Difficult Accessory Pathway Ablation

Raja Selvaraj
Professor of Cardiology, JIPMER
Rules
- Do not ablate without making a diagnosis
- Do not ablate without mapping completely
- Do not ablate unless you are sure you can recognize and avoid AV block
- Except specific situations, high power ablation does not succeed where low power fails
- Do not ablate for cosmetic reasons
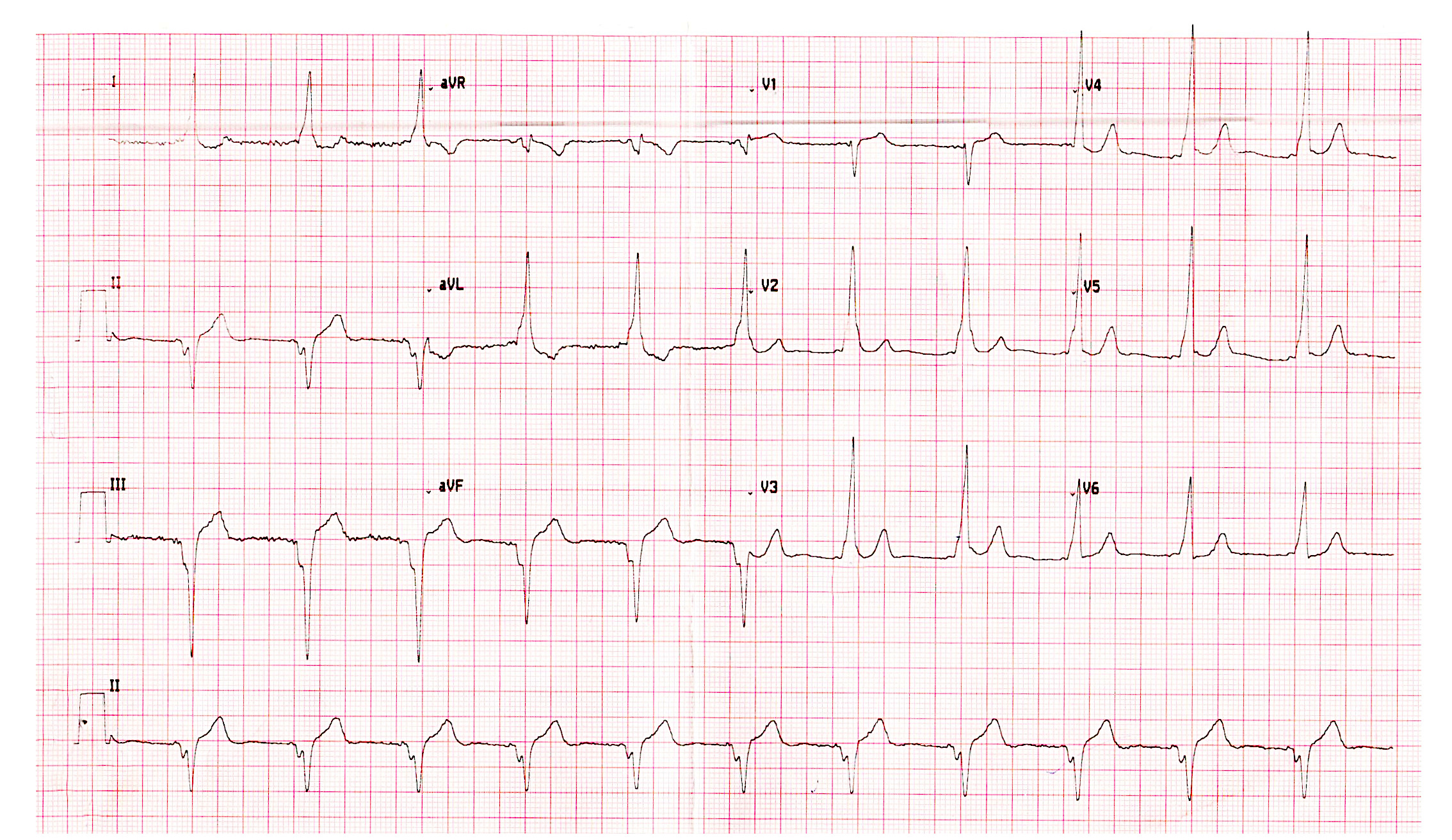
Diagnosis
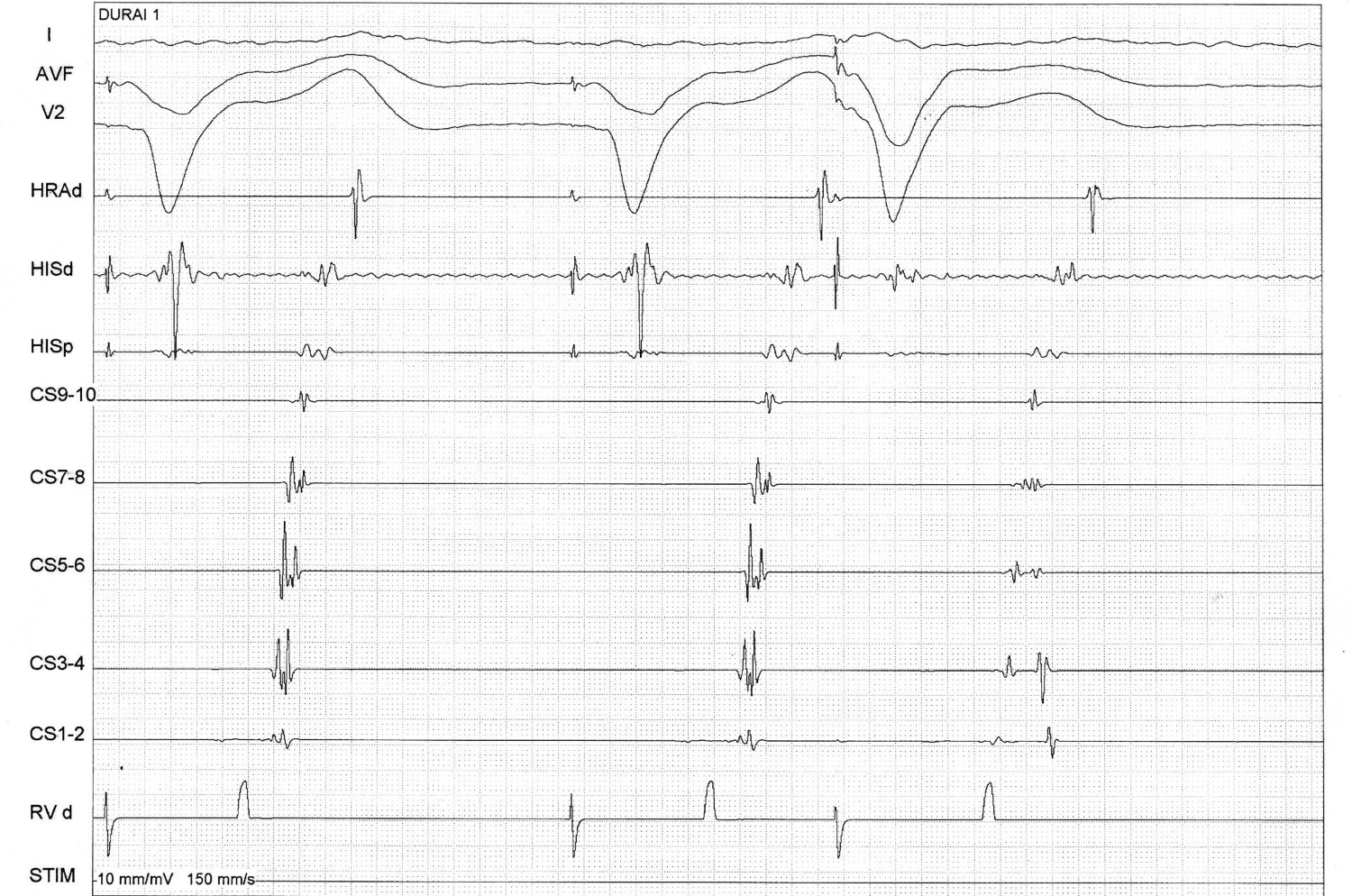
Dont skip the RA catheter
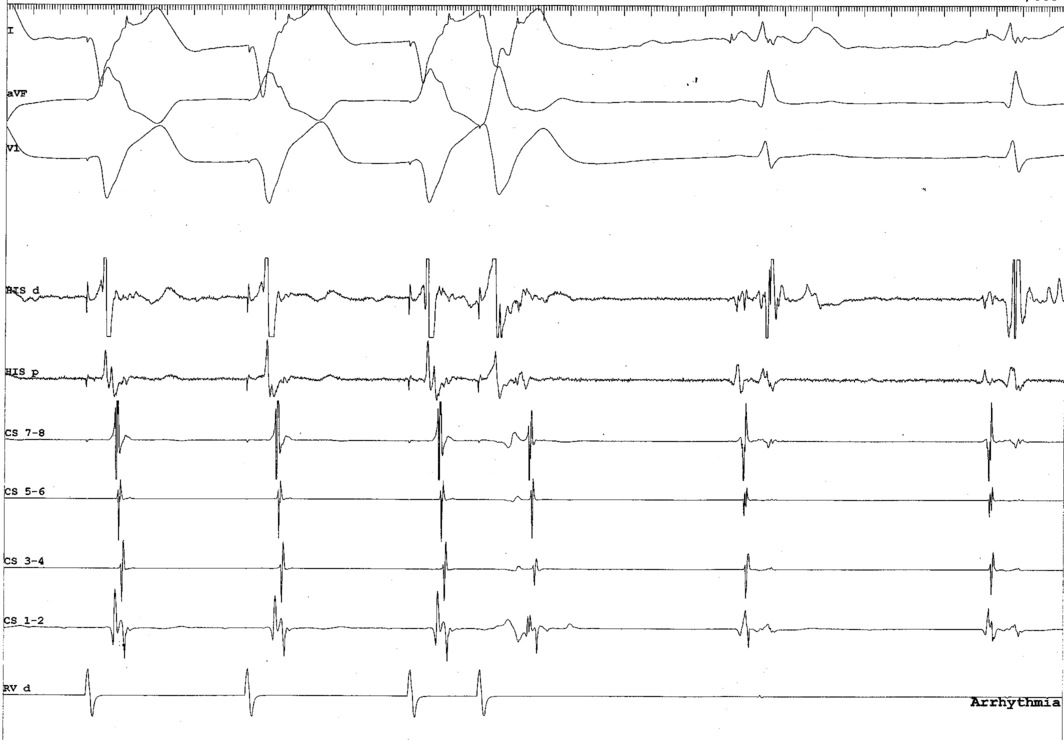
Dont skip the RA catheter
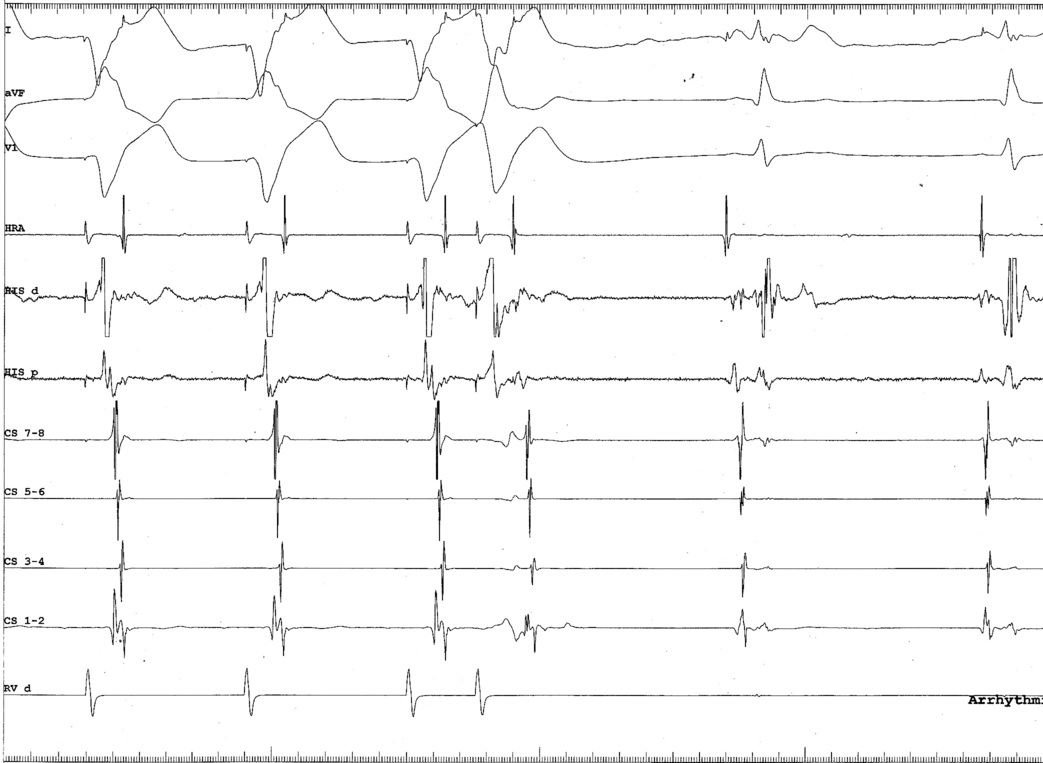
RV catheter at base
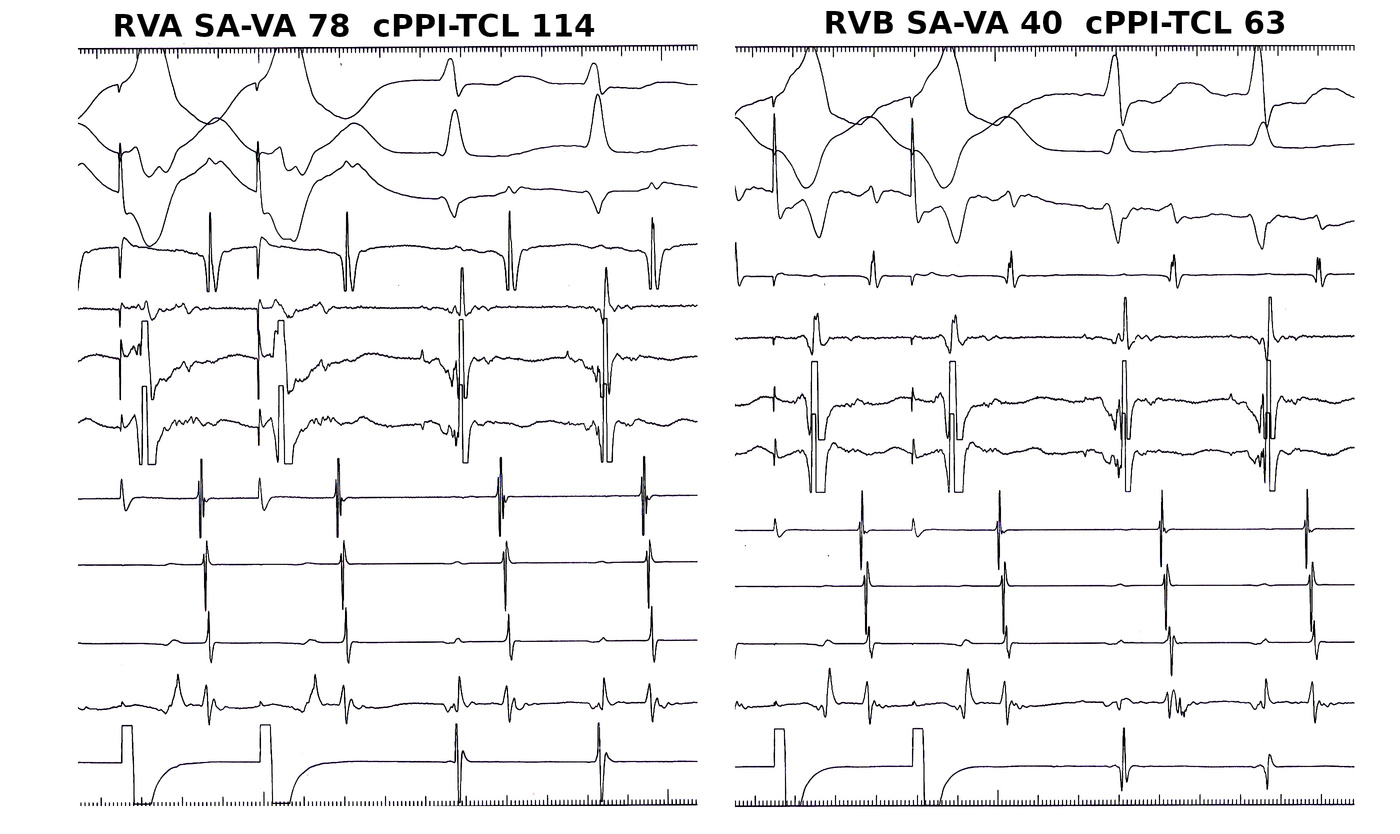
Mapping
Use triggered mode
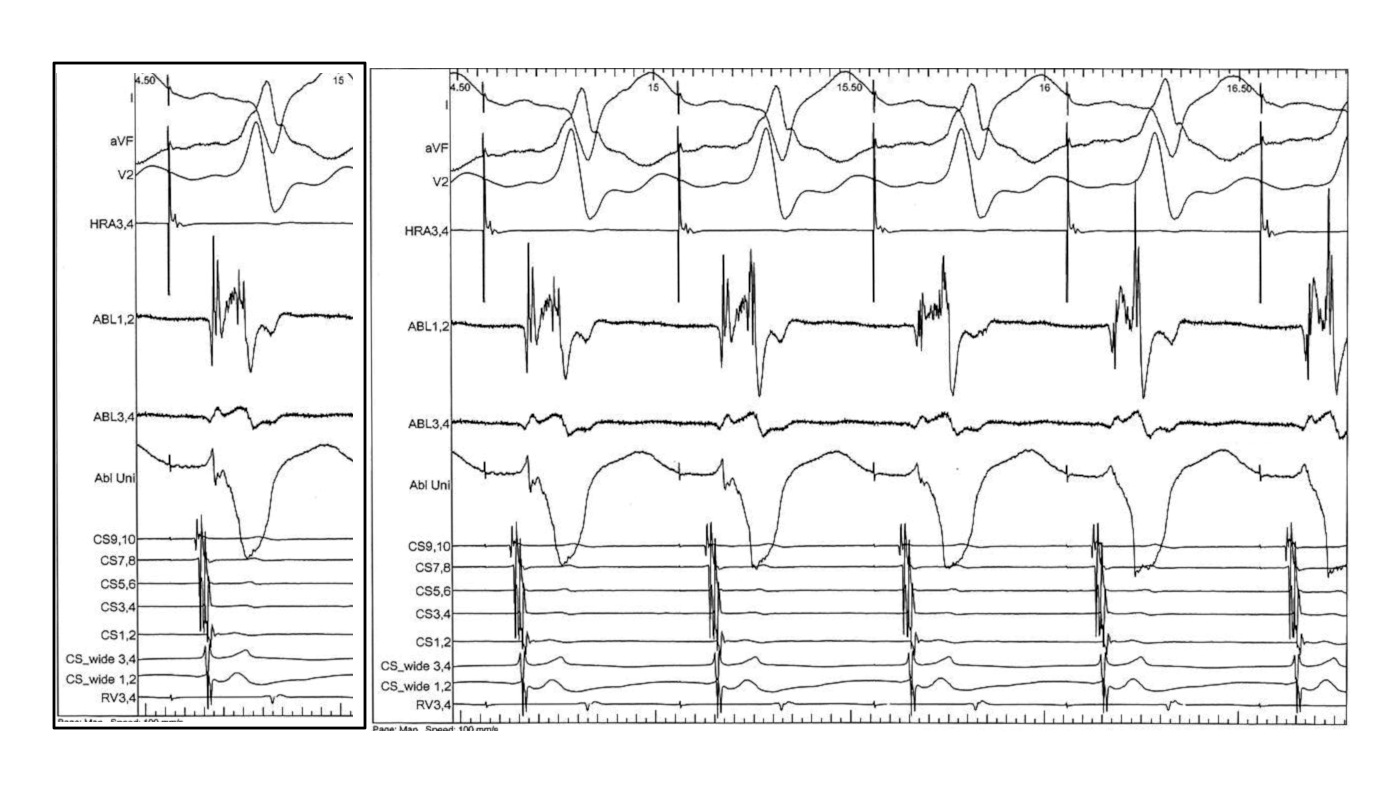
