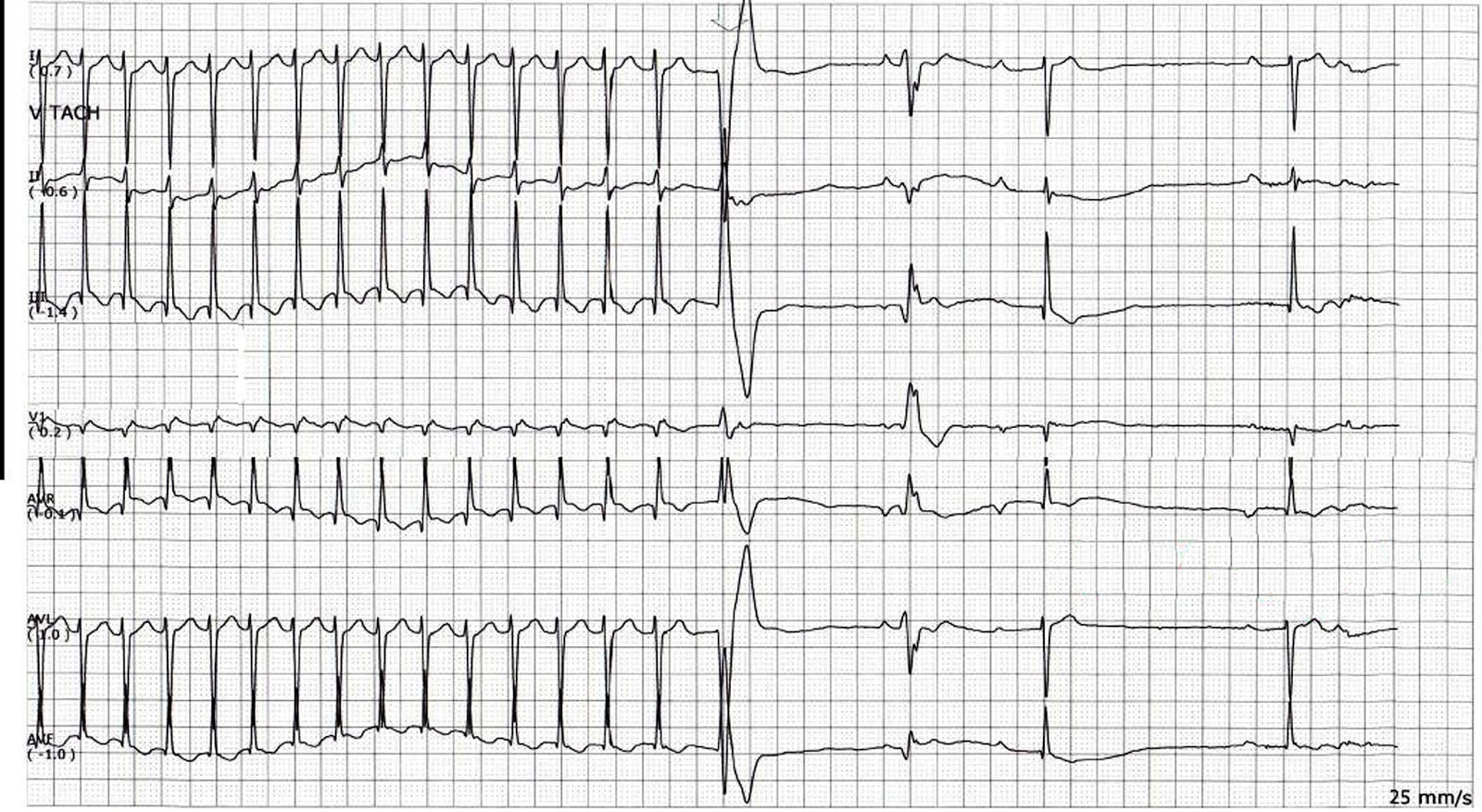
Tachycardia termination - What it tells us
- Mechanism is reentry
- AV junction dependent tachycardia
- Some atrial tachycardias may also terminate
"No change in tachycardia"
- Transient AV block with slowing of rate - not recognised
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Not administered properly
Administration of adenosine
