
Persistent VT after revascularization
Raja Selvaraj
Cardiac Electrophysiologist
Professor of Cardiology
JIPMER
Mechanisms of VT in acute MI
- Ischemia and resultant local electrolyte abnormalities
- Necrosis and healing, surviving purkinje fibers
- Reperfusion
- Electrolyte abnormalities
- Autonomic changes
- Mechanical stretch of failing ventricle
AIVR
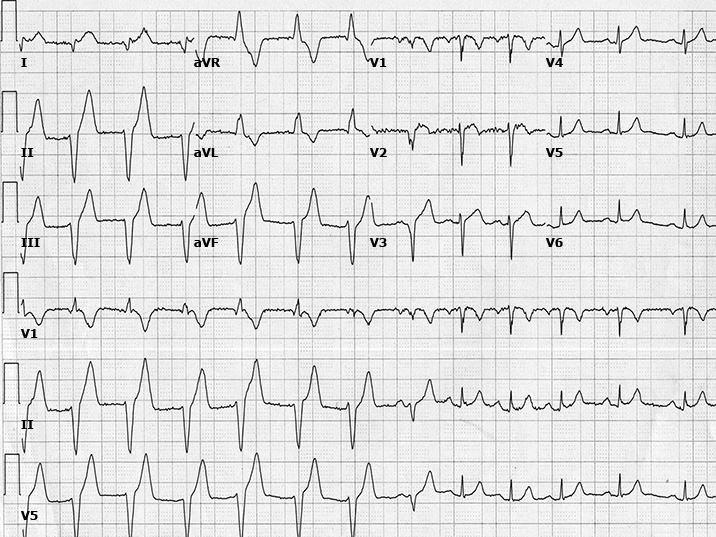
Arrhythmia after CTO PCI
- 342 patients after CTO PCI
- VA in 9 (2.6%) patients
- All were monomorphic VT occurring in median 1 day after PCI
- Patients with VT were older, had worse LVEF
- Mortality rates not different between patients with or without VT
König S et al. Incidence and characteristics of ventricular tachycardia in patients after percutaneous coronary revascularization of chronic total occlusions. PLoS One. 2019 Nov 22;14(11):e0225580..
VT after MI
- GUSTO-1 trial of 40,895 patients who were treated with thrombolytic therapy
- 3.5 percent developed VT
- 4.1 percent VF
- 2.7 percent both VT and VF
- Approximately 80 to 85 percent of these arrhythmias occurred in the first 48 hours
Newby KH et al. Sustained ventricular arrhythmias in patients receiving thrombolytic therapy: incidence and outcomes. The GUSTO Investigators. Circulation. 1998 Dec 8;98(23):2567-73.
VT after primary PCI
- 5.7% developed sustained VT / VF
- 2/3 before end of the procedure
- 90% within 48 hours
Mehta RH et al. Incidence of and outcomes associated with ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention.JAMA. 2009; 301:1779–89.
Early versus late arrhythmias
- Late VT/VF (> 48 h) associated with higher risk of death (1)
- VT/VF any time associated with higher risk of death within 90 days (2)
- Volpi A et al. One-year prognosis of primary ventricular fibrillation complicating acute myocardial infarction. The GISSI (Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Streptochinasi nell’Infarto miocardico) investigators.Am J Cardiol. 1989; 63:1174–8.
- Mehta RH et al. Incidence of and outcomes associated with ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention.JAMA. 2009; 301:1779–89.
