
Approach to VT in Structurally Abnormal Heart
Raja Selvaraj MD DNB FCE (Toronto)
Cardiac Electrophysiologist
Professor of Cardiology
JIPMER
WQRST or VT ?
44 yr old male, CAD, palpitations, BP 90/60
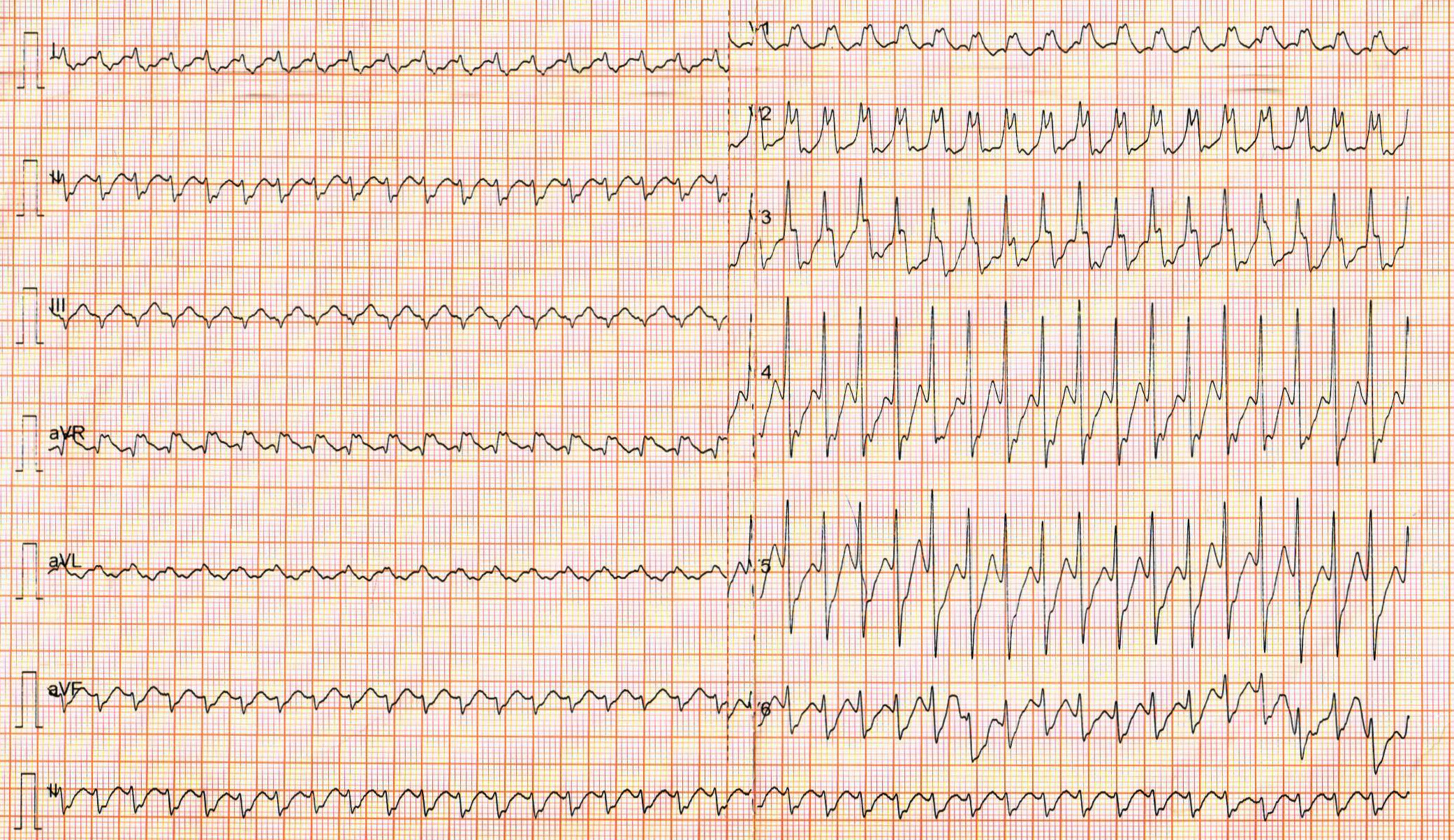
What would you do?
- DC cardioversion
- IV Amiodarone
- IV Adenosine
- IV Lidocaine
WQRST in heart disease is always VT
- Yes
- No
WQRST in heart disease should always be treated as VT
- Yes
- No
VT or SVT - Does it matter ?