Use unipolar EGMs
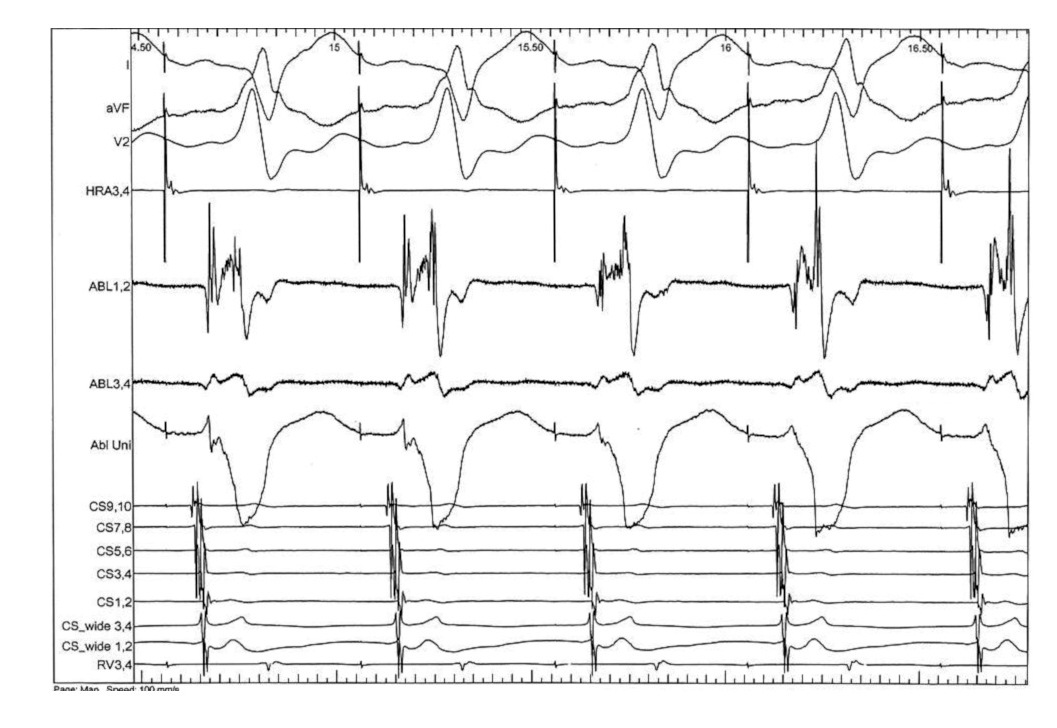
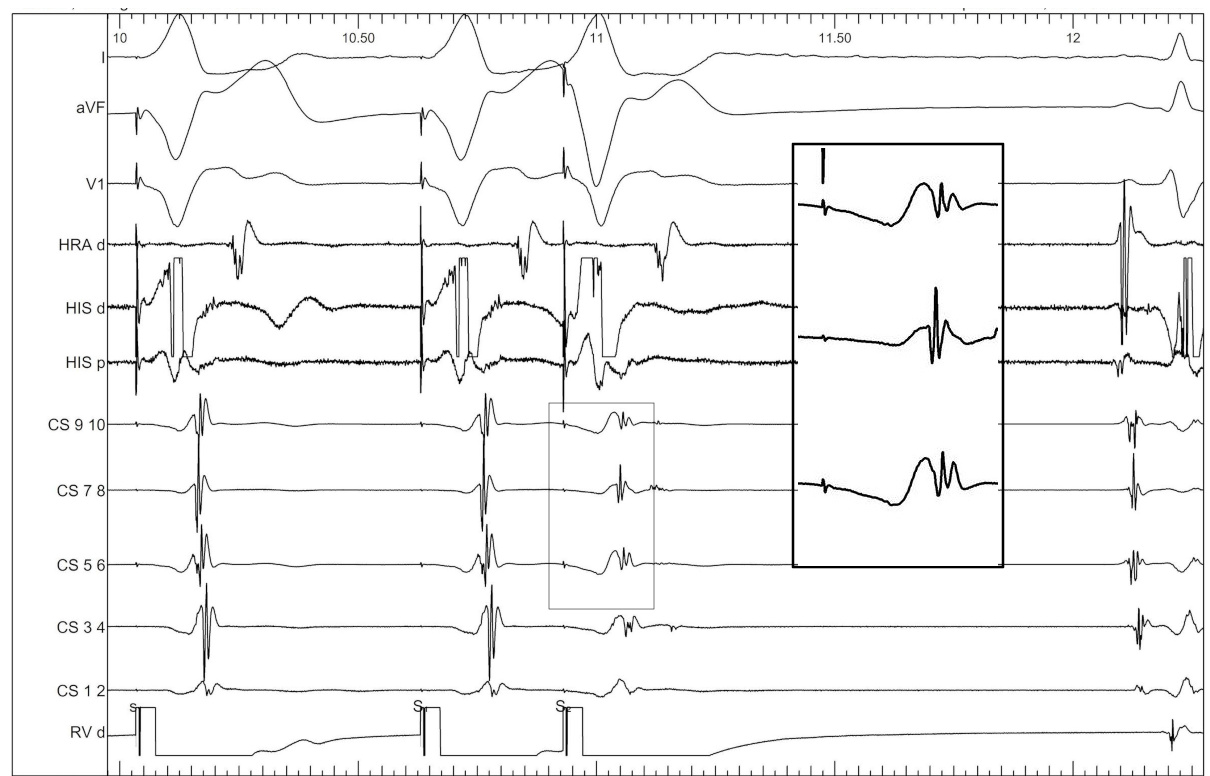
Identify components of the signal
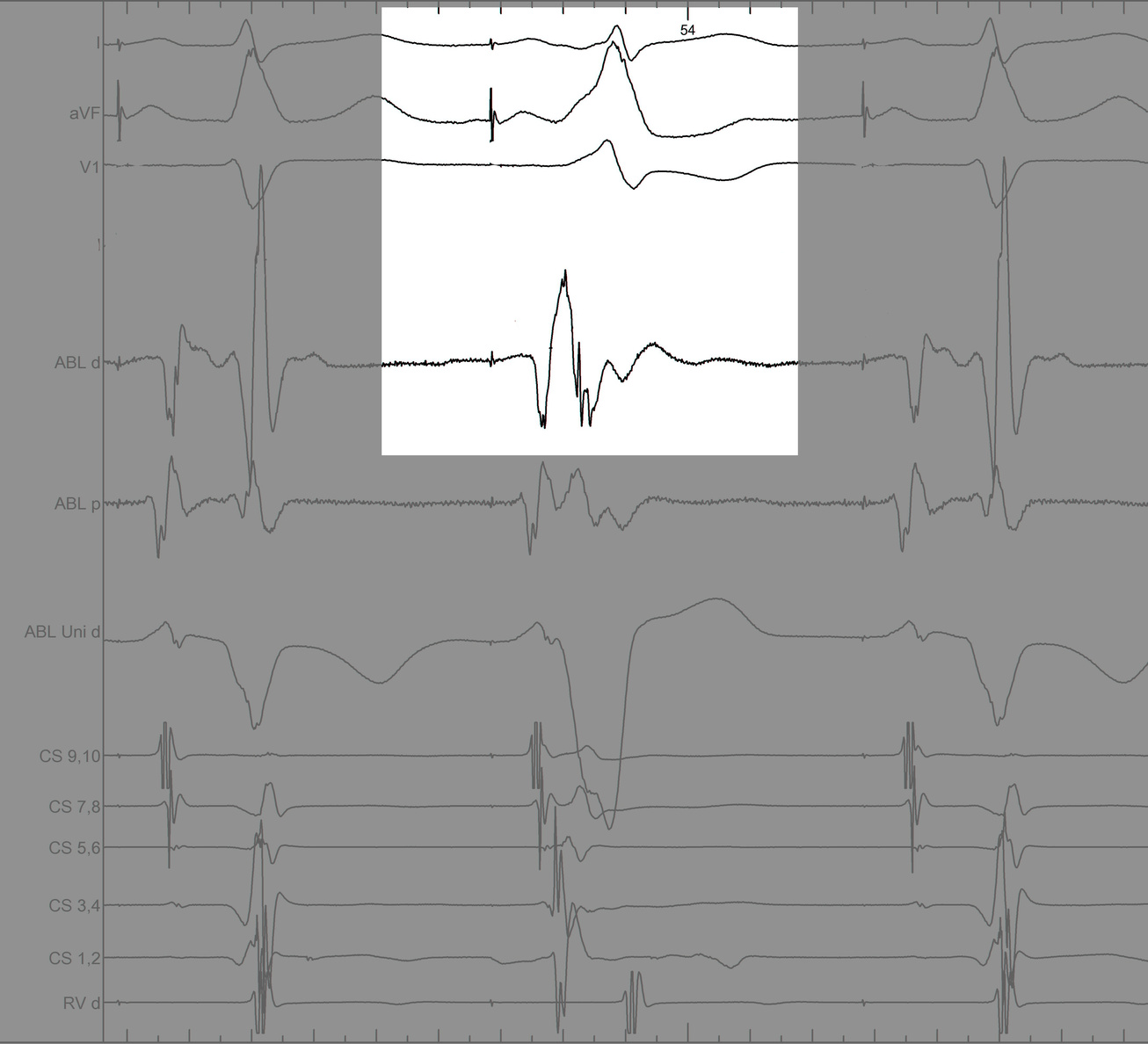
Identify components of the signal
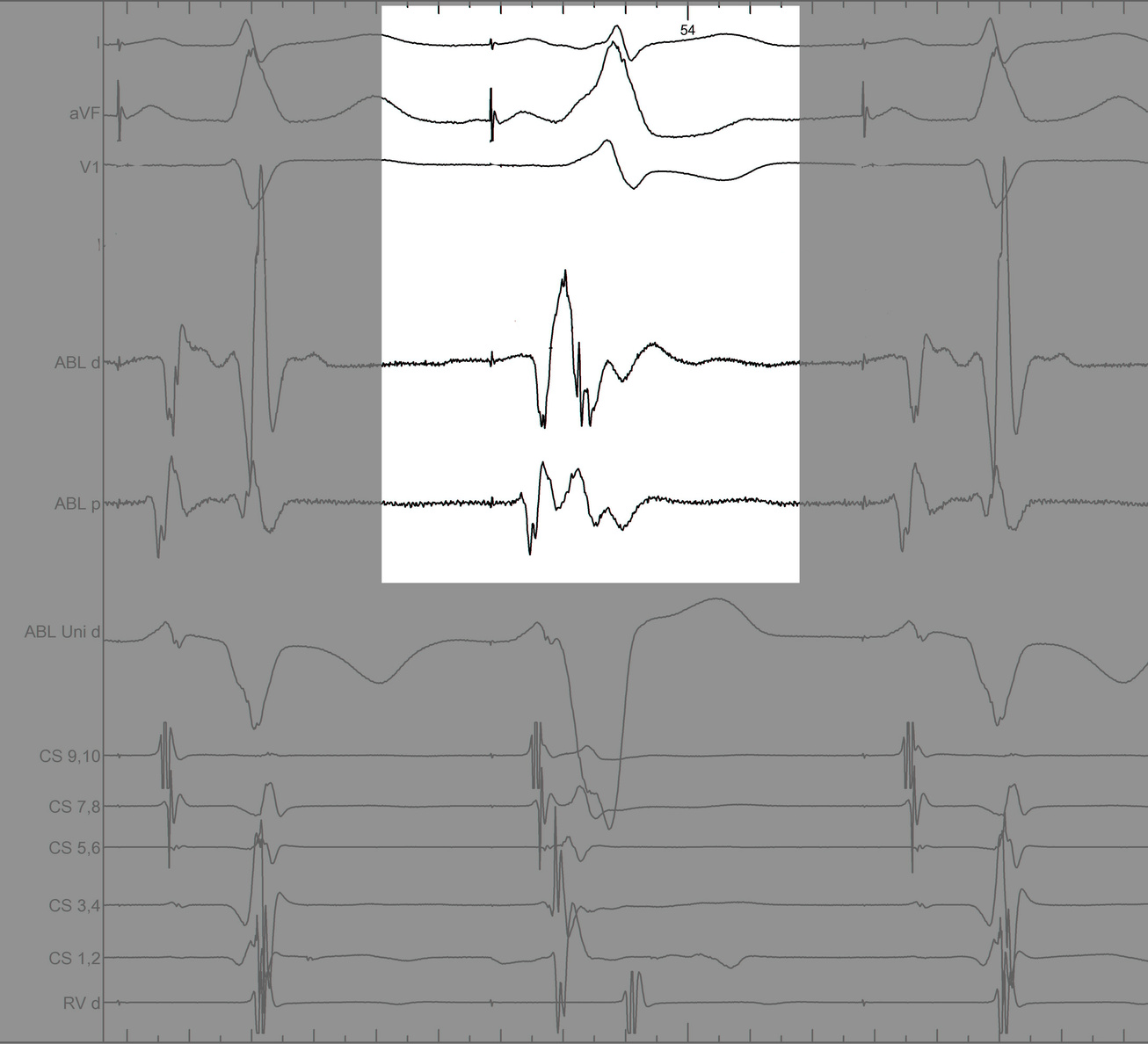
Identify components of the signal
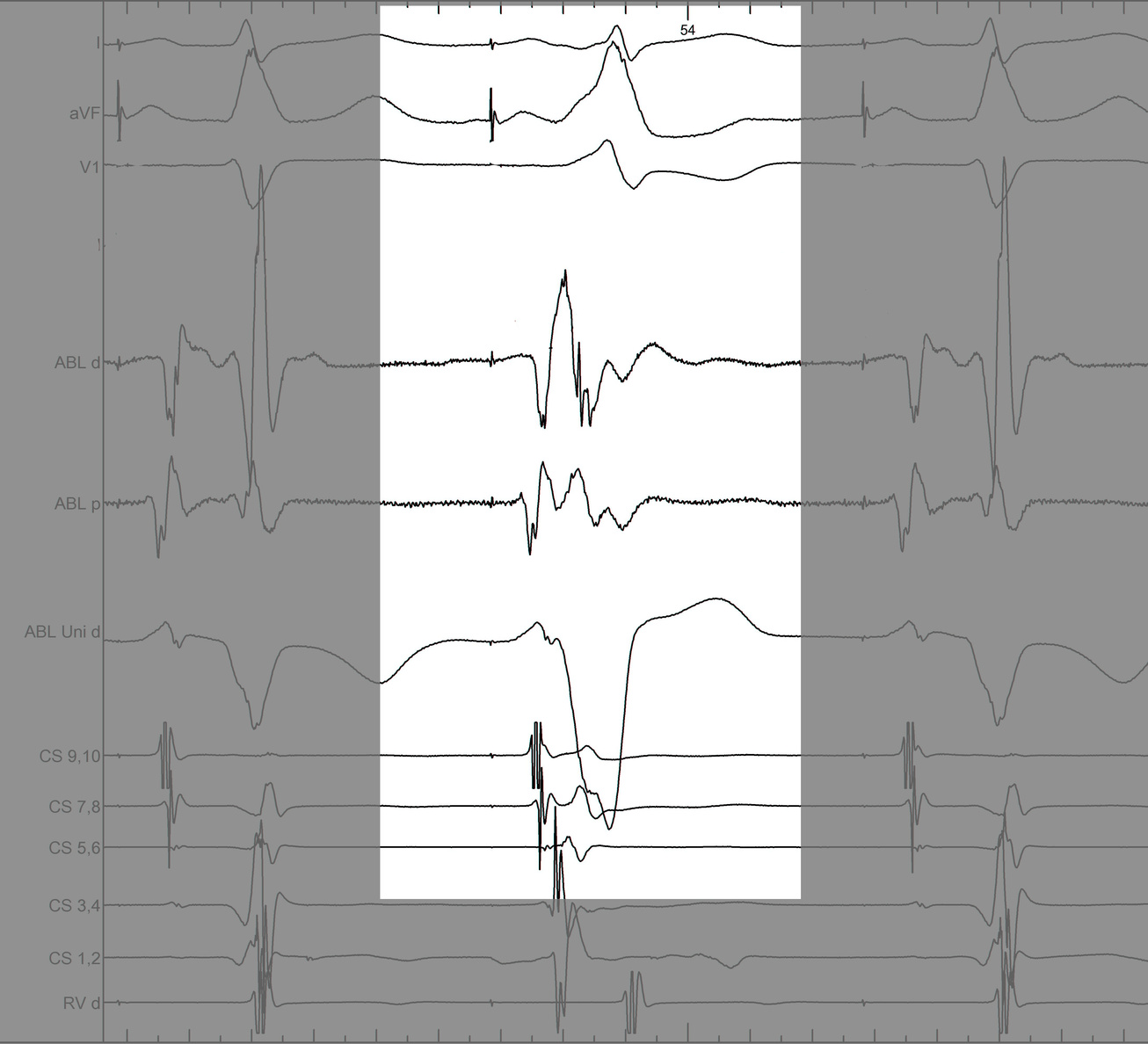
Identify components of the signal
