ECG Deflections and Waveforms
Raja Selvaraj MD DNB FCE (Toronto)
Cardiac Electrophysiologist
Professor of Cardiology
JIPMER
Introduction
The heart is a two chambered organ
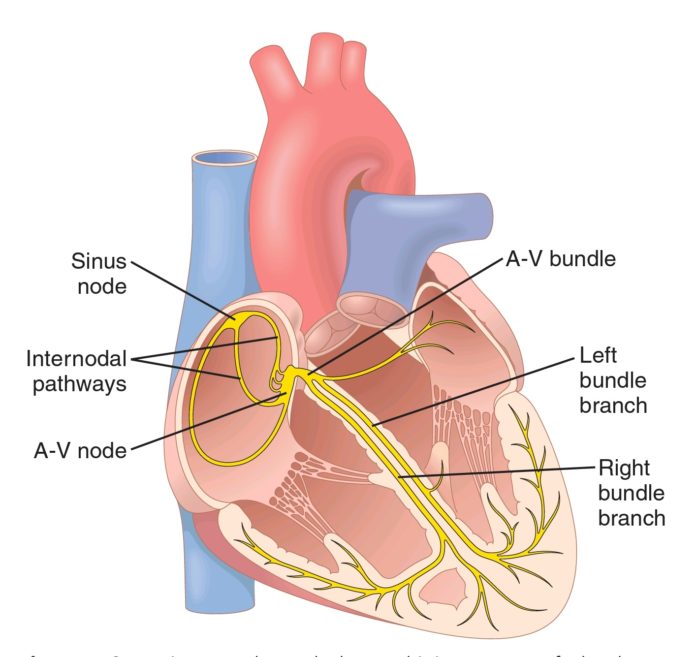
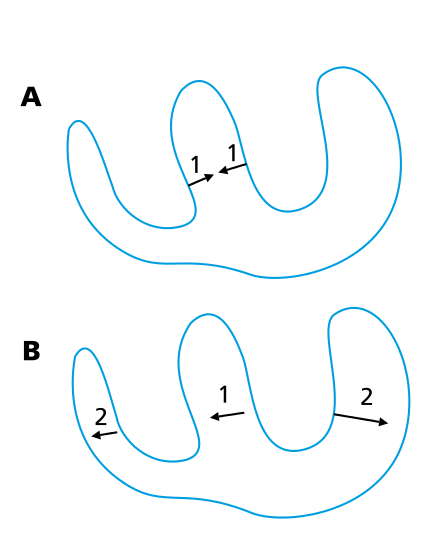
