
Management of Existing Pacemakers and Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators
Raja Selvaraj
Cardiac Electrophysiologist
Professor of Cardiology
JIPMER
Introduction
CIED (Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device)
- Pacemaker
- Defibrillator (ICD)
- Resynchronization therapy devices (CRT-P / CRT-D)
Pacemaker
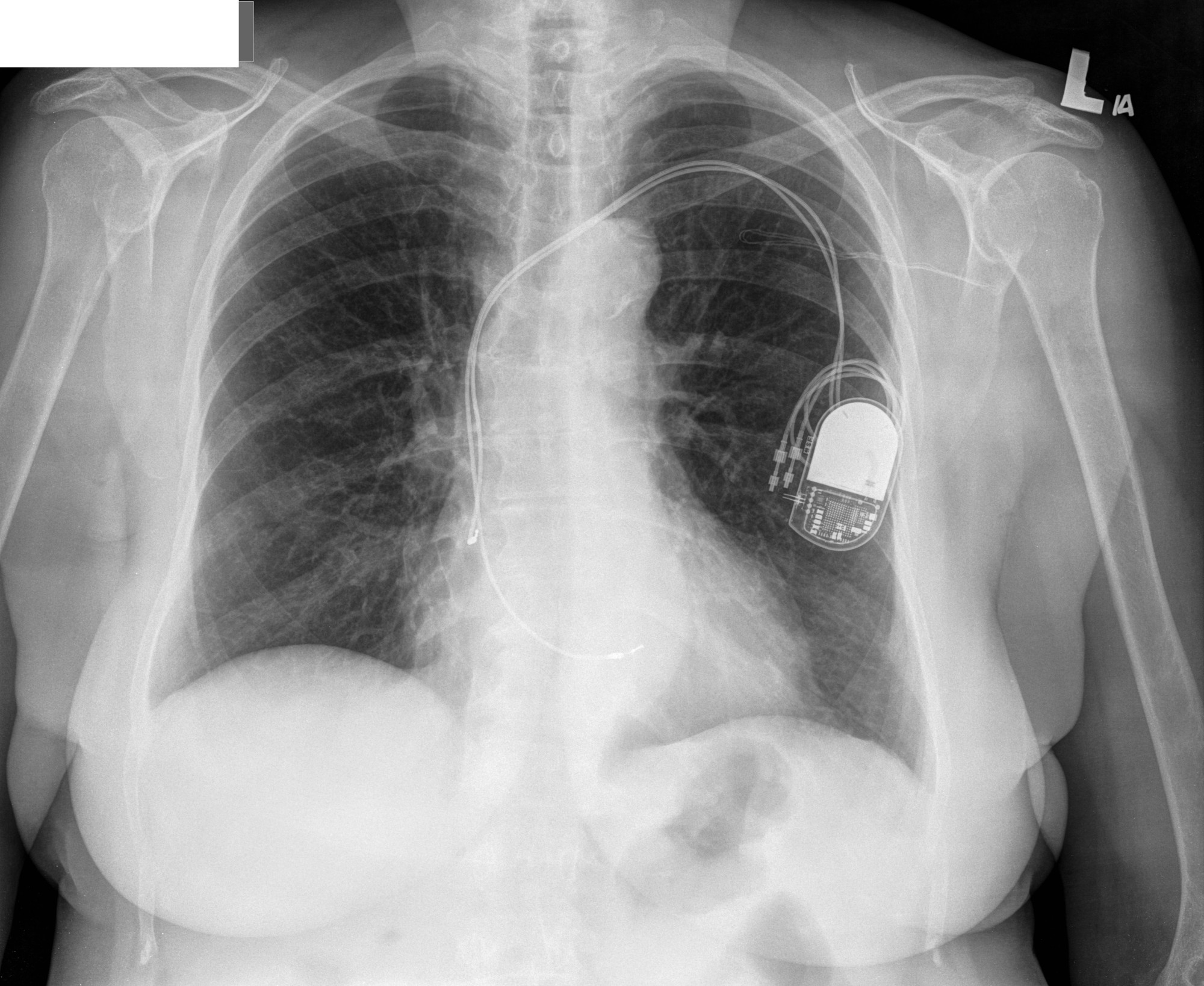
CRT
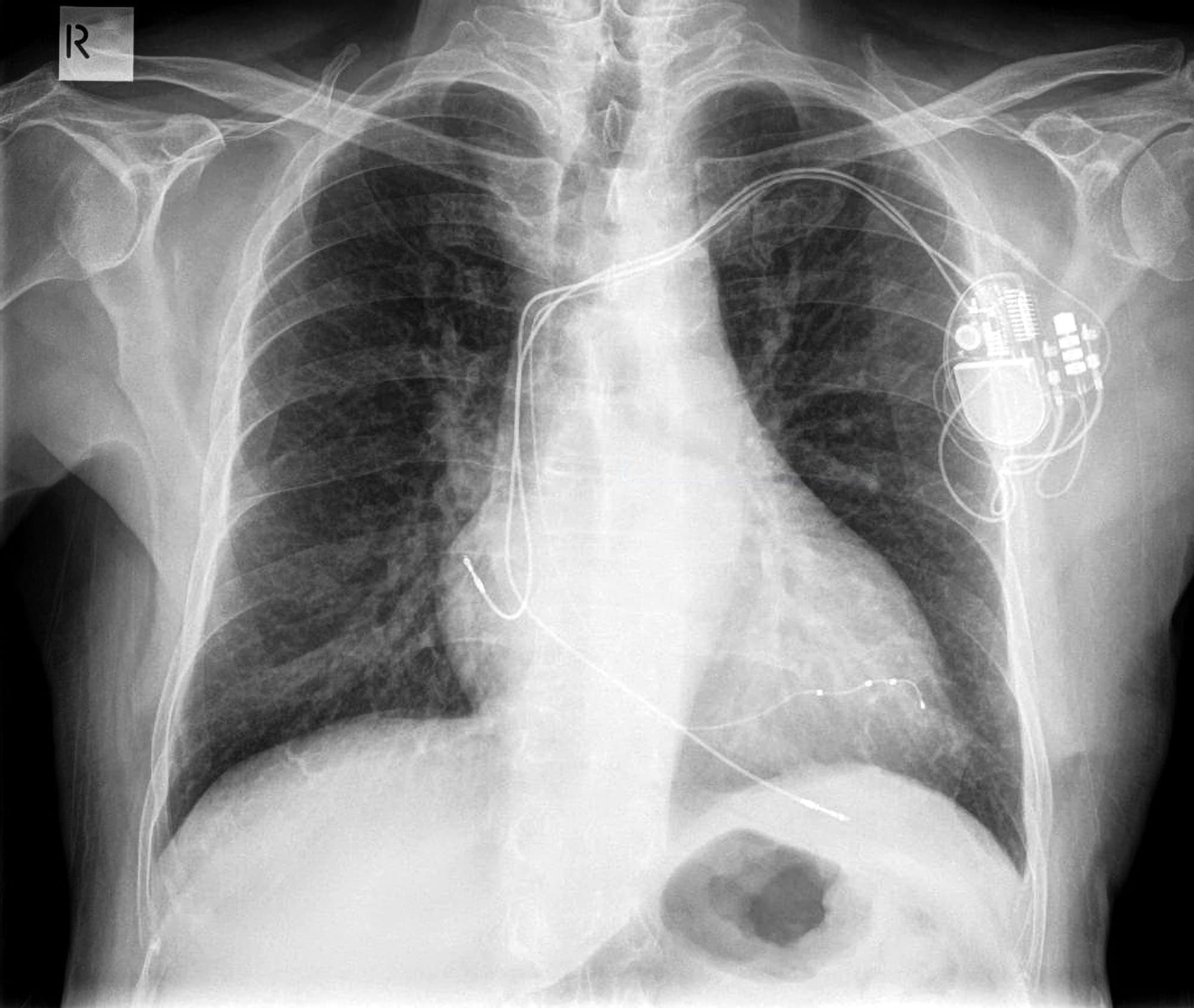
ICD
Functions of CIEDs
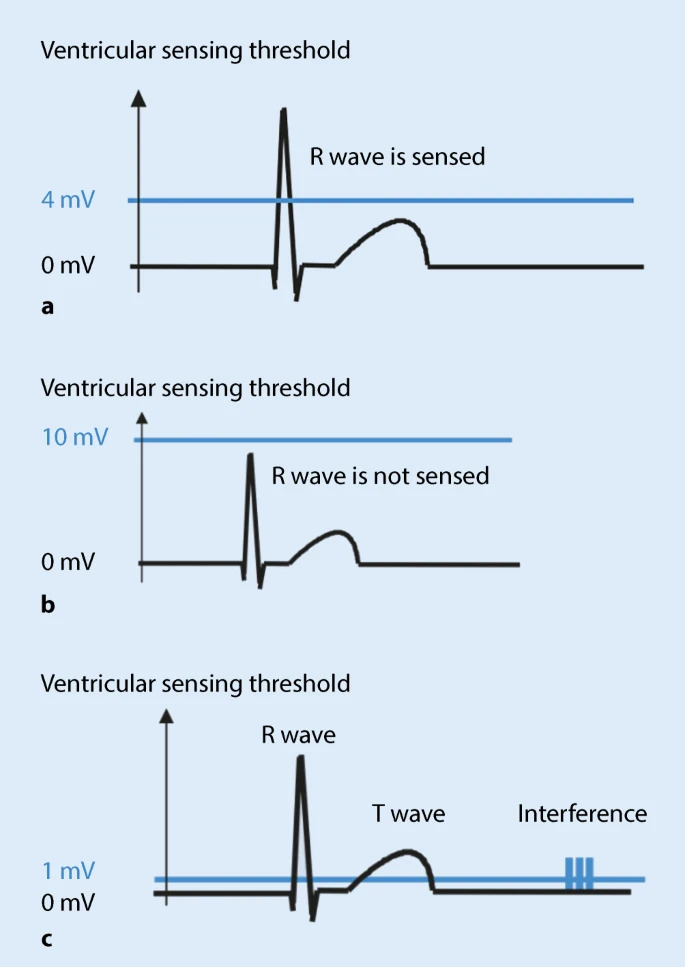
Sensing
Pacing
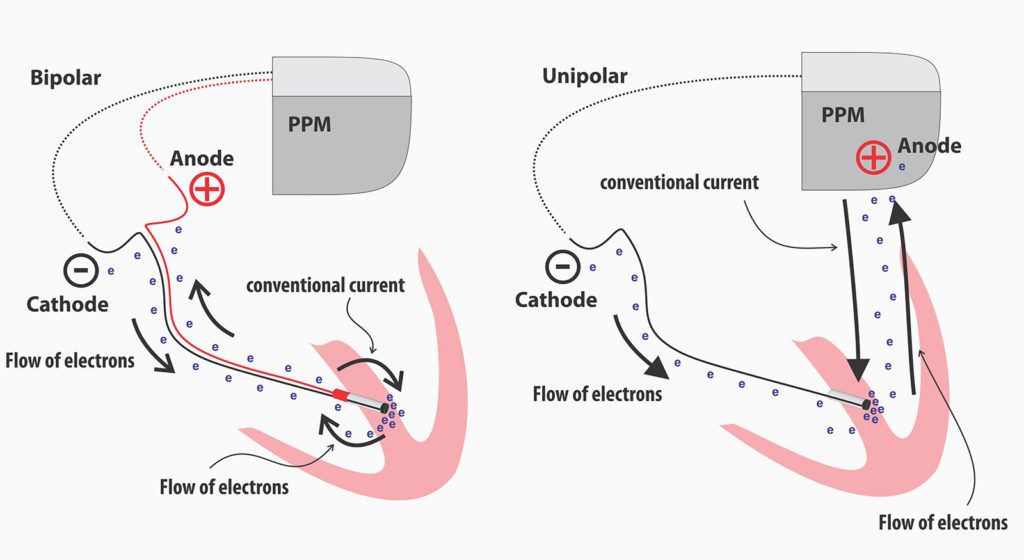