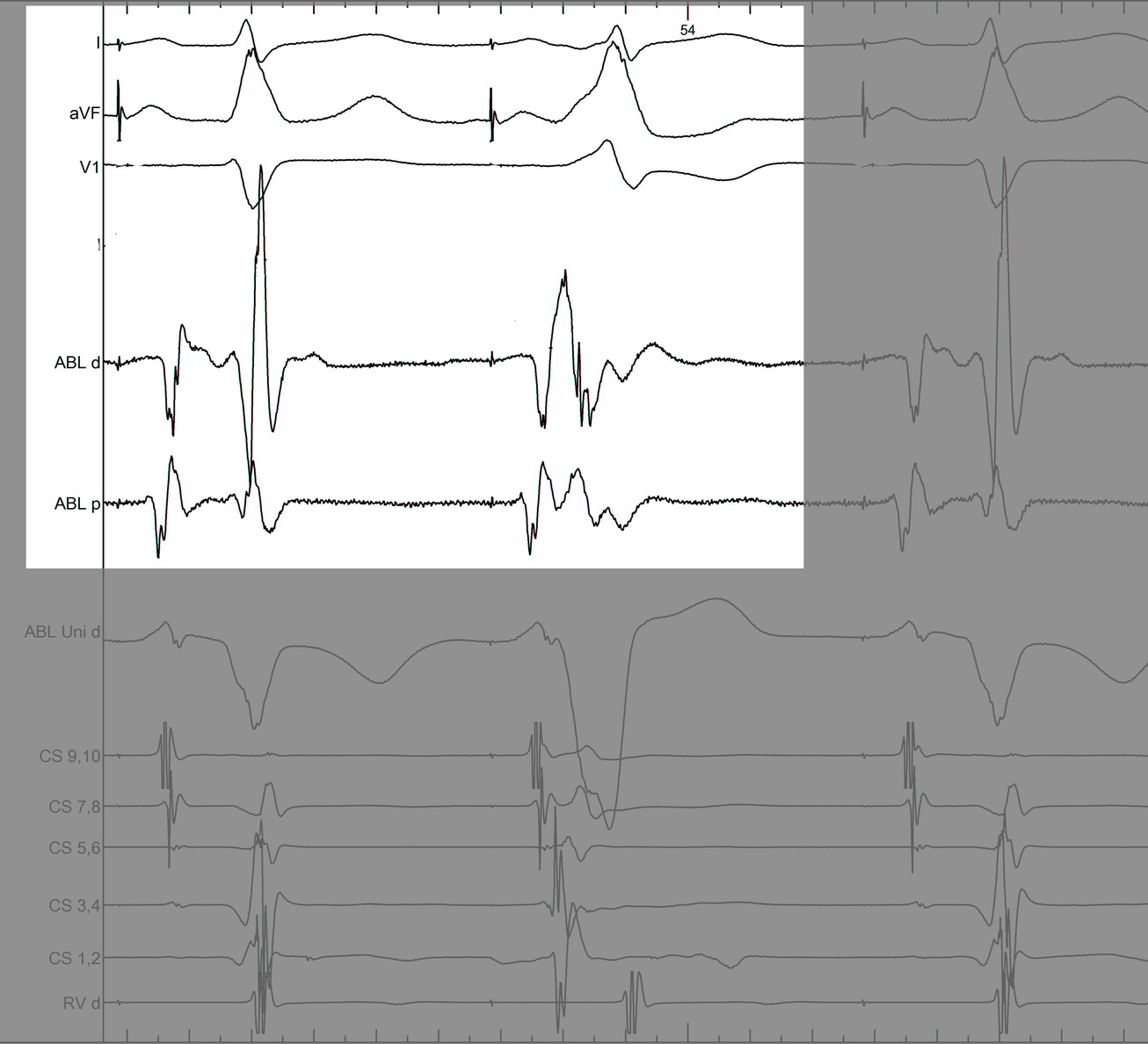
LA-CS potential to identify endocardial / epicardial
LA-CS potential to identify endocardial / epicardial
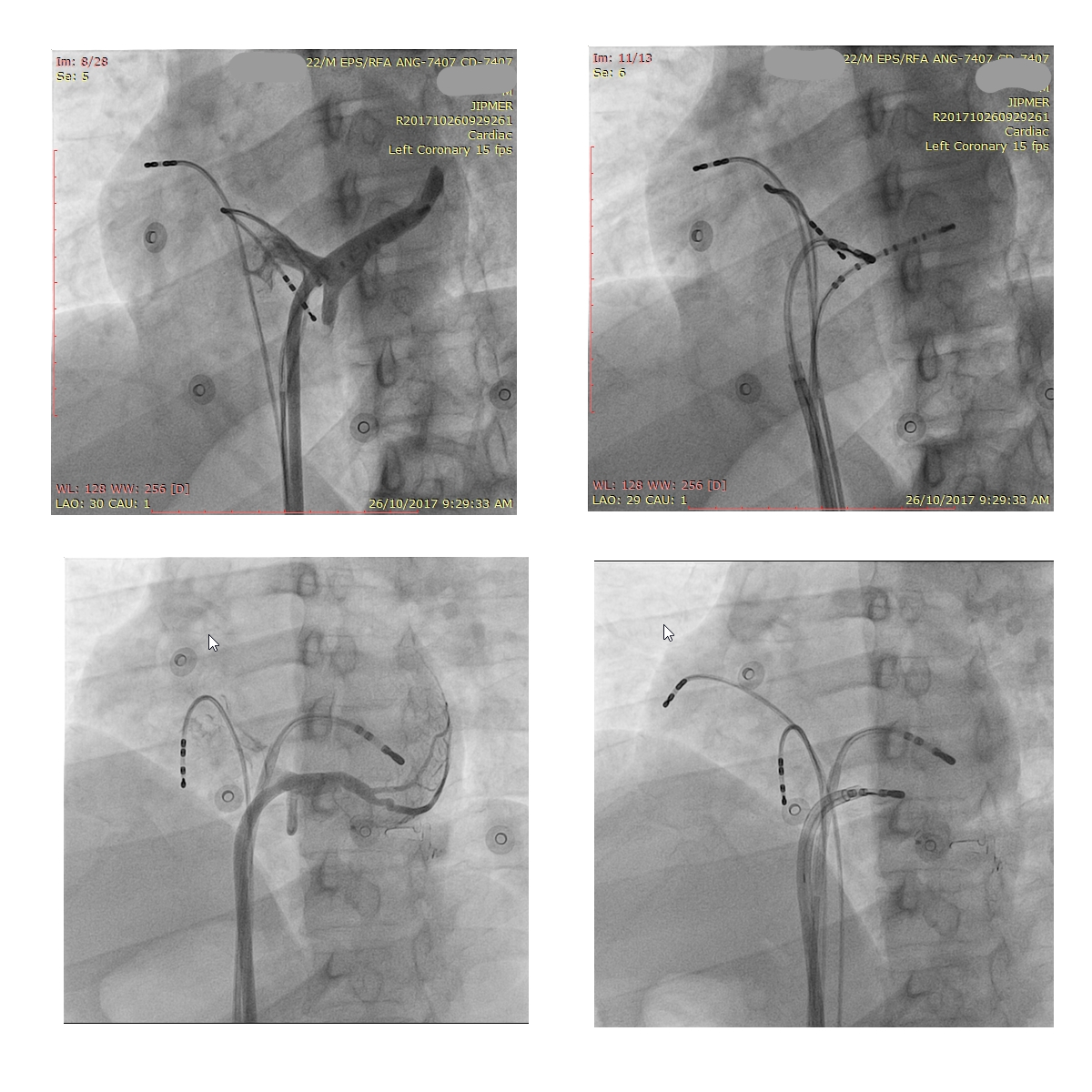
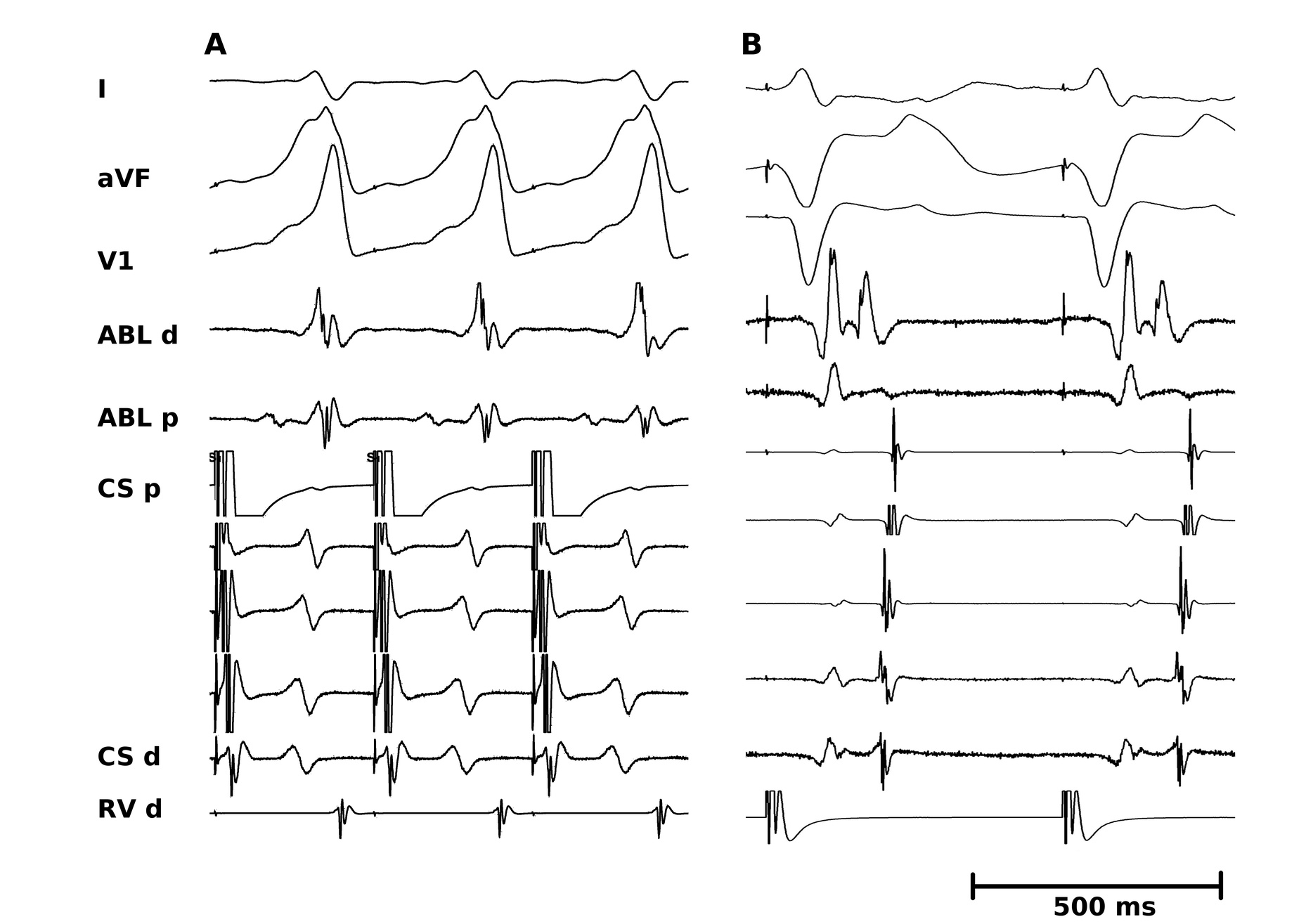
CS diverticulum
Mapping in diverticulum
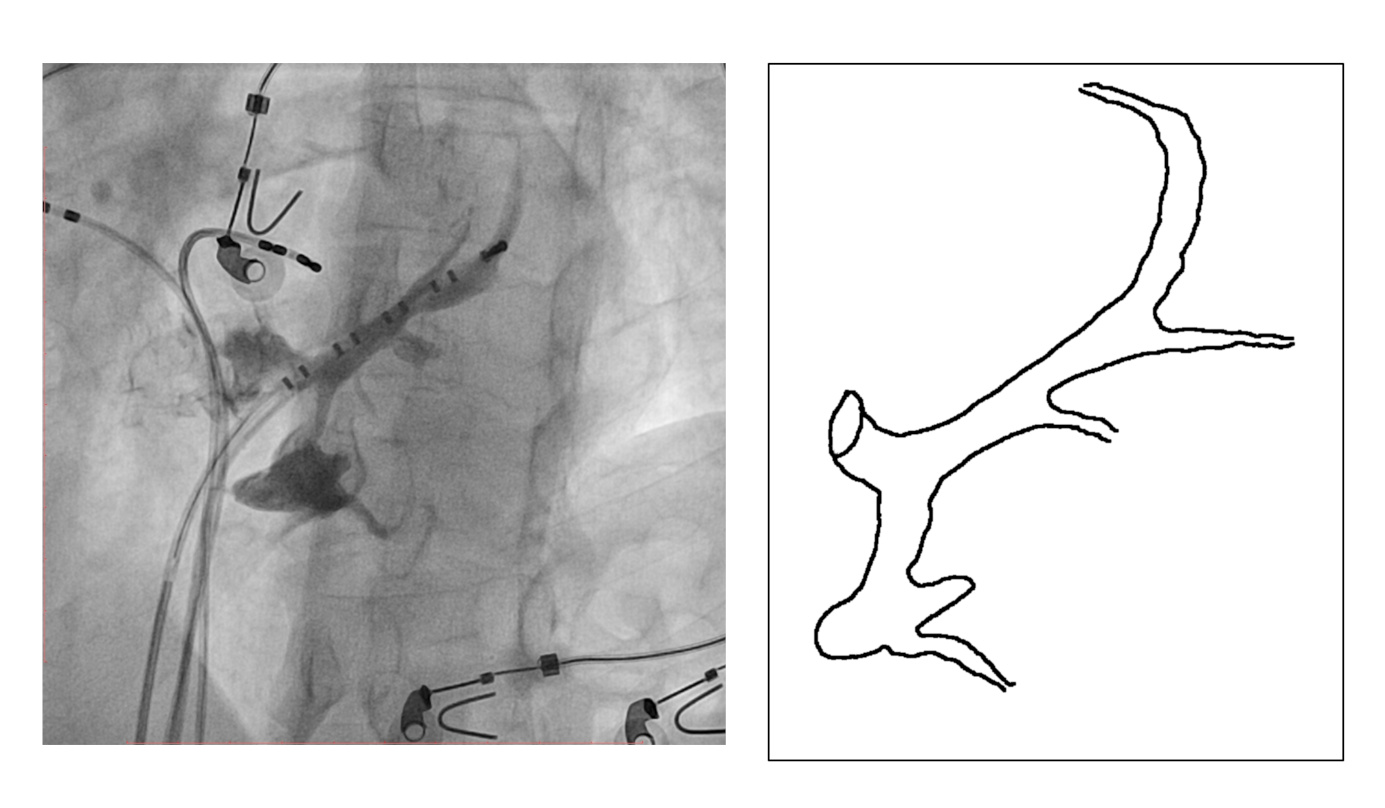
Mapping in diverticulum
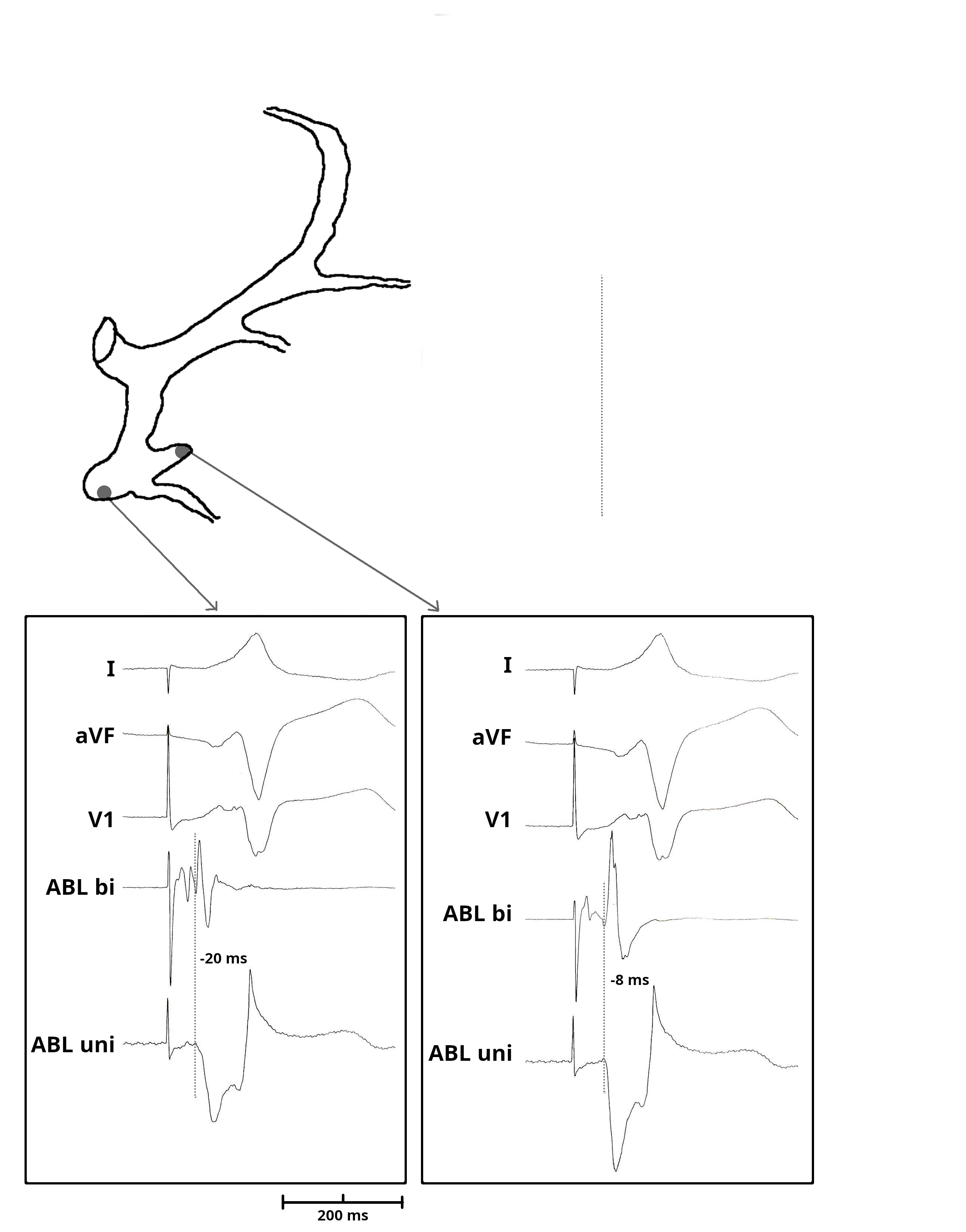