Anatomy of a wave
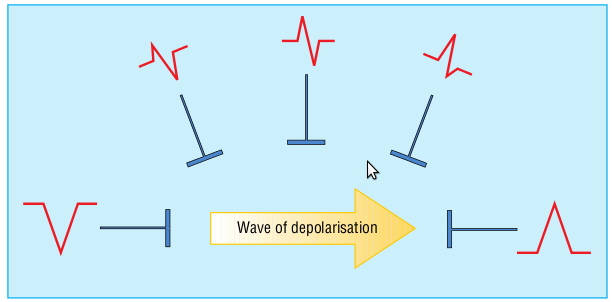
ECG deflection and wavefront
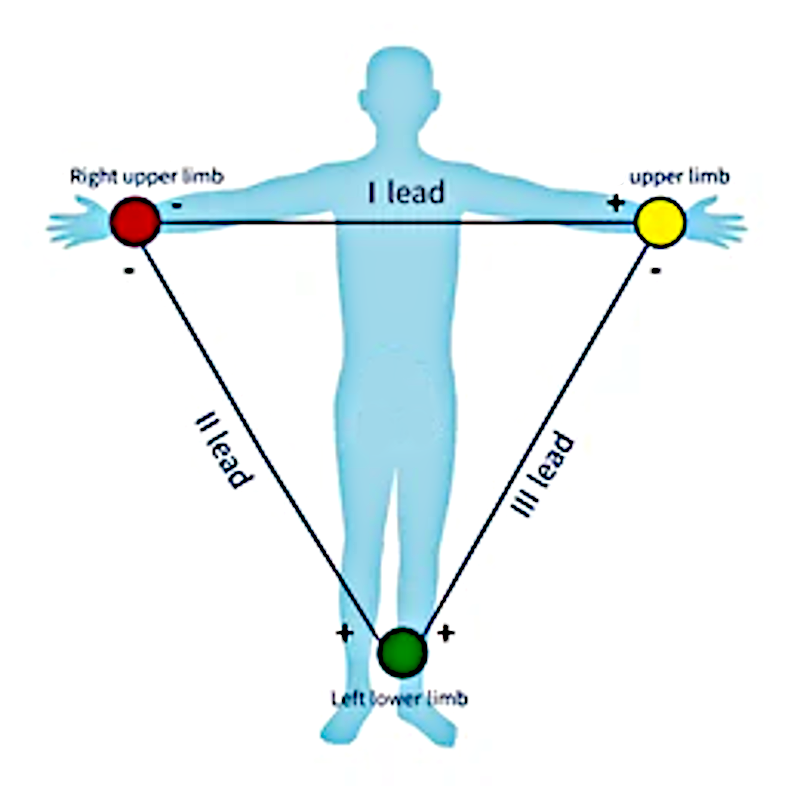
Limb leads
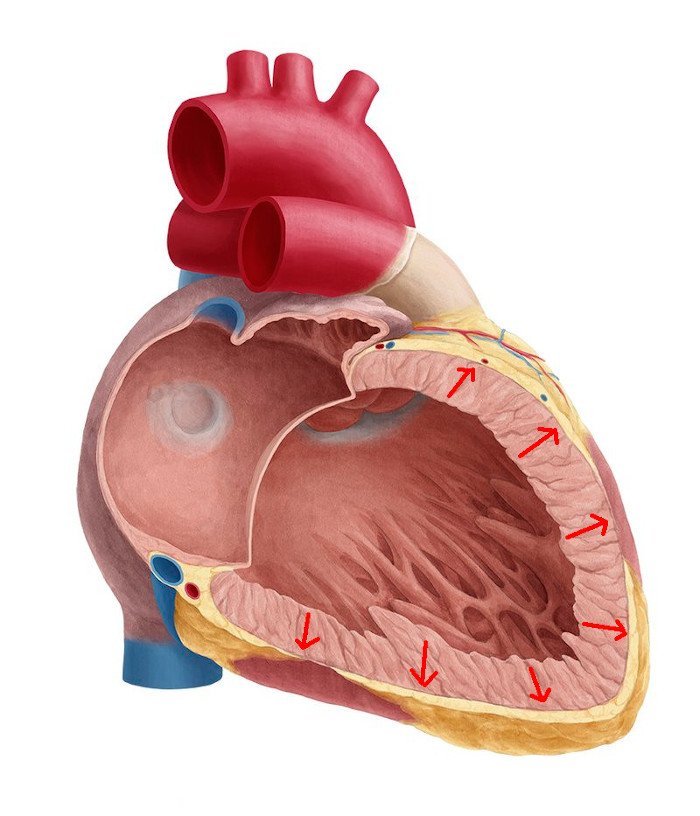
Wavefronts in atrium
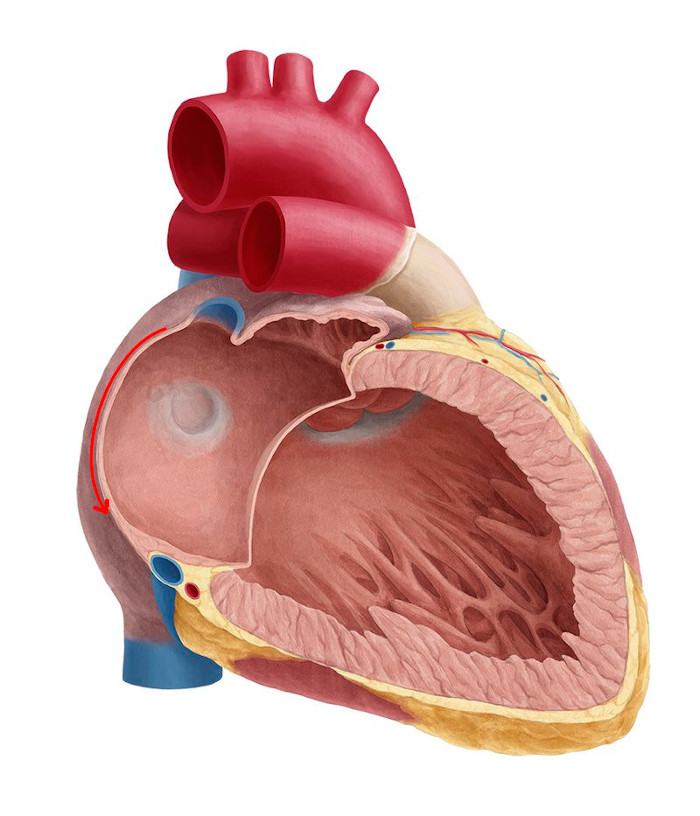