Defibrillation
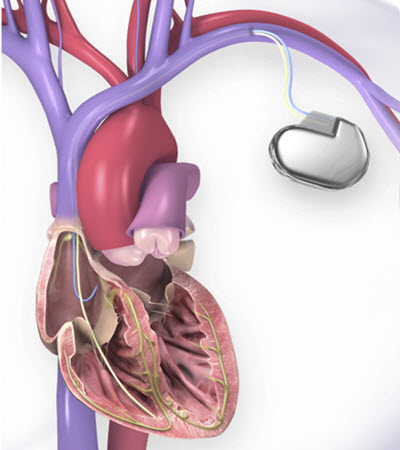
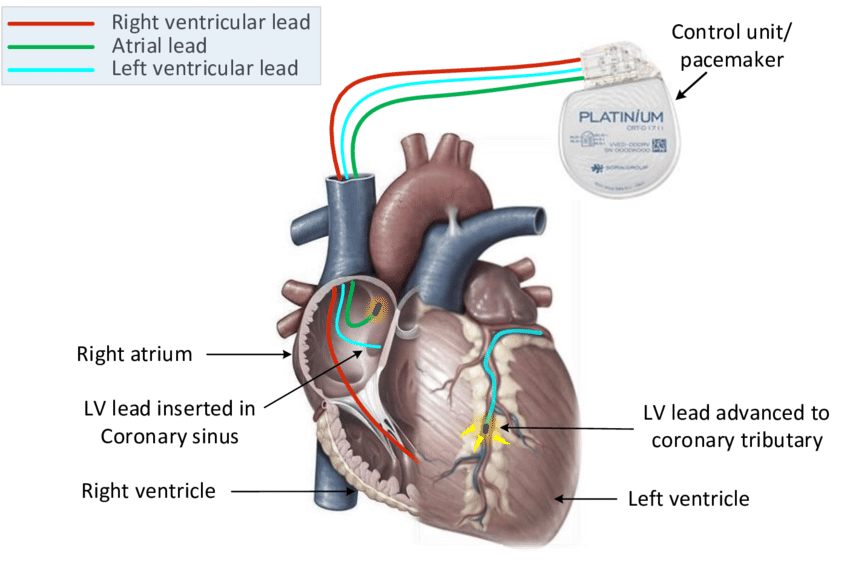
Cardiac Resynchronization
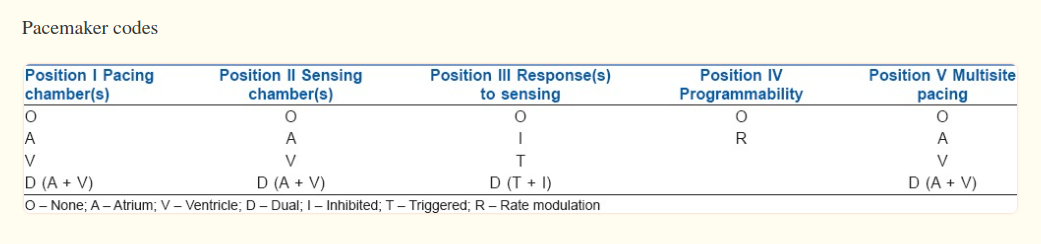
NASPE / BPEG Code
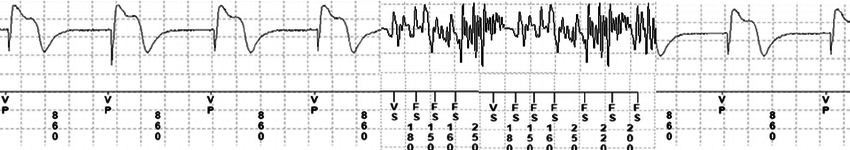
Electromagnetic interference
Potential disruption of operation when in vicinity of a source of electromagnetic field
Sources in OR
- Electro cautery
- Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
- External defibrillation
- Evoked potentials
- Nerve stimulators
- Radiofrequency ablation
What does sensed activity do ?