Mapping in diverticulum
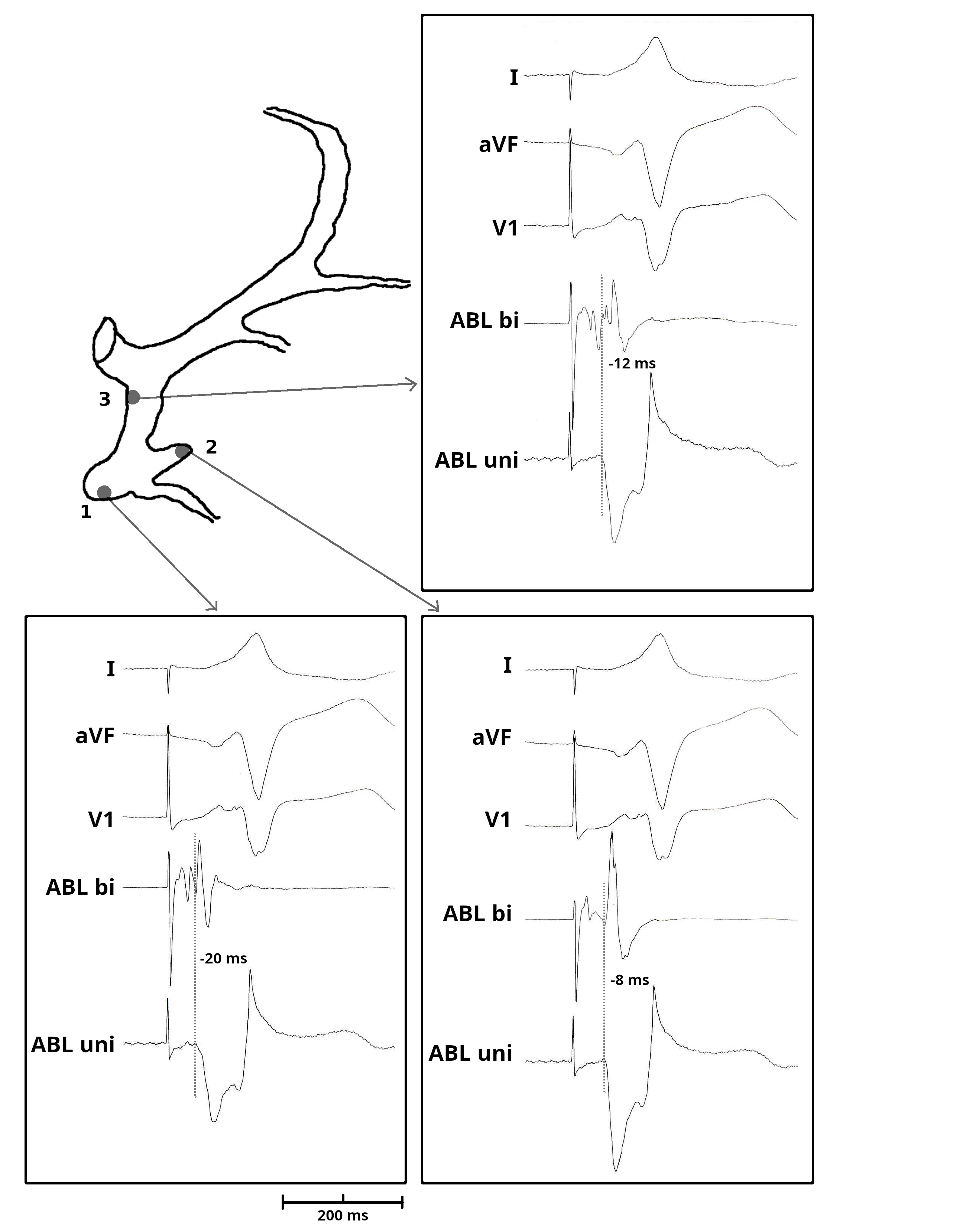
Mapping in diverticulum - CSE potential most important
Selvaraj RJ et al. Radiofrequency ablation of posteroseptal accessory pathways associated with coronary sinus diverticula. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2016 Nov;47(2):253-259. doi: 10.1007/s10840-016-0113-x.
