Management of VT storm
Raja Selvaraj MD DNB FCE (Toronto)
Cardiac Electrophysiologist
Professor of Cardiology
JIPMER
Case presentation
- 48-year-old male
- Acute ST elevation AWMI one month back
- Transient CHB, VF during TPI admission
- Admitted 3 d back with recurrent VT requiring DCCV
- Shifted to us after multiple shocks despite Amiodarone
What is VT storm ?
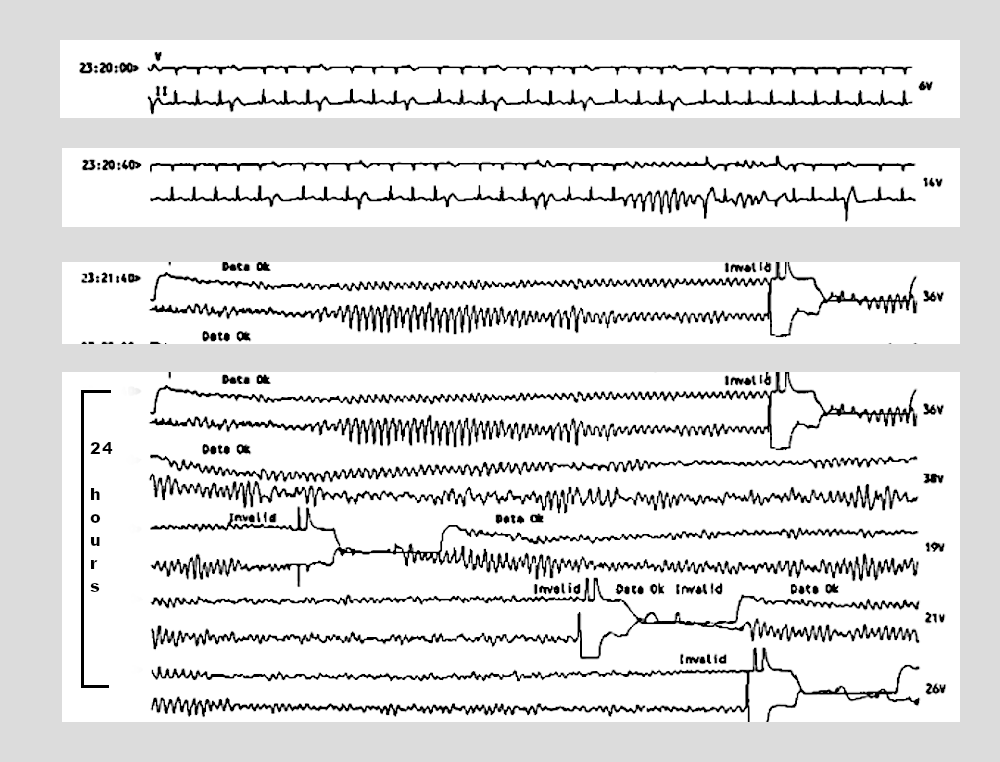
VT storm
- Three or more discrete episodes of VA within 24 hours
- Three or more appropriate ICD shocks within 24 hours, separated by at least 5 minutes
- Incessant VT > 12 hours
- Typically monomorphic VT, but can be polymorphic VT or VF