- Can inhibit pacing
- Can trigger pacing
- Can result in arrhythmia detection
- EMI can also alter device function / damage device
Management of patient with CIED
- Pre operative planning
- Intra operative management
- Post operative management
Preoperative planning
- Evaluation
- Cardiologist evaluation ?
- Device interrogation ?
- Anticipated EMI - Site and type of surgery
Evaluation
- Type of device
- Underlying rhythm
- Underlying heart disease
- Pacing dependent ?
- Needs reprogramming / magnet application ?
Device Interrogation
- If not done recently
- AICD and CRT - 6 months
- Pacemaker - 12 months
- Otherwise review records
Anticipated EMI
- Use of possible EMI sources
- Site of surgery
Above vs below umbilicus
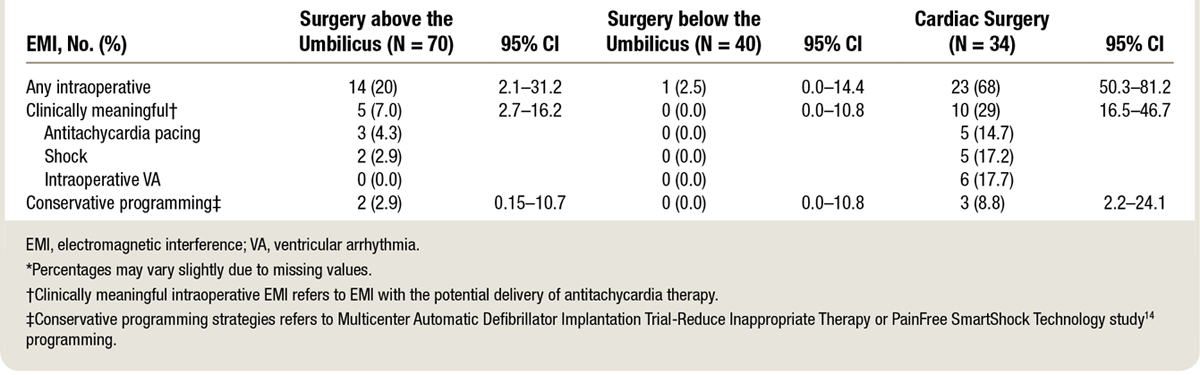
Schulman PM, Treggiari MM, Yanez ND, Henrikson CA, Jessel PM, Dewland TA, Merkel MJ, Sera V, Harukuni I, Anderson RB, Kahl E, Bingham A, Alkayed N, Stecker EC. Electromagnetic Interference with Protocolized Electrosurgery Dispersive Electrode Positioning in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators. Anesthesiology. 2019 Apr;130(4):530-540. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002571. PMID: 30601218.