Wavefronts in ventricle
P wave
Atrial vectors
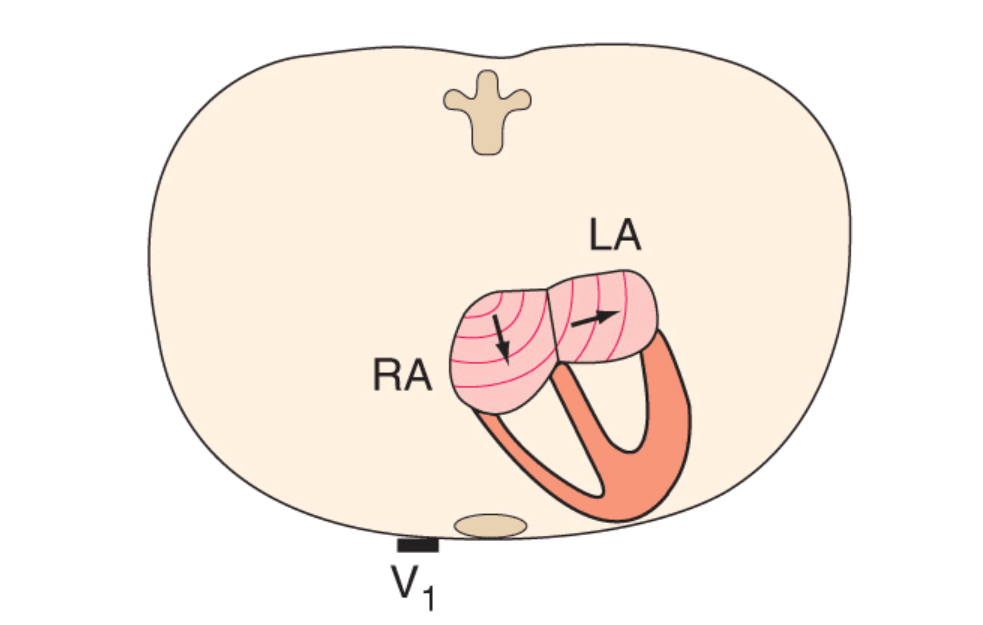
P wave - two atria
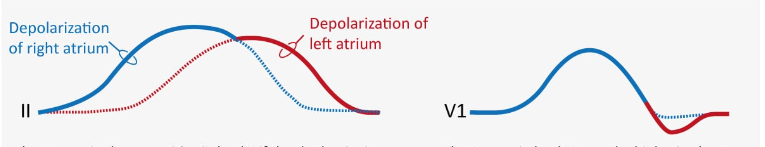
P wave lead II
P wave lead V1
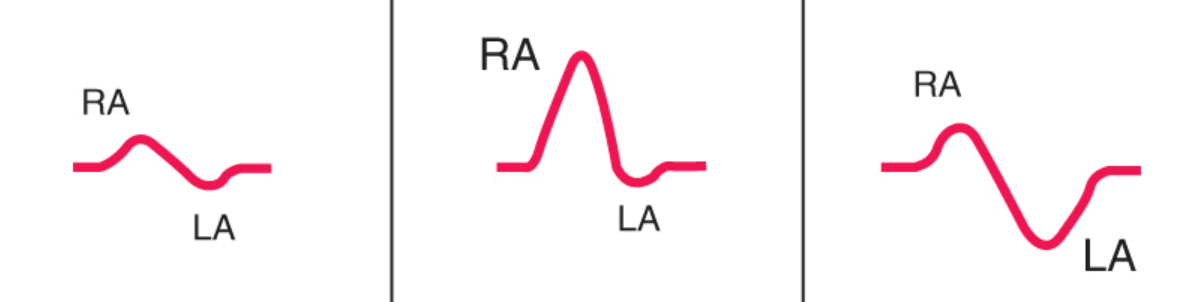
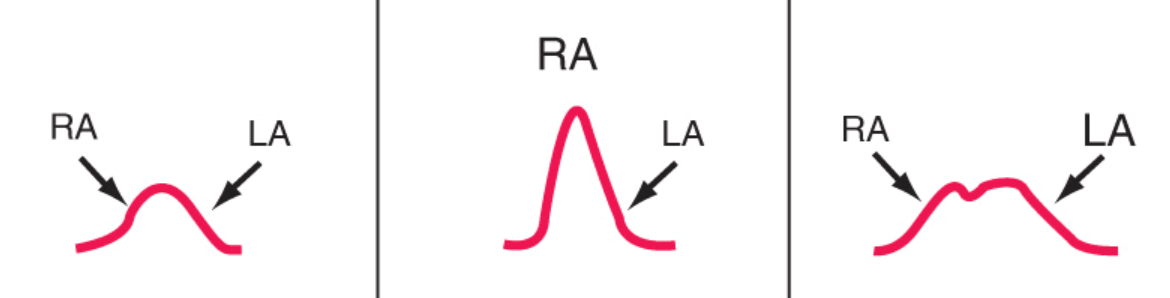