- Typically structural heart disease, but can also be channelopathies
VT storm is not recurrent VT
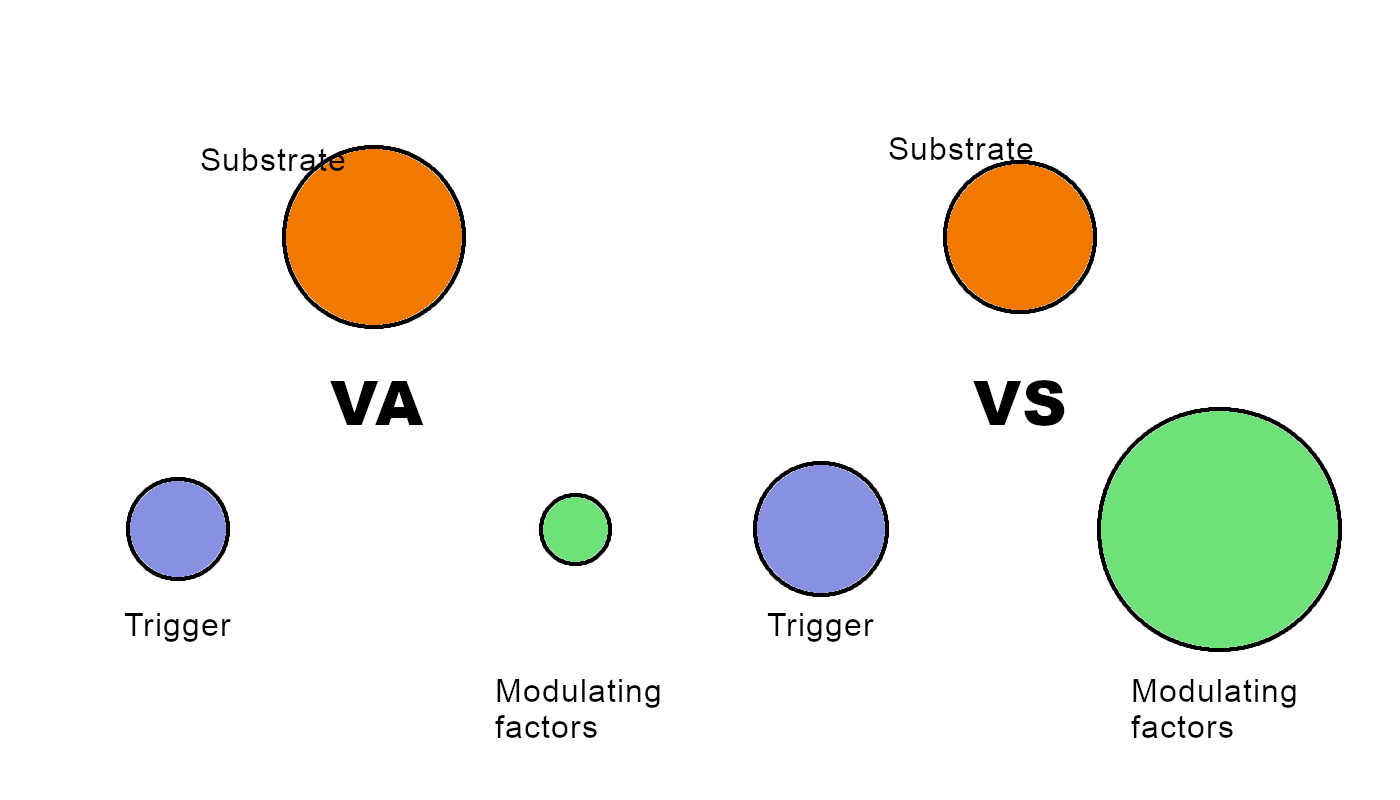
Required two further shocks, BP 80 systolic - What next?
- Inotropes, continue Amiodarone
- Emergency radiofrequency ablation
- Sedation, intubation and ventilation
Treatment - Multimodality
Identify and treat reversible precipitants
- Myocardial ischemia
- Electrolyte abnormalities - Hypokalemia
- Sepsis
- Heart failure
- Non compliance to medications
Device interrogation and reprogramming
- Identify inappropriate therapies
- Reprogram to reduce shocks
- Disable ICD shocks
- Temporarily discontinue LV pacing
Ablation for LV pacing induced ES