Intraoperative management
- Reduce EMI
- Alter device function to reduce risk from EMI
- Monitor rhythm for bradycardia
- Monitor for tachyarrhythmias and be prepared to treat
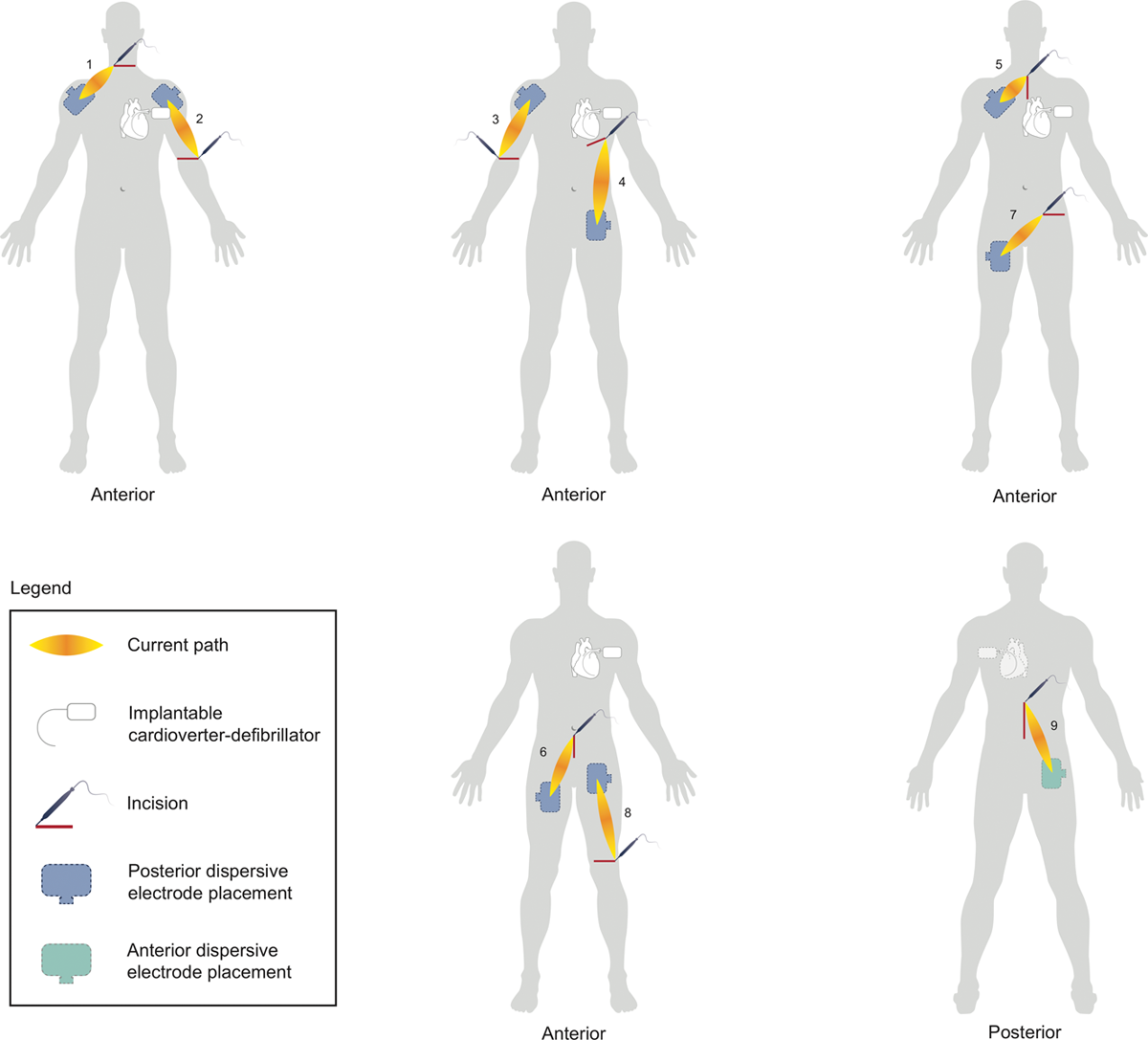
Reducing EMI
- Dispersive electrode placement
- Cautery modifications
Cautery modifications
- Use of bipolar cautery
- Planned placement of dispersive electrode
- Short bursts
Protocolized dispersive electrode
Monitoring of rhythm
- ECG may be obscured by noise
- Pulse oximeter waveforms
- Arterial pressure when available
- Remember that heart rate may be fixed and not usable for hemodynamic monitoring
Alter device function - Magnet or reprogramming
When is it needed
- Supra-umbilical surgery
- Monopolar cautery
- Pacing dependent patient or
- Patient with ICD
What does magnet application do ?