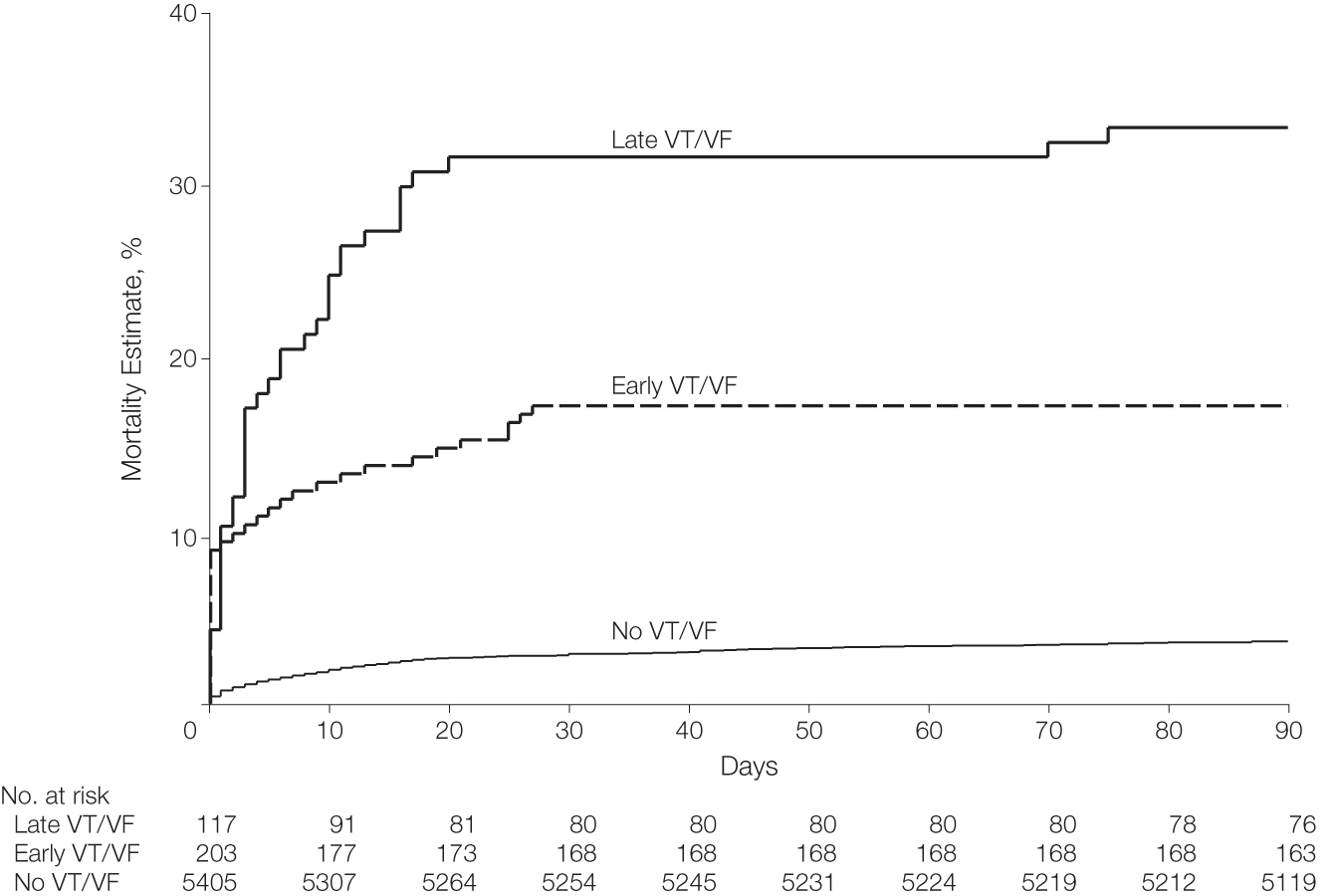
Mehta RH et al. Incidence of and outcomes associated with ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention.JAMA. 2009; 301:1779–89.
Management
- ? Ischemia - Revascularization
- Correction of electrolyte abnormalities
- Pharmacological therapy
- Other measures
- Ablation
- ICD
Revascularization
- Polymorphic VT / VF
- Other evidence of ischemia
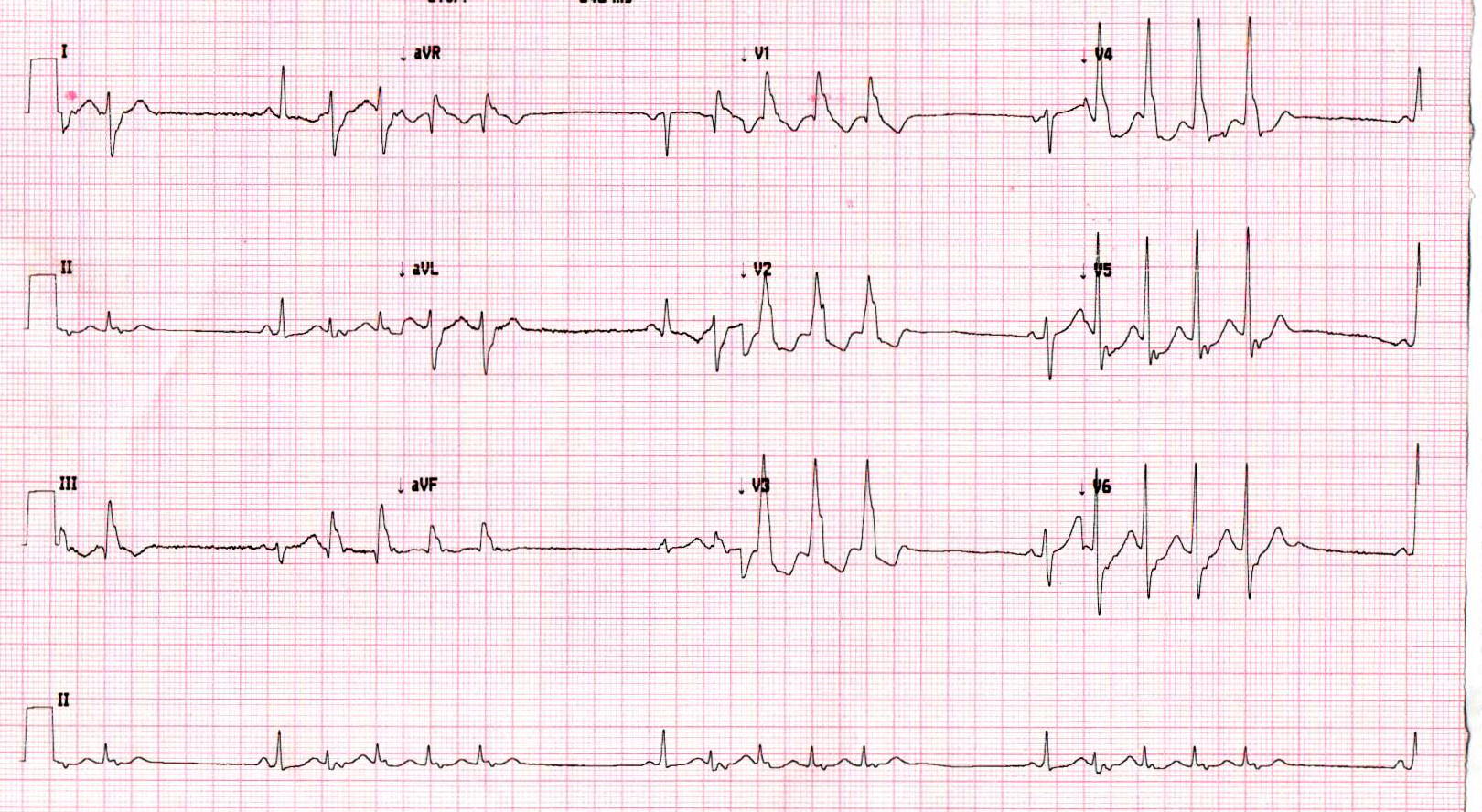
Electrolyte abnormalities
- Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia are common
- Associated with VA during an acute MI
- Magnesium should be repleted to facilitate replacement of the potassium
Beta blockers
- Only antiarrhythmic that improves survival
- Reduce inotropes
- Sedation
Huang BT et al. Meta-analysis of relation between oral b-blocker therapy and outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115:1529–1538. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.02.057
Lidocaine
- Class Ib
- May be beneficial (1)
- May be neutral
- Mexilitene
Piccini JP et al. Antiarrhythmic drug therapy for sustained ventricular arrhythmias complicating acute myocardial infarction. Crit Care Med. 2011;39:78–83. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181fd6ad7.
Amiodarone
- Safe with structural heart disease
- Time to take effect
Ranolazine
- Reduced NSVT
- No change in other outcomes
Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E et al. The risk of sudden cardiac death in patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome and prolonged QTc interval: effect of ranolazine. Europace. 2013;15:429–436. doi: 10.1093/europace/eus400