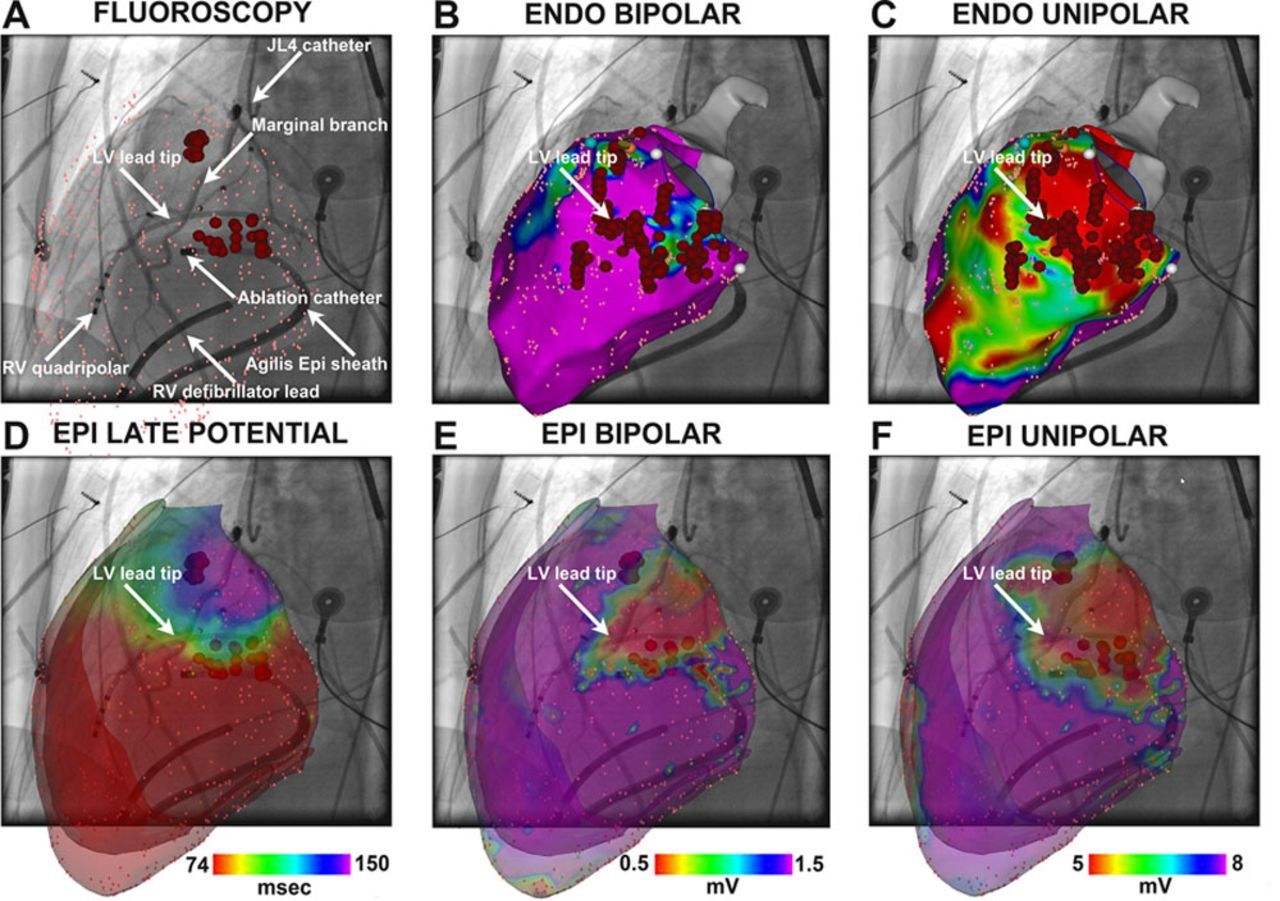
Roque C, Trevisi N, Silberbauer J, Oloriz T, Mizuno H, Baratto F, Bisceglia C, Sora N, Marzi A, Radinovic A, Guarracini F, Vergara P, Sala S, Paglino G, Gulletta S, Mazzone P, Cireddu M, Maccabelli G, Della Bella P. Electrical storm induced by cardiac resynchronization therapy is determined by pacing on epicardial scar and can be successfully managed by catheter ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2014 Dec;7(6):1064-9.
Pharmacotherapy
- Amiodarone
- Sotalol
- Lignocaine / Mexilitene
Invasive hemodynamic support
- IABP
- LVAD
- ECMO
- Sedated, intubated and ventilated
- Beta blocker
- Amiodarone continuing
- Trial of IV lignocaine