In absence of diverticulum, map along tributaries
AP slant - Earliest A and earliest V may be distant
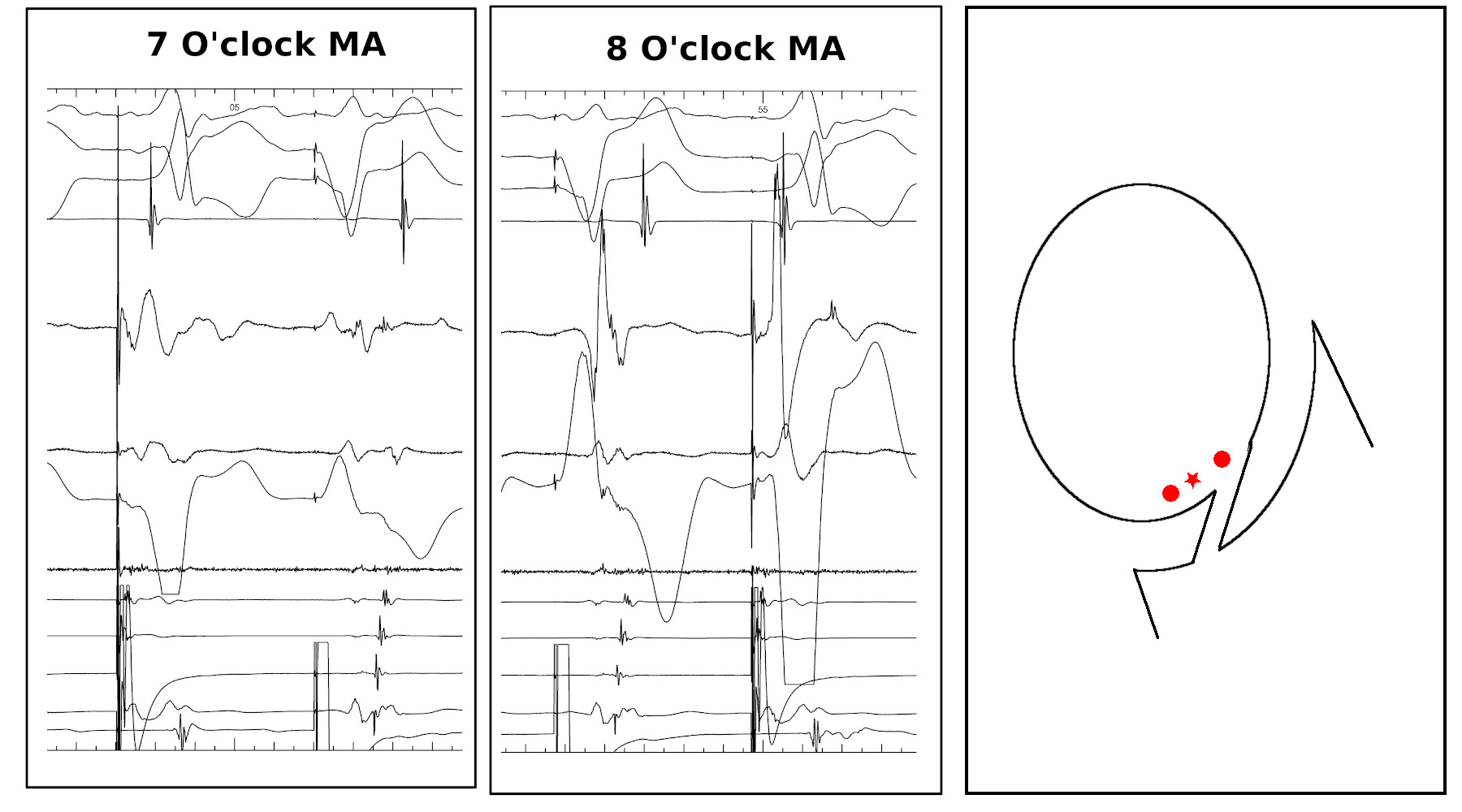
AP slant - AP potential more important
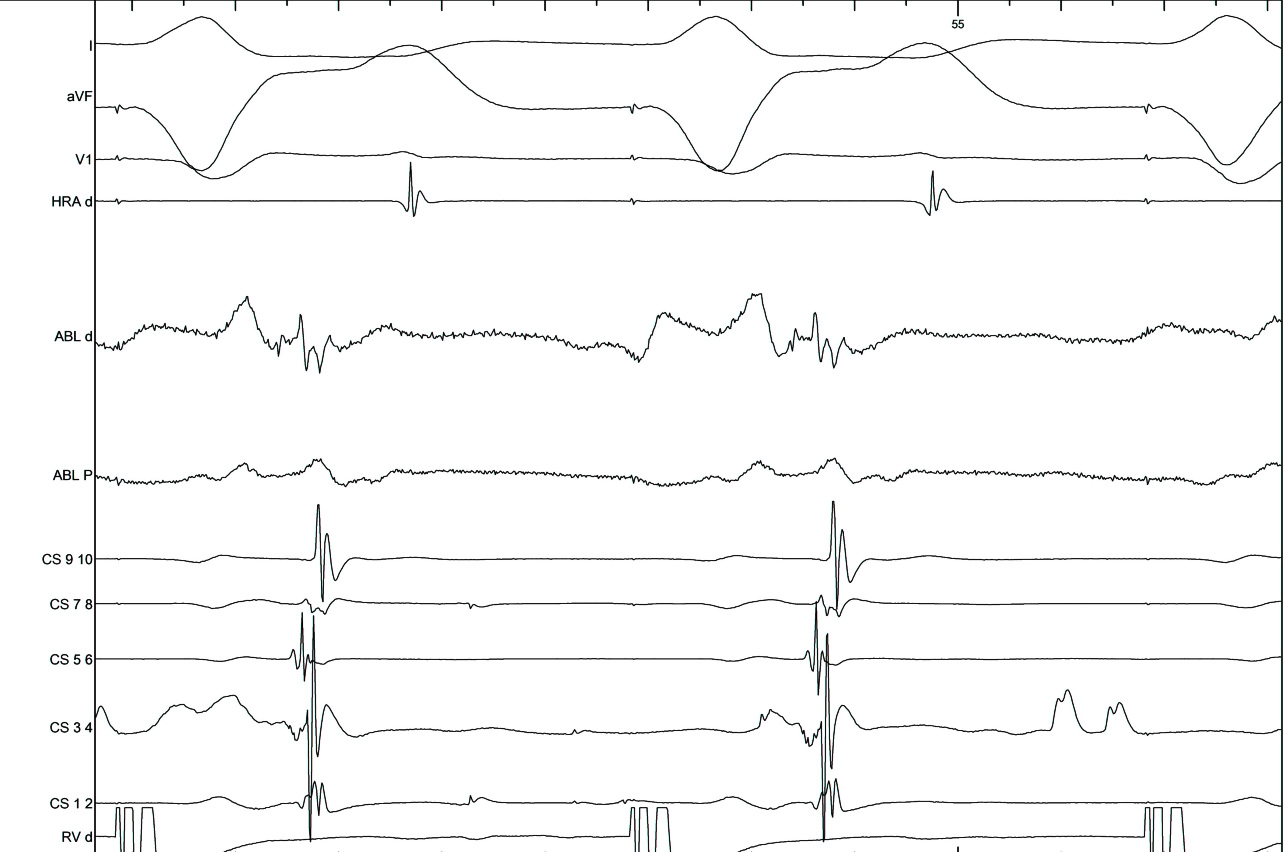
Try to avoid bumping, but use it when it happens
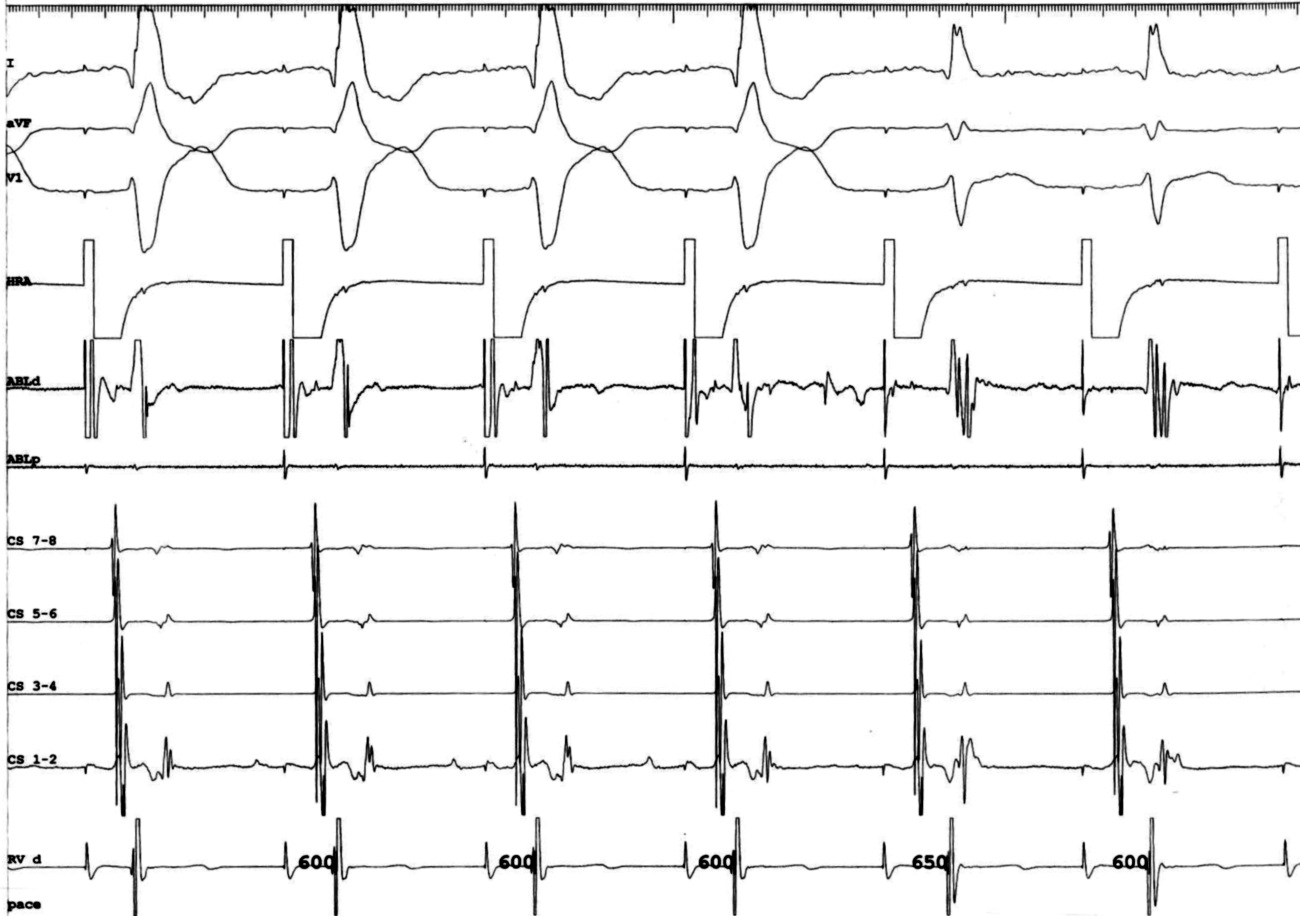
Ablation