- Yes
- No
Similar patient, treated elsewhere
- DCCV done
- LVEF 40%
- Referred for ICD implant
Make effort to identify mechanism
- Call it WQRST
- Record 12-lead ECGs
- Adenosine
ACLS - Tachyarrhythmia with pulse
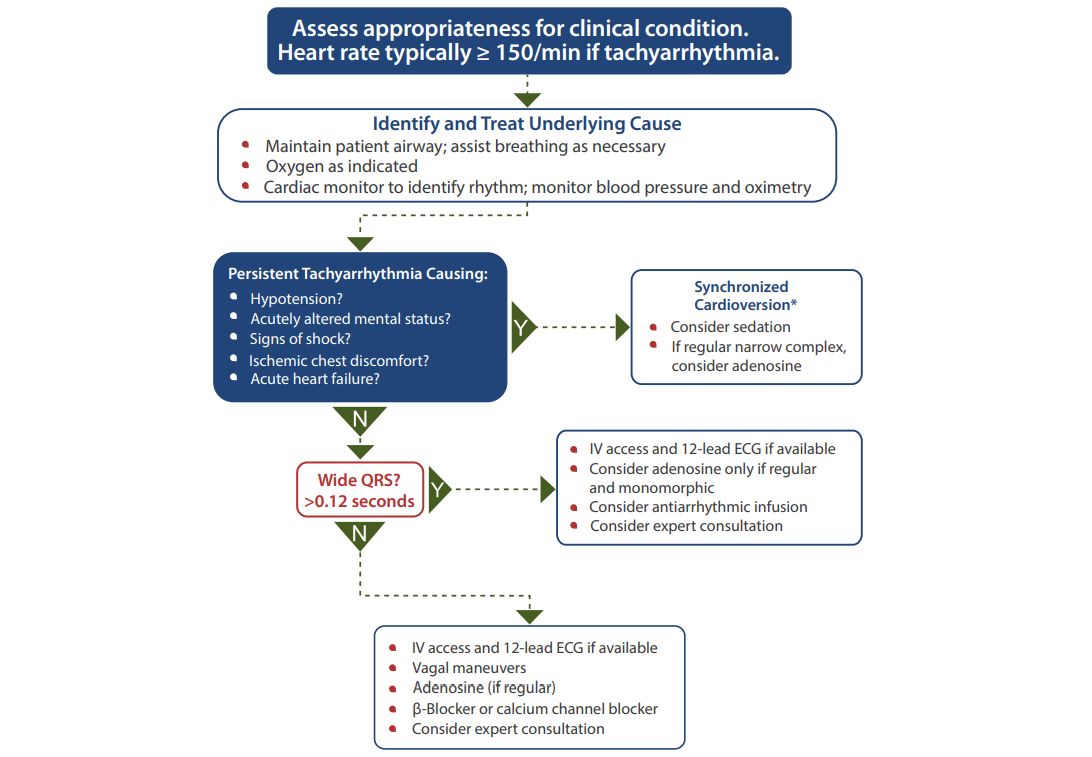
Adenosine during WQRST
- Ventricular rate slows transiently with A>V