- Episodes of sustained VT continuing
Radiofrequency ablation
- Consider in all ES unresponsive to medical management
- Early ablation may be favourable in select subsets
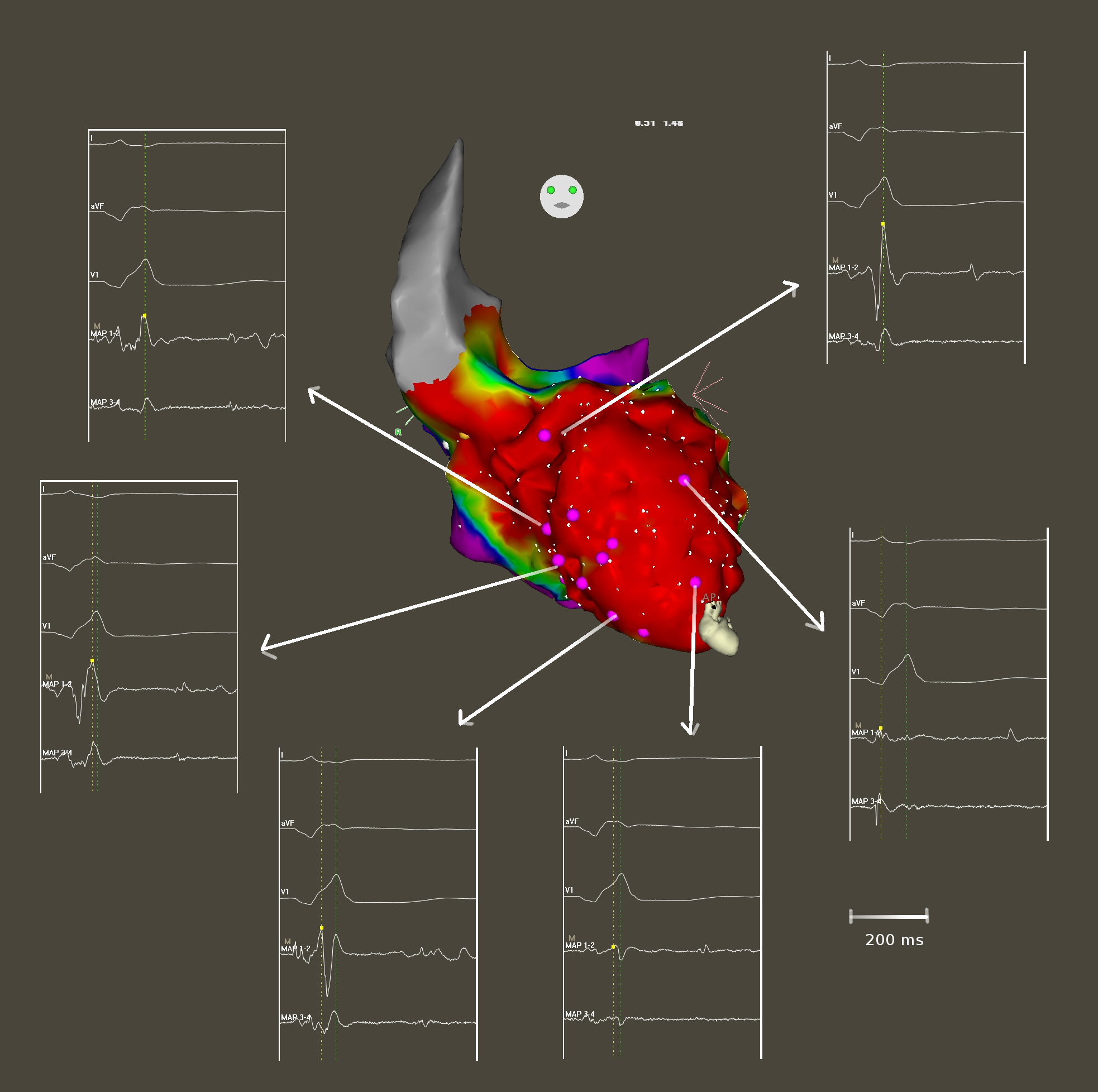
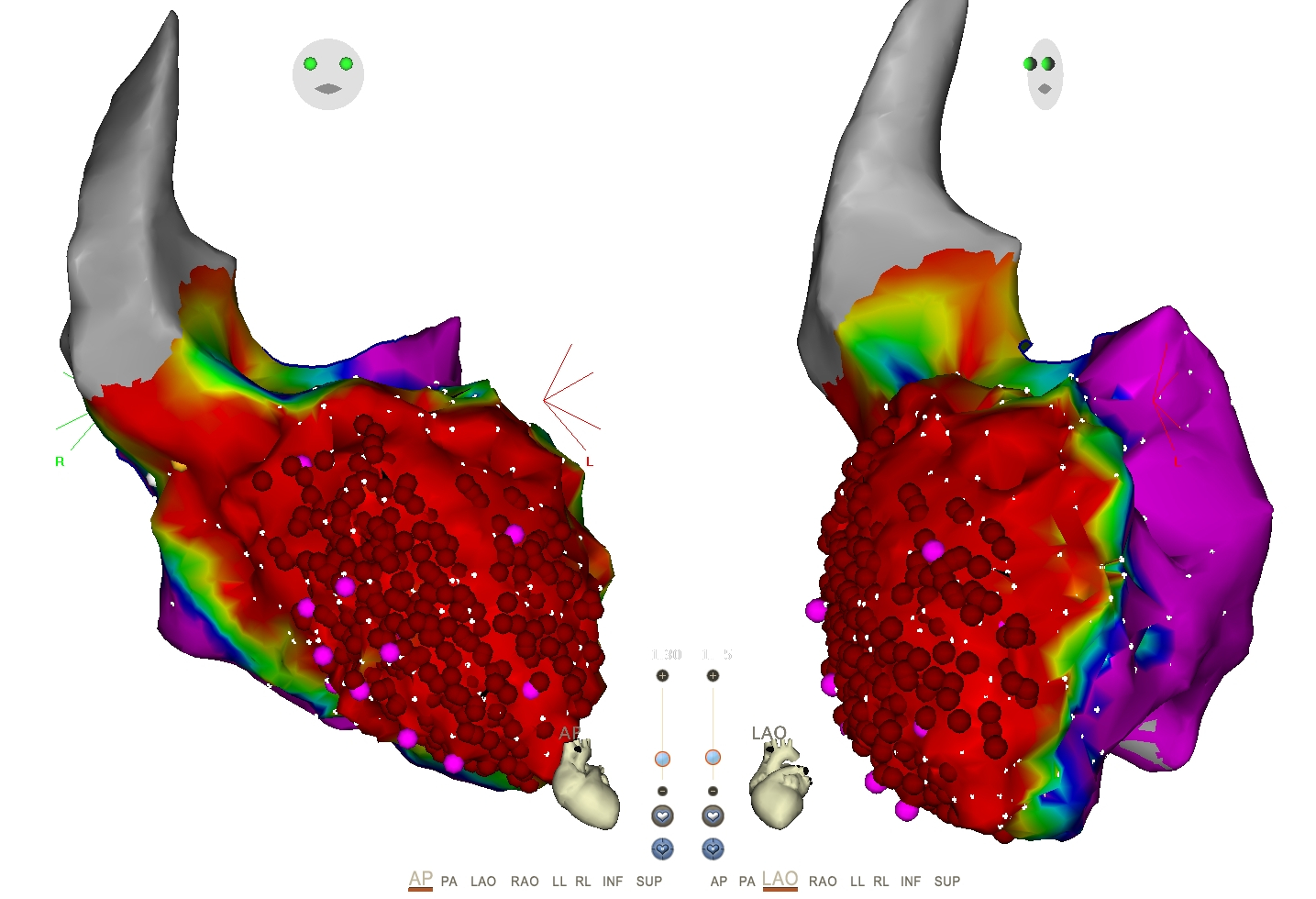
Outcomes with early ablation
Carbucicchio C, Santamaria M, Trevisi N, Maccabelli G, Giraldi F, Fassini G, Riva S, Moltrasio M, Cireddu M, Veglia F, Della Bella P. Catheter ablation for the treatment of electrical storm in patients with implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: short- and long-term outcomes in a prospective single-center study. Circulation. 2008 Jan 29;117(4):462-9
Ablation of triggering PVCs