Other P waves
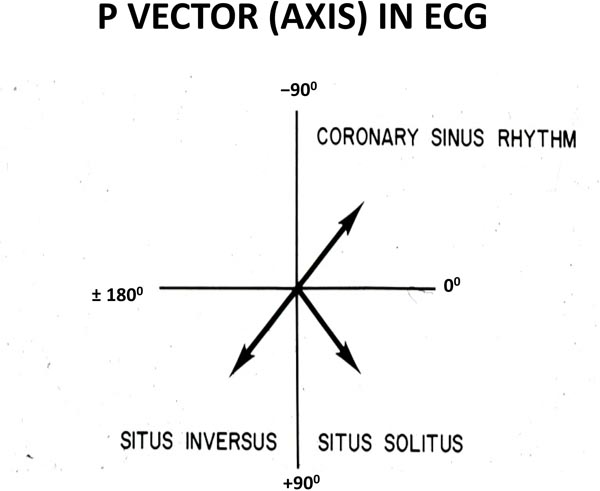
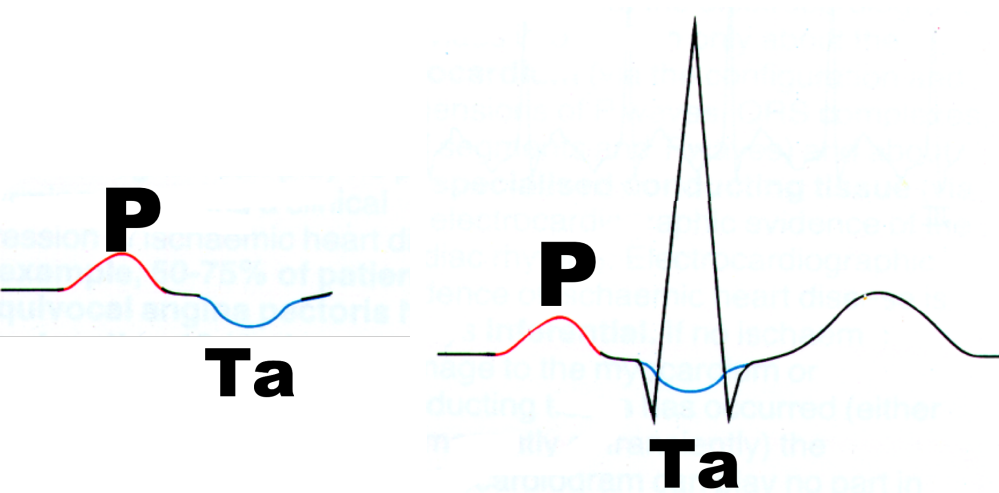
Ta wave
QRS and T waves
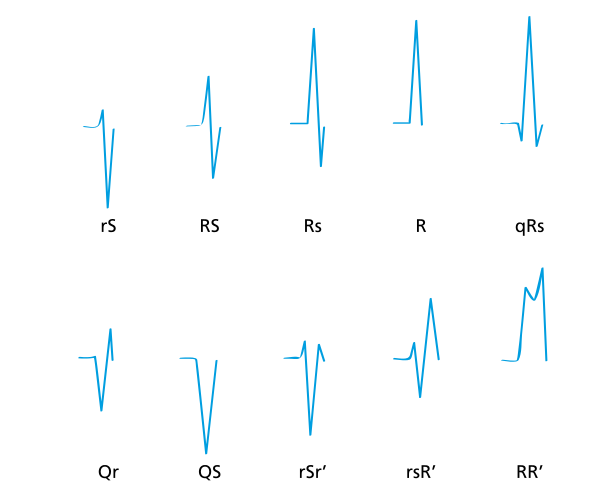
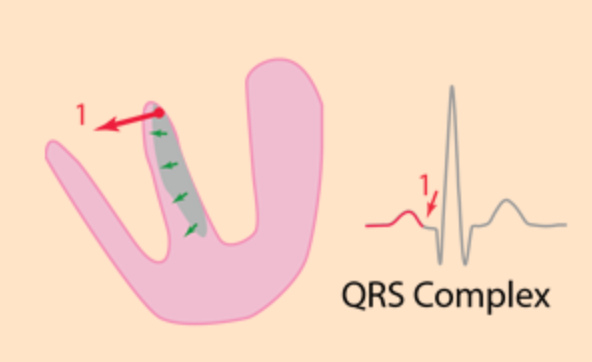
QRS - Terminology