- Converts pacing to asynchronous mode in pacemakers
- Changes rate to "magnet rate"
- Disables tachyarrhythmia therapies in ICD
Advantages of magnet
- More accessible
- Convenient
- Needs no training
- Quick to reverse
- Convenient in emergency setting
Disadvantages of magnet
- Asynchronous pacing not always desirable - may trigger R-on-T
- Rapid rate may not be desirable
- Does not convert AICD to asynchronous pacing
- Difficulty in obtaining and confirming response from device
- Difficult in procedures where patient is not supine
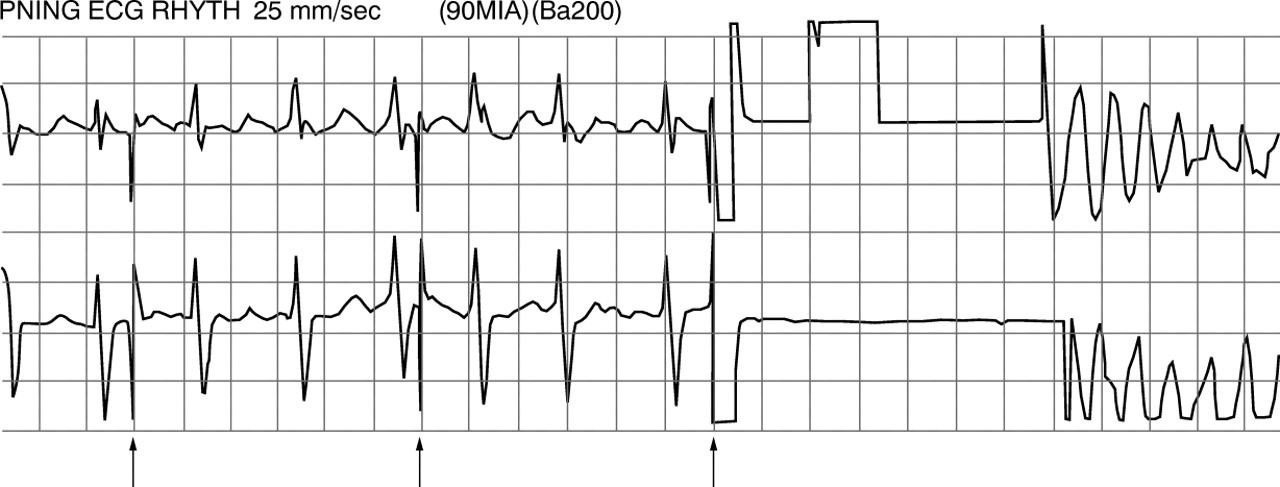
BŐHM A, SZÉKELY A, PRÉDA IVentricular fibrillation provoked by cardioversion and asynchronous pacingHeart 2000;83:424.
Reprogramming
- Pacemakers - Reprogram to asynchronous mode when pacing dependent and EMI anticipated, turn off rate adaptive pacing
- ICD - Program tachyarrhythmia therapies off when EMI anticipated
Management of ventricular arrhythmia
- Patient with ICD turned off needs to be in a monitored setting
- Remove magnet or restore ATP therapies for ICD
- External defibrillation / cardioversion
- Antero posterior paddle position
Summary
- More patients in OR are going to have a CIED
- Anaesthetist should have some knowledge of CIEDs
- However, always preferable to involve a cardiologist / heart rhythm specialist
- Evaluation and reprogramming as needed is preferable to routine magnet placement