- Early post MI
- VF storm with normal heart
- Purkinje system, outflow tract, papillary muscles, tricuspid annulus
Sympathetic modulation
- Sedation
- Beta blockers
- Neuraxial modulation
Sedation
- Sedation
- Deep sedation
- Intubation and mechanical ventilation
Beta blockers
- Key to pharmacologic management
- Short acting agent Esmolol when hemodynamic compromise
- Propranolol may be superior to Metoprolol
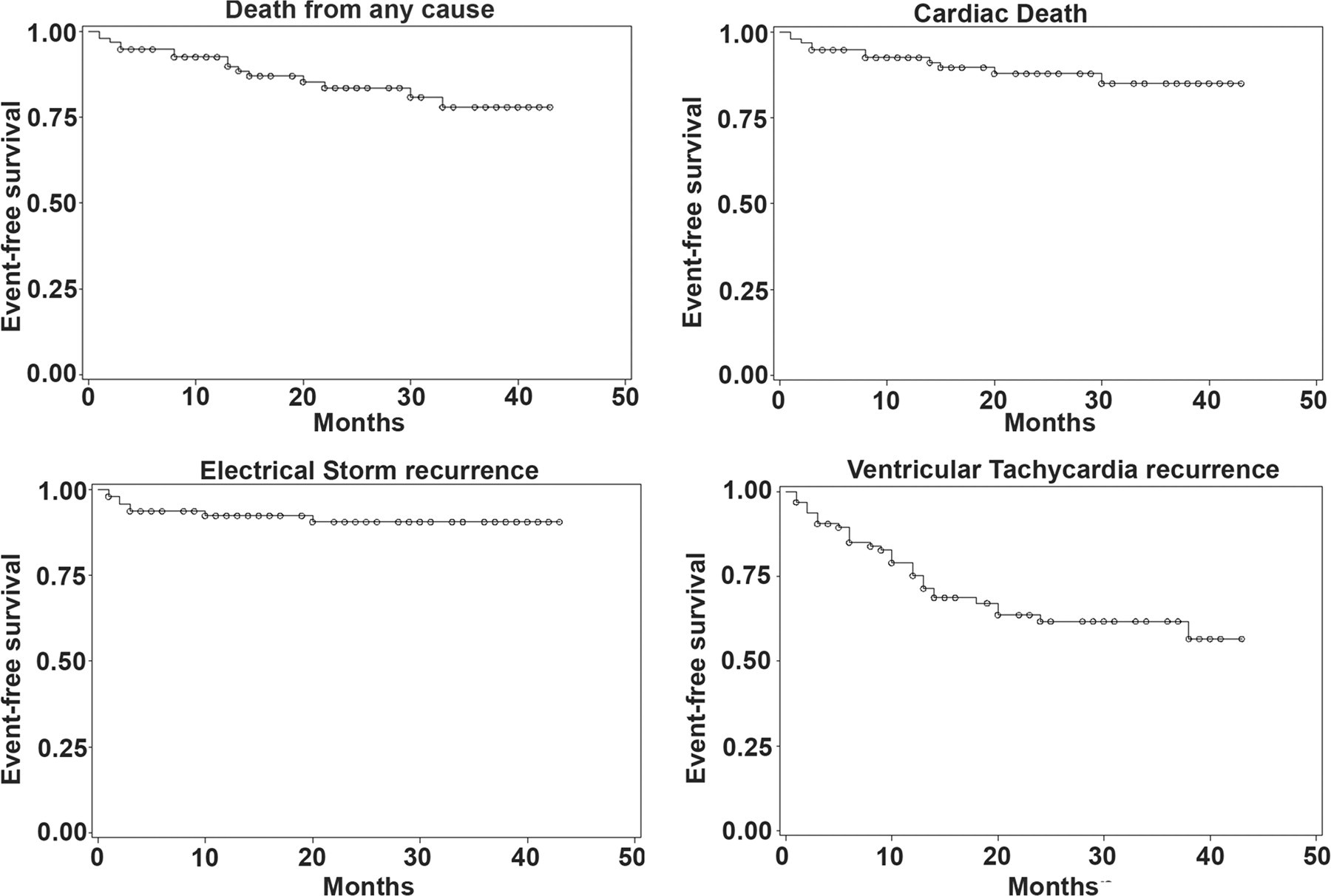
Beta blockade superior to AAD
Nademanee K, Taylor R, Bailey WE, Rieders DE, Kosar EM. Treating electrical storm: sympathetic blockade versus advanced cardiac life sup- port-guided therapy. Circulation 2000;102:742–7.