- Tachycardia terminates
- Tachycardia continues with no change
- Tachycardia continues, VA dissociation appears
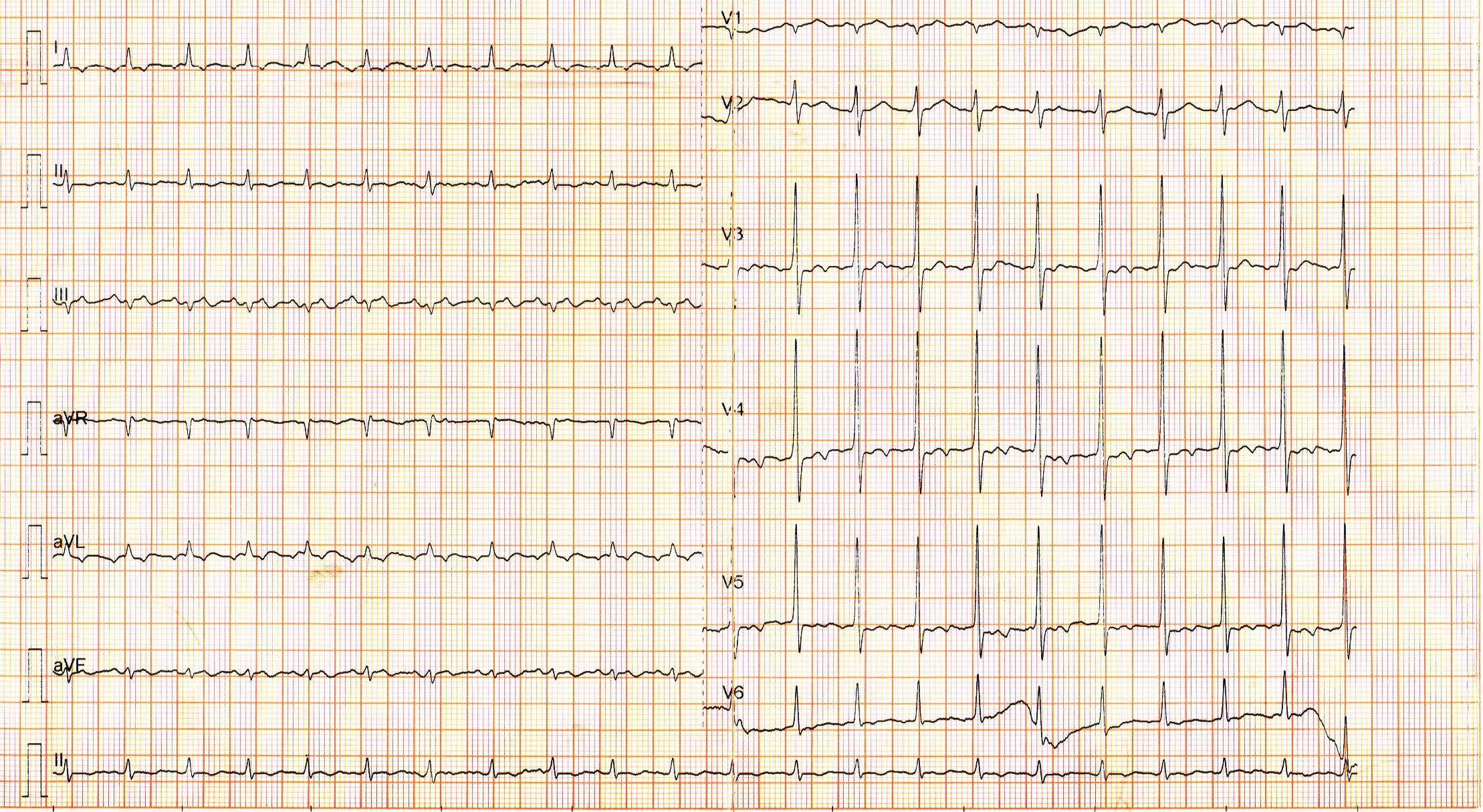
Adenosine showed response 1, treated with AV nodal blockers
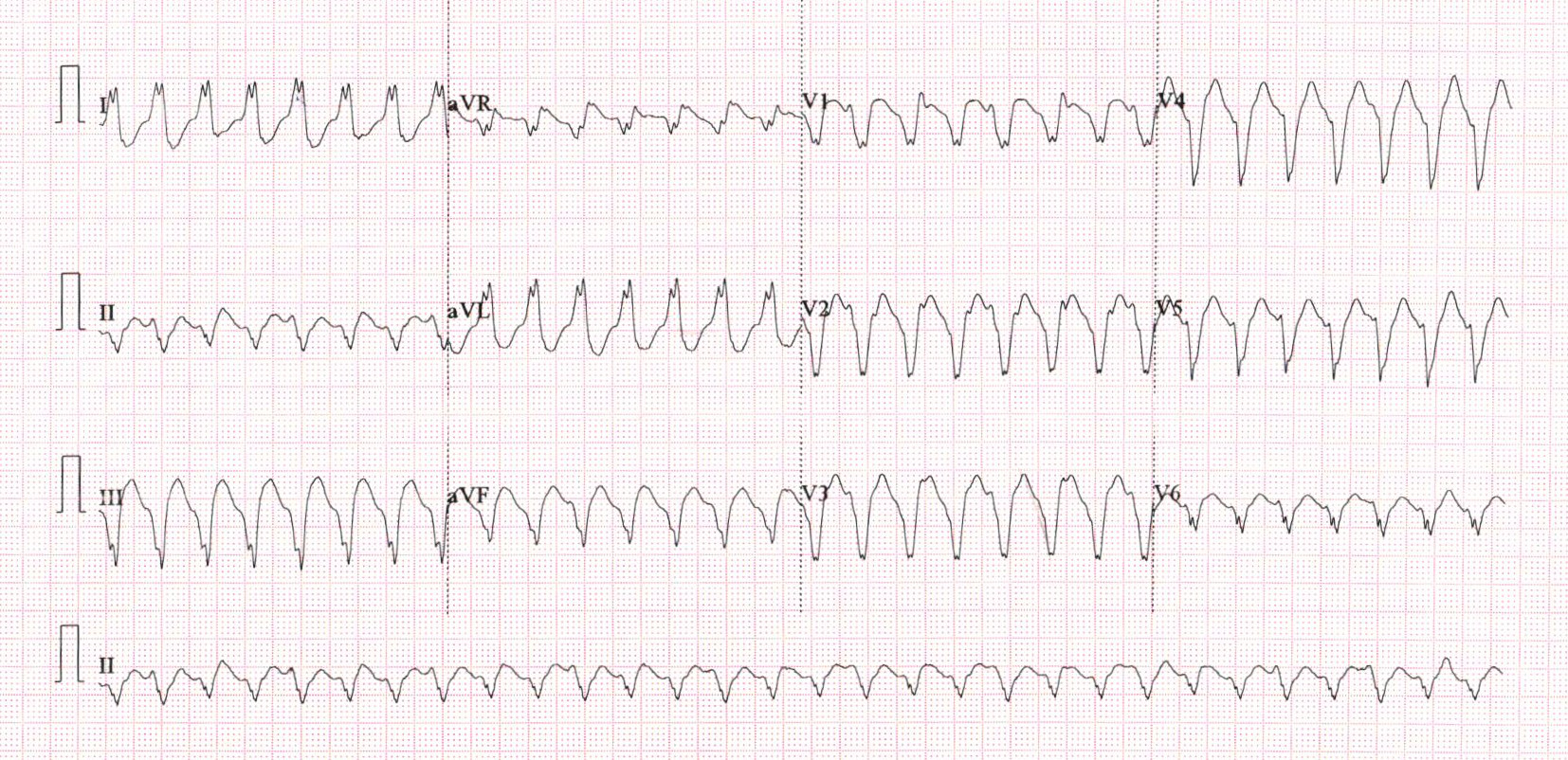
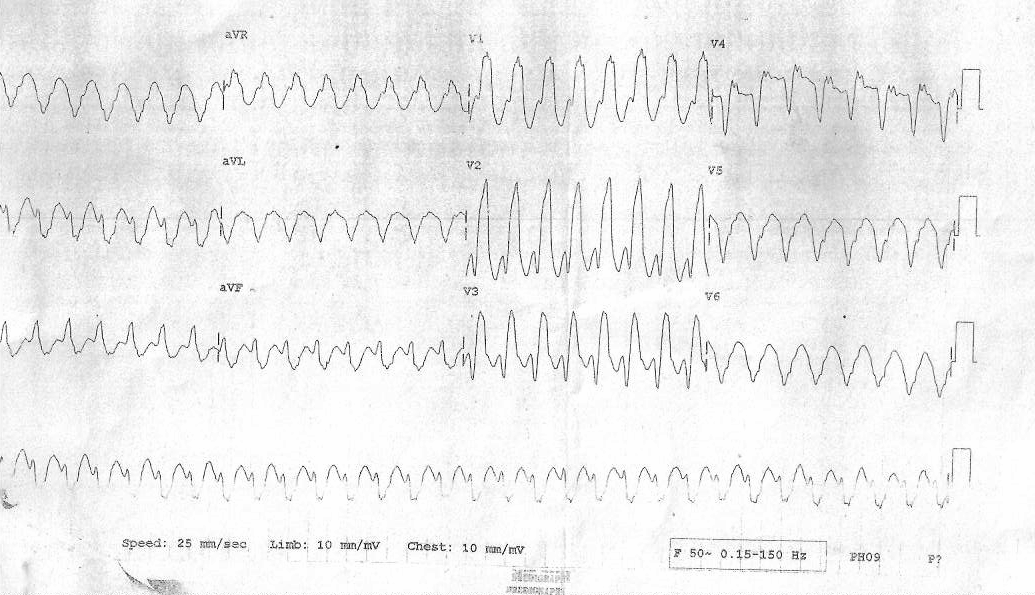
When is WQRST VT ?
Substrate
Likely substrate ?