Sedation
- Reduces sympathetic outflow
- Deep sedation in VT storm
Sympathetic blockade
- Stellate ganglion block
- Thoracic epidural anaesthesia
Bourke T et al. Neuraxial modulation for refractory ventricular arrhythmias: value of thoracic epidural anesthesia and surgical left cardiac sympathetic denervation. Circulation. 2010 Jun 1;121(21):2255-62.
Overdrive pacing
- Suppress automaticity
- Induce exit block
- Terminate / prevent reentry
Ablation
- 70% success
- Periprocedural mortality - 3%
- Long term mortality - 18%
- Ablate automatic foci, reentry, substrate
Stevenson WG et al. Multicentre Themocool VT Ablation Trial Investigators. Irrigated radiofrequency catheter ablation guided by electroanatomic mapping for recurrent ventricular tachycardia after myocardial infarction: The Multicentre Thermocool Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation Trial. Circulation. 2008;118:2773–2782. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.788604.
Mechanical circulatory support
- Helps reduce inotrope use
- Supports procedures
- IABP, Impella, VA-ECMO
ICD
- Not in acute phase
- Secondary prevention for VA after 48 hours
Summary
- Persistent VT after revascularization in MI uncommon, but difficult problem
- Most occur early in course
- Sympathetic blockade is key to management
- Late arrhythmias indicate high long term risk of sudden death and benefit from ICD