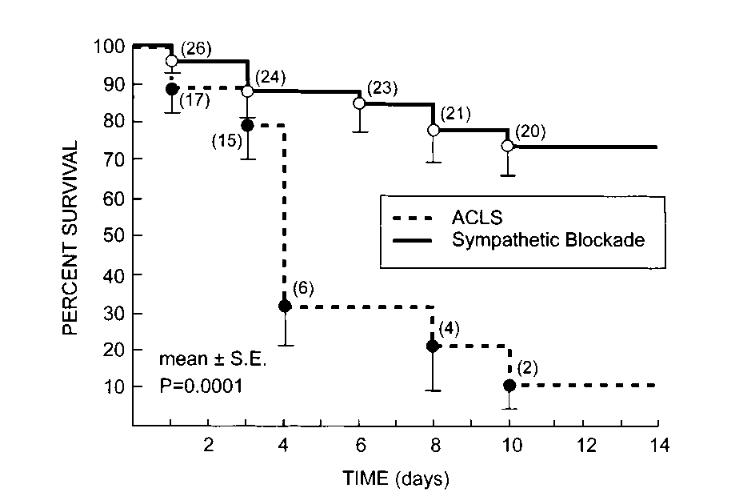
Neuraxial modulation
- Thoracic Epidural Anaesthesia
- Stellate ganglion blockade
- Cardic sympathetic denervation
- Renal sympathetic denervation
Thoracic Epidural Anaesthesia
- 0.25% Bupivacaine in epidural space
- 1 ml followed by 2 ml/h
- Bridge
- Bailout after failed ablation
Stellate Ganglion Blockade
- Left or bilateral
- Percutaneous USG guided
Surgical Sympathetic Denervation
- Lower half of stellate ganglion and T2-T4 ganglia
- Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery
Left or bilateral CSD
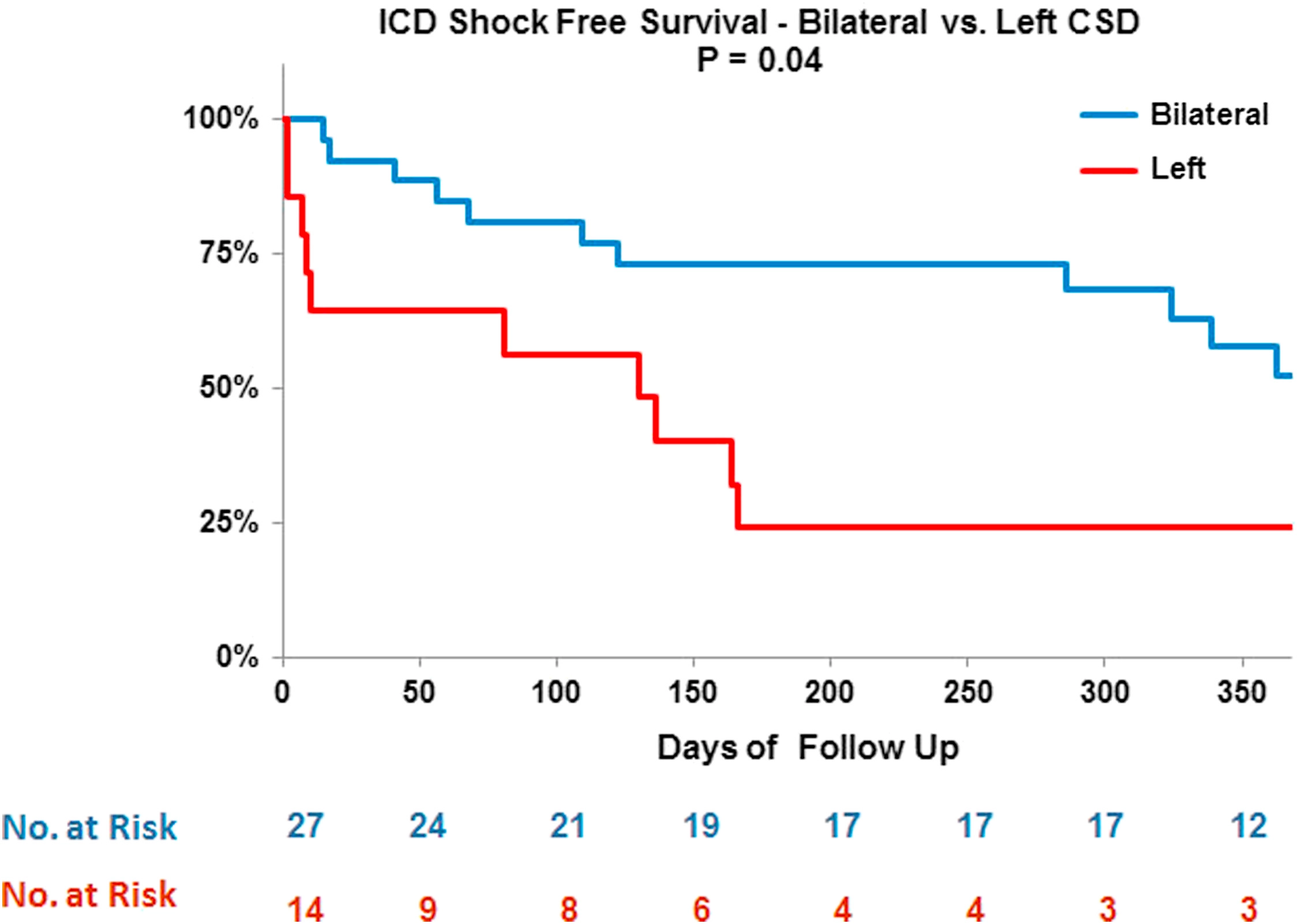