Sinus ECG
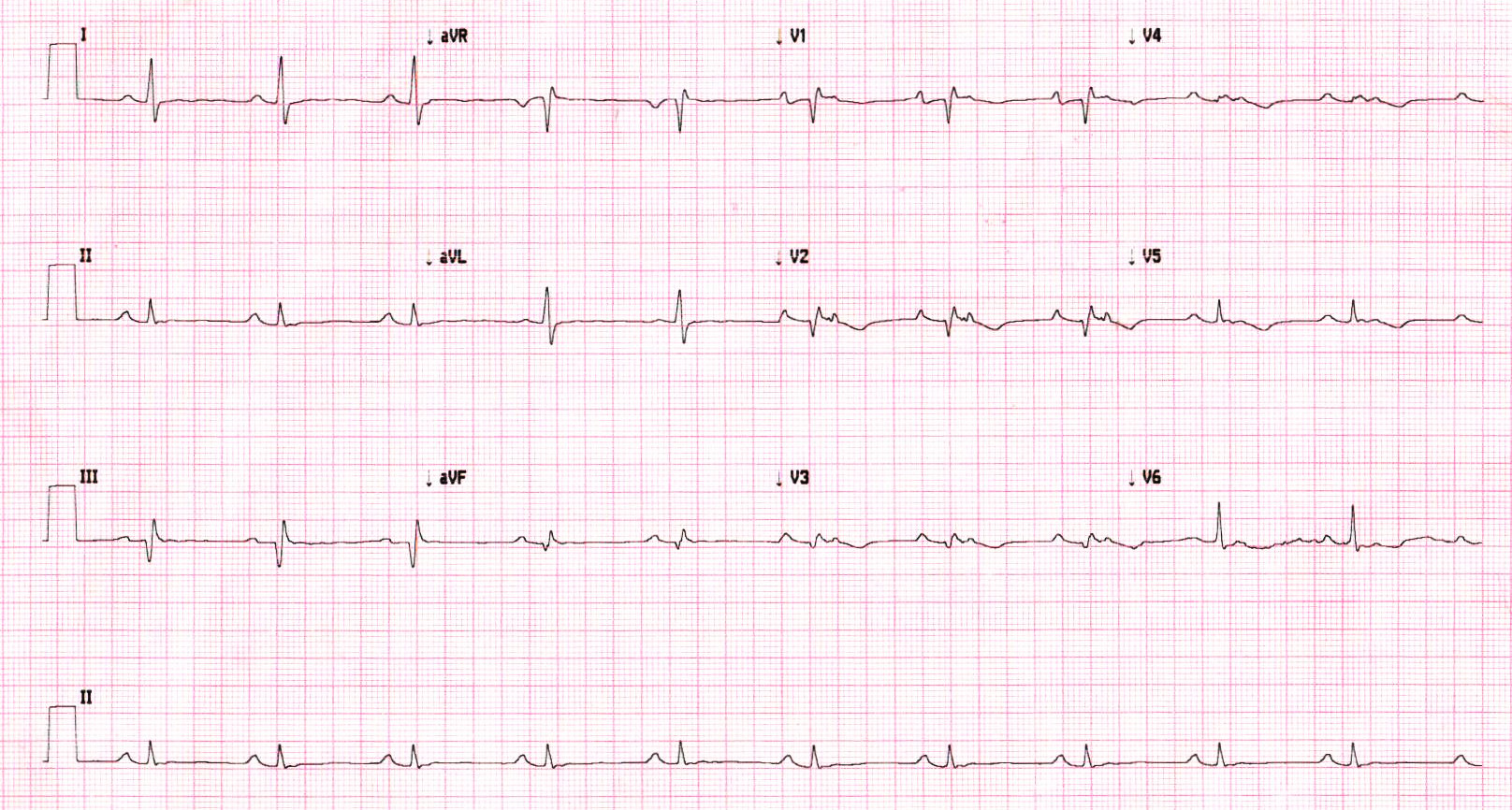
Likely substrate ?
Long term management
Management
- ICD
- Pharmacological management
- Ablation
ICD
- Indicated in all structural heart disease with sustained VA
- Stable VA vs unstable VA
- LVEF
Scenario
- 54 male
- IWMI 6 years back
- walk-in VT
- LVEF 45%
Management
- CAG
- Beta blockers
- Anti-arrhythmics
- ICD
- Ablation
CAG
- Polymorphic VT / VF can be due to reversible ischemia
- Sustained monomorphic VT not due to ischemia
- Modest elevation of biomarkers does not indicate ischemia
- Re test after 3 months if possibly reversible after revascularization