Ablate septal APs during tachycardia when possible
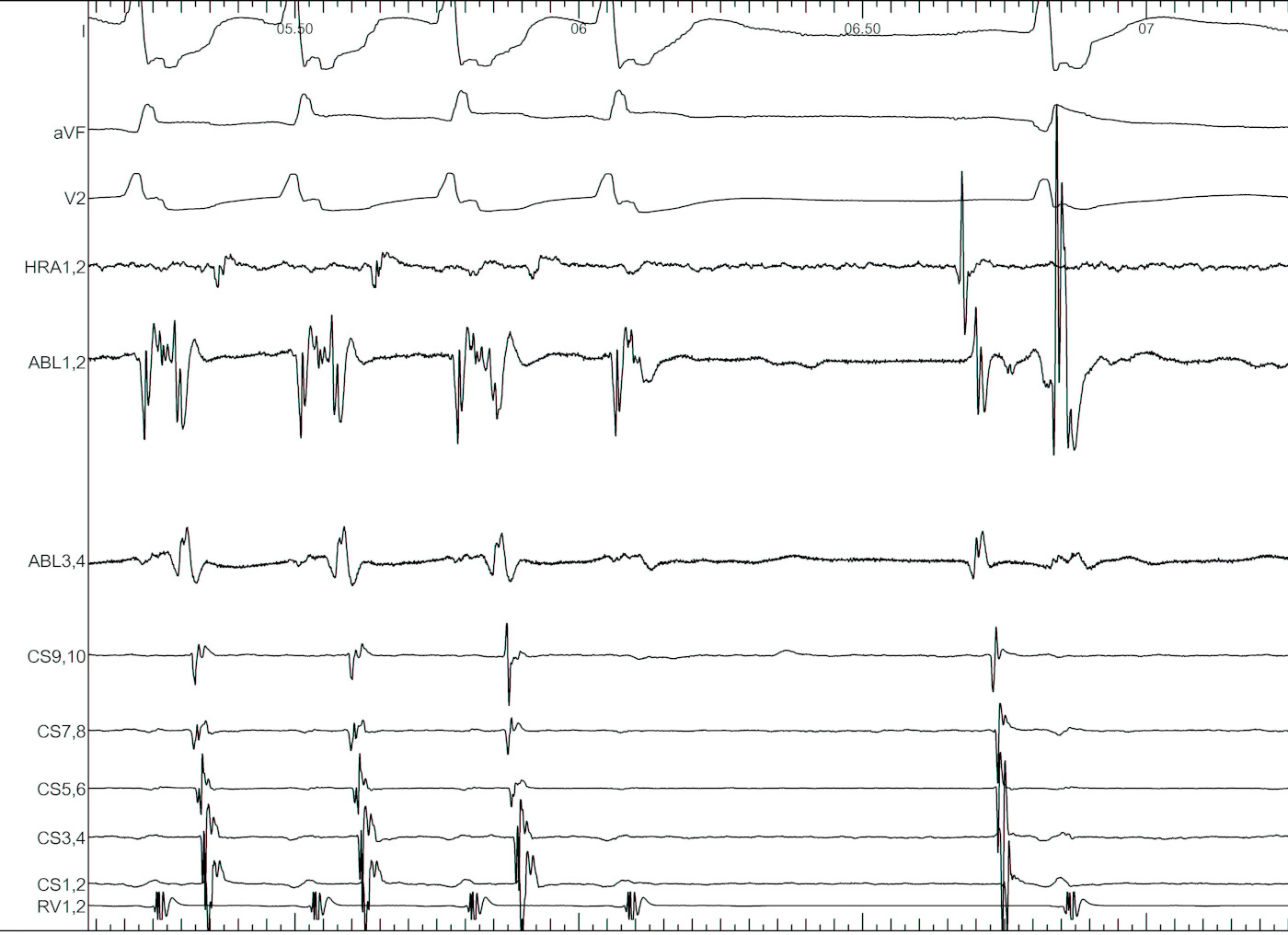
Entrain when ablating free wall AP during tachycardia
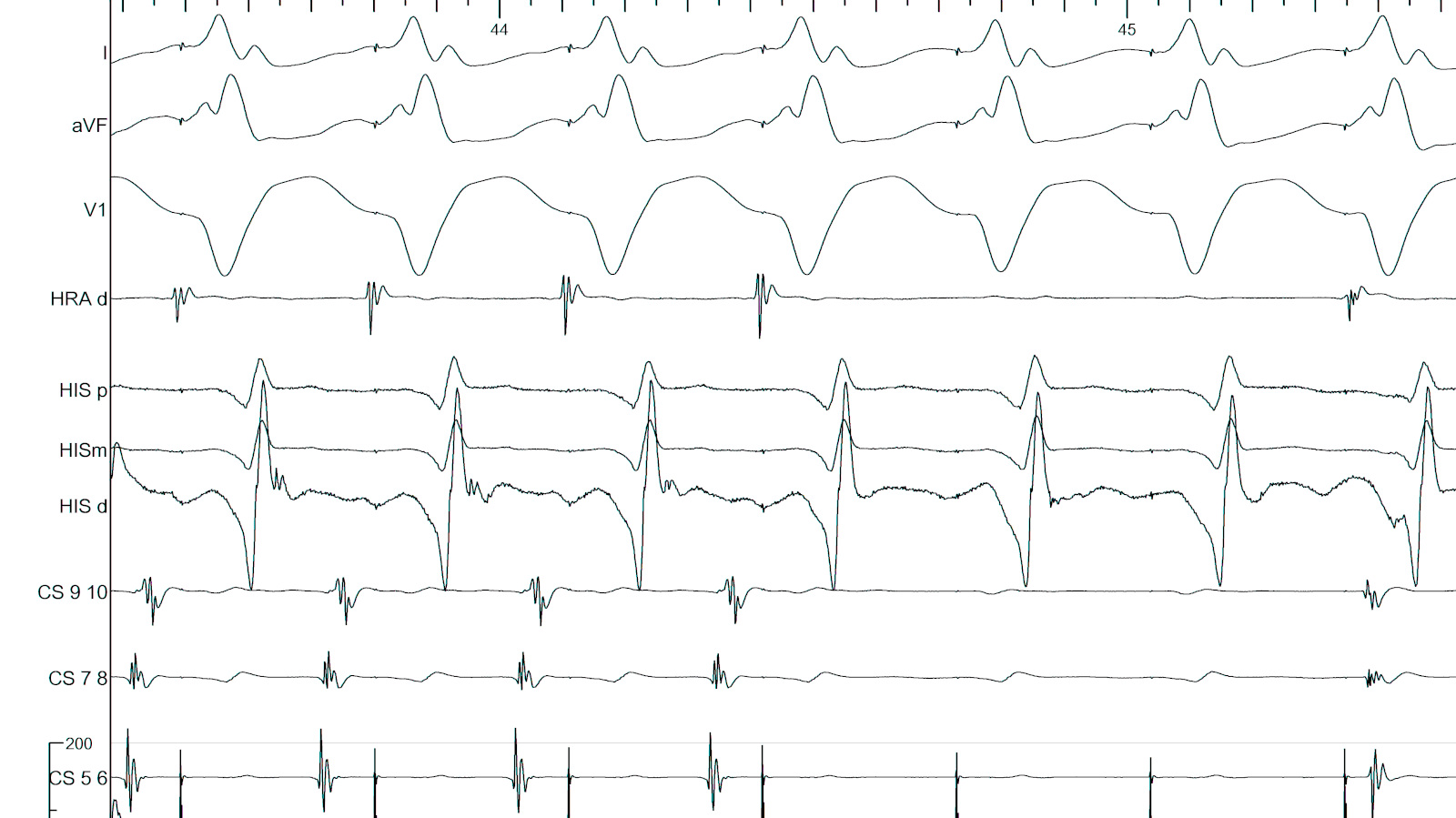
Isthmus block
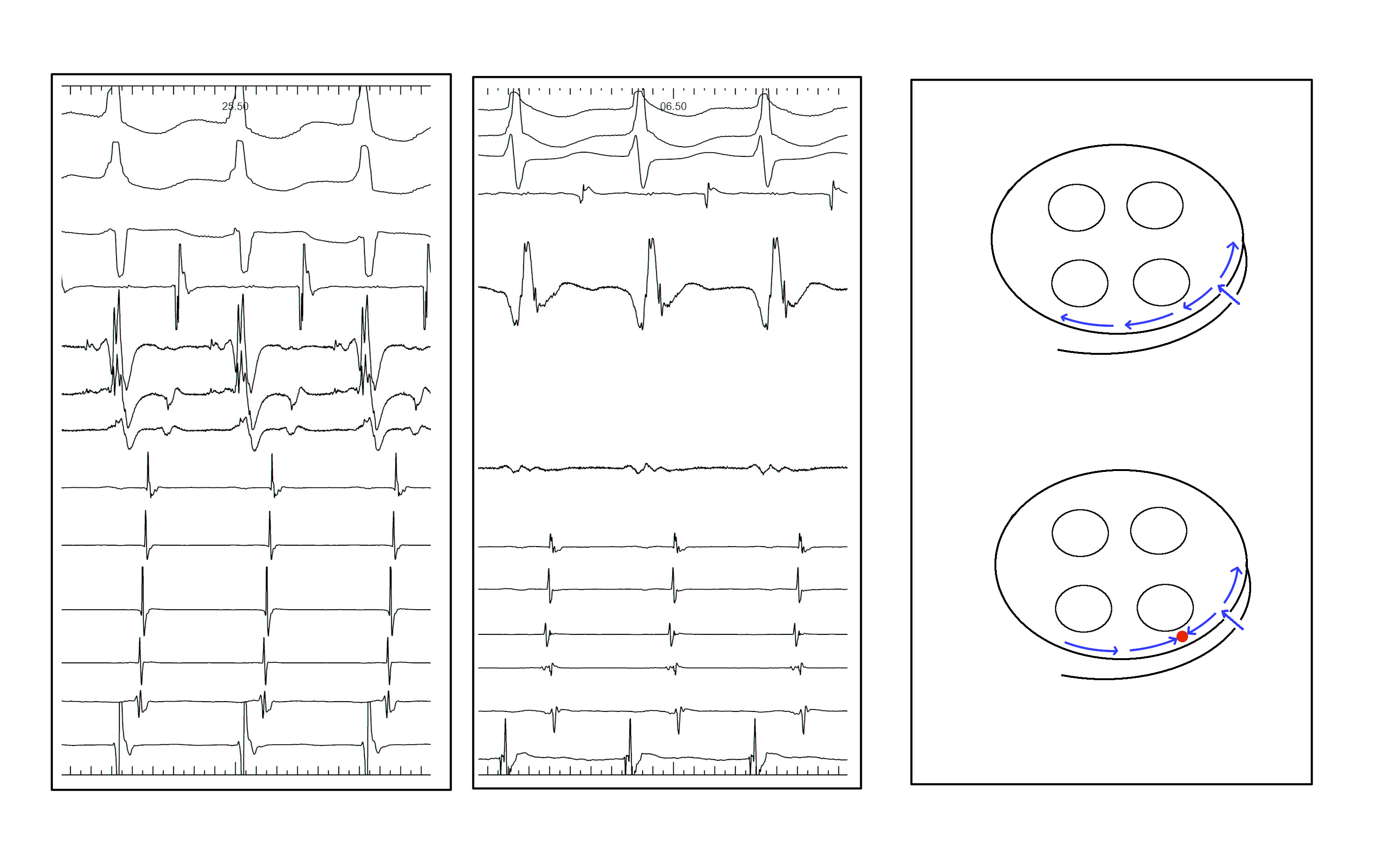
Anteroseptal AP may be ablated from non coronary cusp
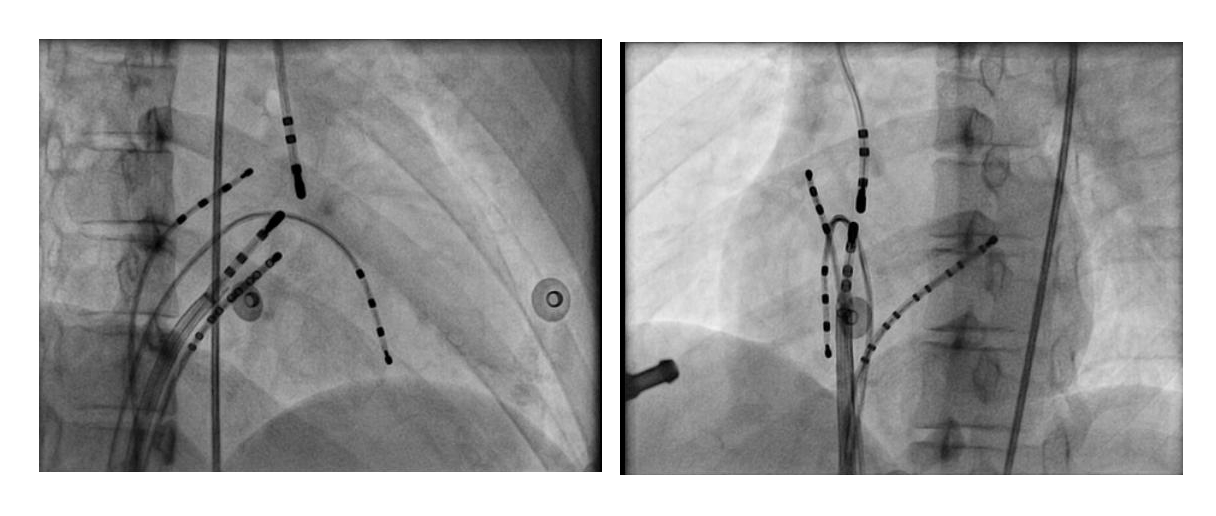