Vaseghi M, Gima J, Kanaan C, Ajijola OA, Marmureanu A, Mahajan A, Shivkumar K. Cardiac sympathetic denervation in patients with refractory ventricular arrhythmias or electrical storm: intermediate and long-term follow-up. Heart Rhythm. 2014 Mar;11(3):360-6
Renal Sympathetic Denervation
- Reduces central sympathetic efflux to the heart
- Benefit shown in small studies
VT storm is a bad prognostic indicator
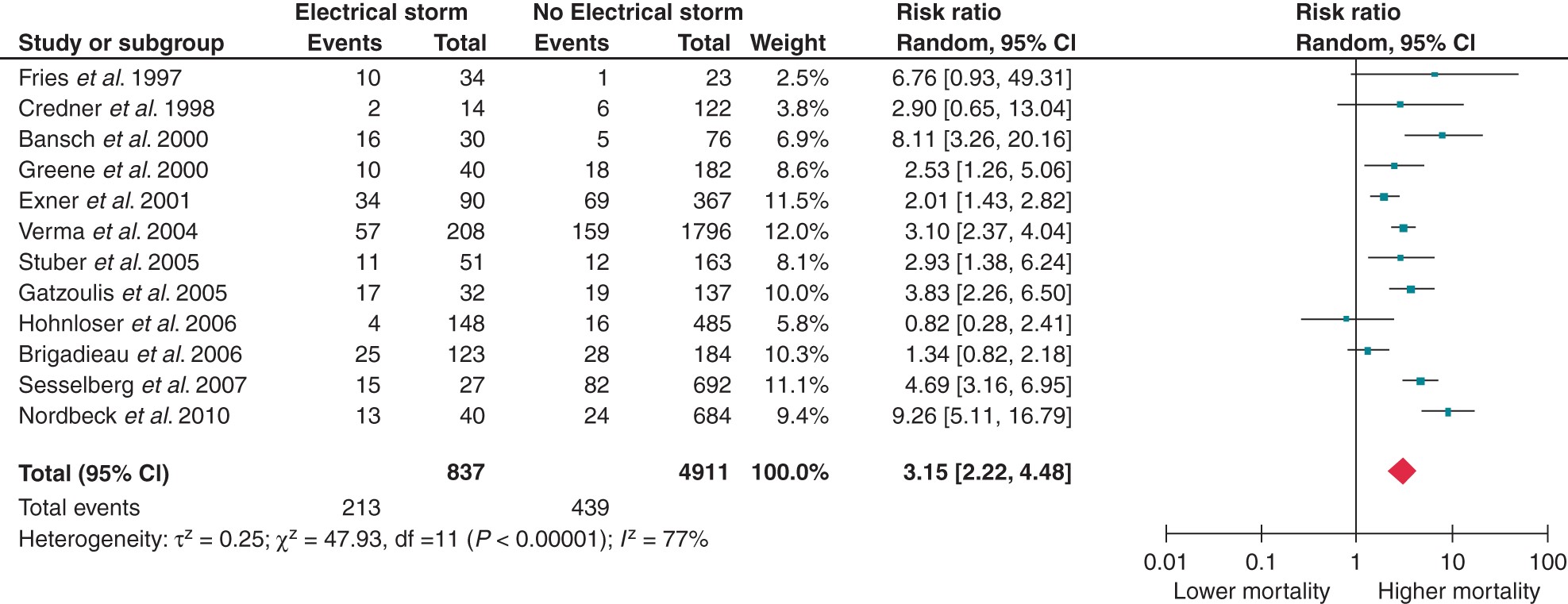
Guerra F, Shkoza M, Scappini L, Flori M, Capucci A. Role of electrical storm as a mortality and morbidity risk factor and its clinical predictors: a meta-analysis. Europace 2014;16:347–53.