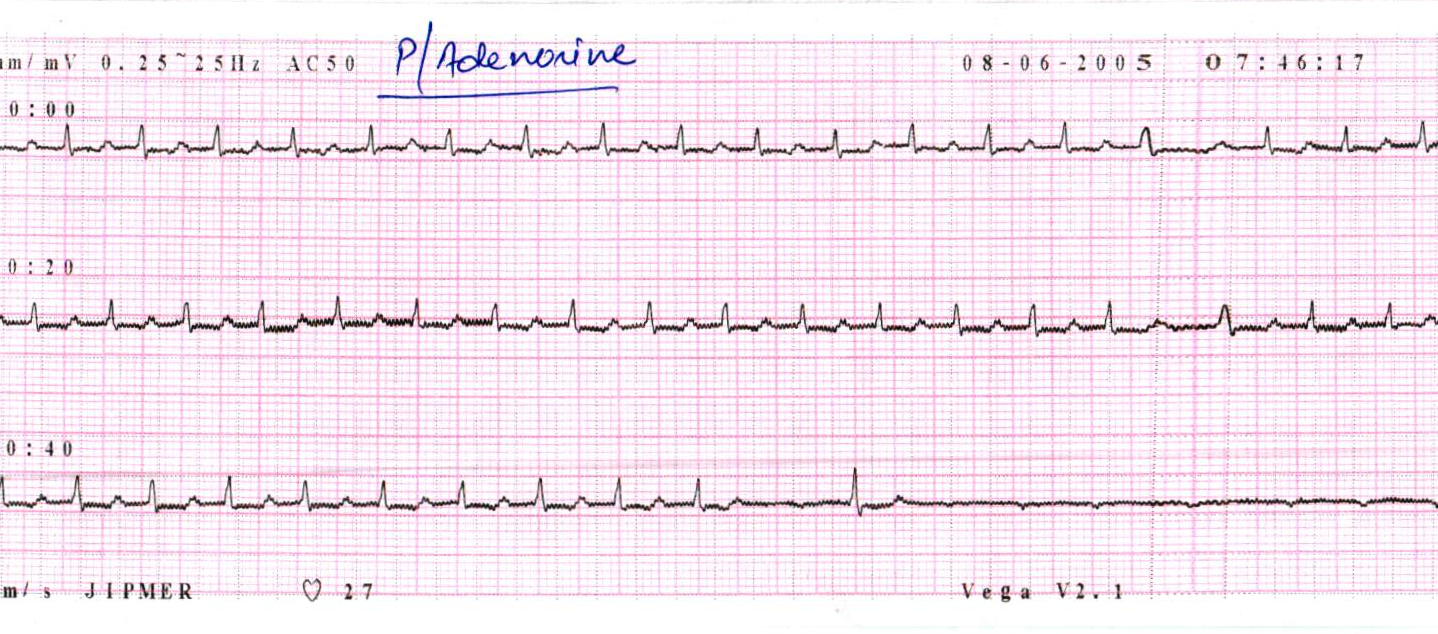
Tachycardia continuation with AV block
- AV junction independent tachycardia
- Atrial tachycardia / flutter
- Rate control possible
Tachycardia terminates and immediately reinitiates
- Differentiate ventricular rate slowing
- Termination indicates reentry, reinitiation because of frequent PACs usually
- Higher doses will not help !
- DC Cardioversion will not help !