What do the guidelines say about ICD?
- Hemodynamically unstable sustained VT / VF - class I A
- Structural heart disease, stable sustained VT - class I B
- Sustained VT with normal or near normal LV function - class IIa C
Patient can only afford ICD or ablation. What would you recommend?
ICD
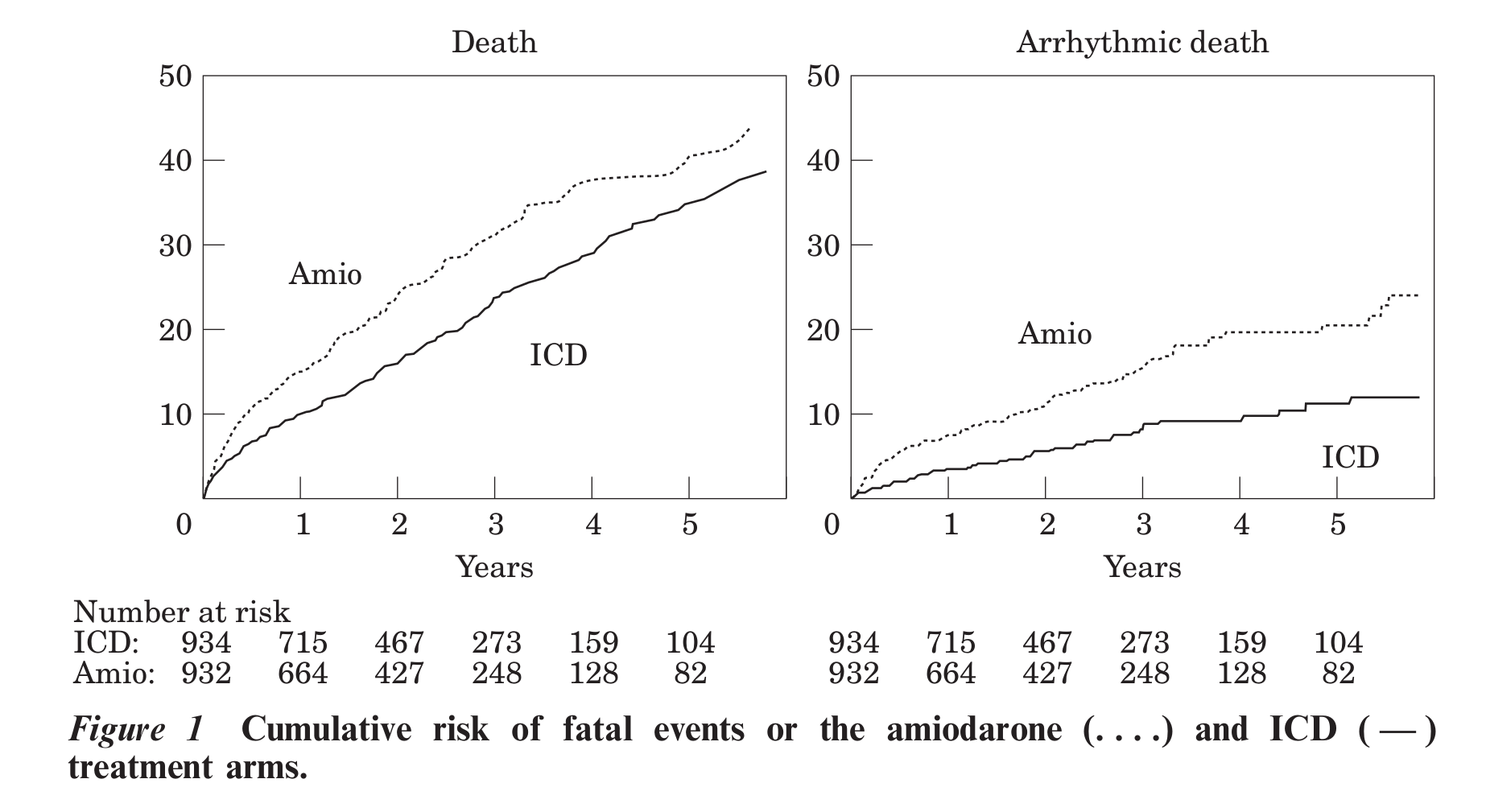
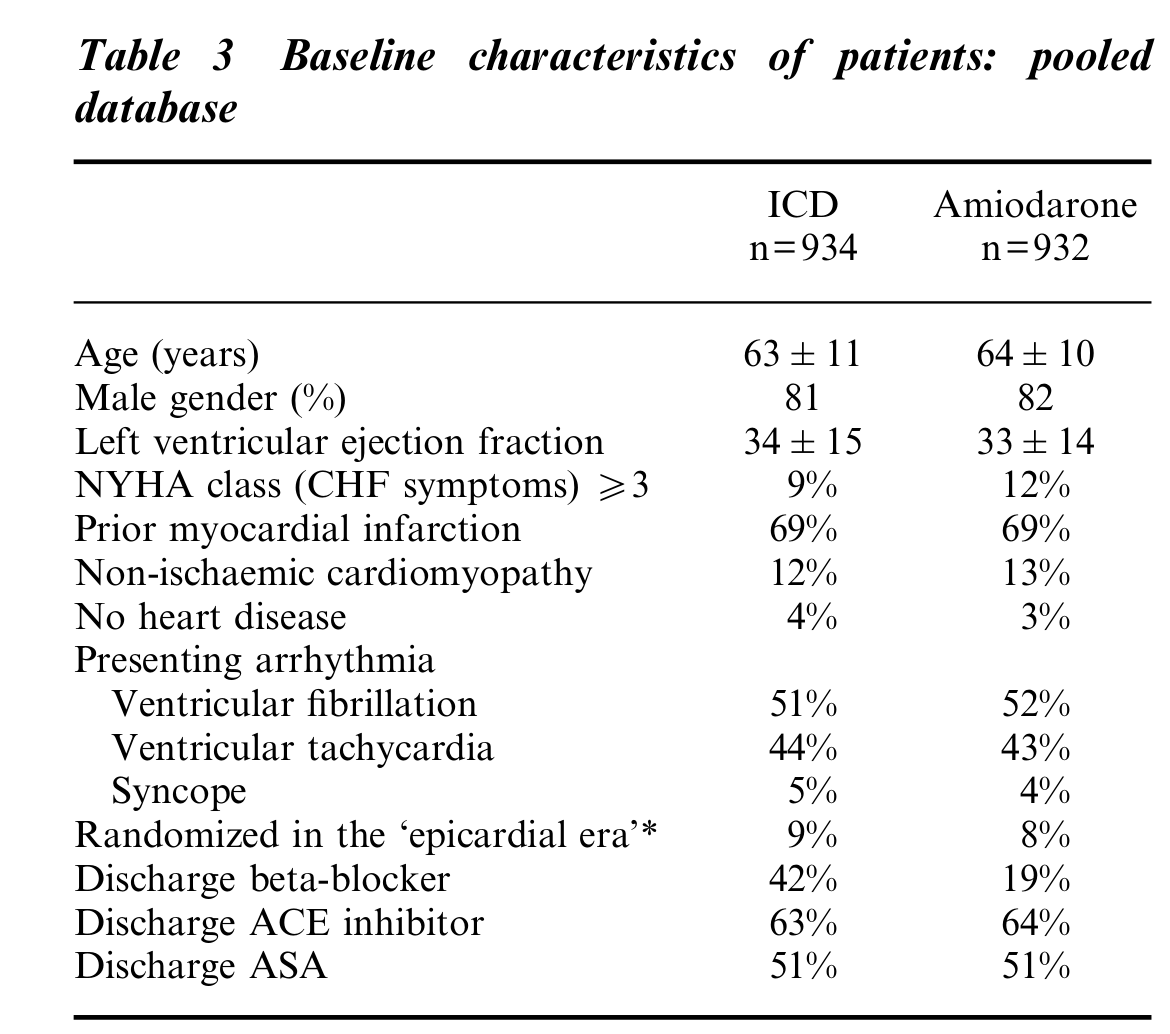
Connolly et al. Metaanalysis of ICD secondary prevention trials
ICD secondary prevention trials metaanalysis
- 29 implants to save one life per year of follow up
- Benefit after 3 years?