MADIT II substudy
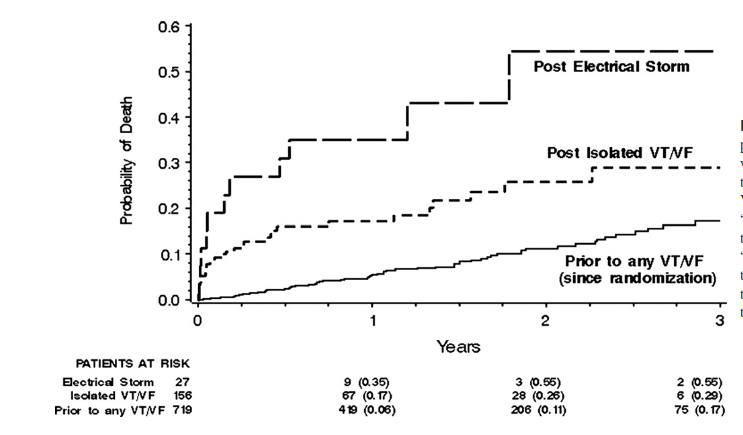
Sesselberg HW, Moss AJ, McNitt S, Zareba W, Daubert JP, Andrews ML, Hall WJ, McClinitic B, Huang DT; MADIT-II Research Group. Ventricular arrhythmia storms in postinfarction patients with implantable defibrillators for primary prevention indications: a MADIT-II substudy. Heart Rhythm. 2007 Nov;4(11):1395-402.
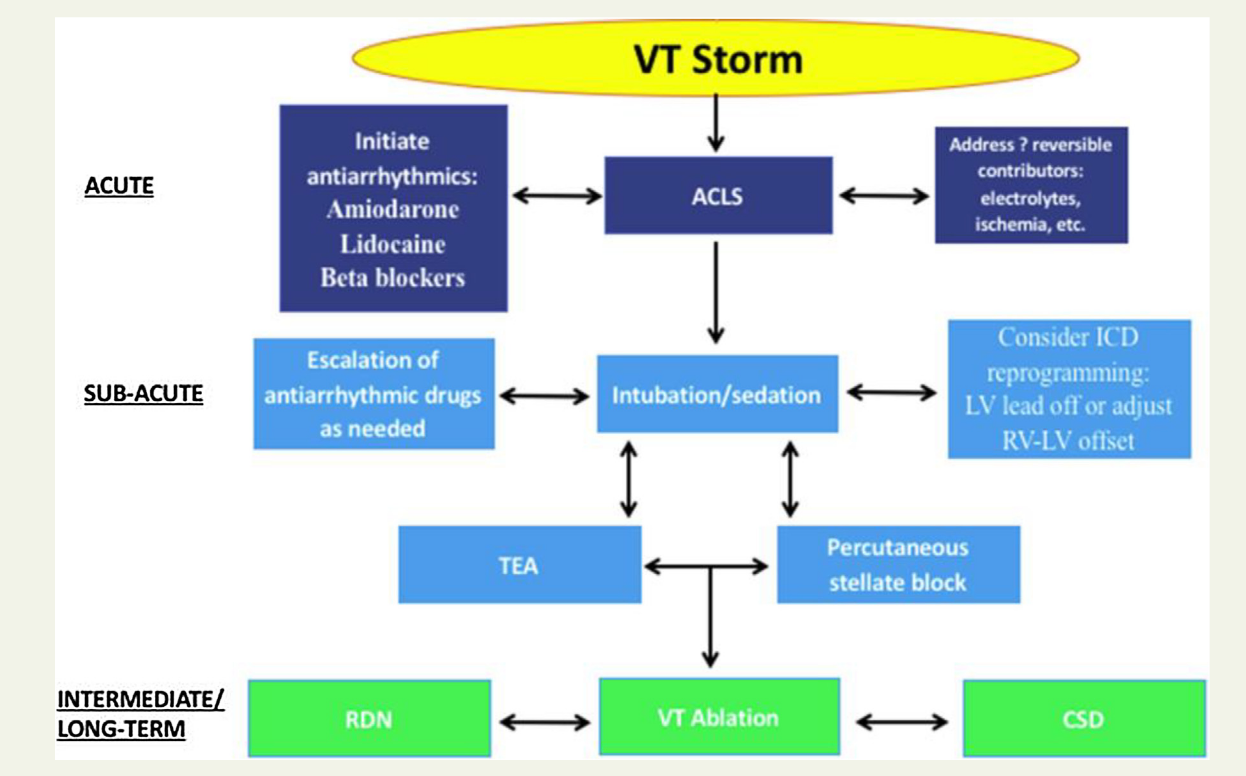
Geraghty L, Santangeli P, Tedrow UB, Shivkumar K, Kumar S. Contemporary Management of Electrical Storm. Heart Lung Circ. 2019 Jan;28(1):123-133.