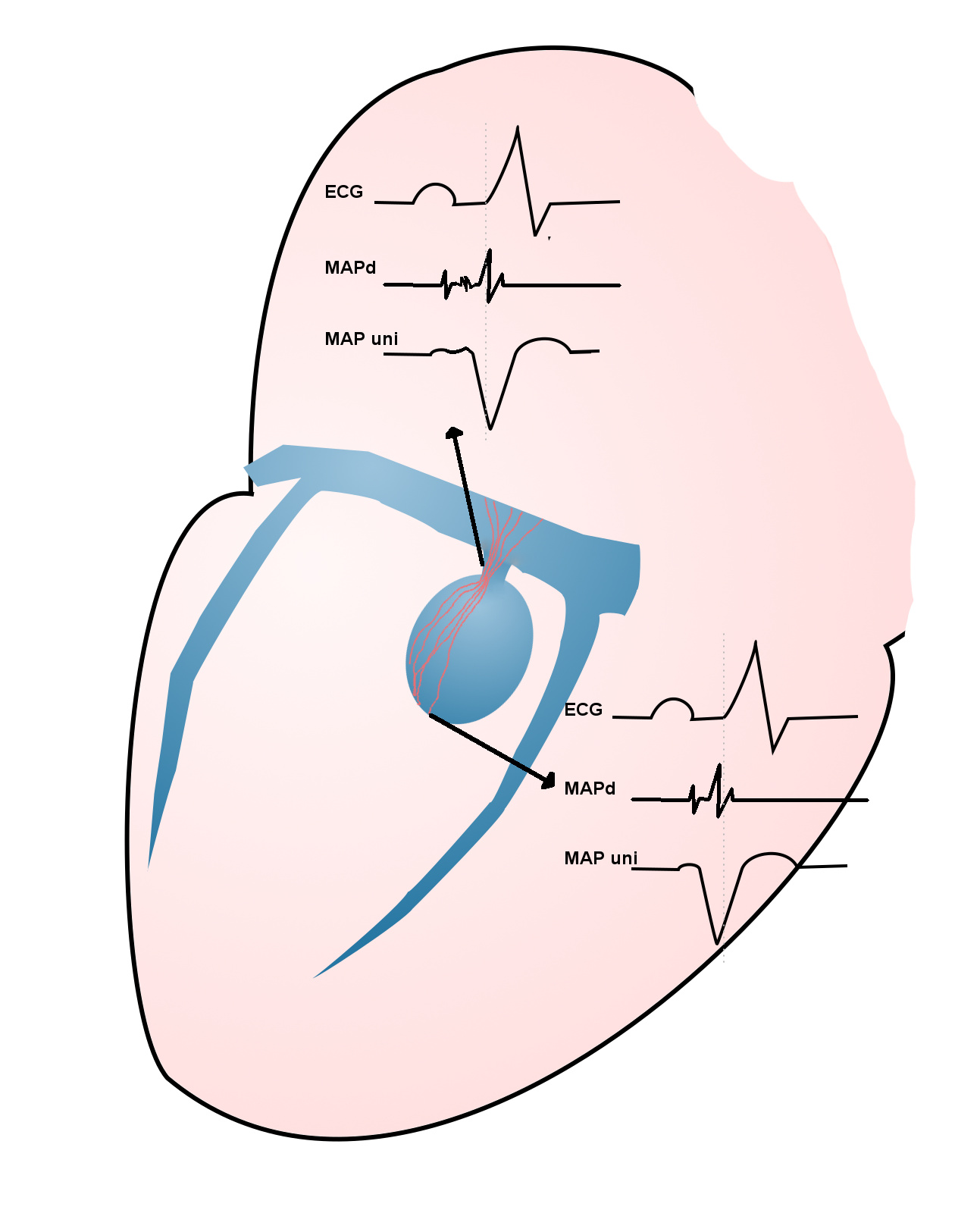
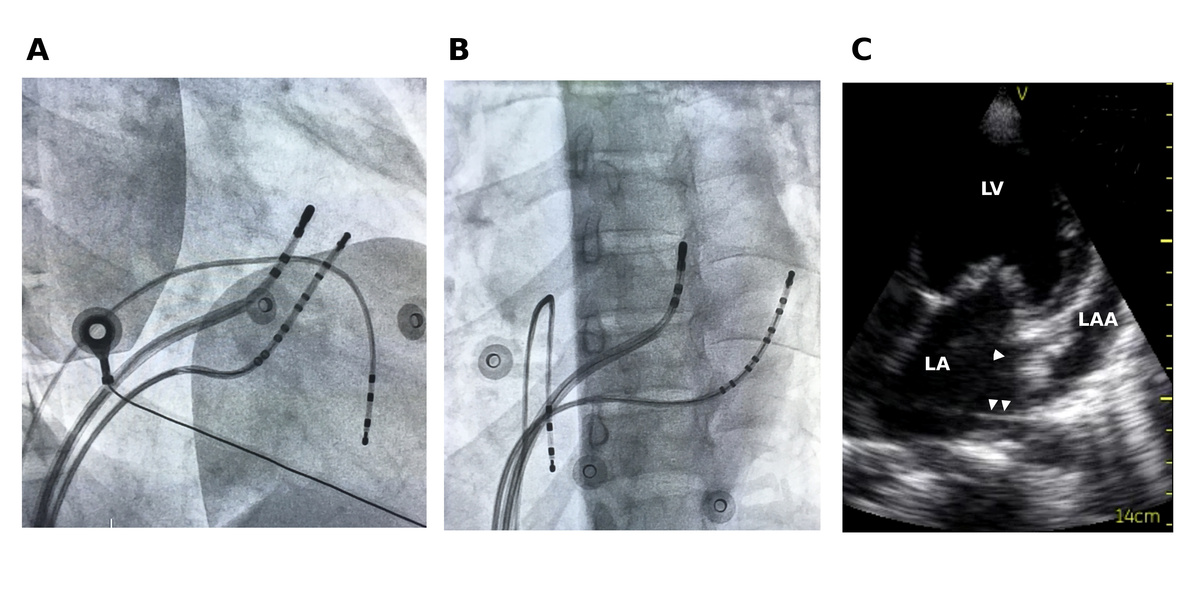
Non annular location of AP
Non annular location of AP
Summary
- Dont make easy ablations difficult
- Accurate diagnosis
- Precise mapping
- Difficult ablations
- Risk of AV injury
- CS diverticulum
- Non annular locations