- Increase in survival by 1/3 years after 6 years of follow up
Importance of EF
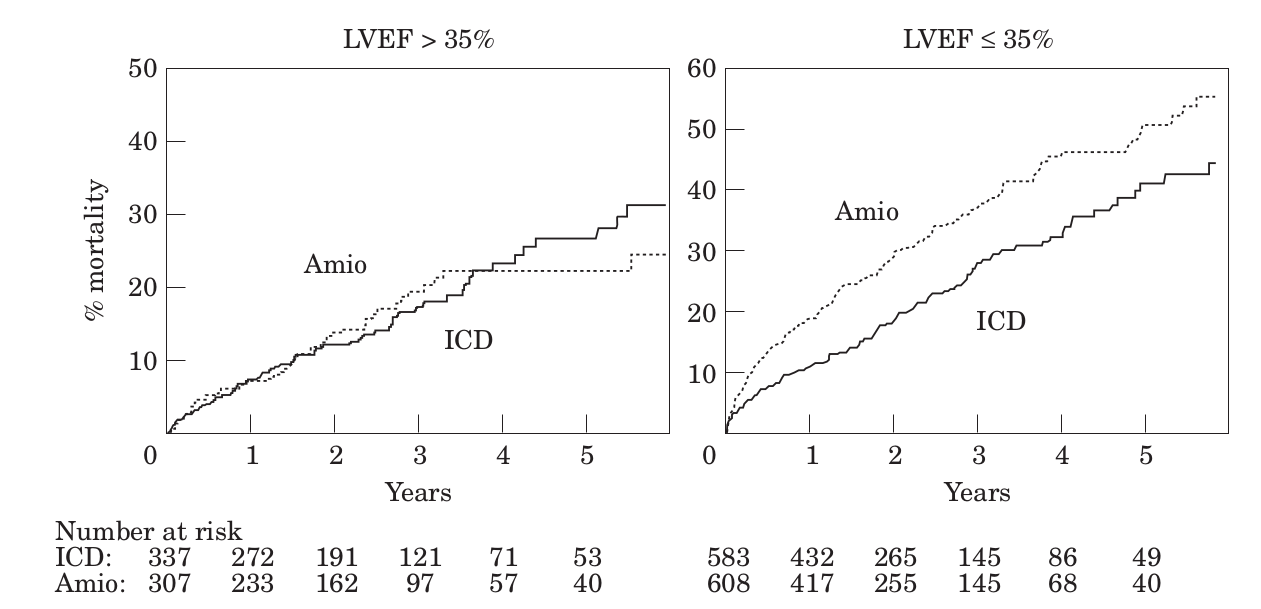
Beta blockers in secondary prevention
Connolly et al. Metaanalysis of ICD secondary prevention trials
Appropriate use criteria
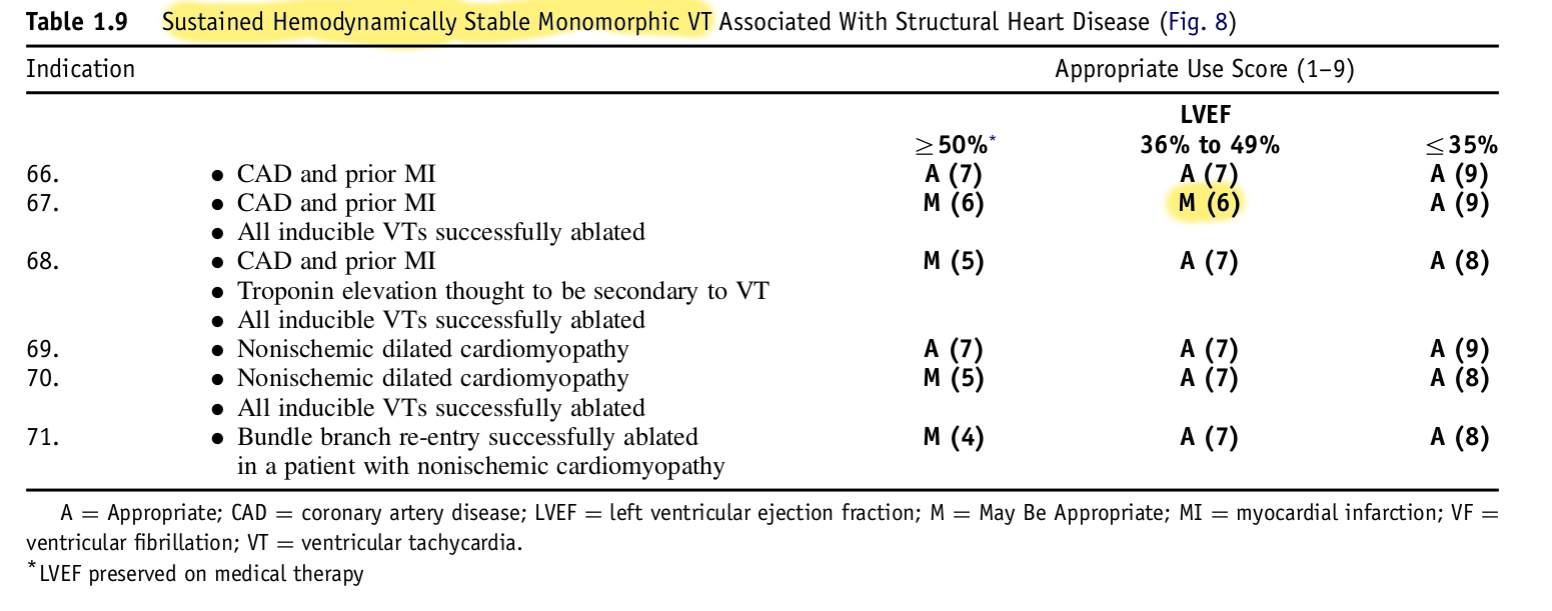
Why is ICD not sufficient ?