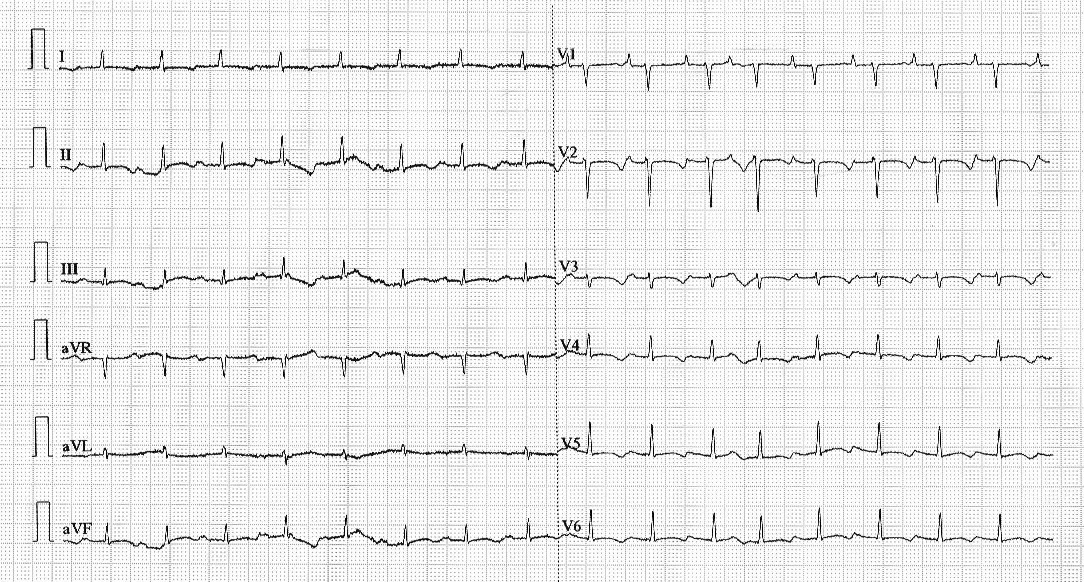
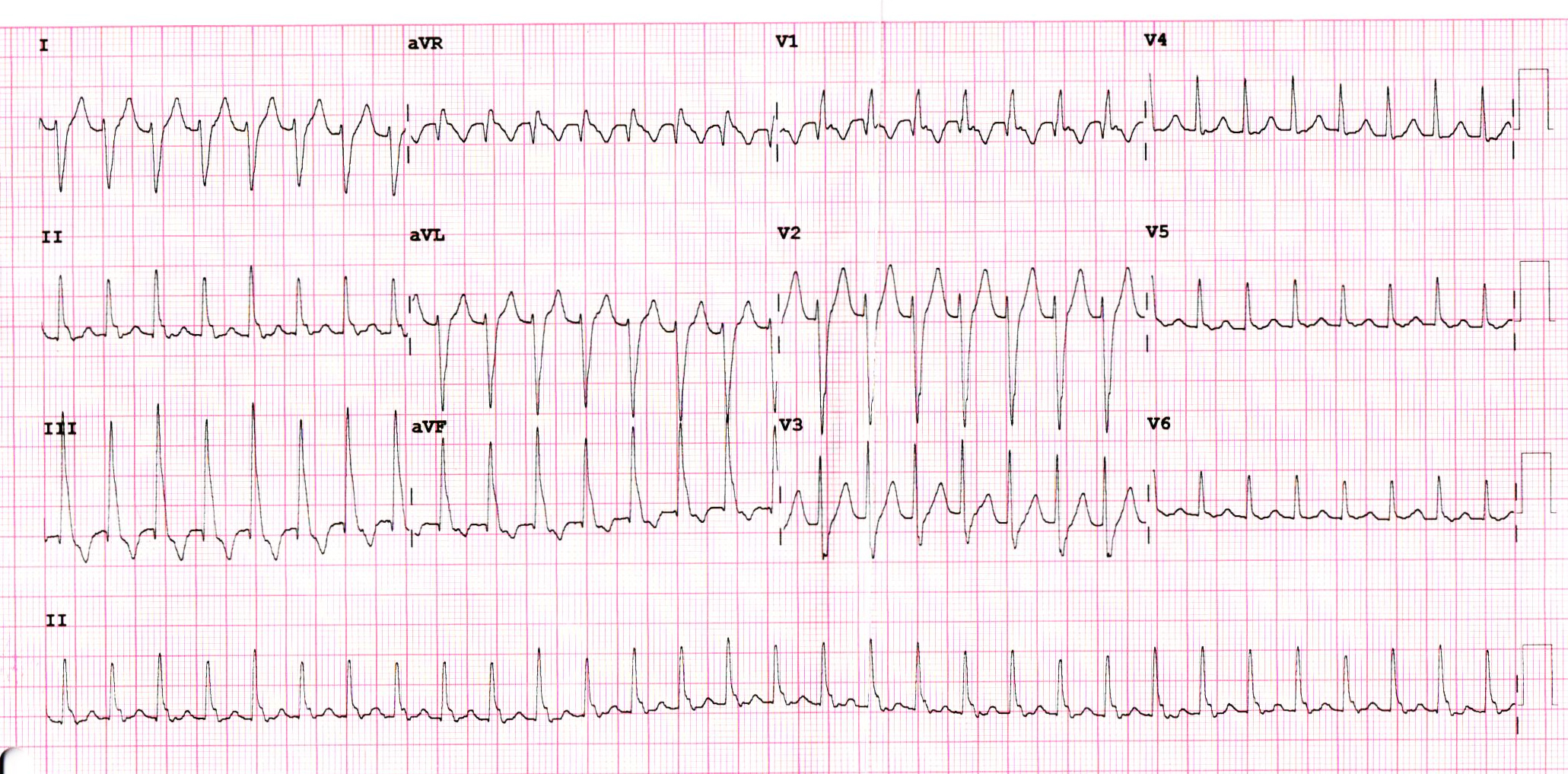
Learning from the sinus rhythm ECG
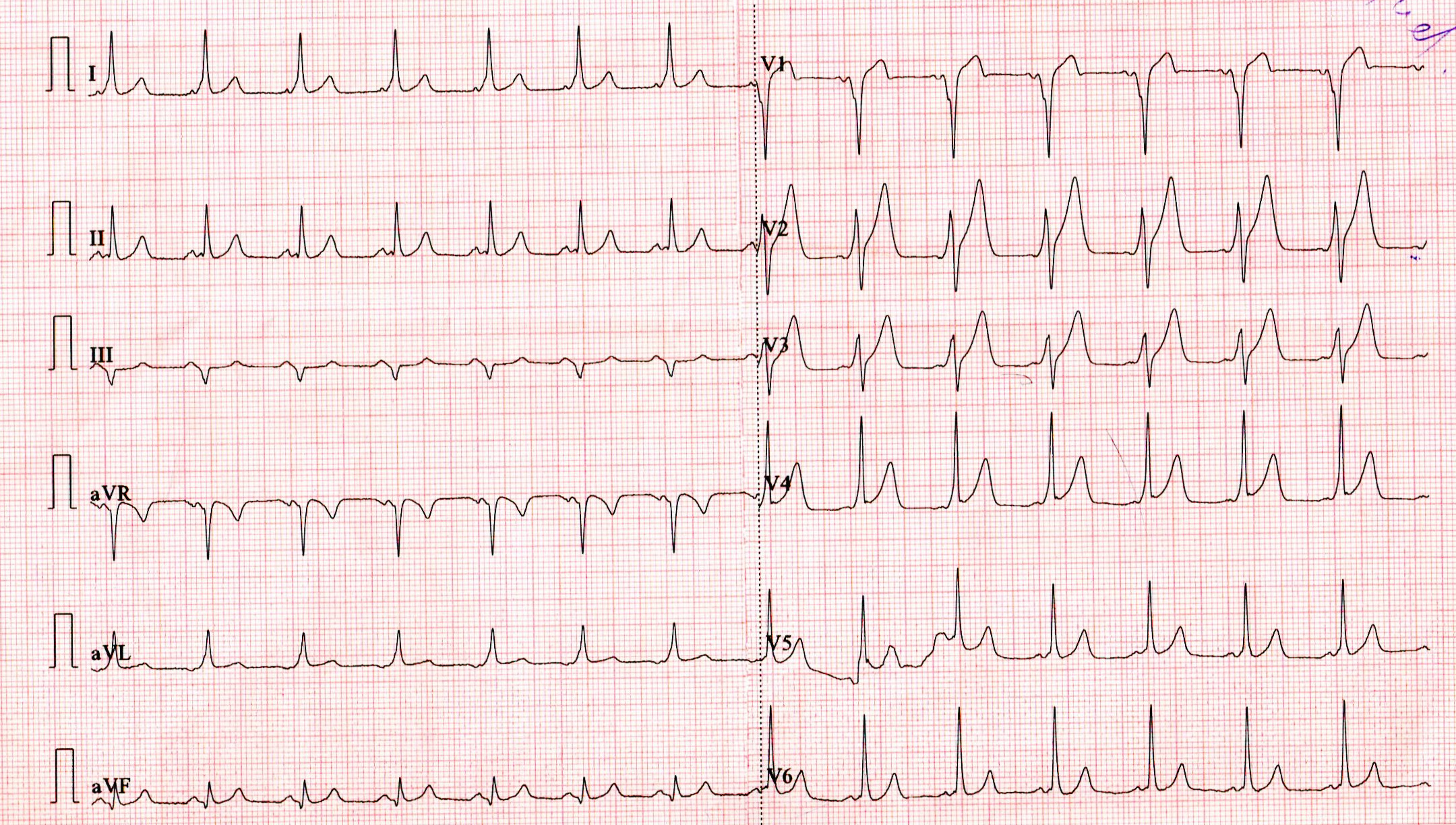
Long term management
EP study / ablation
- Preexcitation - needs evaluation (non invasive or invasive)
- Recurrent tachycardia, especially drug refractory