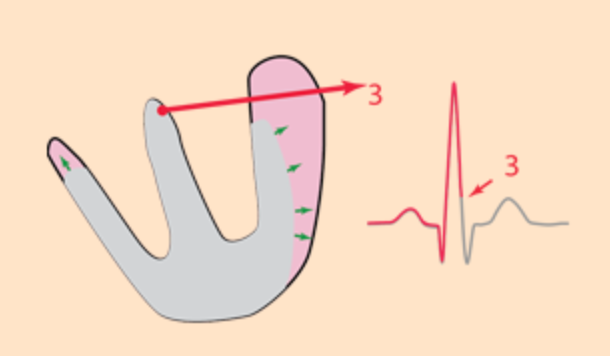
Ventricular activation
Septal q
Ventricular activation
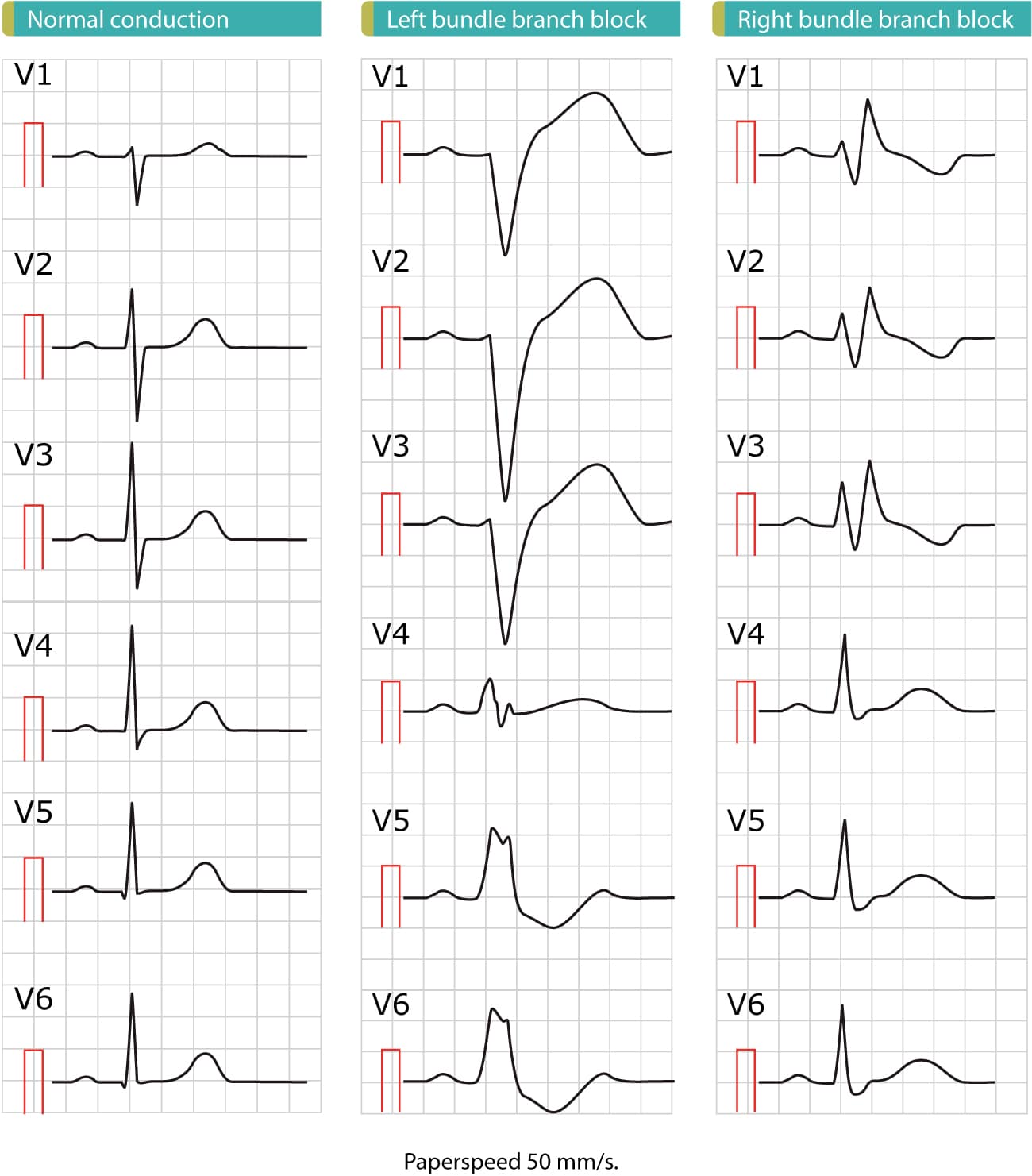
Bundle branch blocks
T wave
Summary
What have we learnt ?
- Electrical activation occurs as waves of depoalrisation and repolarisation
- Wavefronts moving towards or away from recording electrode produce a deflection in the ECG
- Deflections produced by the atrium and ventricle can be used to infer the activation patterns
- Forms the basis for all further discussion on the ECG