- Shocks are painful and decrease QOL
- Associated with increased mortality (1)
- Recurrent VT may itself result in sudden death despite ICD
Sweeney et al. Differences in effects of electrical therapy type for ventricular arrhythmias on mortality in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator patients. Heart Rhythm 2010;7:353–360
Pharmacological management
- Don't forget beta blockers
- Amiodarone
- Mexilitene
Mexiletine as adjunctive therapy with Amiodarone failure
- 29 patients with recurrent ICD therapies on Amiodarone
- Mexiletine added or replaced Amiodarone
- Significant reduction in therapies
- Long term efficacy better when added to Amiodarone
Gao D; Van Herendael H; Alshengeiti L; Dorian P; Mangat I; Korley V; Ahmad K; Golovchiner G; Aves T; Pinter A. Mexiletine as an adjunctive therapy to amiodarone reduces the frequency of ventricular tachyarrhythmia events in patients with an implantable defibrillator.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013; 62(2):199-204 (ISSN: 1533-4023)
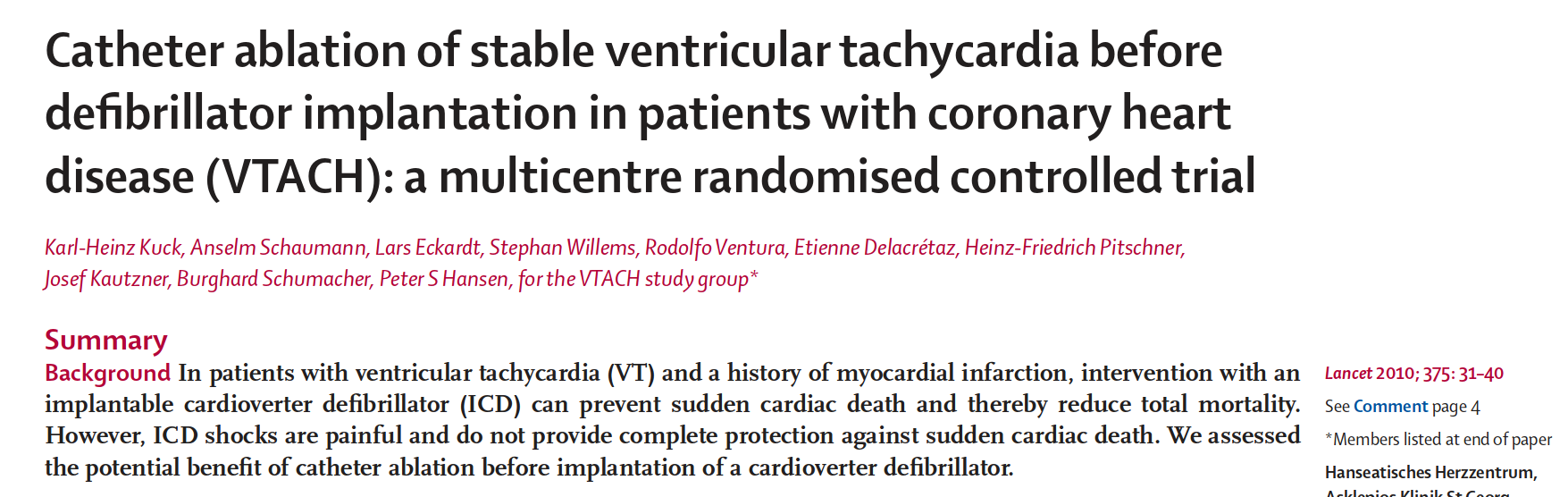
Ablation
- Significant reduction in recurrences when used as first line
- Superior to AAD with failed amio
- Does not reduce mortality
Ablation as first line
Ablation as first line
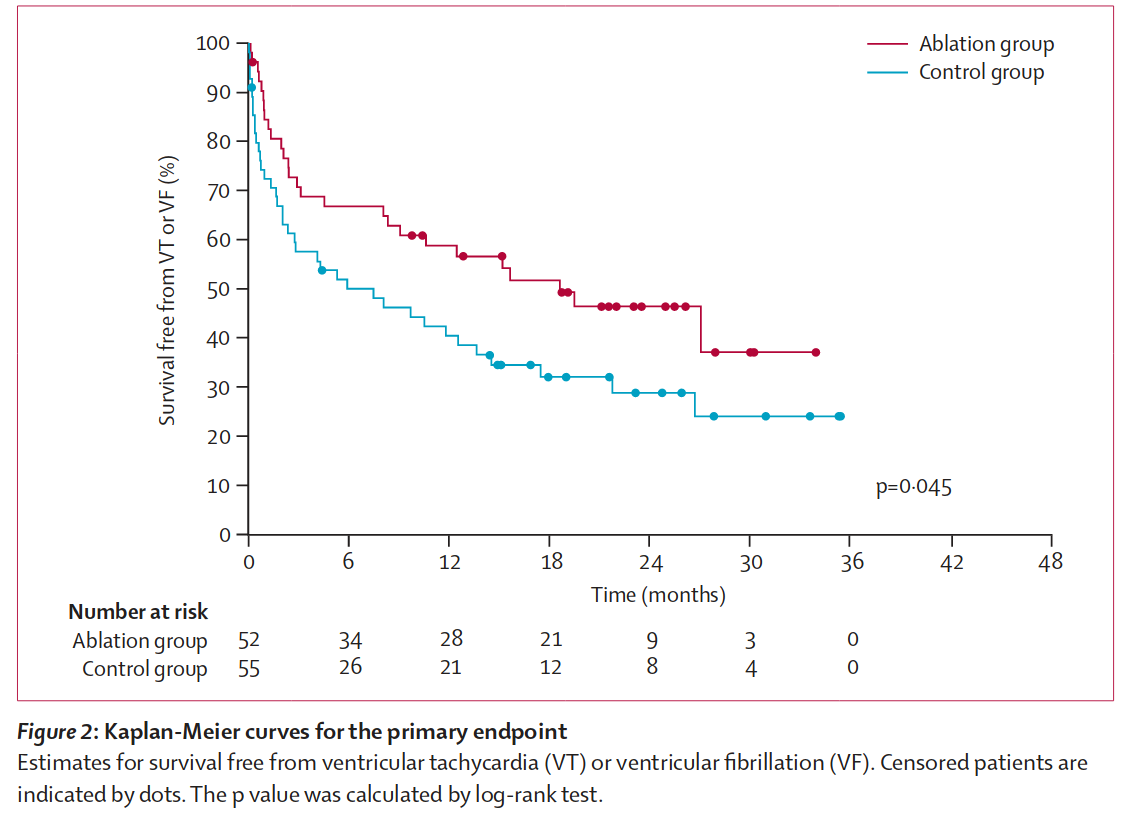
Ablation after recurrence on AAD

Ablation after recurrence on AAD
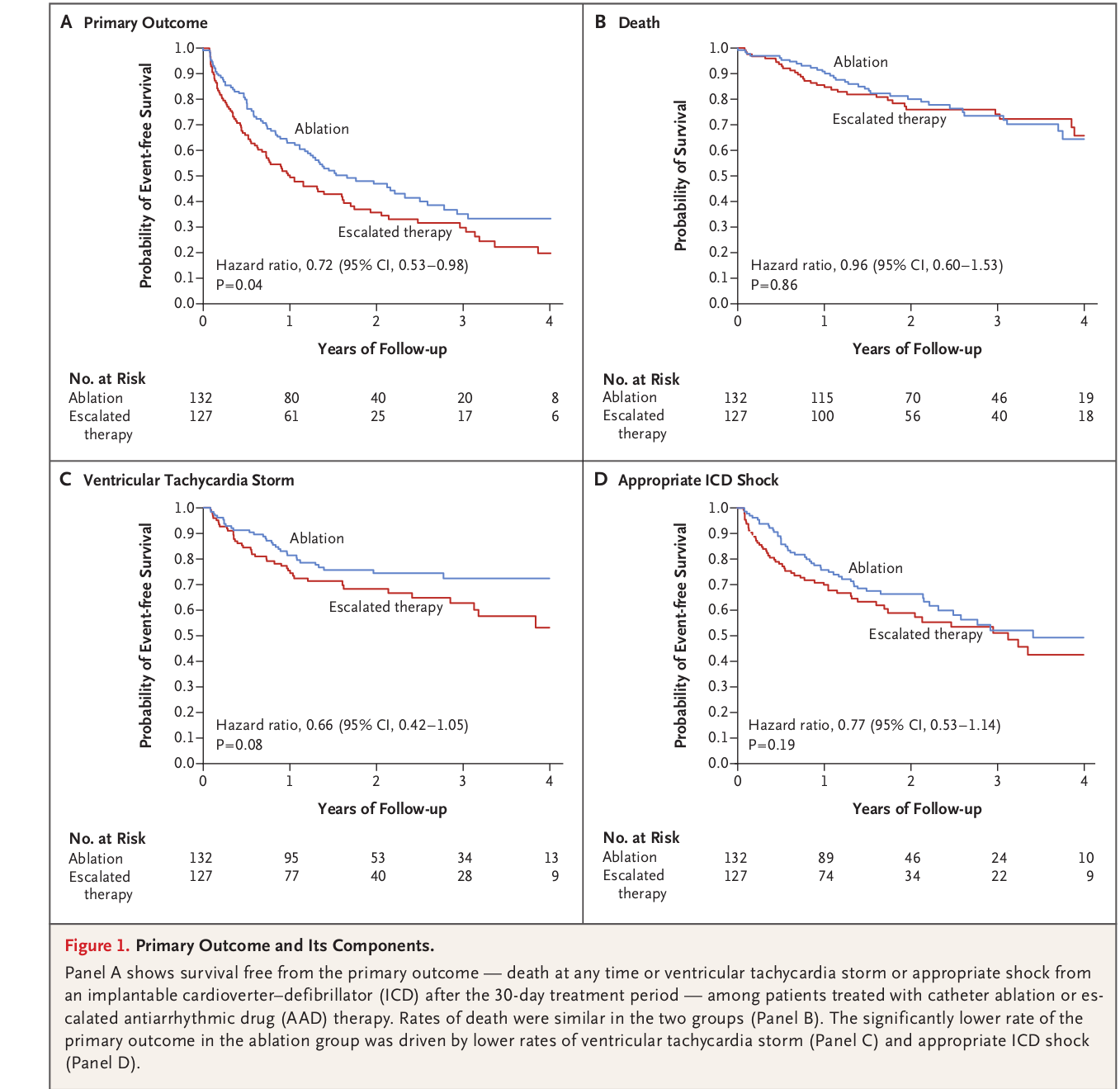
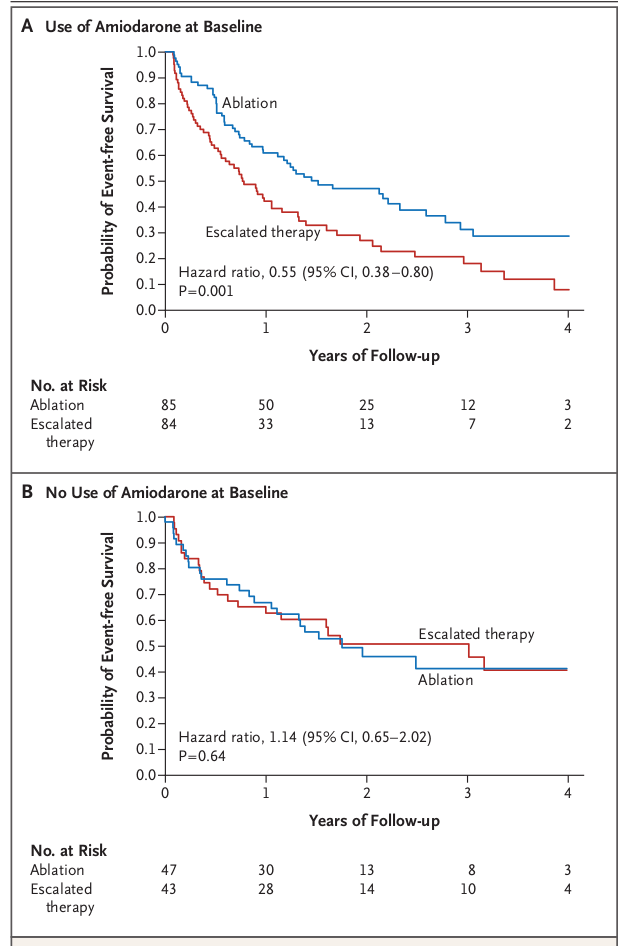
Ablation after recurrence on AAD
Summary
- WQRST in structural heart disease is most often VT, but not always - and it matters
- VT in structural heart disease indicates risk of sudden death and benefits from ICD
- However, the risk and therefore the benefit depend on EF and presenting arrhythmia
- Pharmacological treatment is needed in all patients
- Ablation very useful in patients with recurrence on drugs