- Incessant tachycardia / LV dysfunction
- Avoided in very young unless absolutely required
Intermittent preexcitation
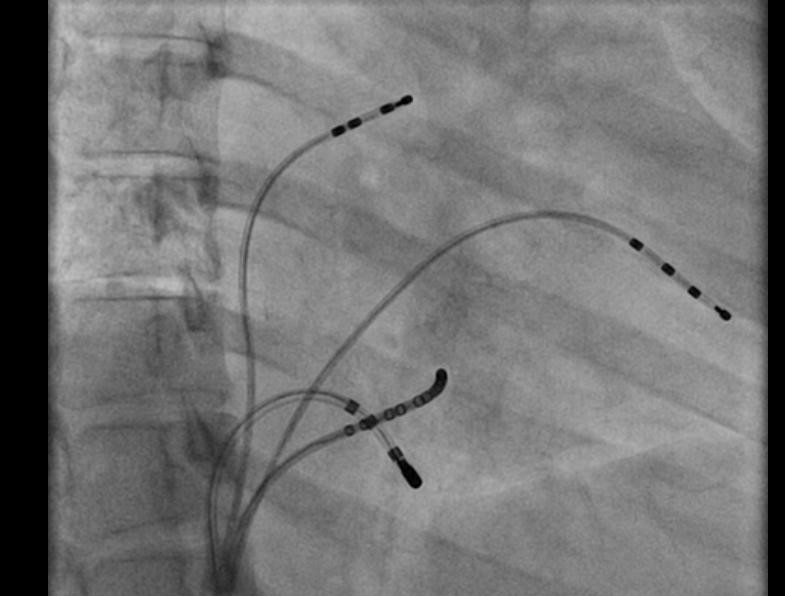
RF ablation
Pharmacologic management
- Beta blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Digoxin
- Amiodarone
- Flecainide
- Ivabradine
Miscellaneous
Ebsteins anomaly
Fascicular VT
VA block with Adenosine
Summary and learning points
- Adenosine - Diagnostic and therapeutic
- Preexcitation - Alters prognosis and management strategies
- RF ablation highly effective - Known when to refer for the same